Introduction to ORMs

Why ORM?
Object-Relational Impedance Mismatch:
Basically, OO doesn't talk with SQL
- Lots of SQL for lots of objects
- RDBMs' dialect
- Write/change/maintain nightmare
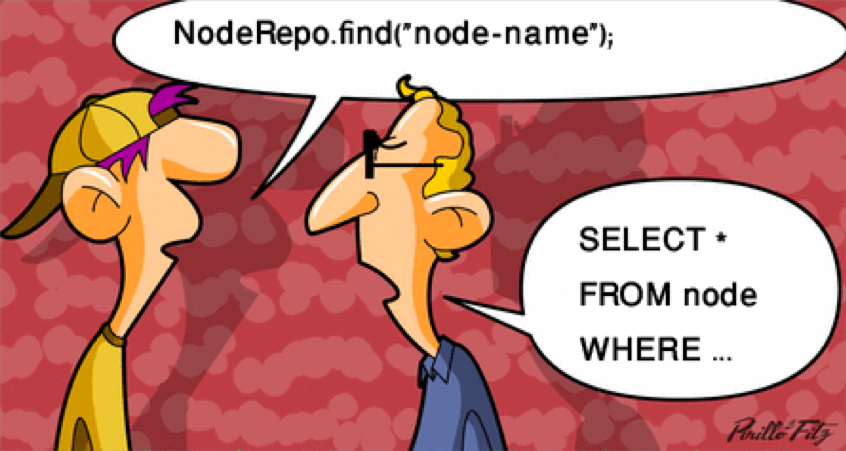
Remind me, why do we use RDBMS?
- High performance and powerful
- Available everywhere
- Proven
- In theory
- and in practice
- Known in almost every language
- Almost no dominant replacements
Solution: ORM
Object-relational Mapping (ORM) is a way of mapping between objects and relational databases.
ORM Benefits
-
Productivity
-
OOP
-
Validation
-
No need to write SQL
-
-
Performance
-
Cache Objects
-
Lazy/Eager Loading
-
Lazy Updating
-
-
Portability
- Different SQL dialects
-
Protection
- Against SQL injection attacks, sanitizing, and escaping data
ORM Architecture
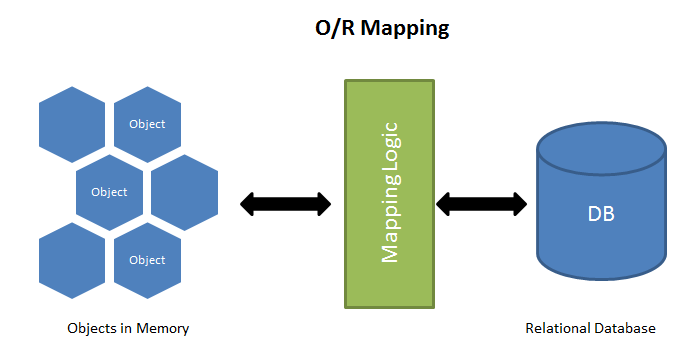
Without ORM
With ORM
-- Creating a Tasks table w/o an ORM
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
id serial PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
title character varying(125) NOT NULL,
description character varying(125) NOT NULL,
deadline DATE NOT NULL,
);
-- Querying w/o an ORM
SELECT * FROM tasks;
-- Inserting a new tasks
-- into the Tasks table w/o an ORM
INSERT INTO tasks (
default,
'pay bills',
'very important',
10/10/16
);// Define mapping between a
// model and a table w/ an ORM
var Task = sequelize.define('tasks', {
title: Sequelize.STRING,
description: Sequelize.TEXT,
deadline: Sequelize.DATE
});
// Querying with an ORM
Task.findAll();
// Create a new task w/ an ORM
Task.create({
title: 'pay bills',
description: 'very important task',
deadline: new Date('2016-10-10T14:30:00')
})
.then(function(task){
...
});Disadvantages of
ORM
-
Can add complexity to code
- Potential increases processing overhead
- ORM might dictate DB design
Demo
Sequelize + Express


Resources
Copy of ORM
By Ray Farias
Copy of ORM
Introduction to Object Relational Mapping
- 1,832



