Solving Common Web Component Problems
with Server Side Rendering
Simon MacDonald
@macdonst@mastodon.online
Index
What are Web Components?
Web Components is a suite of different technologies allowing you to create reusable custom elements — with their functionality encapsulated away from the rest of your code — and utilize them in your web apps.
– MDN
〞
Oh, you mean React



Let's address the elephant in the room right away
- Reusable Components
- DOM Syncing
- Stateful
- Not the platform
React
- Reusable Components
- Interoperable
- Accessible
- Part of the platform
WC's
What are Web Components (Part Deux)?
Custom elements
Custom elements
<hello-world name="Simon">
<h1>Hello Simon</h1>
</hello-world>Shadow dom
Shadow dom
<hello-world name="Simon">
#shadow-root
<h1>Hello <span>Simon</span></h1>
</hello-world>Html templates
Html templates
<hello-world>
#shadow-root
<h1>
Hello <slot name="name"></slot>
</h1>
<span slot="name">Simon</span>
</hello-world>Index

Why are Web Components useful?
aside is anyone actually using web components?

sure seems like it
Apps made with web components
Index

Problem: Flash of Unstyled Content (fouc)
A flash of unstyled content is an instance where a web page appears briefly with the browser's default styles prior to loading an external CSS stylesheet, due to the web browser engine rendering the page before all information is retrieved
– Wikipedia
〞
Problem: Flash of undefined custom elements (fouce)
You may see a brief flash of unstyled HTML where your custom elements should be when the page loads. This is not dissimilar to FOUC, which occurs when HTML is displayed before the stylesheet has loaded.
〞
Fouce example
Why does Fouce happen?
- Browser requests HTML
- It encounters an unknown element, "hello-world"
- The browser treats the unknown element as an inline element
- No styles are applied due to the Shadow DOM boundary
- Browser loads the web components JavaScript
- The web component is instantiated, and the encapsulated CSS & JavaScript is applied
- FOUCE HAPPENS!!!
Problem: Shadow DOM doesn't play well with native forms
Shadow dom vs forms example
Index

Solutions

Fouce solution
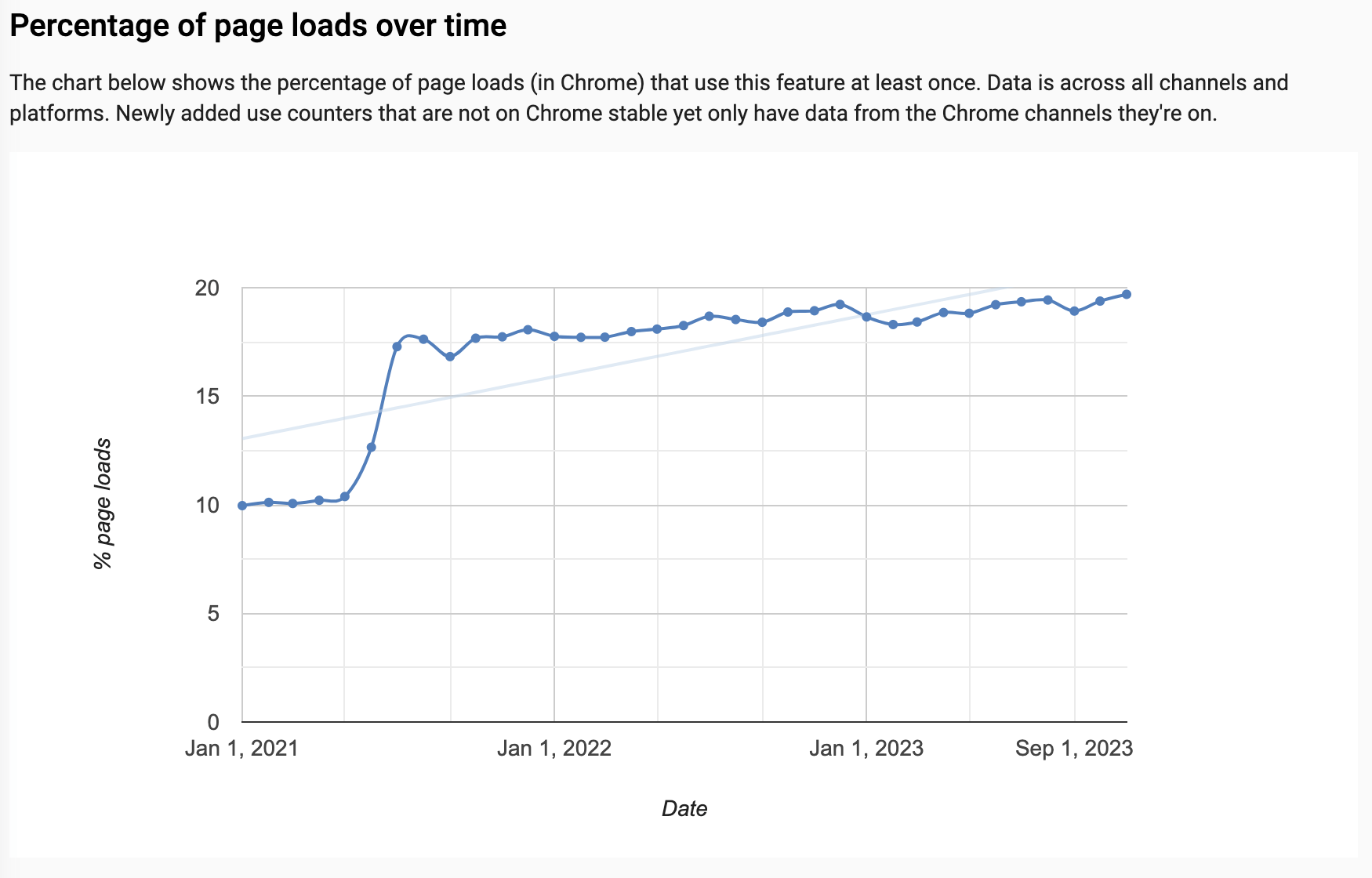
Declarative Shadow DOM
Proposal to allow rendering elements with shadow DOM (aka web components) using server-side rendering.
〞
Declarative Shadow DOM
Declarative Shadow DOM
<hello-world>
#shadow-root
<style>
h1 { color: red }
</style>
<h1>
Hello <slot name="name"></slot>
</h1>
<span slot="name">Simon
</span></hello-world>
Shadow DOM doesn't play well with native forms Solution














PROBLEM CAUSED BY JS
ASK FOR
SOLUTION
FACE* and Element Internals
*Form Associated Custom Elements
Is there a solution we can use today?

〞
We can't solve problems by using the same kind of thinking we used when we created them.
– Albert Einstein


what is enhance?
Author
Enhance allows developers to write components as pure functions that return HTML. Then render them on the server to deliver complete HTML immediately available to the end user.
Standards
Enhance takes care of the tedious parts, allowing you to use today’s Web Platform standards more efficiently. As new standards and platform features become generally available, Enhance will make way for them.
Progressive
Enhance allows for easy progressive enhancement so that working HTML can be further developed to add additional functionality with JavaScript.
Enhance is a web standards-based HTML framework. It’s designed to provide a dependable foundation for building lightweight, flexible, and future-proof web applications.
enhance fouce solution
stopping fouce
- Browser requests HTML
- Enhance expands your custom elements on the server as well as hoisting your encapsulated styles to the page's head tag
- It encounters an unknown element, "hello-world"
- The browser treats the unknown element as an inline element, but your CSS is already loaded, so it is styled properly
- Browser loads the web components JavaScript
- The web component is instantiated, and your custom element is "enhanced"
enhance fouce solution
export default function HelloWorld({ html }) {
return html`
<style>
h1 { color: red }
</style>
<h1>
Hello <slot name="name"></slot>
</h1>`
}<hello-world>
<span slot="name">Simon</slot>
</hello-world>HTML
Javascript
enhance shadow dom vs forms solution
enhance shadow dom vs forms solution
export default function MyButton({ html }) {
return html`
<style>
button {
color: white;
background-color: black;
border-radius: 3px;
}
</style>
<button>
<slot></slot>
</button>`
}<form action="javascript:alert('hello')">
<input type="text" name="name">
<input type="password" name="password">
<my-button>
Login
</my-button>
</form>HTML
Javascript
Benefits of enhance
All components are server side renderable with no changes.
Leverage your CSS skills and style encapsulation in the light DOM.
Use slots without the shadow DOM
Avoid excessive JavaScript code by leveraging the platform and web standards
Thanks!
Wey Wey Web: Solving Common Web Component Problems
By Simon MacDonald
Wey Wey Web: Solving Common Web Component Problems
- 1,048



