CSS BASICS

CSS

Is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language. Most often used to set the visual style of web pages and user interfaces written in HTML and XHTML
Along with HTML and JavaScript, CSS is a cornerstone technology used by most websites to create visually engaging webpages, user interfaces for web applications, and user interfaces for many mobile applications
CSS is used to describe the appearance of the webpage
Oppa, Gangnam Style!
- Unfortunately, the CSS language is considerably different from the HTML language
- However, like HTML, it is very easy to understand and write
One ring to rule them all
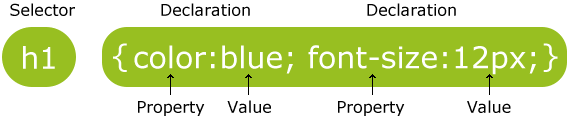
CSS has a very straightforward syntax. Your CSS is divided into rules. Each rule has two parts: a selector and one or more declarations (each of which has a property and a value). Here's an example rule :
I choose you!
The selector does exactly what it sounds like: it selects certain parts of your HTML document. There're a few ways for you to do this. The simplest is to simply u se a tag name (this'll select all the <h1> tags in your document):
h1 {
*put your declarations here
}Keepin' it Classy
Another way is to use IDs and Classes. This is useful if you want to only select one or a few of a certain tag. They both correspond to special attributes that you can use on any tag.
Use IDs to uniquely identify a single tag:
<div id="myfavdiv">Hiyya!</div>And select them in CSS with a hash (#) followed by the ID:
#myfavdiv {
*declarations go here*
}Use classes to identify groups of tags:
<div class="smalldivs">itsy-bitsy</div>
<div class="smalldivs">tiny</div>And select them with a period (.) followed by the class:
.smalldivs {
*declarations go here*
}Declare war on boring!
Once you've selected a set of elements, use declarations to change their visual properties. Declarations come after a selector, and are enclosed in curly-brackets {like these}. Each declaration has the format:
property: value;Don't forget that semi-colon! It'll lead to big problems later on!
Fun-sized!
- Often, you'll want to fine-tune the size of an element. CSS is just the tool for the job!
- CSS has 4 properties for size
- Width and Height do exactly what you'd expect
- Margin specifies the width of an invisible border OUTSIDE the element's actual border, while
- Padding specifies the width of an invisible border WITHIN the element's actual border
Background
CSS Units
- CSS has several different units for expressing a length.
- Many CSS properties take "length" values, such as width, margin, padding, font-size, border-width, etc.
- Length is a number followed by a length unit, such as 10px, 2em, etc.
- A whitespace cannot appear between the number and the unit. However, if the value is 0, the unit can be omitted.
- For some CSS properties, negative lengths are allowed.
- There are two types of length units: relative and absolute.
Relative Lengths
em
Relative to the font-size of the element (2em means 2 times the size of the current font)
vw
Relative to font-size of the root element
rem
Relative to 1% of the width of the viewport
vh
Relative to 1% of the height of the viewport
%
Take length in percent
Relative length units specify a length relative to another length property. Relative length units scales better between different rendering mediums.
Absolute Lengths
The absolute length units are fixed and a length expressed in any of these will appear as exactly that size.
cm
centimeters
mm
millimeters
in
inches (1in = 96px = 2.54cm)
points (1pt = 1/72 of 1in)
pt
px
pixels (1px = 1/96th of 1in). Pixels (px) are relative to the viewing device
Units
CSS Colors
Colors are displayed combining RED, GREEN, and BLUE light.
- CSS colors are defined using a hexadecimal (HEX) notation for the combination of Red, Green, and Blue color values (RGB). The lowest value that can be given to one of the light sources is 0 (HEX 00). The highest value is 255 (HEX FF).
- HEX values are written as 3 double digit numbers, starting with a # sign.
| Color | Color HEX | Color RGB |
|---|---|---|
| #000000 | rgb(0,0,0) | |
| #FF0000 | rgb(255,0,0) | |
| #00FF00 | rgb(0,255,0) | |
| #0000FF | rgb(0,0,255) | |
| #FFFF00 | rgb(255,255,0) | |
| #00FFFF | rgb(0,255,255) | |
| #FF00FF | rgb(255,0,255) | |
| #C0C0C0 | rgb(192,192,192) | |
| #FFFFFF | rgb(255,255,255) |
Hexadecimal Colors
- Hexadecimal color values are supported in all major browsers.
- A hexadecimal color is specified with: #RRGGBB, where the RR (red), GG (green) and BB (blue) hexadecimal integers specify the components of the color. All values must be between 00 and FF.
- For example, the #0000ff value is rendered as blue, because the blue component is set to its highest value (ff) and the others are set to 00.
RGB Colors
- RGB color values are supported in all major browsers.
- An RGB color value is specified with: rgb(red, green, blue). Each parameter (red, green, and blue) defines the intensity of the color and can be an integer between 0 and 255 or a percentage value (from 0% to 100%).
- For example, the rgb(0,0,255) value is rendered as blue, because the blue parameter is set to its highest value (255) and the others are set to 0.
- Also, the following values define equal color: rgb(0,0,255) and rgb(0%,0%,100%).
RGBA Colors
- RGBA color values are supported in IE9+, Firefox 3+, Chrome, Safari, and in Opera 10+.
- RGBA color values are an extension of RGB color values with an alpha channel - which specifies the opacity of the object.
- An RGBA color value is specified with: rgba(red, green, blue, alpha). The alpha parameter is a number between 0.0 (fully transparent) and 1.0 (fully opaque).
Selectors
- CSS selectors allow you to select and manipulate HTML elements.
- CSS selectors are used to "find" (or select) HTML elements based on their id, class, type, attribute, and more.
Do NOT start a selector name with a number!
element Selector
The element selector selects elements based on the element name.
You can select all <p> elements on a page like this: (all <p> elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color)
id Selector
- The id selector uses the id attribute of an HTML element to select a specific element.
- An id should be unique within a page, so the id selector is used if you want to select a single, unique element.
class Selector
The class selector selects elements with a specific class attribute
Grouping Selectors
You can group the selectors, to minimize the code
To group selectors, separate each selector with a comma
Validation
Why Validate?
- Validation as a debugging tool
- Validation as a future-proof quality check
- Validation eases maintenance
- Validation helps teach good practices
- Validation is a sign of professionalism
http://jigsaw.w3.org/css-validator/ - Validator
FONT
CSS font properties define the font family, boldness, size, and the style of a text.
Difference Between Serif and Sans-serif Fonts

CSS Font Families
In CSS, there are two types of font family names:
- generic family - a group of font families with a similar look (like "Serif" or "Monospace")
- font family - a specific font family (like "Times New Roman" or "Arial")
| Generic family | Font family | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Serif |
Times New Roman Georgia |
Serif fonts have small lines at the ends on some characters |
| Sans-serif |
Arial Verdana |
"Sans" means without - these fonts do not have the lines at the ends of characters |
| Monospace |
Courier New Lucida Console |
All monospace characters have the same width |
Font Family
- The font family of a text is set with the font-family property.
- The font-family property should hold several font names as a "fallback" system. If the browser does not support the first font, it tries the next font.
- Start with the font you want, and end with a generic family, to let the browser pick a similar font in the generic family, if no other fonts are available.
- Note: If the name of a font family is more than one word, it must be in quotation marks, like: "Times New Roman".
Font Style
The font-style property is mostly used to specify italic text.
This property has three values:
- normal - The text is shown normally
- italic - The text is shown in italics
- oblique - The text is "leaning" (oblique is very similar to italic, but less supported)
Font Size
The font-size property sets the size of the text
- You should not use font size adjustments to make paragraphs look like headings, or headings look like paragraphs.
- Always use the proper HTML tags, like <h1> - <h6> for headings and <p> for paragraphs.
- The font-size value can be an absolute, or relative size.
- Absolute size:
- Sets the text to a specified size
- Does not allow a user to change the text size in all browsers (bad for accessibility reasons)
- Absolute size is useful when the physical size of the output is known
- Relative size:
- Sets the size relative to surrounding elements
- Allows a user to change the text size in browsers
font variant
In a small-caps font, all lowercase letters are converted to uppercase letters. However, the converted uppercase letters appears in a smaller font size than the original uppercase letters in the text.
normal
The browser displays a normal font. This is default
small-caps
The browser displays a small-caps font
font weight
The font-weight property sets how thick or thin characters in text should be displayed.
normal
Defines normal characters. This is default
bold
normal
lighter
Defines thick characters
Defines thicker characters
Defines lighter characters
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
Defines from thin to thick characters. 400 is the same as normal, and 700 is the same as bold
CSS Text
CSS gives you precise control over typography in your Web pages, allowing you to set parameters such as the spacing between lines, words and even letters, and the alignment and indenting of text.
Text Color
The color property is used to set the color of the text.
- a HEX value - like "#ff0000"
- an RGB value - like "rgb(255,0,0)"
- a color name - like "red"
With CSS, a color is most often specified by:
Text Alignment
- The text-align property is used to set the horizontal alignment of a text.
- Text can be centered, or aligned to the left or right, or justified.
- When text-align is set to "justify", each line is stretched so that every line has equal width, and the left and right margins are straight (like in magazines and newspapers).
Text Decoration
The text-decoration property is used to set or remove decorations from text
Text Transformation
The text-transform property is used to specify uppercase and lowercase letters in a text.
Text Indentation
The text-indent property is used to specify the indentation of the first line of a text.
direction
The direction property specifies the text direction/writing direction.
ltr
The writing direction is left-to-right. This is default
rtl
The writing direction is right-to-left
letter spacing
The letter-spacing property increases or decreases the space between characters in a text.
line height
The line-height property specifies the line height.
text-shadow
The text-shadow property adds shadow to text.
text-shadow: h-shadow v-shadow blur-radius color;h-shadow
v-shadow
blur-radius
color
The position of the horizontal shadow
The position of the vertical shadow
Optional. The blur radius. Default value is 0
Optional. The color of the shadow
vertical align
The vertical-align property sets the vertical alignment of an element.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| baseline | Align the baseline of the element with the baseline of the parent element. This is default |
| length | Raises or lower an element by the specified length. Negative values are allowed |
| % | Raises or lower an element in a percent of the "line-height" property. Negative values are allowed |
| sub | Aligns the element as if it was subscript |
| super | Aligns the element as if it was superscript |
| top | The top of the element is aligned with the top of the tallest element on the line |
| text-top | The top of the element is aligned with the top of the parent element's font |
| middle | The element is placed in the middle of the parent element |
| bottom | The bottom of the element is aligned with the lowest element on the line |
| text-bottom | The bottom of the element is aligned with the bottom of the parent element's font |
VERTICAL ALIGN
white space
The white-space property specifies how white-space inside an element is handled.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| normal | Sequences of whitespace will collapse into a single whitespace. Text will wrap when necessary. This is default |
| nowrap | Sequences of whitespace will collapse into a single whitespace. Text will never wrap to the next line. The text continues on the same line until a <br> tag is encountered |
| pre | Whitespace is preserved by the browser. Text will only wrap on line breaks. Acts like the <pre> tag in HTML |
| pre-line | Sequences of whitespace will collapse into a single whitespace. Text will wrap when necessary, and on line breaks |
| pre-wrap | Whitespace is preserved by the browser. Text will wrap when necessary, and on line breaks |
WHITE SPACE
word spacing
The word-spacing property increases or decreases the white space between words.
Class work
Create a web page using all the properties from this presentation
Use inline and and internal styles
Home work
Create a web page using all the properties and all the selectors from this presentation using external stylesheet
- https://events.yandex.ru/lib/talks/561/ CSS: Значения и единицы измерения. Шрифт. Свойства текста
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/vvedenie-v-css Введение в CSS
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/preimushchestva-stiley Преимущества стилей
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/sposoby-dobavleniya-stiley-na-stranitsu Способы добавления стилей на страницу
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/bazovyy-sintaksis-css Базовый синтаксис CSS
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/znacheniya-stilevykh-svoystv Значения стилевых свойств
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/selektory-tegov Селекторы тегов
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/klassy Классы
- http://htmlbook.ru/samcss/identifikatory Идентификаторы
THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION
CSS Basics
CSS Basics
By sinelshchikovigor
CSS Basics
- 1,176



