
Large-scale agent-based simulations of the transport system Replicability and application cases in France

Macroscopic transport modeling
Classic four-step models
- Travel demand generated in (large) zones
- Focus on large flows between these zones
- For the morning or evening commute
- For limited user groups
- Question: Where to add capacity?


Macroscopic transport modeling


Classic four-step models
- Travel demand generated in (large) zones
- Focus on large flows between these zones
- For the morning or evening commute
- For limited user groups
- Question: Where to add capacity?



Macroscopic transport modeling


Classic four-step models
- Travel demand generated in (large) zones
- Focus on large flows between these zones
- For the morning or evening commute
- For limited user groups
- Question: Where to add capacity?




Agent-based transport modeling










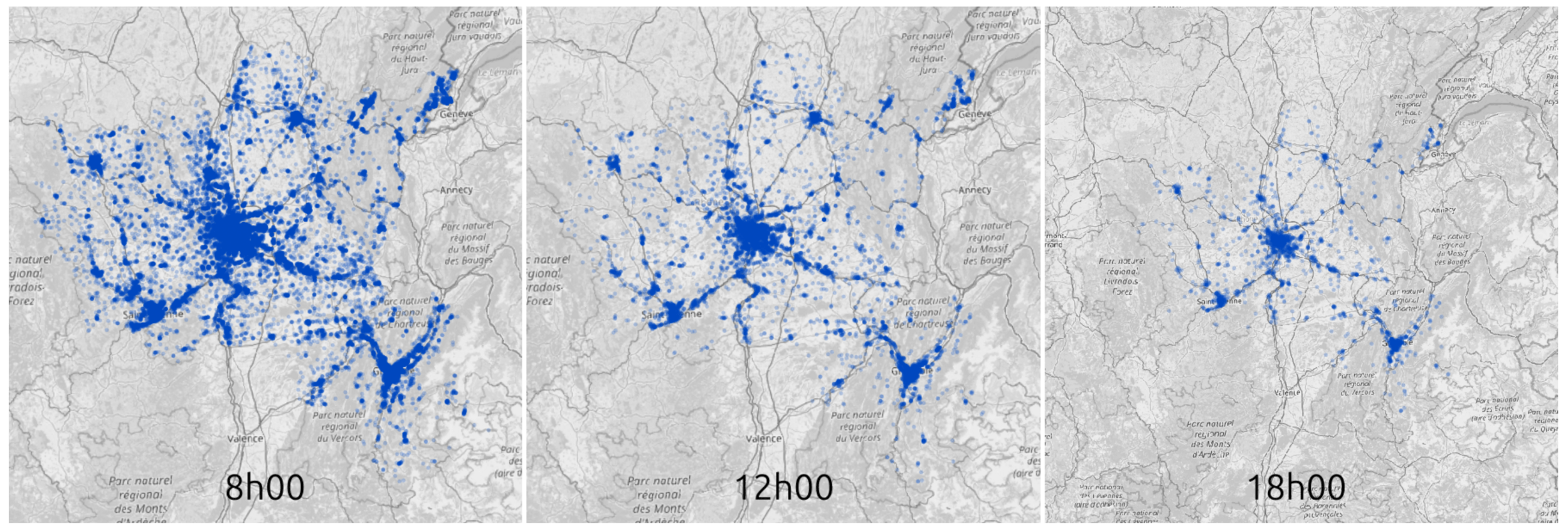
0:00 - 8:00
08:30 - 17:00
17:30 - 0:00
0:00 - 9:00
10:00 - 17:30
17:45 - 21:00
22:00 - 0:00





- Individual travellers with daily activities
- Moving from one activity to another
- Simulation of the entire day
- Highly detailed interaction between travellers and services
- Multitude of (design) questions can be answered


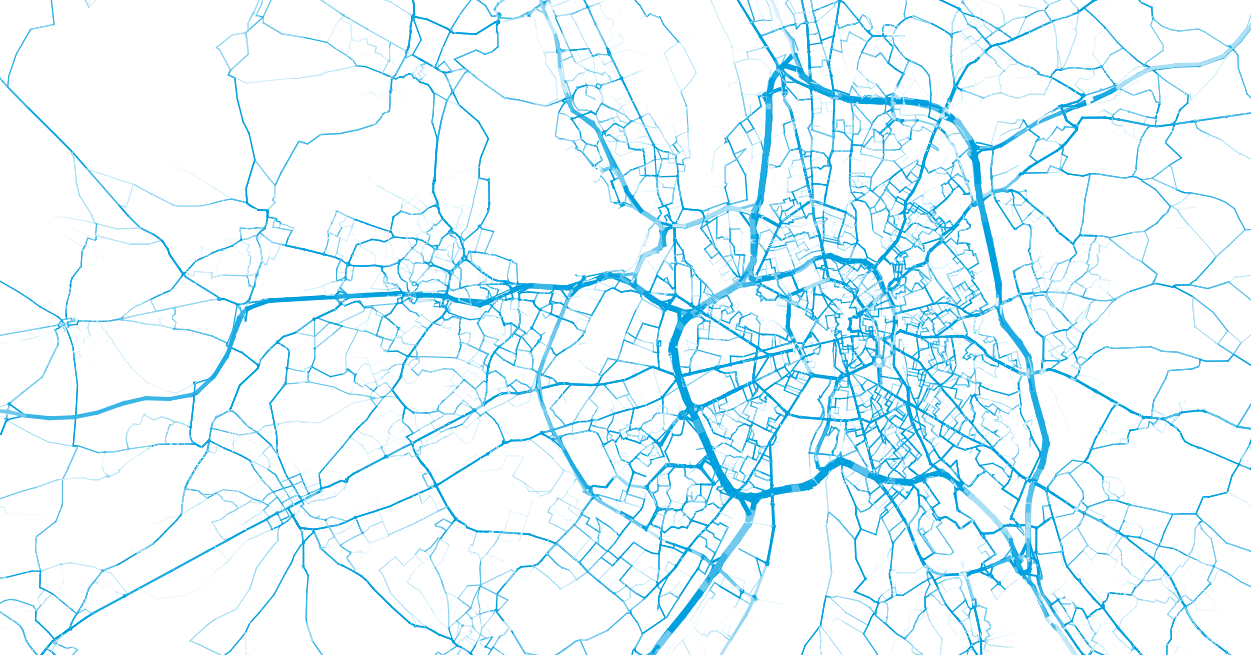
Transport modeling chain
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results


Transport modeling chain
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results


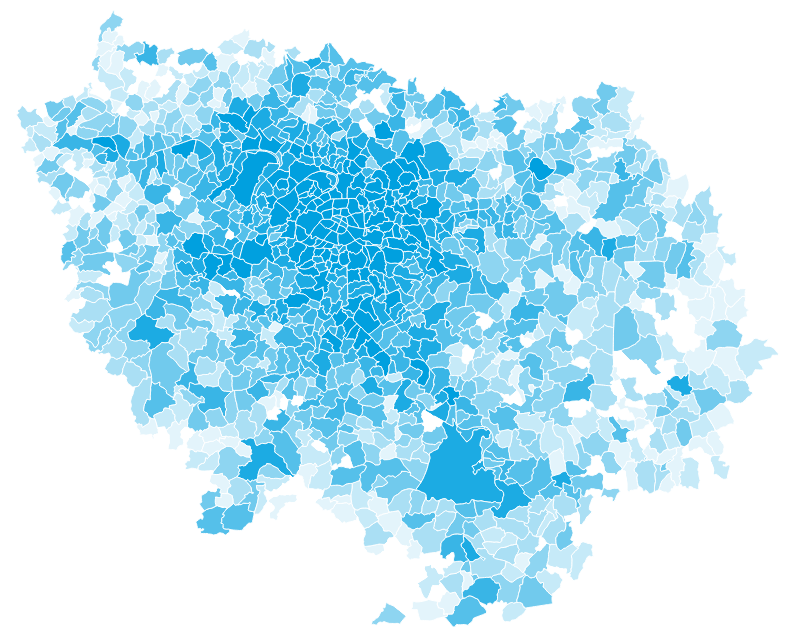
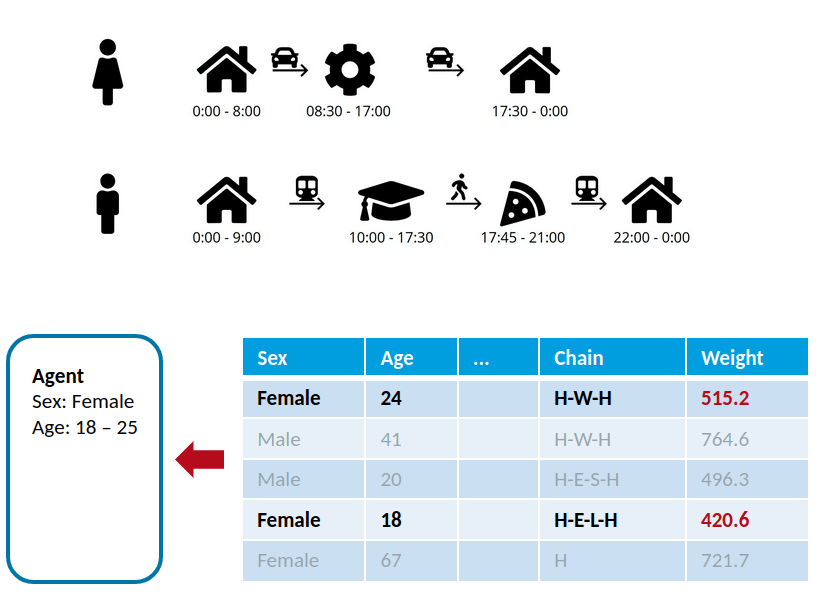
Synthetic populations: Introduction
Definition
- Representation digital version of the real population of a territory
- Persons (single-level) or households with persons (two-level) population
- Households and persons with individual attributes
- Persons with individual activity chains



0:00 - 8:00
08:30 - 17:00






0:00 - 9:00
10:00 - 17:30
17:45 - 21:00
22:00 - 0:00



17:30 - 0:00


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Data
Goals
- Generate individual households and persons
- Choose a distinct place of residence

French population census
| Household ID | Person ID | Zone | Age | Sex | ... | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 512 | 1 | 75013 | 35 | f | ... | 3.2 |
| 512 | 2 | 75013 | 32 | m | ... | 3.2 |
| 516 | 1 | 75019 | 42 | m | ... | 4.1 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Upsampling of persons using Truncate-Replicate-Sample (TRS)


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Data
Goals
- Generate individual households and persons
- Choose a distinct place of residence
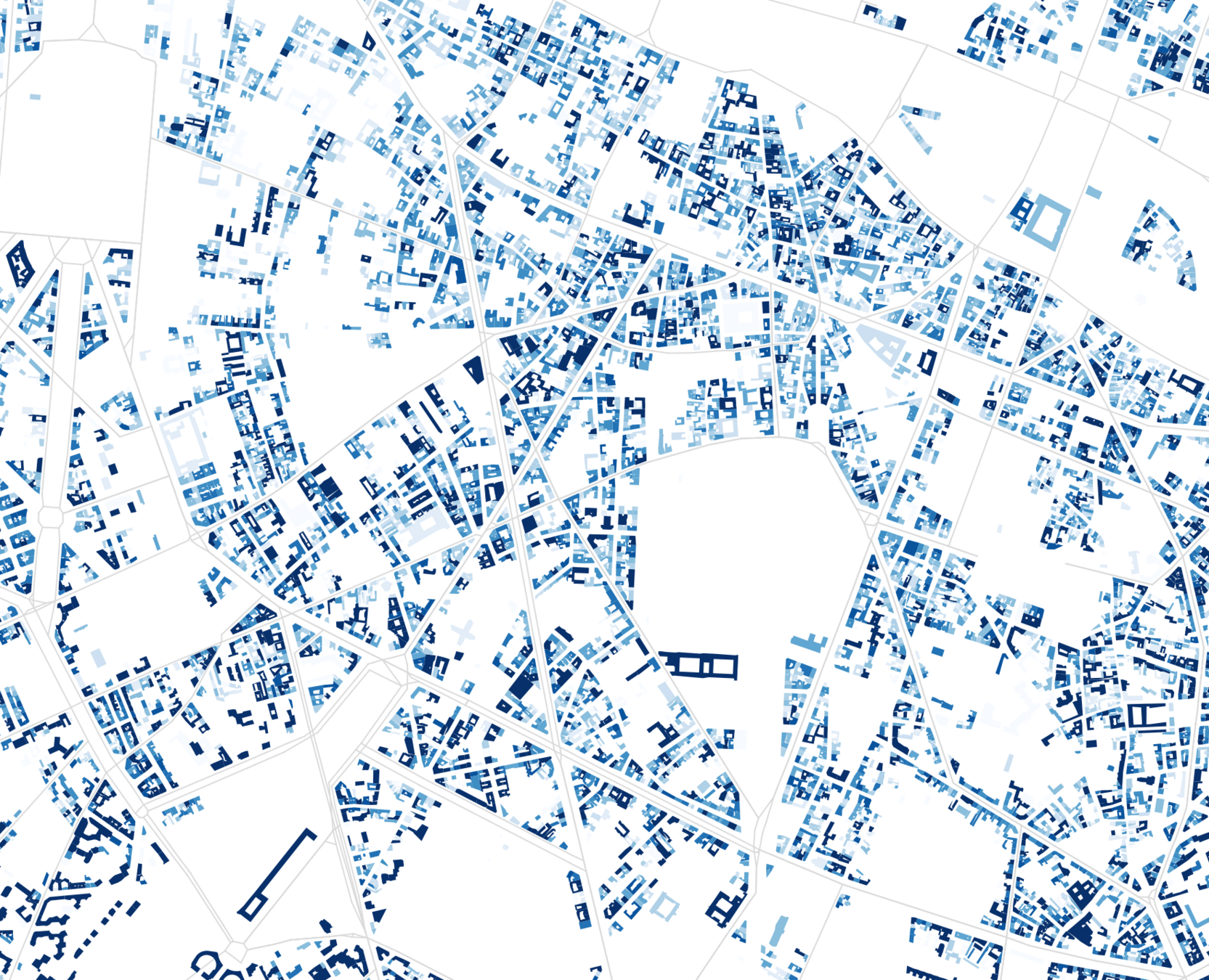
Sampling by number of housing units per building

French bulding database

French address database


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Goal
- Choose work places and education locations

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD



French work
commuting matrix


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Goal
- Choose work places and education locations

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD


French work
commuting matrix

National enterprise
database
with facilities by number of employees




Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Goal
- Choose work places and education locations

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD

French education
commuting matrix

Permanent facility
database
with education facilities and attendants





Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Goal
- Generate activity sequences (type, start and end time) for each person

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Statistical Matching


National Household Travel Survey 2008

(Local Household Travel Surveys)


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Goals
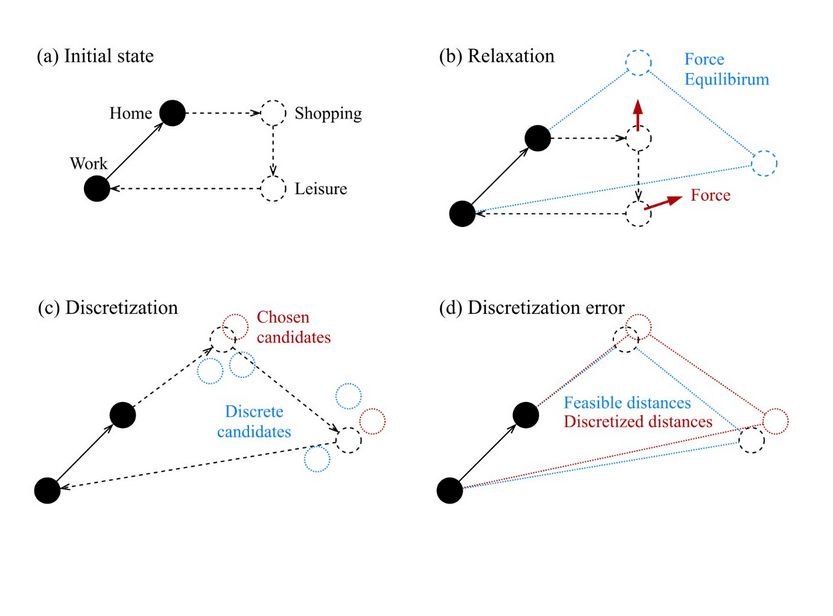
- Choose locations of secondary (shopping, leisure, ...) activities

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Hörl, S., Axhausen, K.W., 2021. Relaxation–discretization algorithm for spatially constrained secondary location assignment. Transportmetrica A: Transport Science 1–20.


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Output
- Three main tables: households, persons, activities
- Supplementary tables: commutes, trips, ...

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
| household_id | income | number_of_cars | ... |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1024 | 85,000 | 2 | ... |
| household_id | person_id | age | sex | employed | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1024 | 1 | 34 | f | true | ... |
| 1024 | 2 | 36 | m | true | ... |
| household_id | person_id | activity_id | start_time | end_time | type | location | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1024 | 1 | 1 | 00:00 | 08:00 | home | (x, y) | ... |
| 1024 | 1 | 2 | 09:00 | 18:00 | work | (x, y) | ... |
| 1024 | 1 | 3 | 19:00 | 24:00 | home | (x, y) | ... |


Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Output
- Three main tables: households, persons, activities
- Supplementary tables: commutes, trips, ...

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
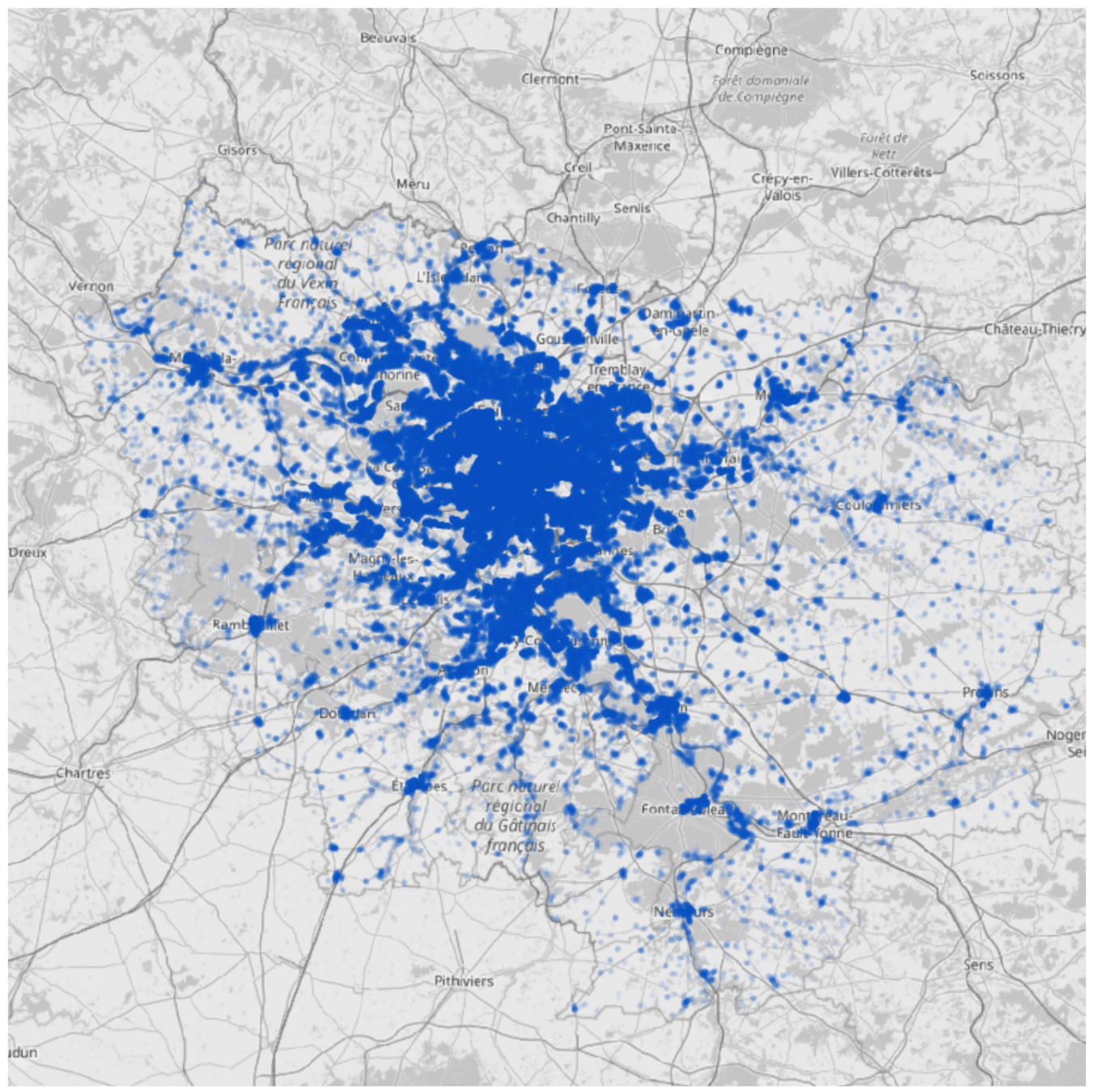
Place of residence
Commuting trips
Hourly work activities



Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Validation
- Comparison with census data, HTS data, ...



Synthetic populations: Pipeline
Pipeline
- Households and persons
- Primary activity locations
- Activity chains
- Secondary activity locations
Data
Validation
- Comparison with census data, HTS data, ...

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD


Synthetic populations: Pipeline

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Open data
Open source
+
=
Replicable research in agent-based transport simulation



Synthetic populations: Pipeline

RP

BAN

BD-TOPO

MOBPRO

MOBETUD

SIRENE

BPE

ENTD
Open data
Open source

+
=


Synthetic populations: Community












Lille
Paris
Strasbourg
Lyon
Toulouse
Bordeaux
Nantes
Rennes

Contributors
Users




eqasim workshop in November 2025
Synthetic populations: Community


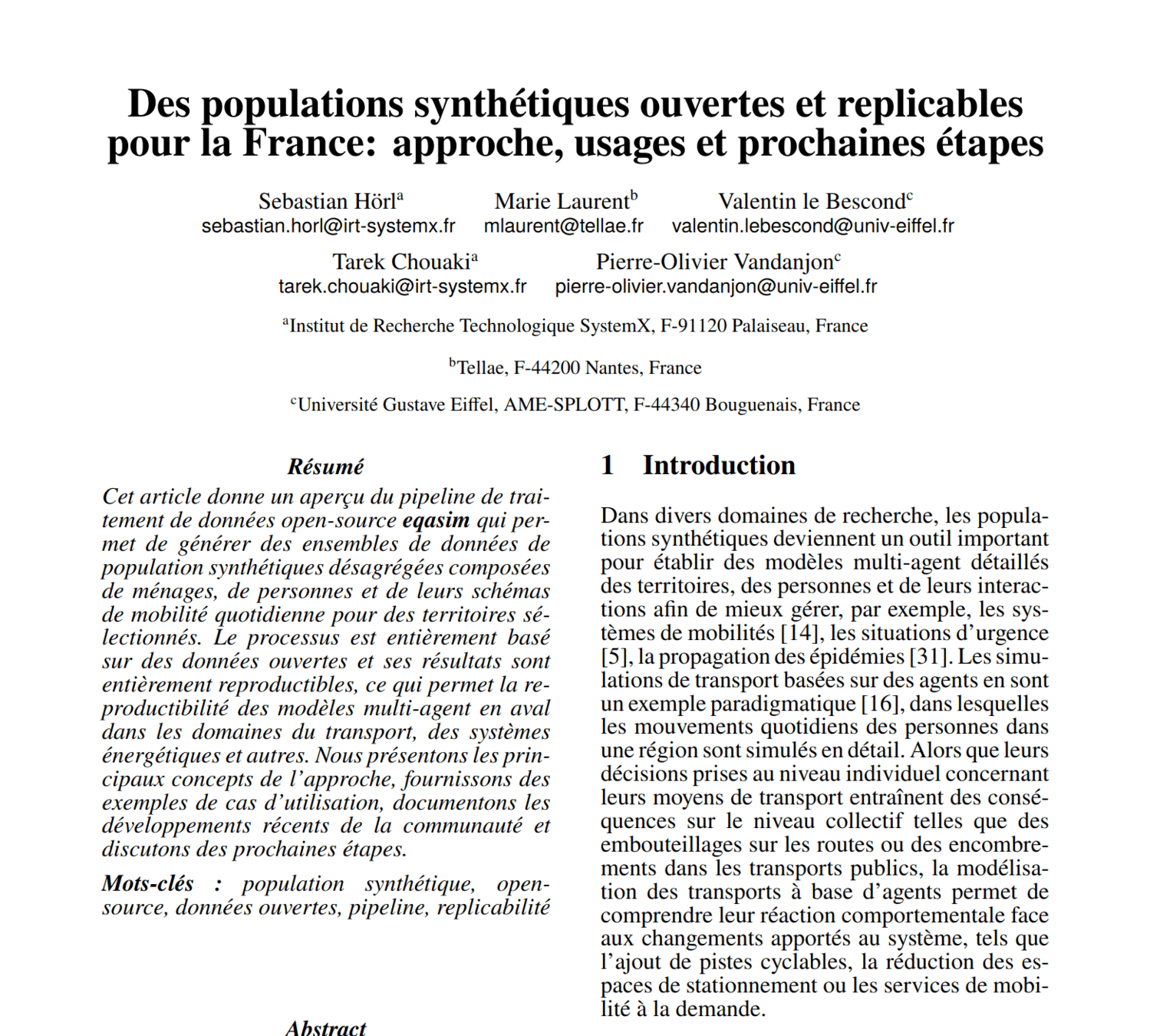

Lille
Paris
Strasbourg
Lyon
Toulouse
Bordeaux
Nantes
Rennes
Synthetic populations: Adaptations
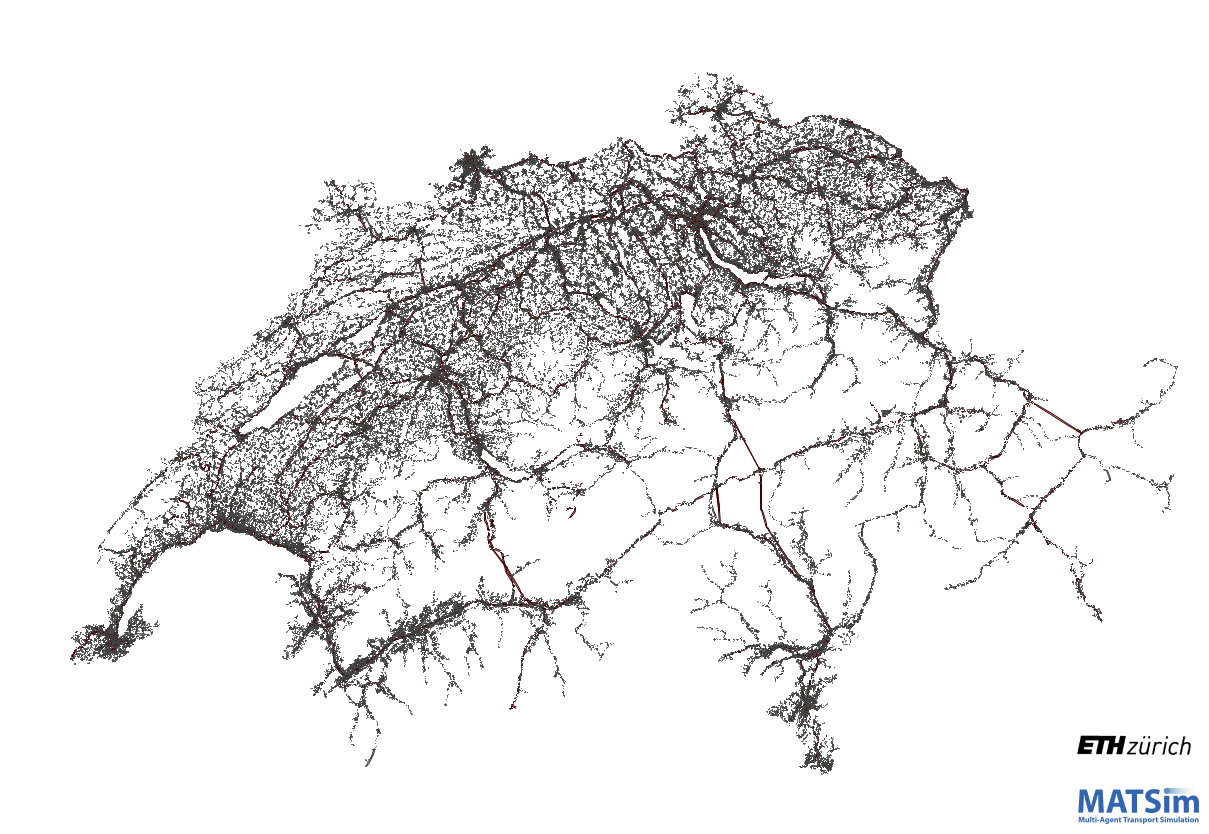
Screenshot Sao Paolo
Copy & paste of the code base
Difficulty of maintenance
São Paulo
Almost same open data available as in France
California
Substantial modifiations required
Switzerland
Not based on open data
(for now)

Paper published in
Regional Studies, Regional Science (2020)
Paper presented at the Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board (2021)
Work in progress at ETH Zurich


Synthetic populations: Adaptations
Cairo: Extreme case, very few data available and not in the right format
Idea: Use data to generate "fake" input to the French pipeline and reuse the code!
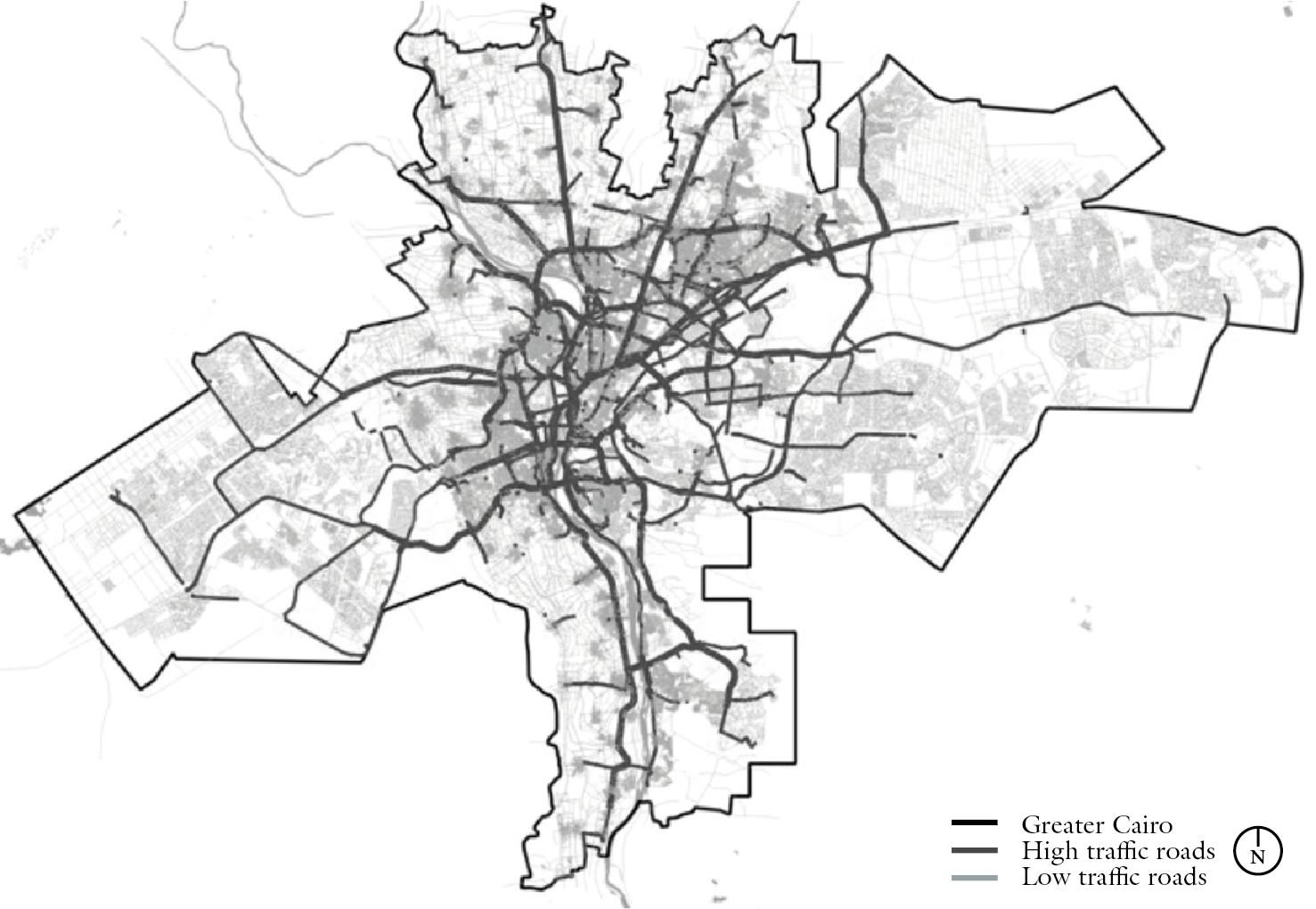
Gall, T., Vallet, F., Reyes Madrigal, L.M., Hörl, S., Abdin, A., Chouaki, T., Puchinger, J., 2023. Sustainable Urban Mobility Futures, Sustainable Urban Futures. Springer Nature Switzerland, Cham.


Synthetic populations: Adaptations
Cairo: Extreme case, very few data available and not in the right format
Idea: Use data to generate "fake" input to the French pipeline and reuse the code!
Bavaria: Set up a robust and replicable pipeline with data replacement
Hörl, S., Burianne, A., Natterer, E., Engelhardt, R., Müller, J. (2025) Towards a replicable synthetic population and agent-based transport model for Bavaria, paper presented at the 23rd International Conference on Practical applications of Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (PAAMS 2025), June 2025, Lille, France.



As part of the national project MINGA
Synthetic populations: Adaptations
Cairo: Extreme case, very few data available and not in the right format
Idea: Use data to generate "fake" input to the French pipeline and reuse the code!
Bavaria: Set up a robust and replicable pipeline with data replacement

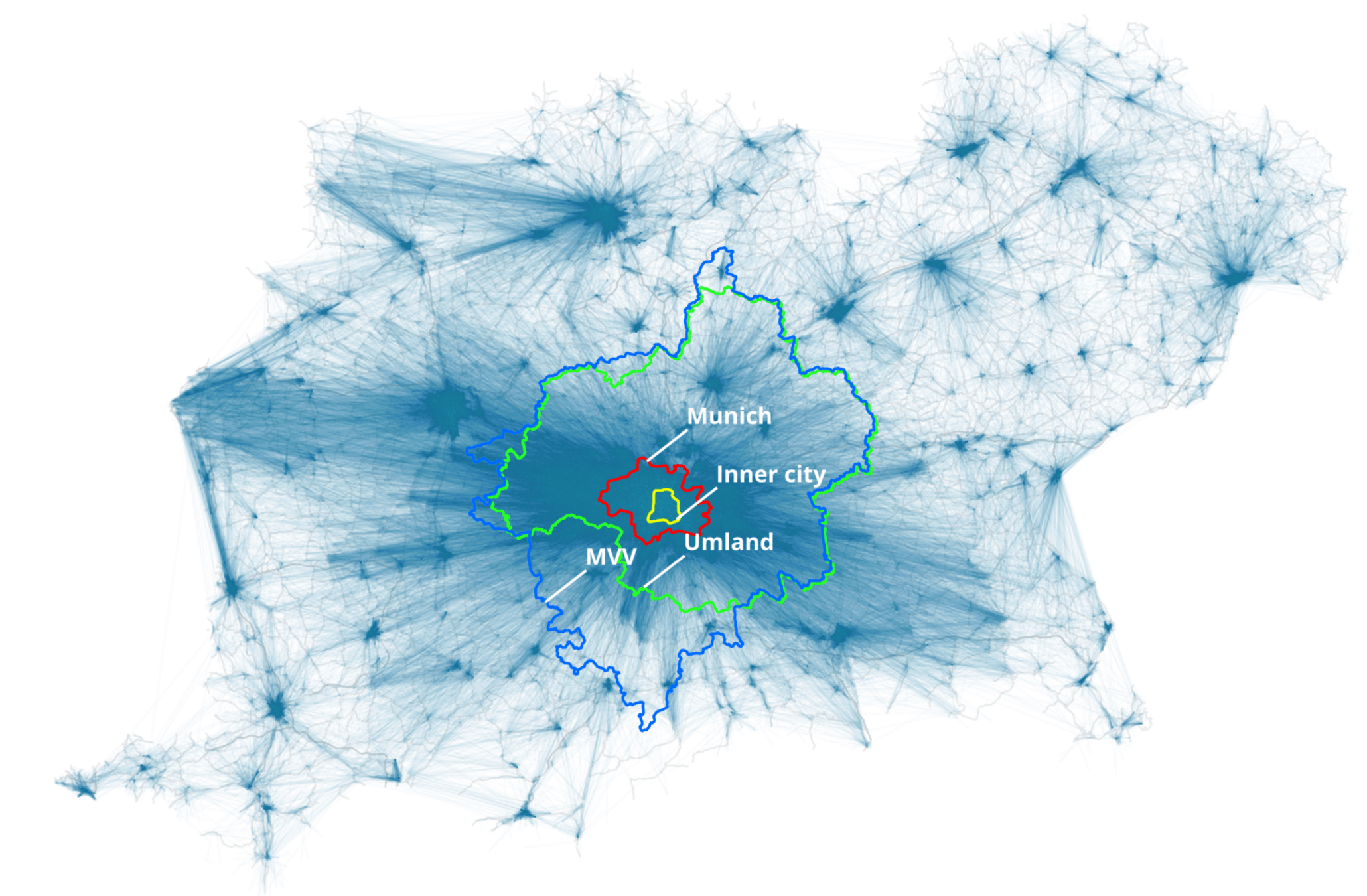



As part of the national project MINGA
Hörl, S., Burianne, A., Natterer, E., Engelhardt, R., Müller, J. (2025) Towards a replicable synthetic population and agent-based transport model for Bavaria, paper presented at the 23rd International Conference on Practical applications of Agents and Multi-Agent Systems (PAAMS 2025), June 2025, Lille, France.

Transport modeling chain
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results


Transport modeling chain
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results


Agent-based simulation: Introduction

GTFS

OpenStreetMap
Synthetic demand
+
Driving car
Metro / Train
Work activity starts


Agent-based simulation: Introduction
Synthetic demand


Agent-based simulation: Introduction
Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand
Daily mobility plans


Agent-based simulation: Introduction
Decision-making
Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand







Experienced travel times, crowding, ...
Daily mobility plans


Agent-based simulation: Introduction
Decision-making
Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand














Experienced travel times, crowding, ...
Daily mobility plans


Agent-based simulation: Introduction
Decision-making
Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand
Experienced travel times, crowding, ...
Daily mobility plans
Update


Agent-based simulation: Introduction
Decision-making
Mobility simulation
Synthetic demand

- Maintained by TU Berlin, ETH Zurich, (IRT SystemX)
- 50+ research users world-wide, SBB, Volkswagen, ...
- Contributor since ~2016
Mode shares
Traffic patterns
Emissions
Noise


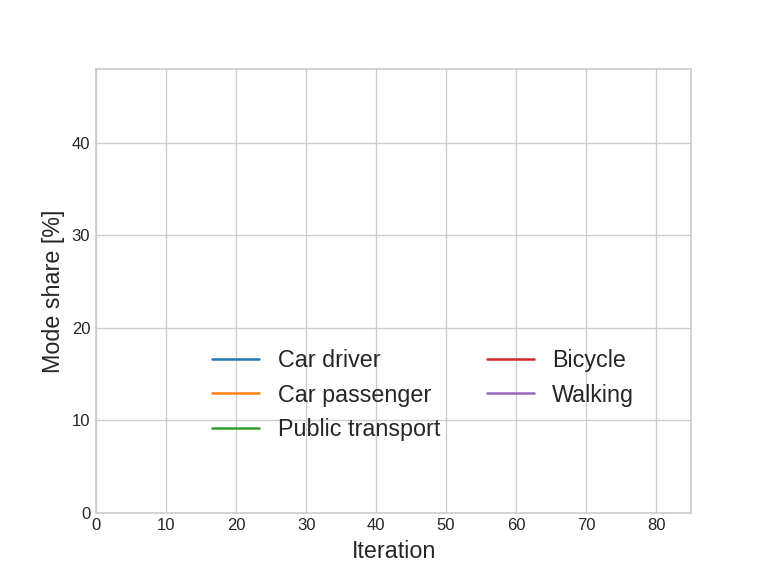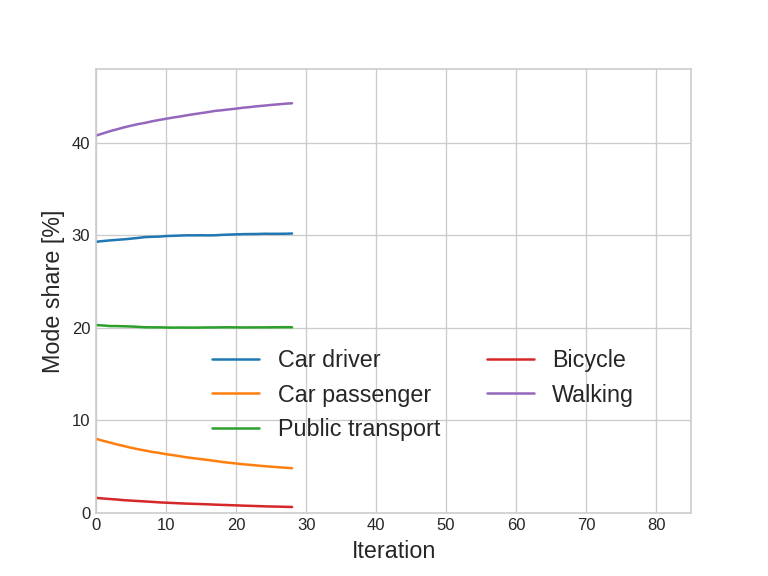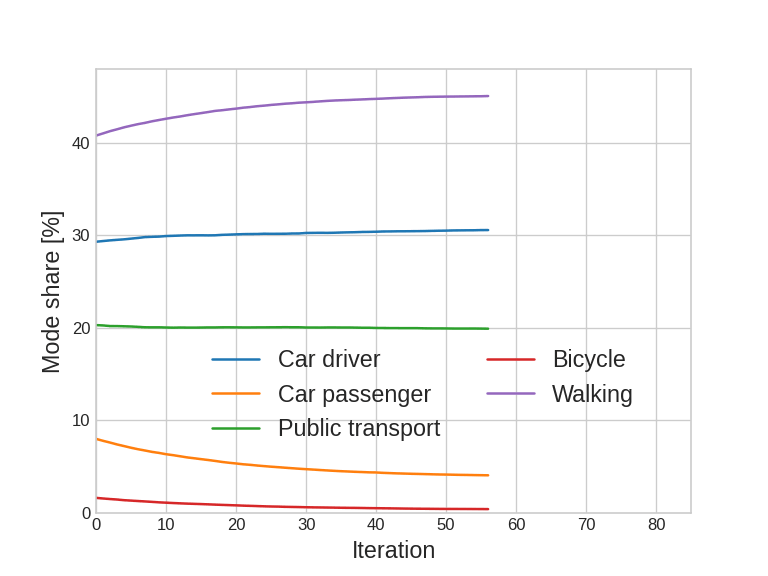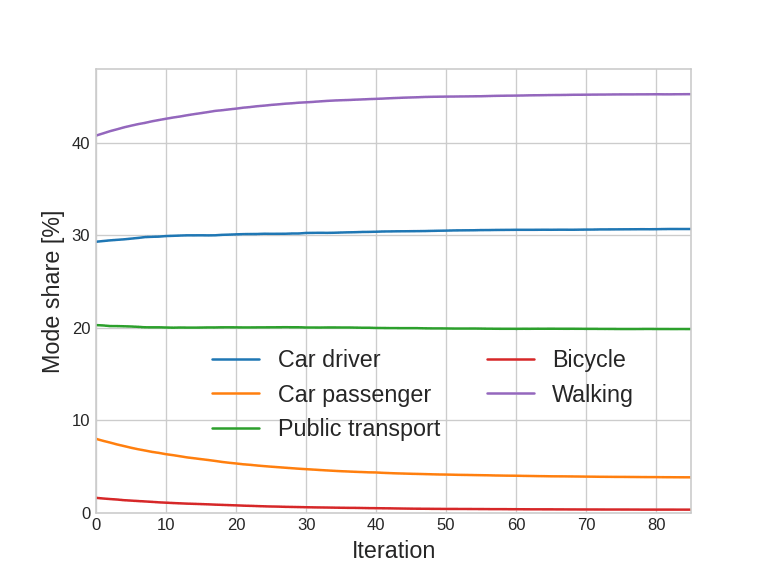
Agent-based simulation: eqasim-java
eqasim-java: A streamlined set-up of MATSim for our standardized synthetic populations


Agent-based simulation: Calibration


Capacity calibration
Validation:
- Global mode share
- Mode share by distance
- CDF of travel times by mode
- Others possible; some within limits (traffic counts, transit counts, ...)

* not the latest results
Agent-based simulation: Calibration


Capacity calibration
Validation:
- Global mode share
- Mode share by distance
- CDF of travel times by mode
- Others possible; some within limits (traffic counts, transit counts, ...)

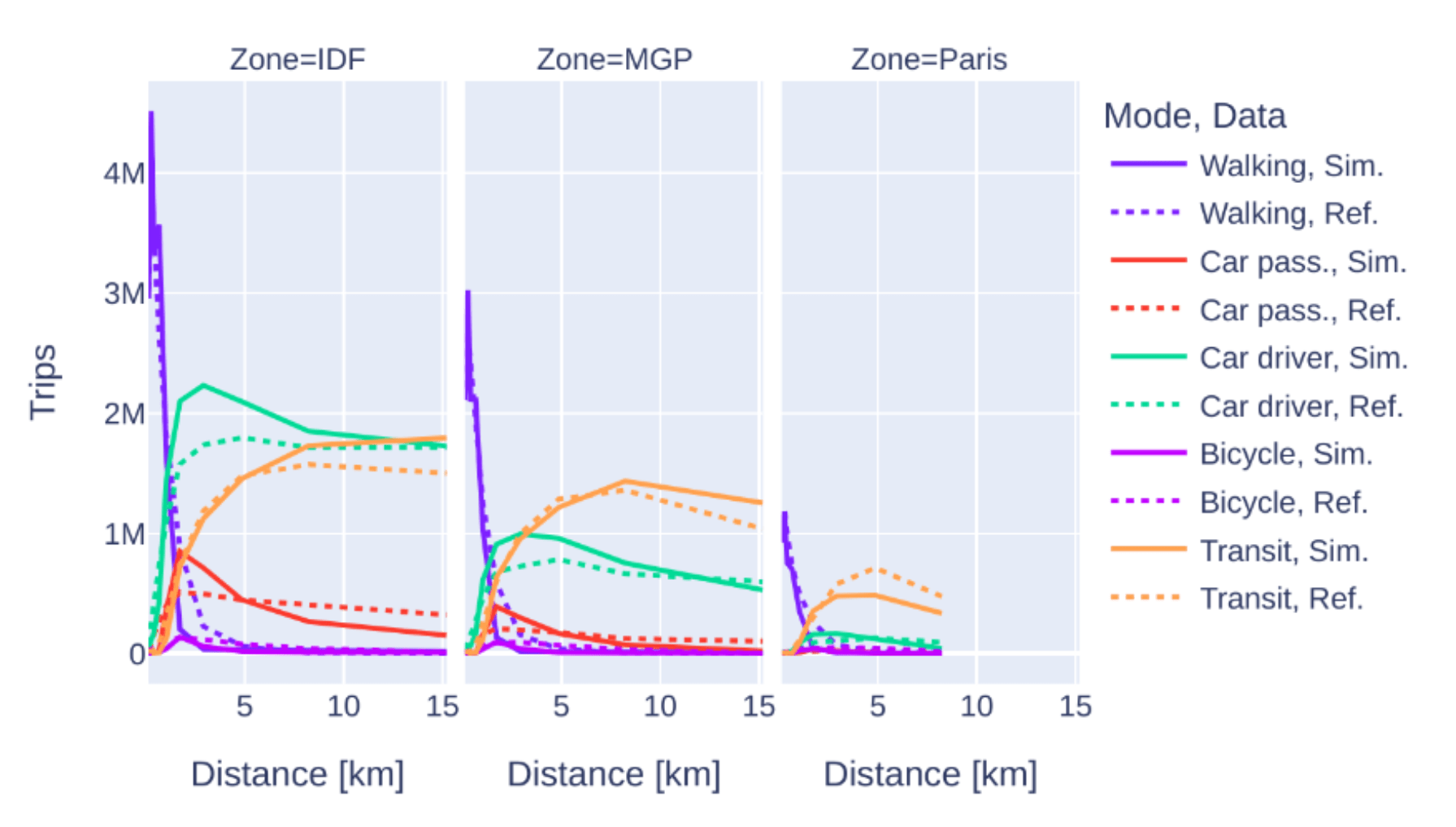
* not the latest results
Agent-based simulation: Calibration


Capacity calibration
Validation:
- Global mode share
- Mode share by distance
- CDF of travel times by mode
- Others possible; some within limits (traffic counts, transit counts, ...)


* not the latest results
Agent-based simulation: Calibration


Capacity calibration
Validation:
- Global mode share
- Mode share by distance
- CDF of travel times by mode
- Others possible; some within limits (traffic counts, transit counts, ...)

* not the latest results
Transport modeling chain
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results


Transport modeling chain
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results


Automated taxi
Pickup
Dropoff
Use cases: On-demand mobility
- An operator centrally controls a fleet of vehicles
- Each vehicle is represented as an agent that receives instructions in each time step
-
Customer agents sent requests to be transported
- Objectives: maximize operator revenue, minimize empty distance, ...


Automated taxi
Pickup
Dropoff
Use cases: On-demand mobility
- An operator centrally controls a fleet of vehicles
- Each vehicle is represented as an agent that receives instructions in each time step
-
Customer agents sent requests to be transported
- Objectives: maximize operator revenue, minimize empty distance, ...
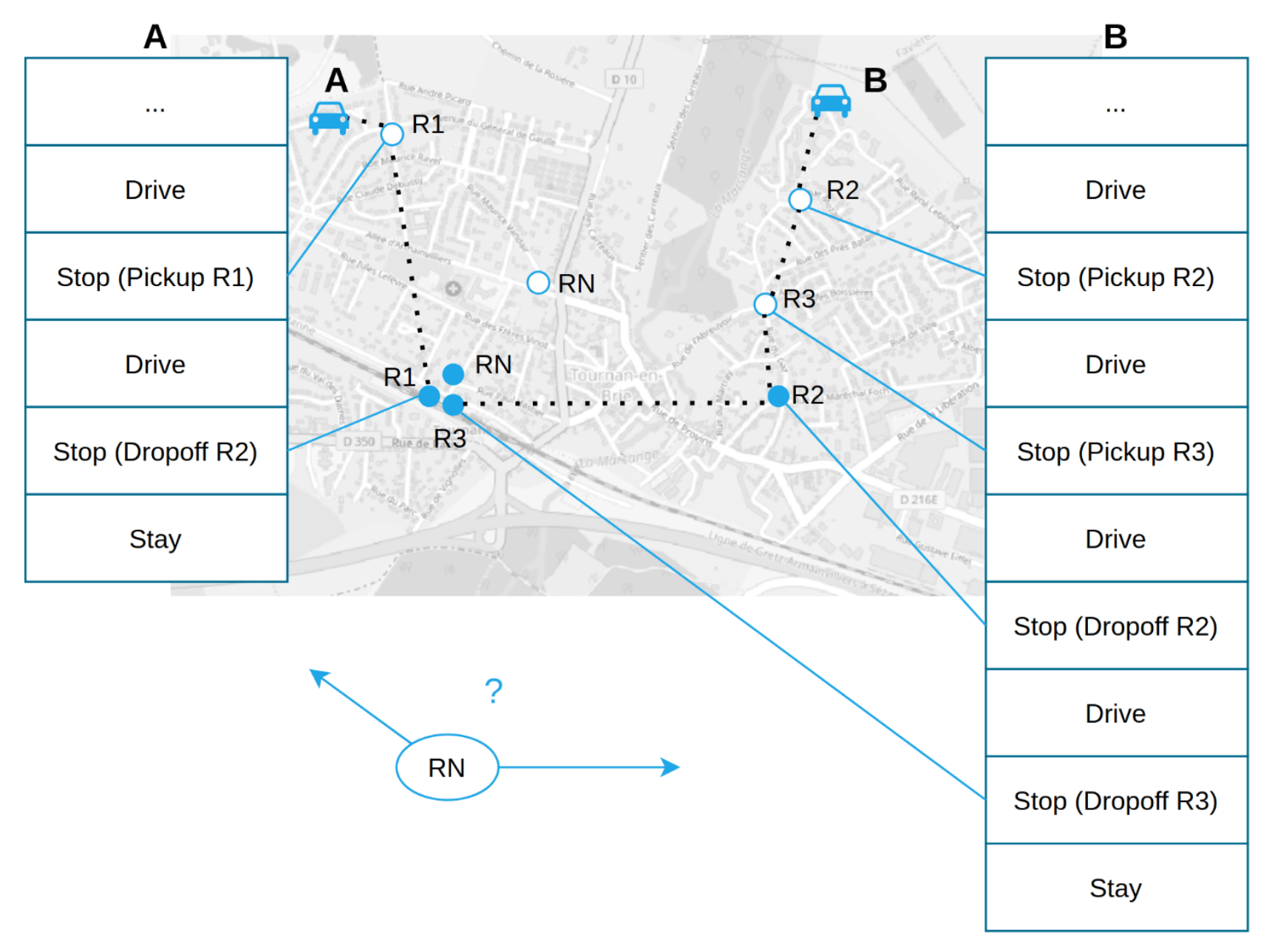
R1


Use cases: On-demand mobility
- Different dispatching strategies provide different outcomes in terms of empty distance, revenue, and wait times
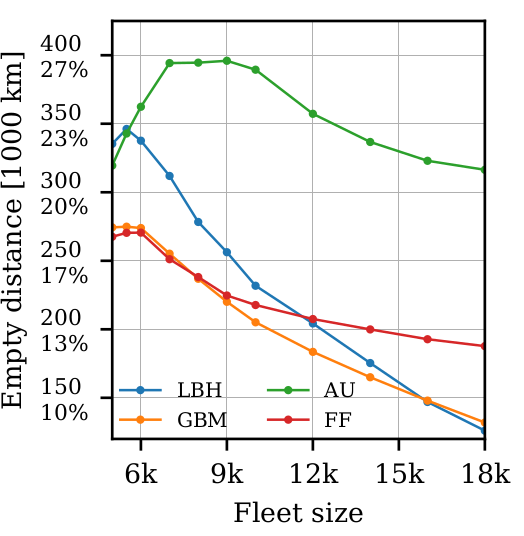
amodeus-science/amodeus

AI Driving Olympics challenge at NeurIPS 2018


Use cases: On-demand mobility
Cost model
Discrete choice model
Mobility simulation
Estimation
Fare per trip and km
Wait time
Outcomes
Passenger distance, empty distance
- The problem becomes even more interesting when customer agents have the choice to use the service or not (dynamic demand)


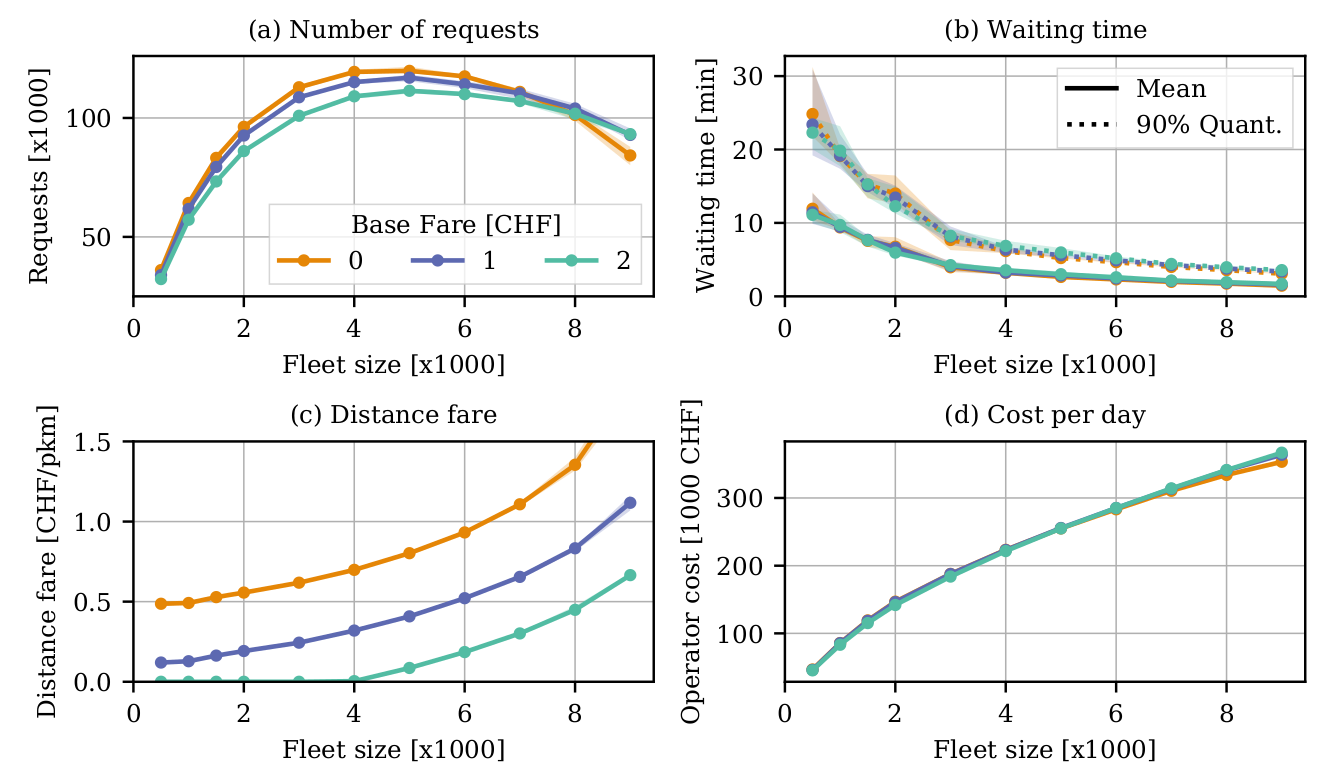
Use cases: On-demand mobility

- Provides an understanding of a mobility service that doesn't exist today
- Shows pathways for policy and regulation


Hörl, S., Becker, F., & Axhausen, K. W. (2021). Simulation of price, customer behaviour and system impact for a cost-covering automated taxi system in Zurich. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 123, 102974.
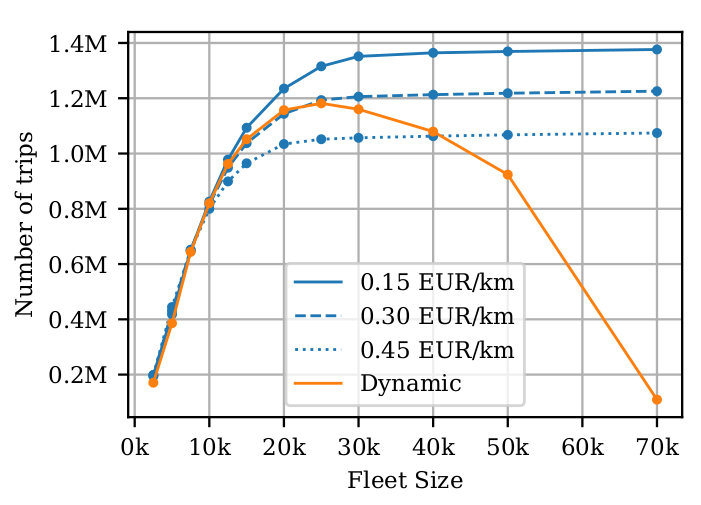
Use cases: On-demand mobility


Hörl, S., Balac, M., & Axhausen, K. W. (2019). Dynamic demand estimation for an AMoD system in Paris. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV 2019), 260–266.
On-demand mobility: Intermodality
- How to combine on-demand mobility systems with public transport?
- How to take into account rejection rates in discrete choice models?
- Various other publications ...
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., Puchinger, J., 2023. Towards Reproducible Simulations of the Grand Paris Express and On-Demand Feeder Services, in: 102nd Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board (TRB 2023). Washington D.C, United States.
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., Puchinger, J., 2023. Control-based integration of rejection rates into endogenous demand ride-pooling simulations, in: 8th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS 2023). IEEE, Nice, France, pp. 1–6.


- How to combine on-demand mobility systems with public transport?
- How to take into account rejection rates in discrete choice models?
- Various other publications ...
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., Puchinger, J., 2023. Towards Reproducible Simulations of the Grand Paris Express and On-Demand Feeder Services, in: 102nd Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board (TRB 2023). Washington D.C, United States.
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., Puchinger, J., 2023. Control-based integration of rejection rates into endogenous demand ride-pooling simulations, in: 8th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS 2023). IEEE, Nice, France, pp. 1–6.


On-demand mobility: Intermodality
- How to combine on-demand mobility systems with public transport?
- How to take into account rejection rates in discrete choice models?
- Various other publications ...
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., Puchinger, J., 2023. Towards Reproducible Simulations of the Grand Paris Express and On-Demand Feeder Services, in: 102nd Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board (TRB 2023). Washington D.C, United States.
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., Puchinger, J., 2023. Control-based integration of rejection rates into endogenous demand ride-pooling simulations, in: 8th International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS 2023). IEEE, Nice, France, pp. 1–6.



On-demand mobility: Intermodality
On-demand mobility: Algorithmic fairness
Do dispatching algorithms discriminate against certain user groups?
- Standard algorithms aim at minimizing wait times, travel times and maximizing revenue
- Do standard algorithms reject mobility-impaired person with longer interactions or larger groups more frequently than others?
-
Yes, they do!
- Can we mitigate the problem?
- Opens a whole new section of research in fleet management
Chouaki, T., Hörl, S., 2024. Comparative assessment of fairness in on-demand fleet management algorithms, in: The 12th Symposium of the European Association for Research in Transportation (hEART). Espoo, Finland.


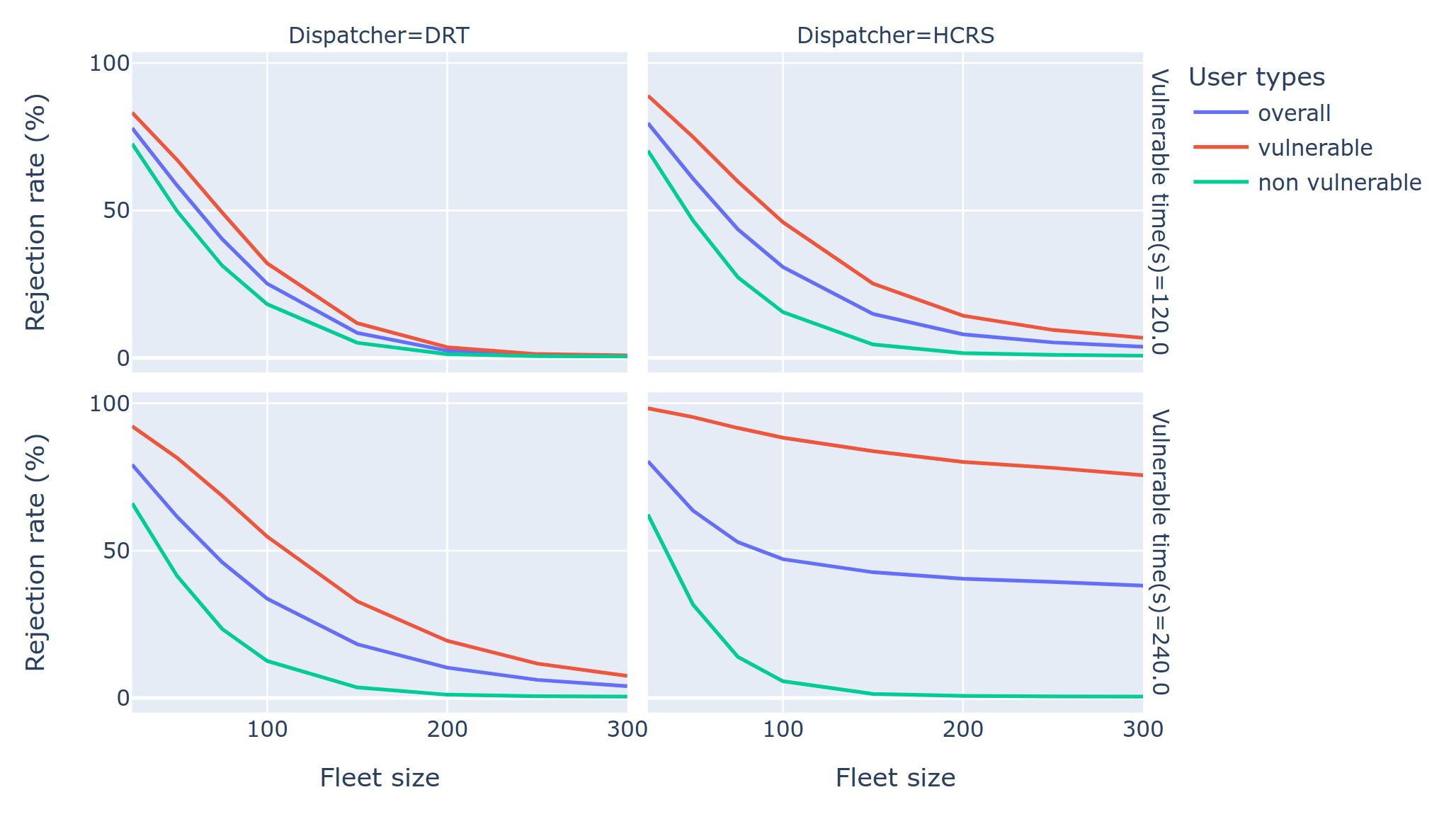
Infrastructure: Charging behaviour


How do people choose between public, home and work chargers for their electric cars?
- Very few data available (surveys and use)
-
Idea
- Assign electric vehicles to the population, then force them to charge (to avoid zero SoC)
- What is their ideal charging configuration, given the provided infrastructure?
- Collective charging strategy selection process (home, work, public) through maximization of scores
- Negative scores for zero SoC, falling below a minimum SoC during the day or at the end, monetary costs, ...
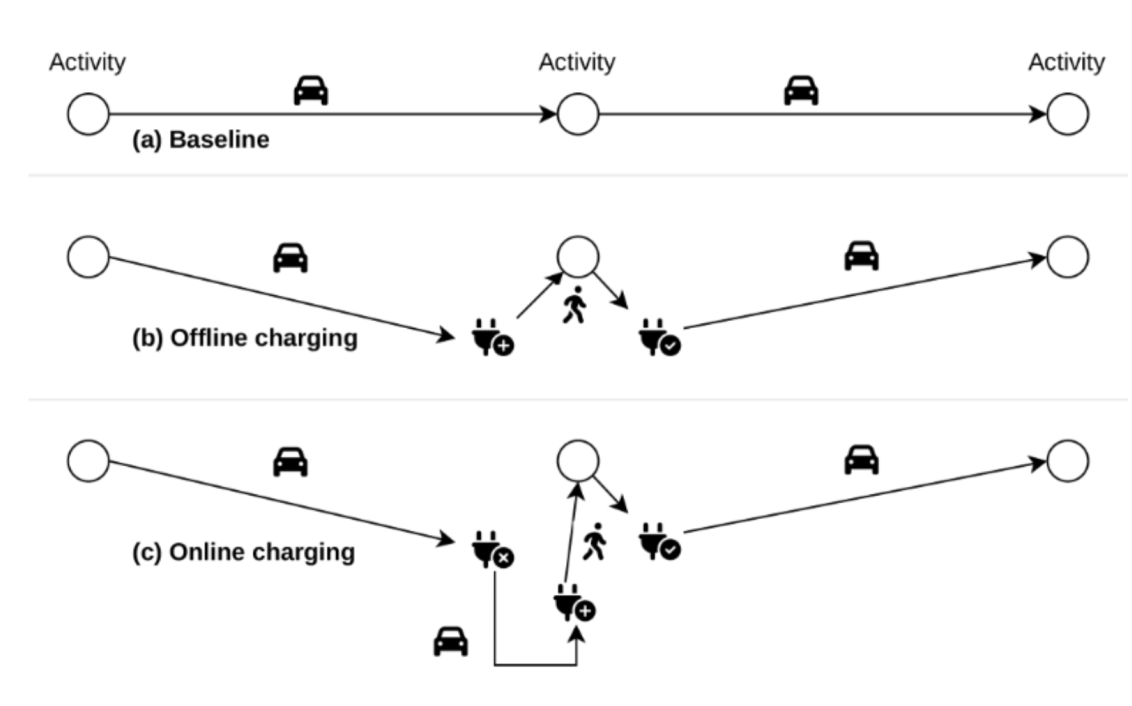

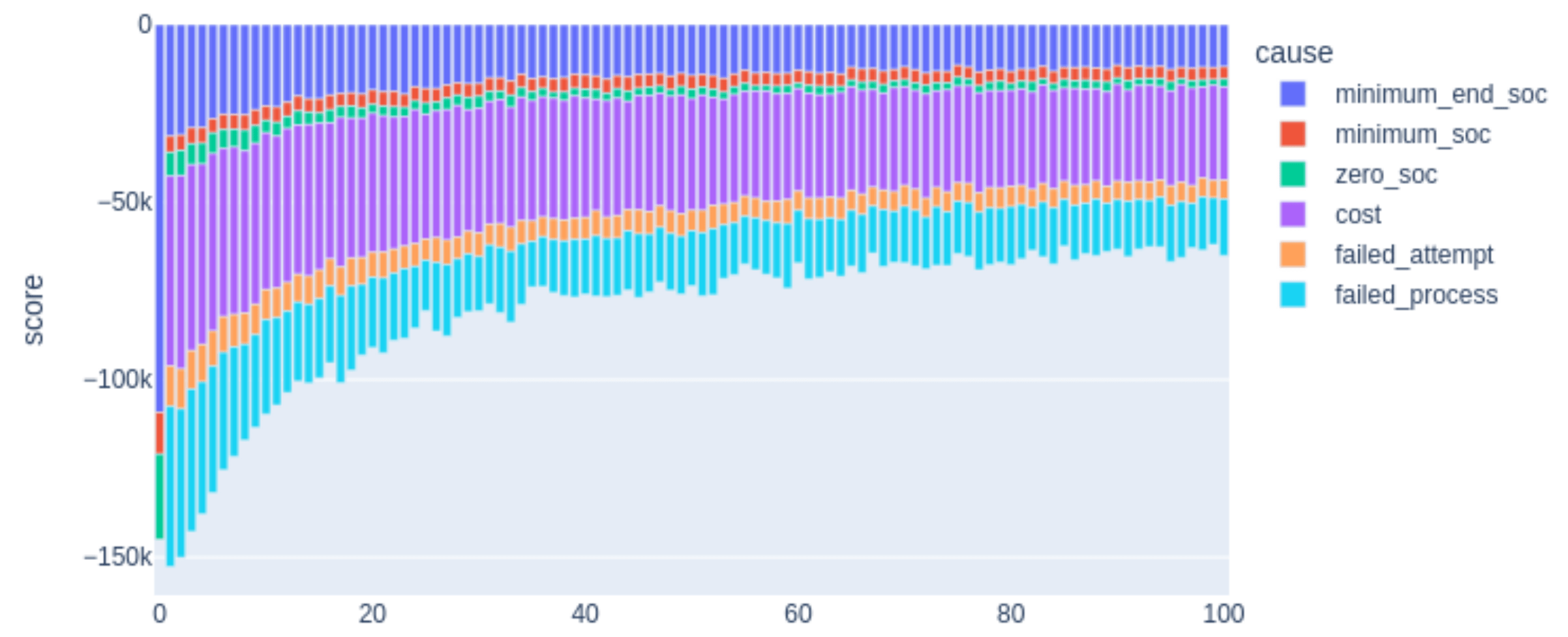
Infrastructure: Charging behaviour


How do people choose between public, home and work chargers for their electric cars?
- Very few data available (surveys and use)
-
Idea
- Assign electric vehicles to the population, then force them to charge (to avoid zero SoC)
- What is their ideal charging configuration, given the provided infrastructure?
- Collective charging strategy selection process (home, work, public) through maximization of scores
- Negative scores for zero SoC, falling below a minimum SoC during the day or at the end, monetary costs, ...


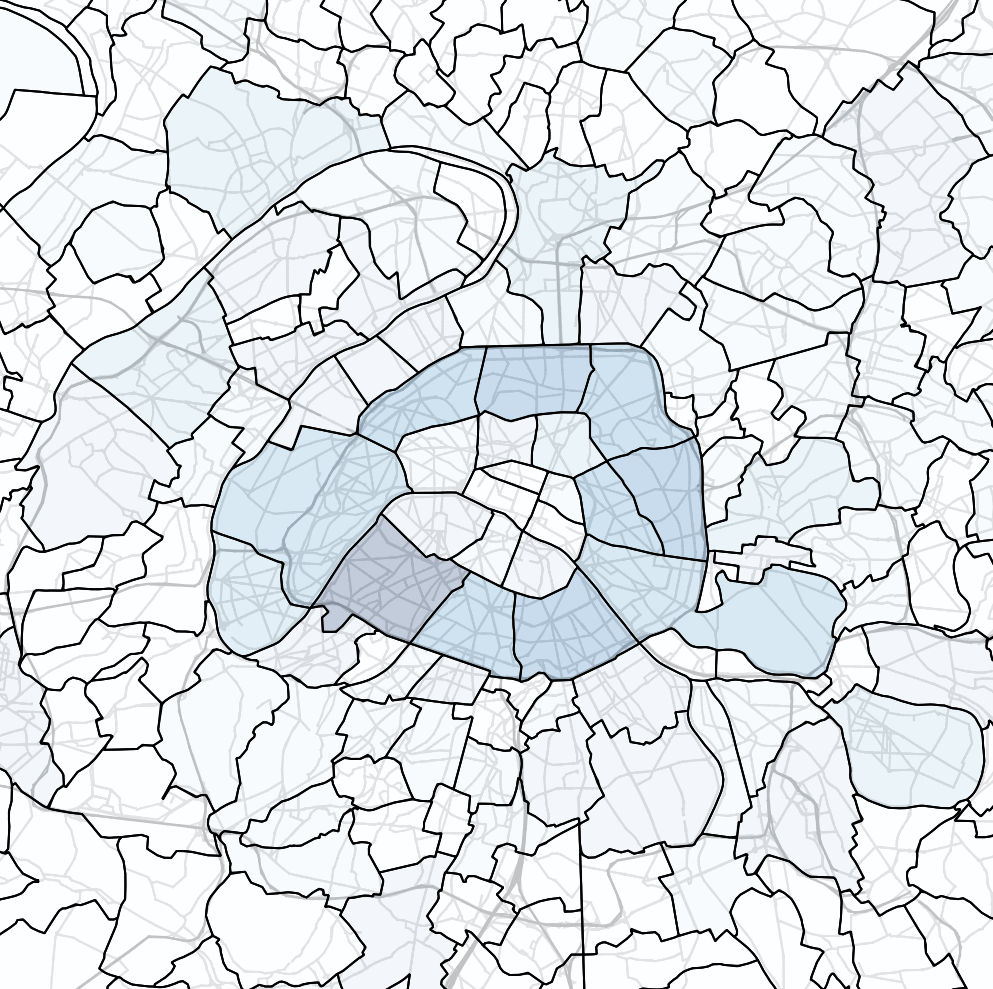
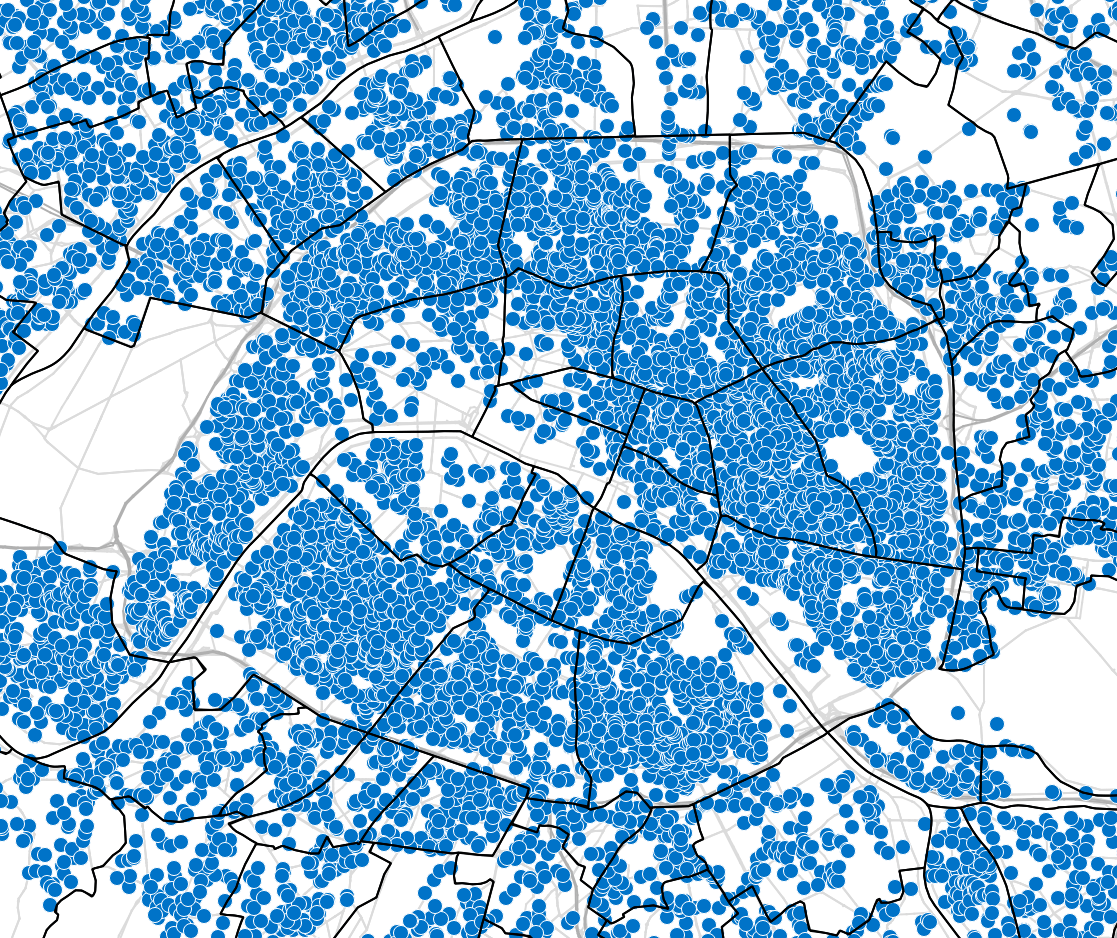
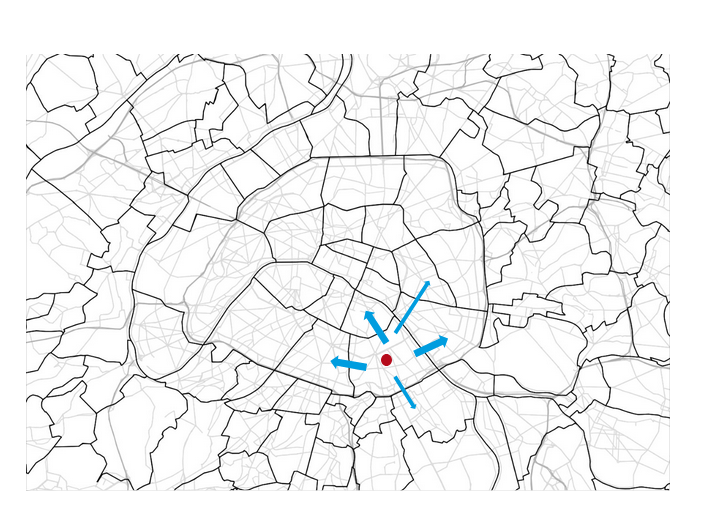
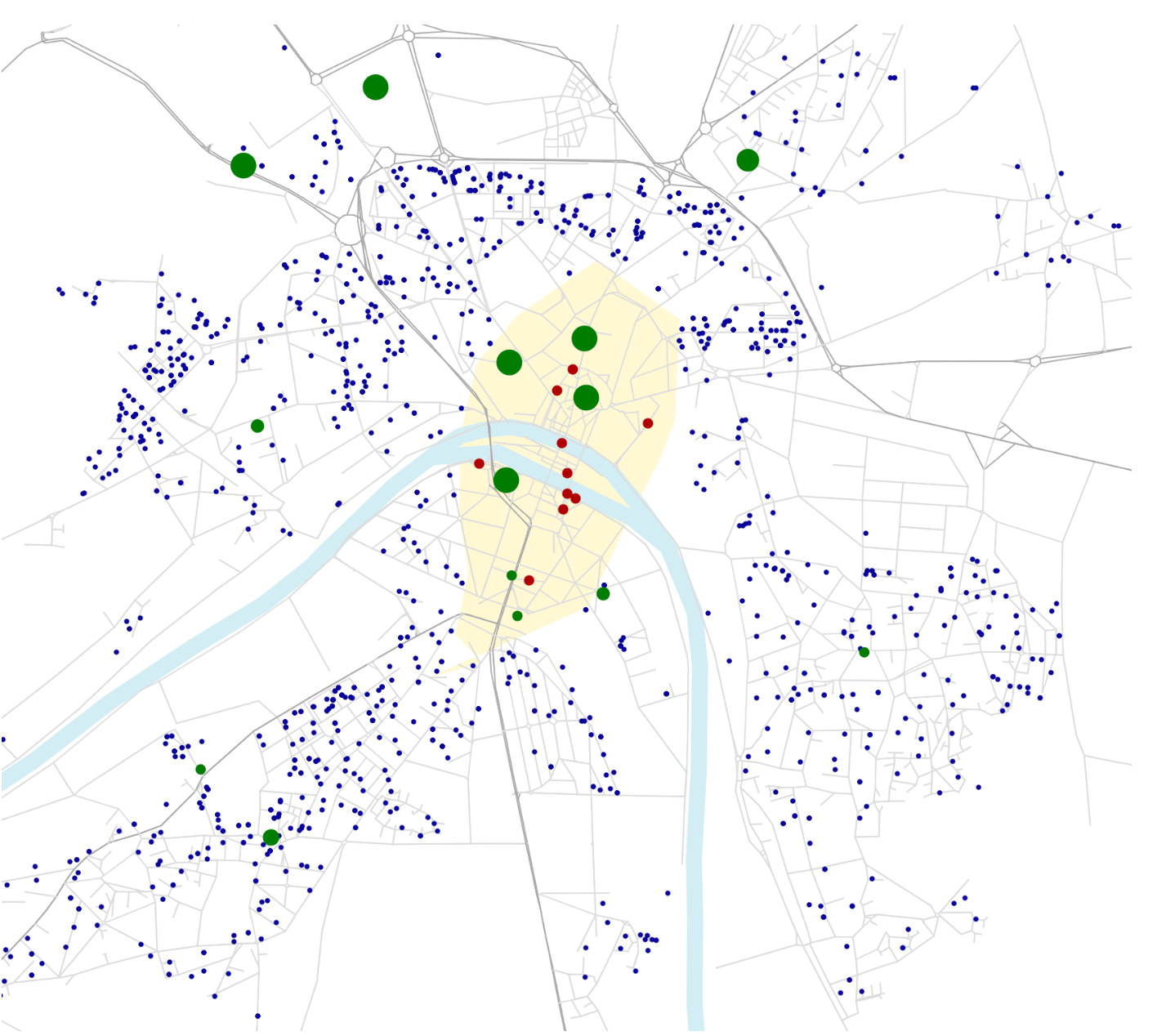
Transport policy: Limited traffic zones



What is the impact of the Limited Traffic Zone in the center of Paris?
- Rule: Non-residents that are not performing an activity in the center of Paris are not allowed to go through the center zone
- We can analyze which persons (agents) are affected by that policy
- We can measure the impact of the policy on the surrounding traffic
- High level estimation of traffic and emission impact
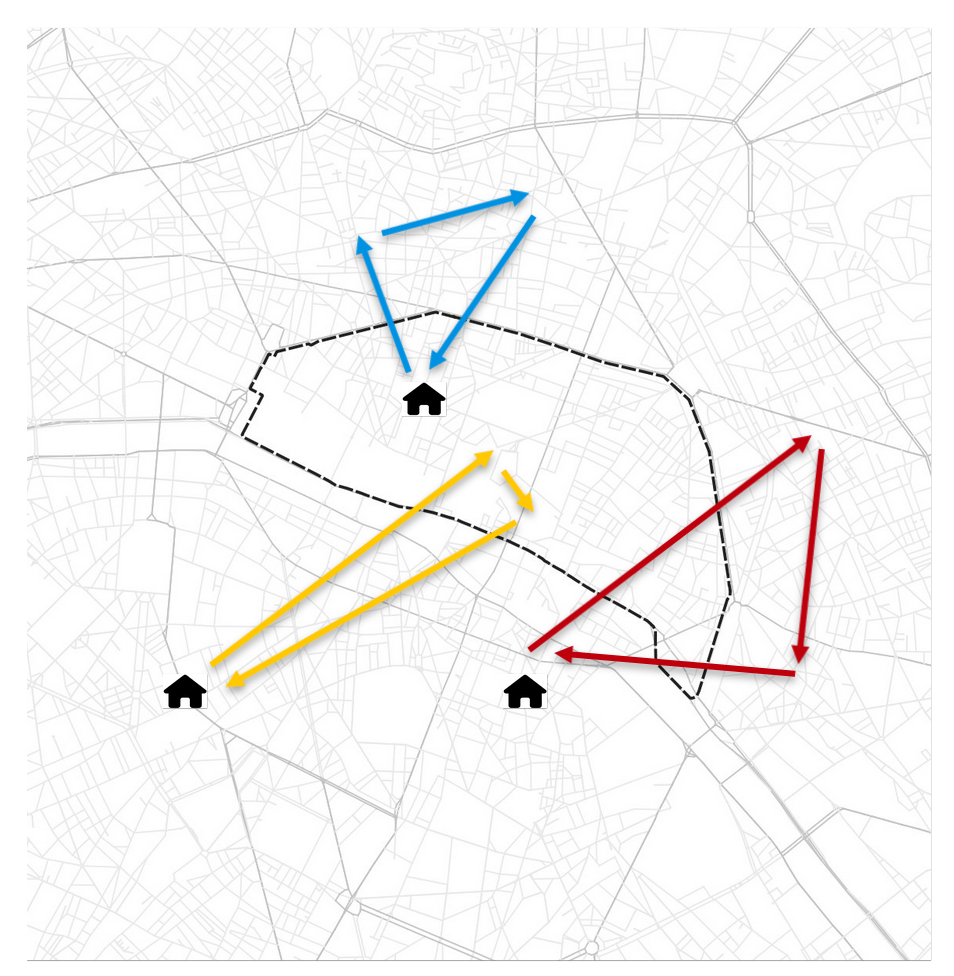
Residents
Transit
Visitors
Transport policy: Limited traffic zones


What is the impact of the Limited Traffic Zone in the center of Paris?
- Rule: Non-residents that are not performing an activity in the center of Paris are not allowed to go through the center zone
- We can analyze which persons (agents) are affected by that policy
- We can measure the impact of the policy on the surrounding traffic
- High level estimation of traffic and emission impact
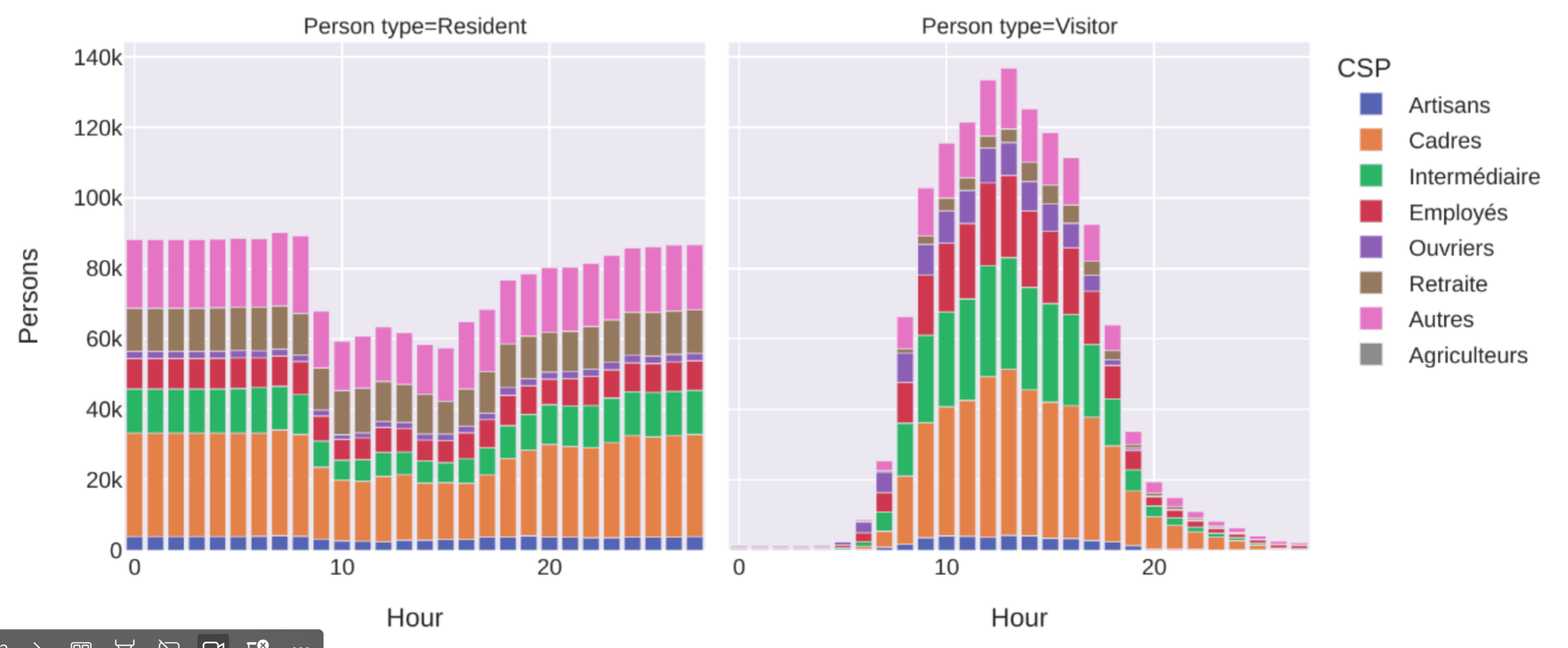

Transport policy: Limited traffic zones


What is the impact of the Limited Traffic Zone in the center of Paris?
- Rule: Non-residents that are not performing an activity in the center of Paris are not allowed to go through the center zone
- We can analyze which persons (agents) are affected by that policy
- We can measure the impact of the policy on the surrounding traffic
- High level estimation of traffic and emission impact
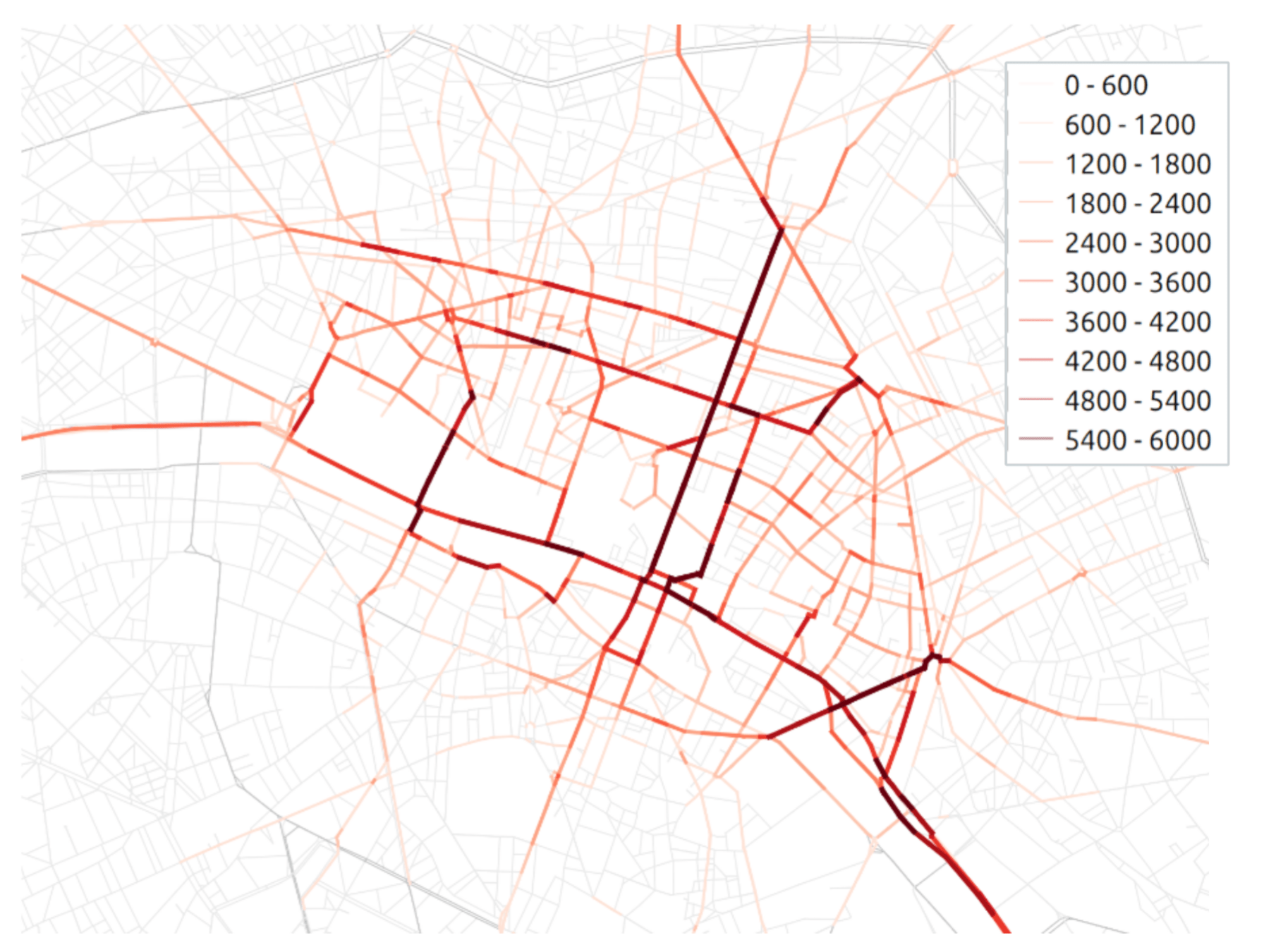
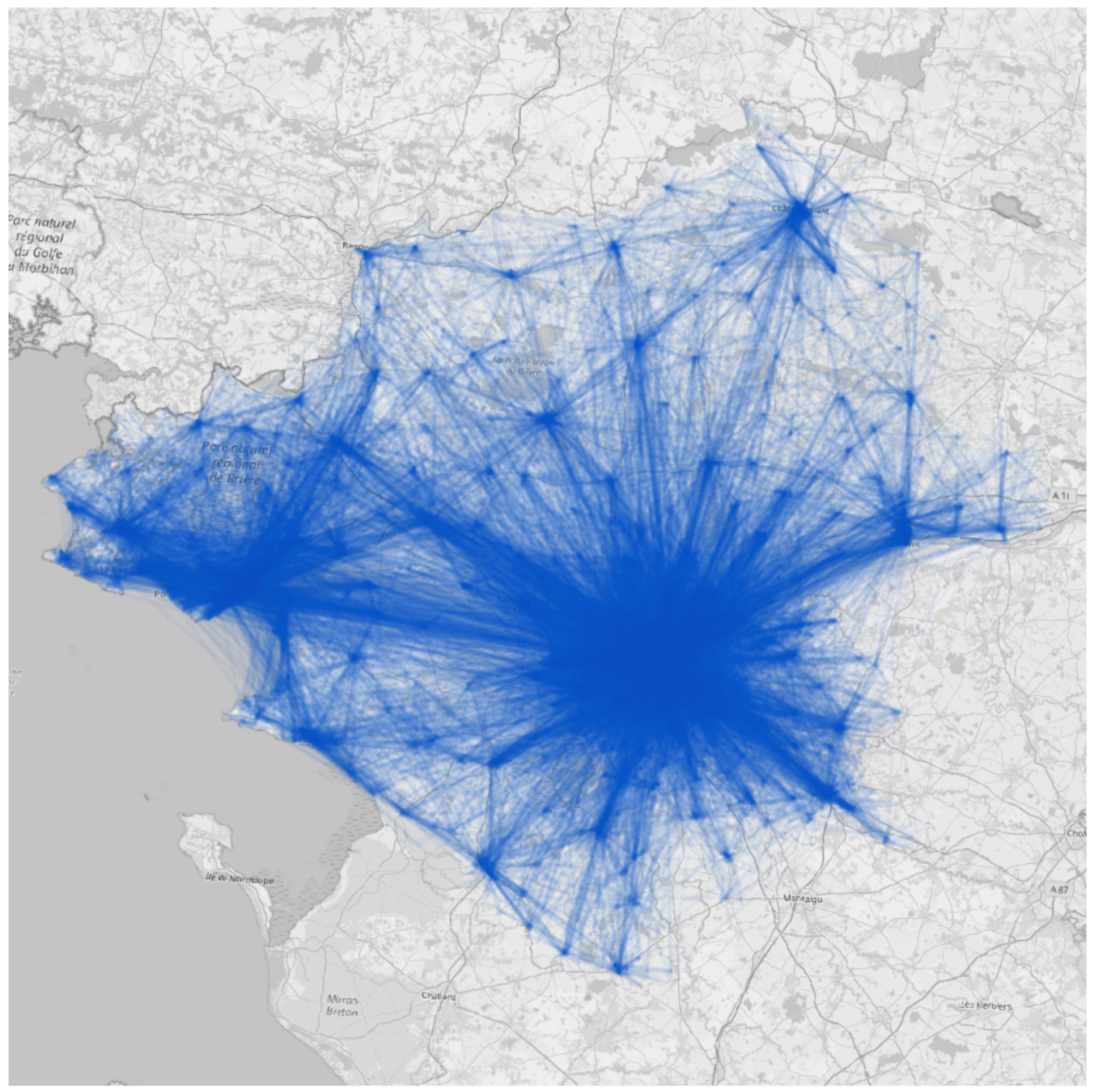
Overall flow related to the ZTL
Transport policy: Limited traffic zones



Transit flow related to the ZTL
What is the impact of the Limited Traffic Zone in the center of Paris?
- Rule: Non-residents that are not performing an activity in the center of Paris are not allowed to go through the center zone
- We can analyze which persons (agents) are affected by that policy
- We can measure the impact of the policy on the surrounding traffic
- High level estimation of traffic and emission impact
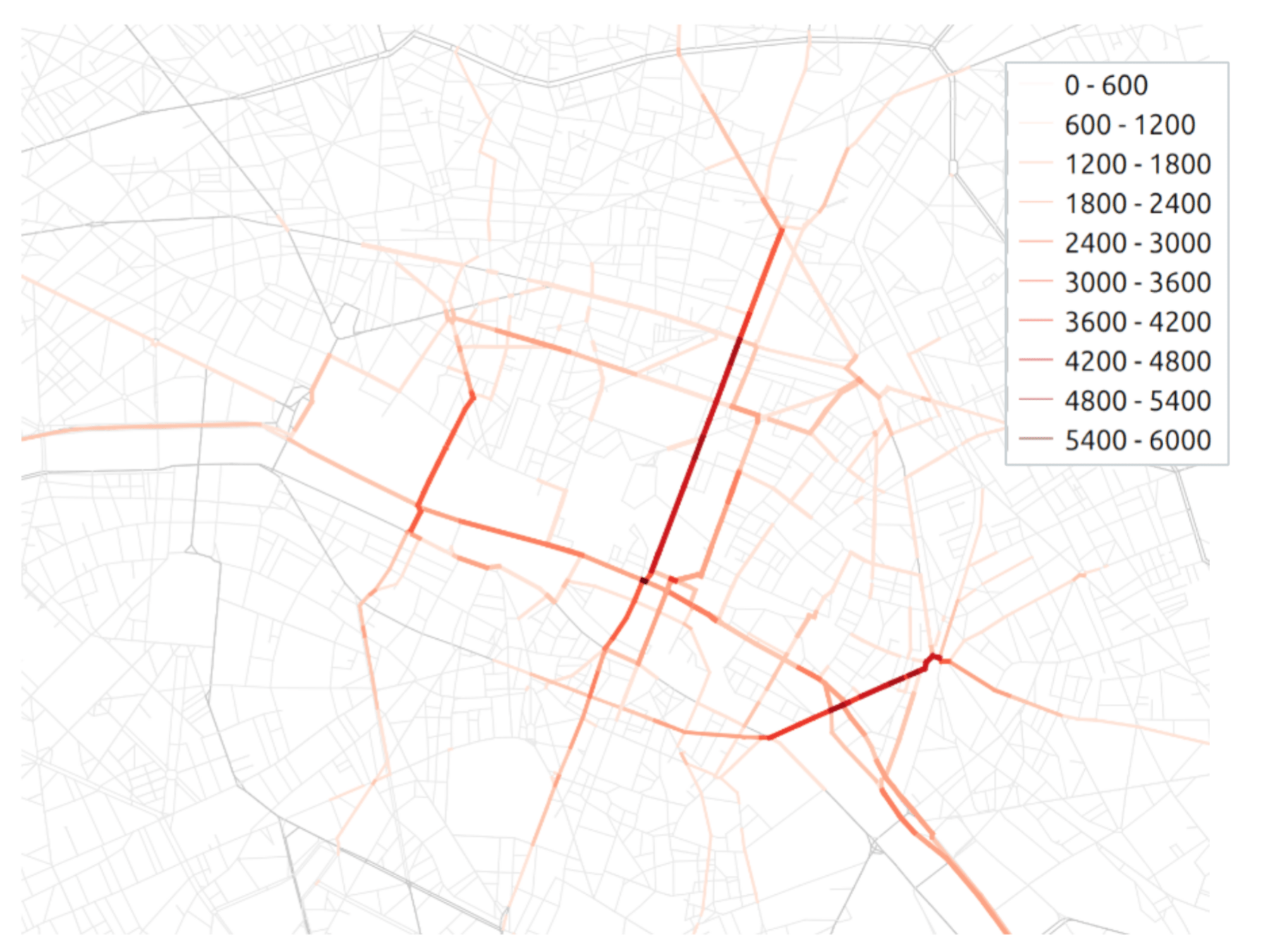
Transport policy: Limited traffic zones



Transit flow related to the ZTL
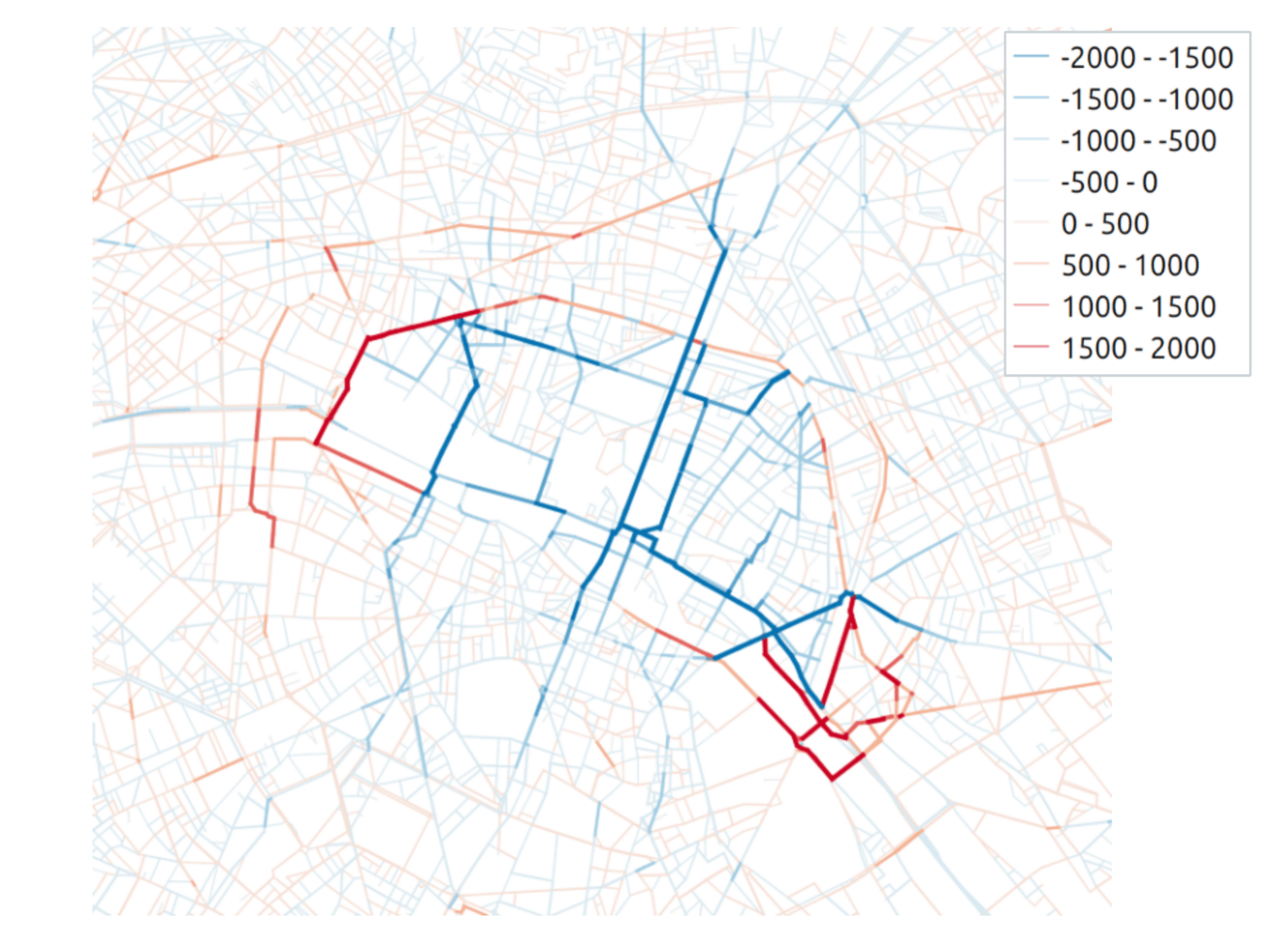
Difference after introduction of ZTL
What is the impact of the Limited Traffic Zone in the center of Paris?
- Rule: Non-residents that are not performing an activity in the center of Paris are not allowed to go through the center zone
- We can analyze which persons (agents) are affected by that policy
- We can measure the impact of the policy on the surrounding traffic
- High level estimation of traffic and emission impact
Transport policy: Parcel deliveries


A detailed study of environmental policies on parcel deliveries
- Obtaining a daily synthetic parcel demand based on a synthetic population for Lyon and statistics (Gardrat)
- Identifying all logistics centers in the area
- Cost structures (vehicles, drivers, operational) for ICVs and BEVs (small, medium, large)
- Definition of one Heterogeneous Fleet VRP per logistics center, sensitive to cost inputs
- Testing of CO2 tax, ICV tax, qualitative policies
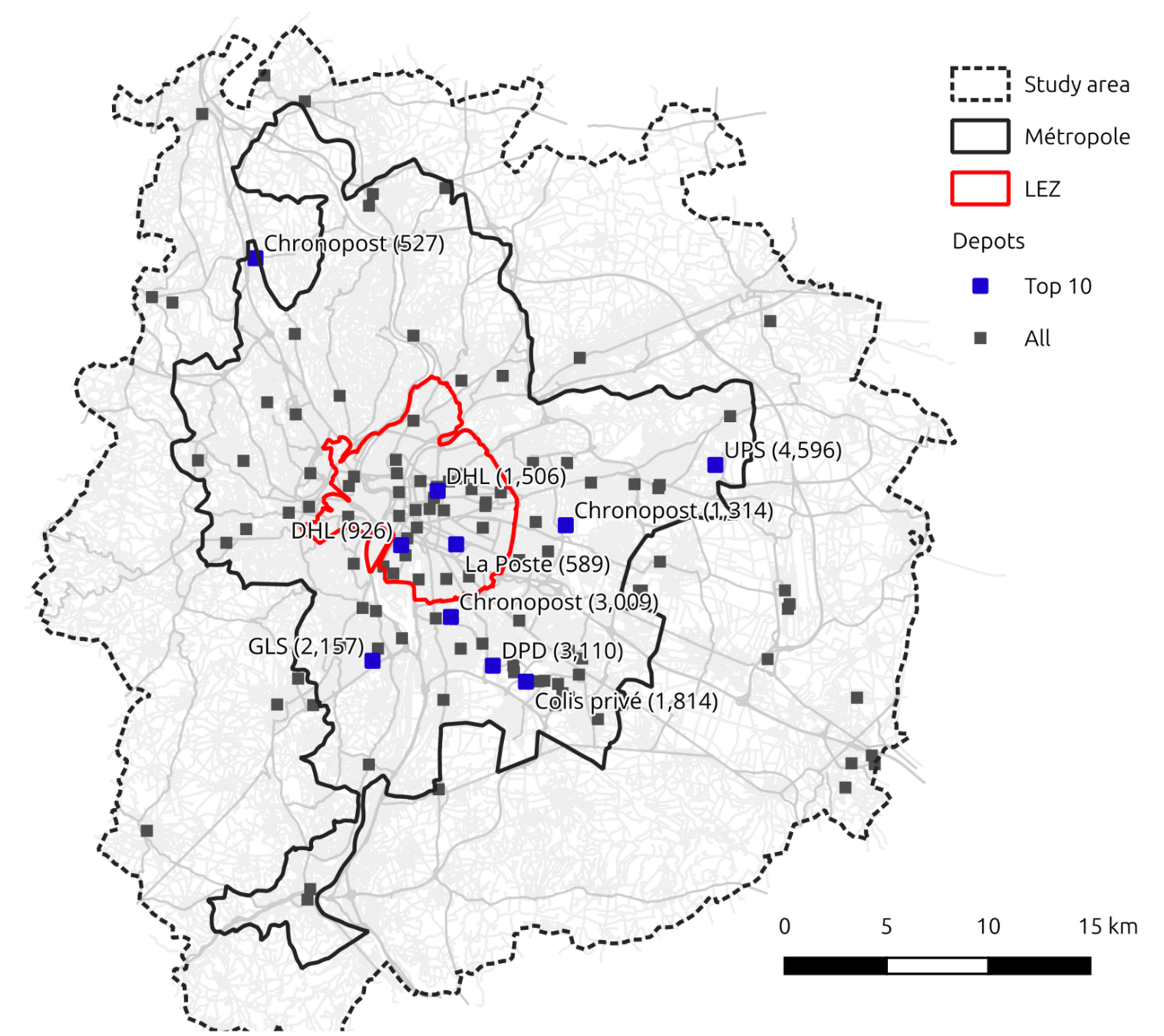

Transport policy: Parcel deliveries


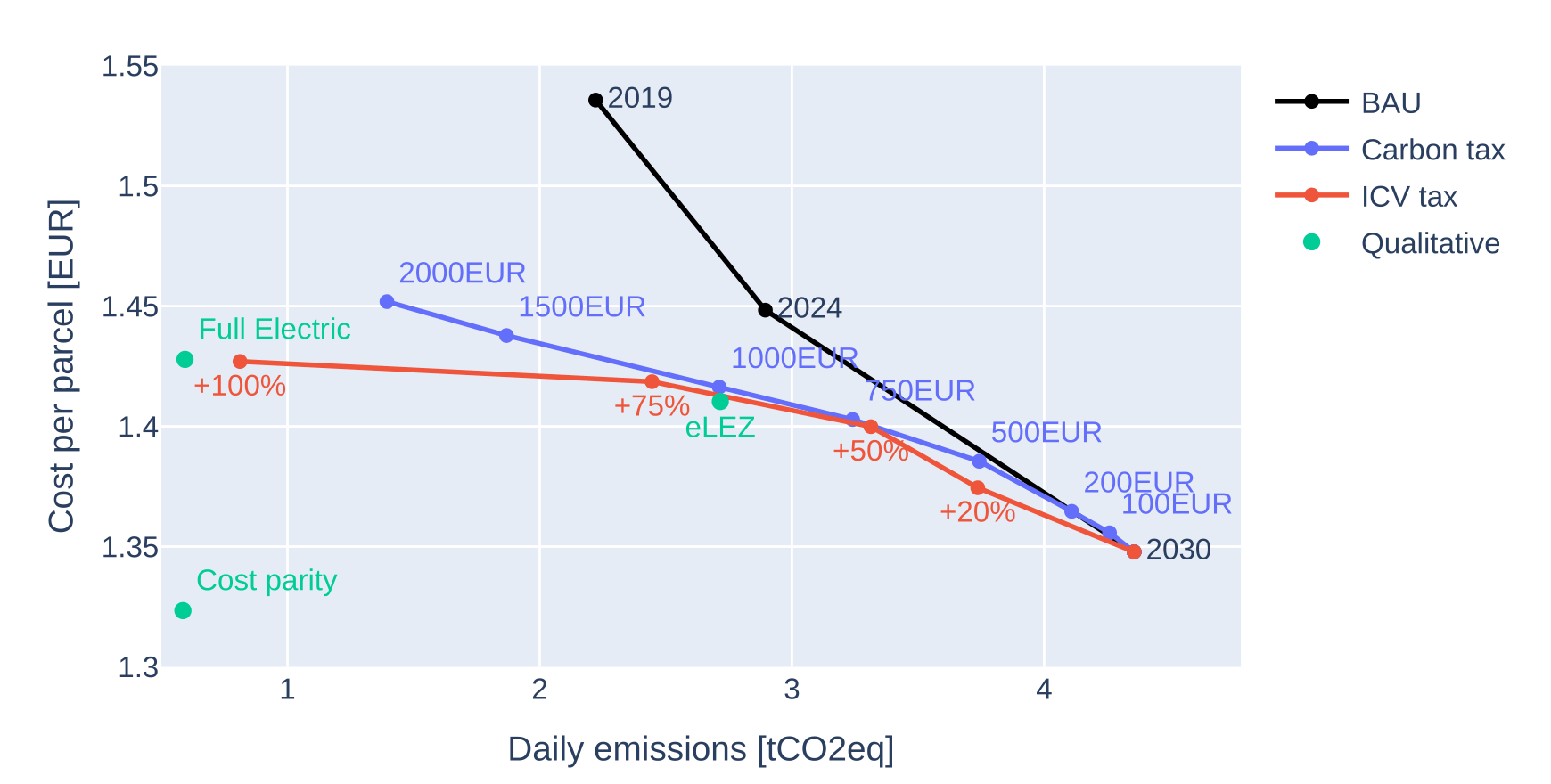
A detailed study of environmental policies on parcel deliveries
- Obtaining a daily synthetic parcel demand based on a synthetic population for Lyon and statistics (Gardrat)
- Identifying all logistics centers in the area
- Cost structures (vehicles, drivers, operational) for ICVs and BEVs (small, medium, large)
- Definition of one Heterogeneous Fleet VRP per logistics center, sensitive to cost inputs
- Testing of CO2 tax, ICV tax, qualitative policies
Hörl, S., Briand, Y., & Puchinger, J. (2025). Decarbonization policies for last-mile parcels: A replicable open-data case study for Lyon. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 146, 104893.

Communication: Interface development



TERRITORIA prize 2024
with Paris Saclay

- Ambition to provide project results through interactive interfaces
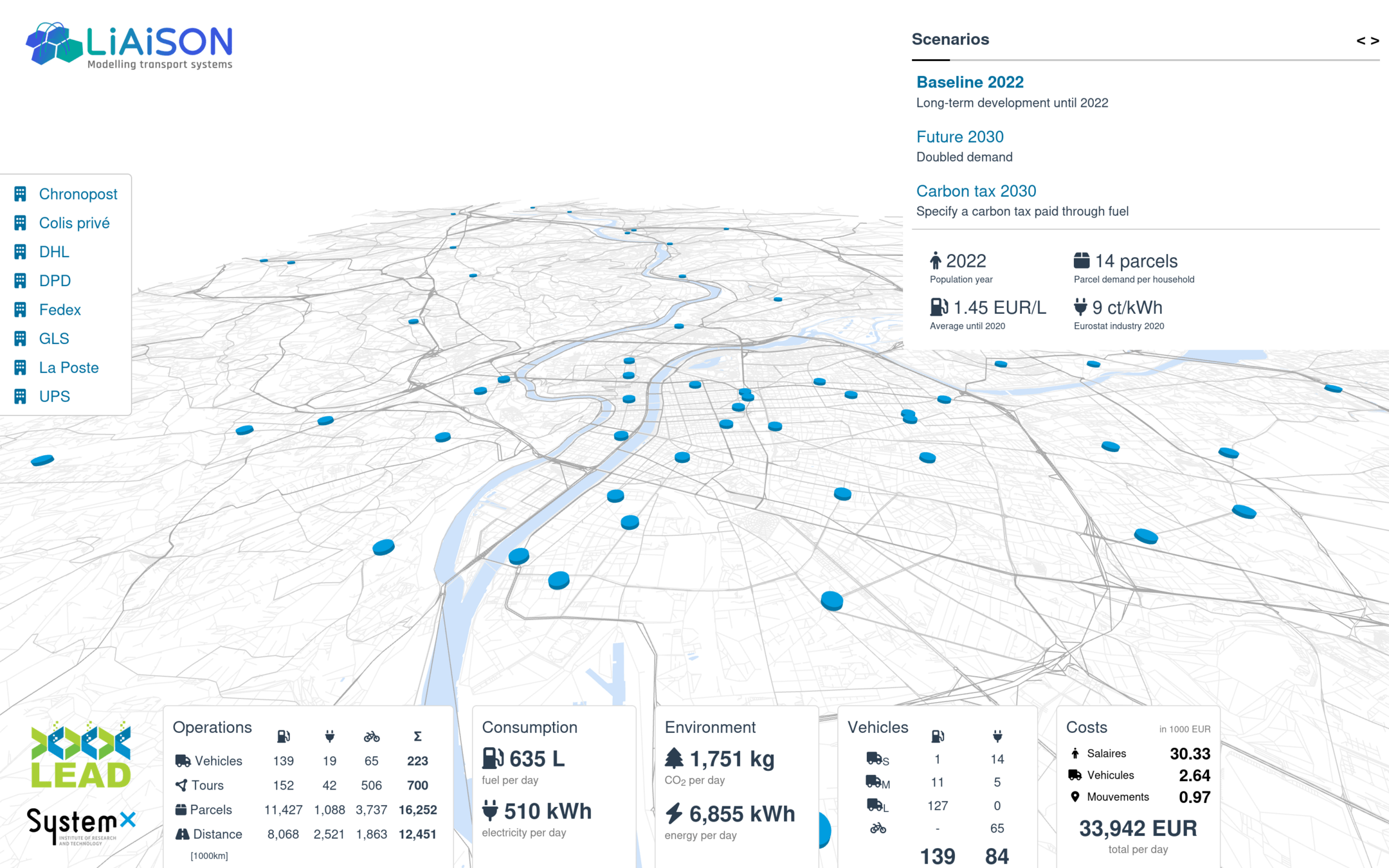
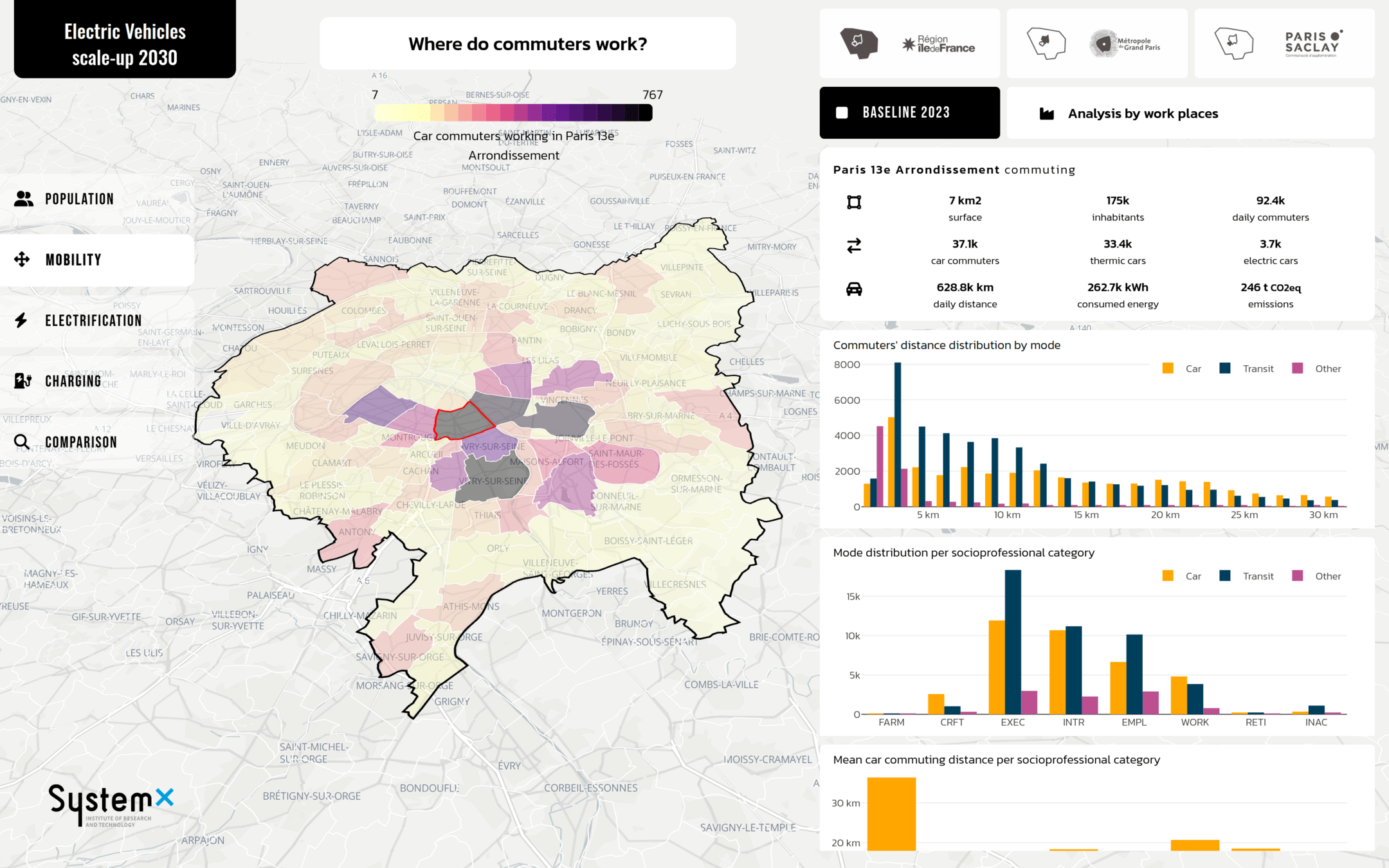
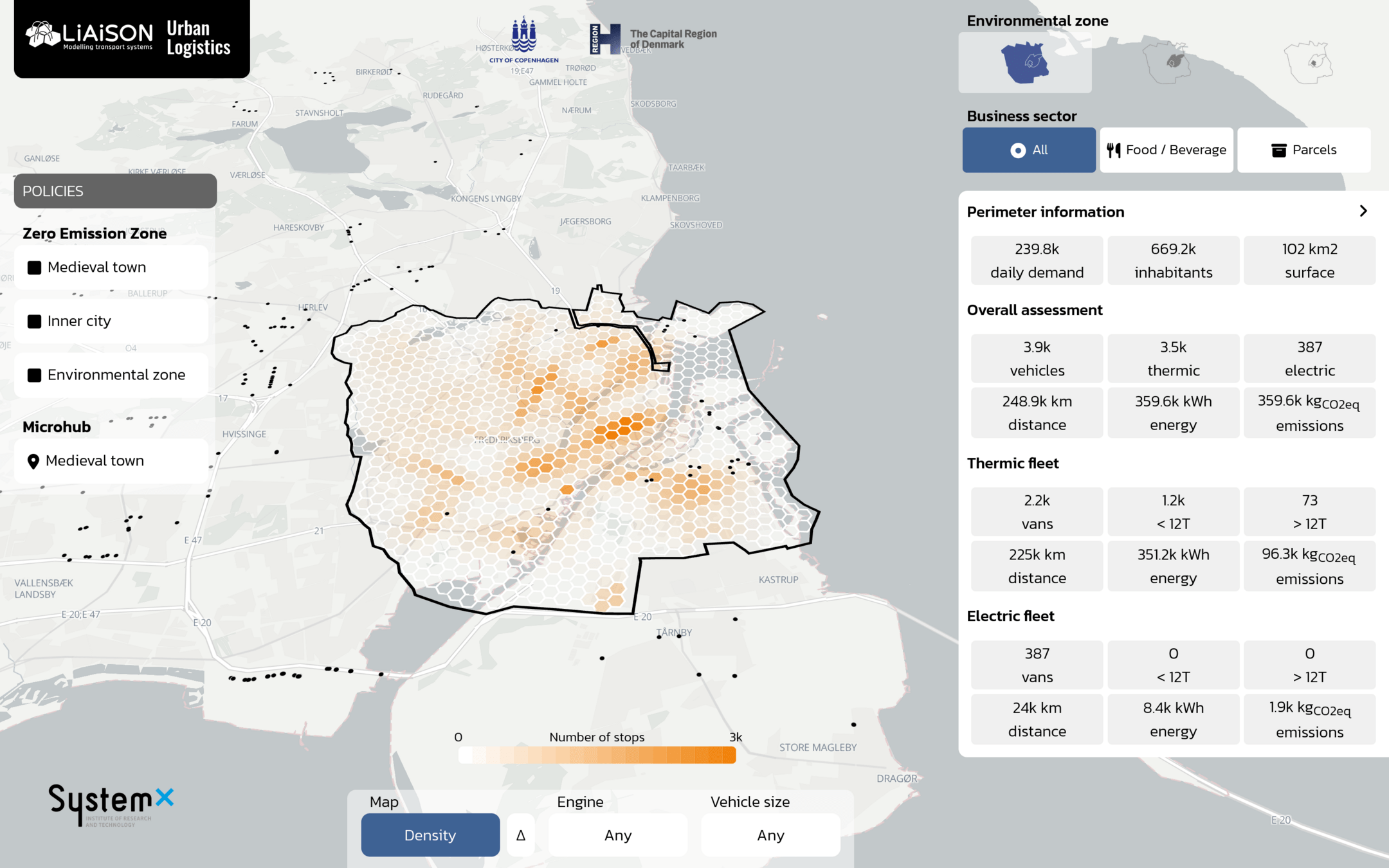
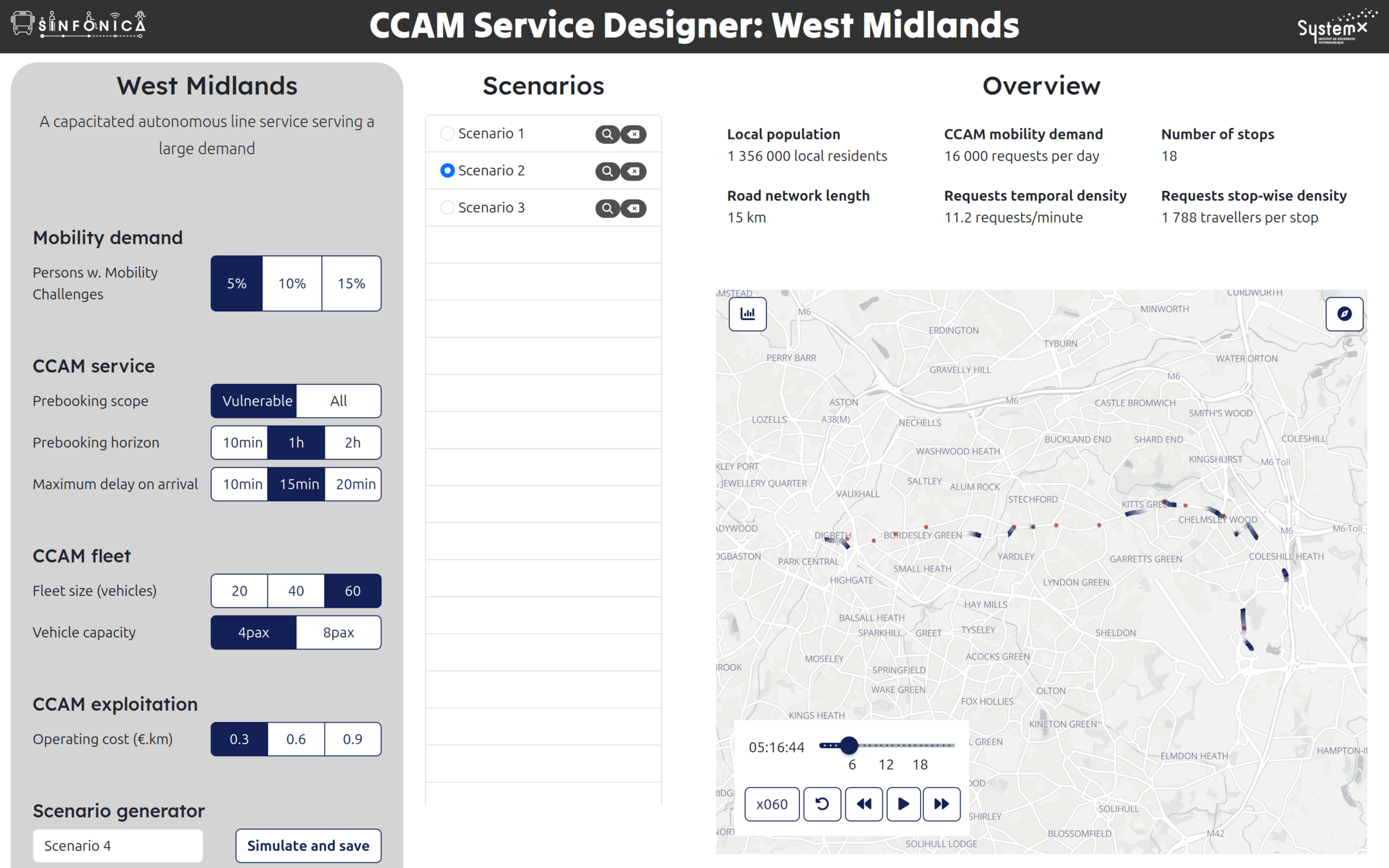
Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results
Transport modeling chain


Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results
Replicability?


Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results
Replicability?
Yes, eqasim-synpop for France and a handful of other cases.
Working on generalizing the methodology.


Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results
Replicability?
Yes, eqasim-synpop for France and a handful of other cases.
Working on generalizing the methodology.
Partly, eqasim-java is accessible. Goal to publish a calibrated fully replicable simulation for Île-de-France in the coming months.


Raw data
Synthetic population
Agent-based transport simulation
Use cases
Results
Replicability?
Yes, eqasim-synpop for France and a handful of other cases.
Working on generalizing the methodology.
Partly, eqasim-java is accessible. Goal to publish a calibrated fully replicable simulation for Île-de-France in the coming months.
Using the new baseline simulation, our goal is to publish upcoming studies in a fully replicable way.


Outlook: Surrogate modeling
Natterer, E. S., Rao, S. R., Tejada Lapuerta, A., Engelhardt, R., Hörl, S., & Bogenberger, K. (2025). Machine learning surrogates for agent-based models in transportation policy analysis. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 180, 105360.


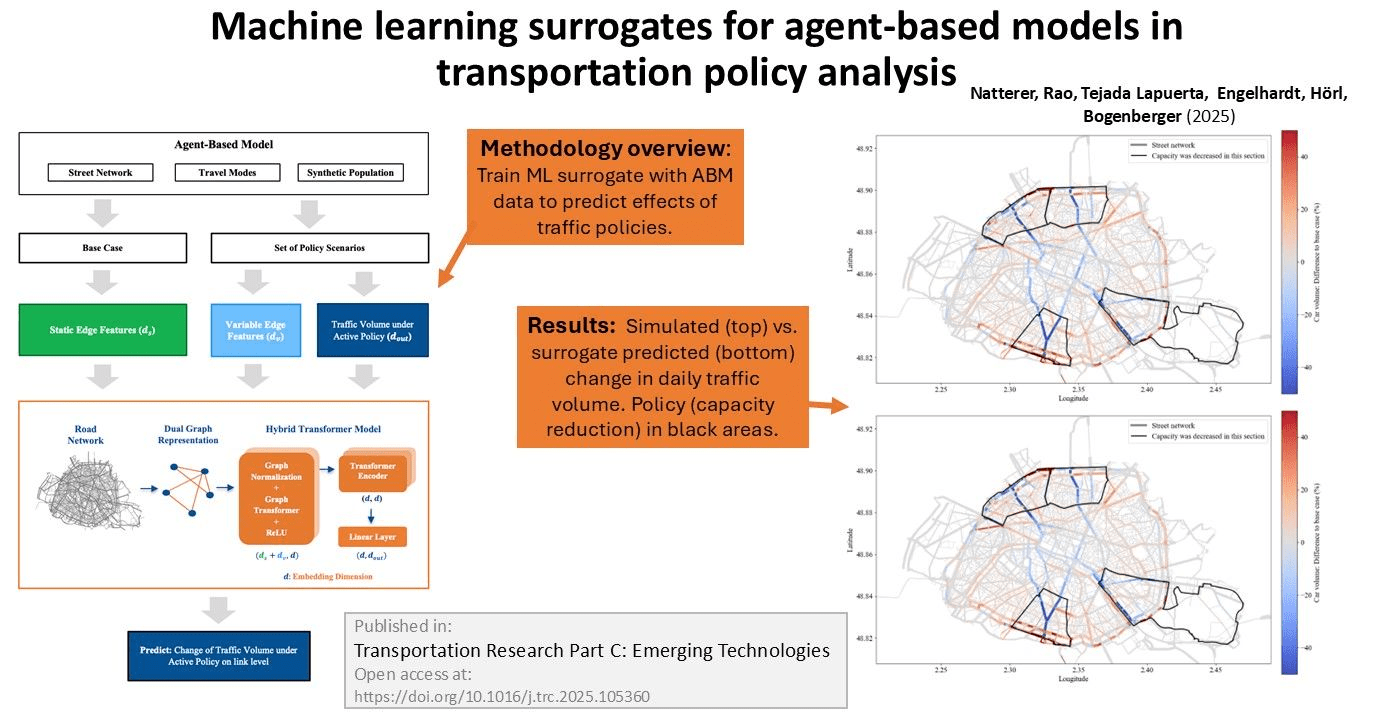

Thank you!
sebastian.horl@irt-systemx.fr

Icons throughout the presentation: https://fontawesome.com
Website
Contact


Large-scale agent-based simulations of the transport system: Replicability and application cases in France
By Sebastian Hörl
Large-scale agent-based simulations of the transport system: Replicability and application cases in France
- 142



