HTML/CSS I
Introduction to HTML & CSS


"Front-end" Languages

A basic website can be built with...
What is HTML?
HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language.
HTML is used to create the structure of our web applications.

HTML Tag Syntax
To create a tag in HTML, use the <> symbols to open the HTML element and </> to close the element. Within the carrots will be the HTML element you are using, and between the opening and closing tags is the content for that element.
<tagname>content</tagname>HTML also has what are called 'void tags' or 'self-closing tags', that contain no content, and need no closing tag.
<voidtag />Setting up HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>The Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- This is a comment -->
</body>
</html>Tells the browser what type of file to expect
Tells the browser everything between the head tag should be read as HTML
Data about our website goes in here
Website content goes in the body tag
Continued...
Setting up HTML Continued
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="best website ever made">
<meta name="keywords" content="greatest, best">
<meta name="author" content="matias perez-ferrero">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>The Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Meta tags are tags that contain data about your website.
Meta tags can include a description, author, keywords, and more.
Continued...
Setting up HTML Continued
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="best website ever made">
<meta name="keywords" content="greatest, best">
<meta name="author" content="matias perez-ferrero">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel='stylesheet' href='styles.css'>
<title>The Title</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>The <link> tag creates a link between the HTML document and external resources
External resources could include fonts, stylesheets, and more
HTML Elements
<h1-6></h1-6><header></header><div></div>Header tags are containers for header information, such as navigation links.
Heading tags denote a heading for content. The lower the number, the more important it is.
Div tags are containers for your content.
<section></section>Section tags are containers for your content.
<nav></nav>Nav tags denote a list of navigation links.
<a></a>Anchor tags denote a link to a file or other website.
<p></p>Paragraph tags are for sections of text.
<span></span>Span tags are for sections of text. They are great for styling specific parts of text within a paragraph tag.
Continued...
HTML Elements Continued
<hr/>, <br/><hr> and <br> are separation tags. <hr> will create white space between elements. <br> will create a line break.
<ul></ul>, <ol></ol>Un-ordered <ul> and Ordered <ol> list tags denote a list, ordered by bullets (<ul>) or by number (<ol>).
<li></li><li> tags denote a list item, used in both <ul> and <ol> lists.
<input/><input> tags provide input boxes for users to type into.
<button></button><button> tags provide a clickable button.
<img/><img> tags are for displaying images on a web page.
<form></form><form> tags denote a form for collecting user input.
<table>, <tr>, <td><table> tags create tables. <tr> creates a table row. <td> creates a table cell.
<footer></footer><footer> tags denote a footer, generally containing copyright info, authorship info, or navigation links.
Parents, Siblings, and Children
HTML elements have relationships to one another
Elements containing other elements are called parents
Elements contained within other elements are called children
Elements next to one another are called siblings
<body>
<div class="parent">
<p class="child">I'm a paragraph tag</p>
</div>
<footer class="sibling"></footer>
</body>Semantic HTML
Semantic HTML provides context and meaning to the structure of our web pages.
Using semantic HTML elements improves accessibility and Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
<!-- Non-semantic HTML -->
<div></div>
<span></span>
<!-- Semantic HTML -->
<section></section>
<header></header>
<h1></h1>You should ALWAYS use semantic tags when available
As of 2019, businesses that fall under ADA Title I or ADA Title III are required to develop a website that offers "reasonable accessibility" to people with disabilities.
HTML Attributes
HTML attributes allow you to add more information to an element. Attributes are added into the opening tag of the element.
<tagname attributeName="value">content</tagname>Example: Input elements use a type attribute to denote what type of input they are.
<input type="text" />
<input type="password" />
<input type="radio" />Display Properties
HTML elements come with a built in 'display' property value
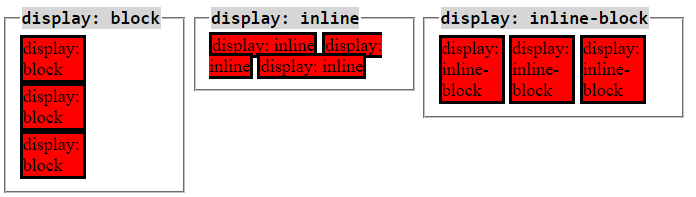
What is CSS?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets
CSS is a presentational language.
CSS is used only for the layout and styling of HTML elements.

CSS Selectors
Selectors are patterns used to select the elements to be styled.
Selectors are followed by a set of curly braces ( { } ) which contain individual style declarations.
Element selector: ( element )
Selects elements by their tag name
Class selector: ( . )
Selects elements by their class attribute
Universal selector: ( * )
selects all elements
Id Selector: ( # )
Selects elements by their id attribute
p {
background-color: cyan;
}.something {
background-color: cyan;
}#anotha-one {
background-color: cyan;
}* {
background-color: cyan;
}Ways to Write CSS
Is written directly into the opening tag of an HTML element
<section style="color: blue;font-size: 18px;">Content</section>Is written by adding a <style> tag in the header and adding CSS to it
<head>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>1) Inline CSS
2) Internal CSS
Continued...
Ways to Write CSS Continued
External CSS is the most common way to write CSS
External CSS is written by creating a separate CSS file and connecting it to the HTML file using a <link> tag in the header.
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
</head>3) External CSS
Reset CSS
Web browsers apply different initial styling to HTML elements.
This can make styling for all browsers difficult.
We can use a Reset CSS file to remove default, browser applied styling.
CSS Combinators
Selectors can also be used with combinators for more specific styling
Group combinator: ( , )
Combines selectors into one block
Descendant Combinator: (space)
Applies to the right-most selector, which is a descendant of the element to its left
Child Combinator: ( > )
Selects all specified direct children of an element
Adjacent Sibling Combinator: ( + )
Selects the first specified sibling element from the same parent element
General Sibling Combinator: ( ~ )
Selects all specified siblings of an element
div p {
background-color: cyan;
}div, p {
background-color: cyan;
}div + p {
background-color: cyan;
}div > p {
background-color: cyan;
}/* Paragraphs that are siblings of and
subsequent to any image */
img ~ p {
background-color: cyan;
}Pseudo Classes
Pseudo classes are keywords that can be added to a selector to specify a special state of the selected elements.
div:hover {
background-color: blue;
}CSS Specificity
When an element has conflicting styles added to it, CSS specificity determines which style is used.
It works like a point system. The highest score styling block is applied.
Selecting the element: 1 point
Selecting the class: 10 points
Selecting the id: 100 points
Inline Styling: 1000 points
<body>
<div class="test" id="test"></div>
</body>HTML
CSS
#test {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: cyan;
}
.test {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: blanchedalmond
}
The Box Model
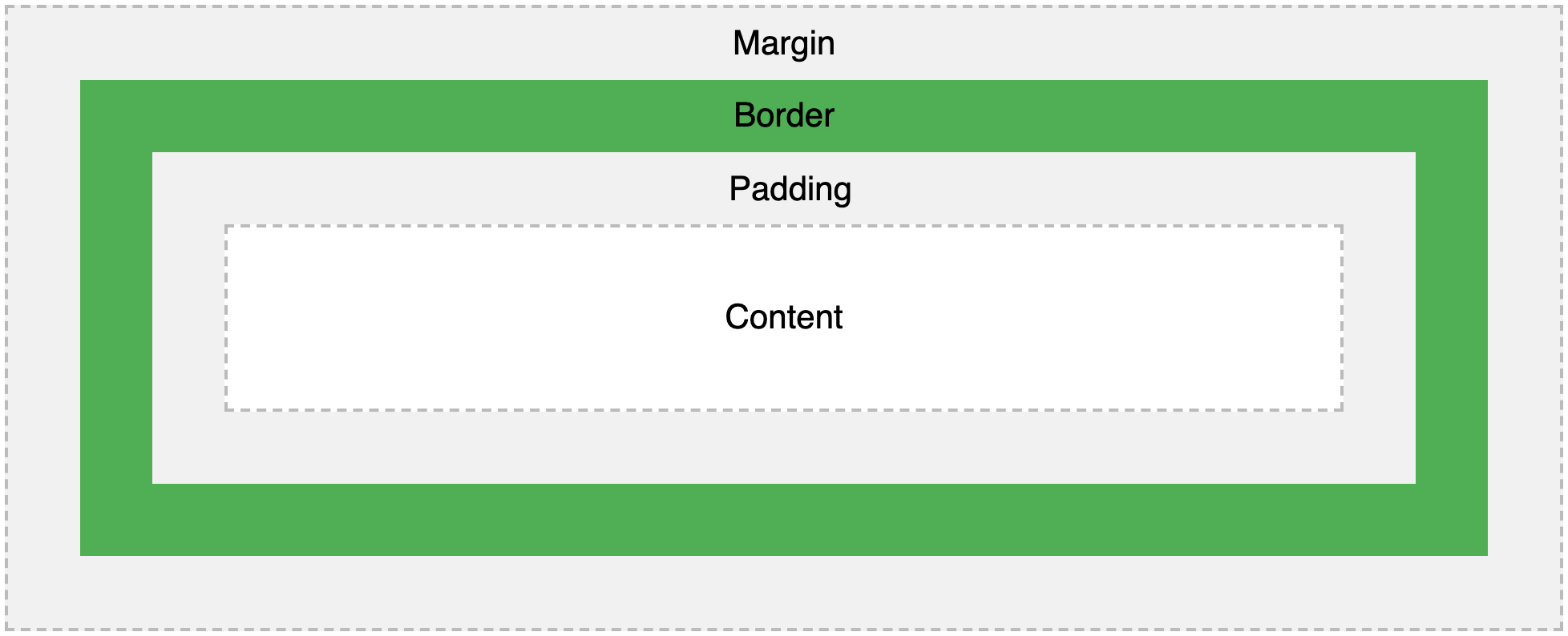
The box model refers to the design and layout of an element, and consists of margin, border, padding, and content.
Box Sizing Properties
When applying margin, border, and padding to our element, we are changing the total size of the element.
To control how the total size is calculated, this we can use Box Sizing Properties.
box-sizing: content-box
- Default setting
- Adds margin, border and padding to the overall size of the element even if height and width are explicitly specified
box-sizing: border-box
- Margin, border, and padding do not increase the total size of the element beyond a specified height or width
CSS Text Properties
font-size: changes the font size of selected text
color: changes the font size of selected text
font-family: changes the font family of selected text
line-height: determines the space between two inline elements
text-align: aligns the text within an element
font-weight: changes the boldness of selected text
letter-spacing: determines the space between each character
CSS Background Properties
background-color: changes the background color of an element
background-image: assigns an image to the background of an element
background-size: assigns the size of a background image
background-position: adjusts the alignment of a background image
background-repeat: determines how the background image is repeated
CSS Height and Width Units
CSS has various units to determine height and width.
pixels (px): pixels are the most common absolute unit
percent (%): relative unit based on the size of the parent container
view-height (vh): percent relative to the viewport
view-width (vw): percent relative to the viewport
Commonly Used Units
CSS Float Property

The float property places an element to the right or left of its container, and allows inline elements to wrap around it.
Wireframes and Mockups
Copy of HTML/CSS I
By Scott Sutherland
Copy of HTML/CSS I
Introduction to HTML/CSS
- 225
