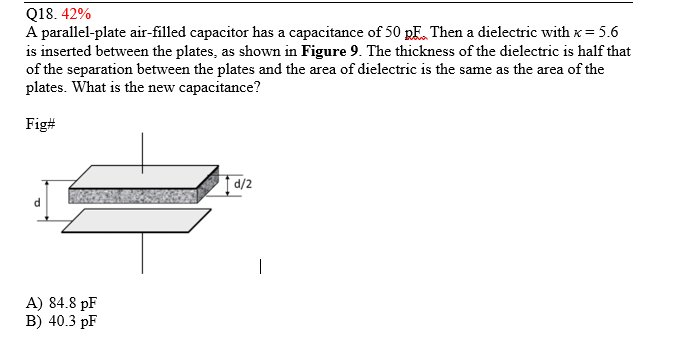
\text{A parallel-plate air-filled capacitor has a capacitance of $50 \, \text{pF}$. Then a dielectric with $\kappa = 5.6$ is inserted between the plates, as shown in Figure 9. The thickness of the dielectric is half that of the separation between the plates and the area of dielectric is the same as the area of the plates. What is the new capacitance?
}
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
P




5.0 \text{ }\Omega
10 \text{ }\Omega
4.0 \text{ }\Omega
\xi
15 \text{ }V
15 \text{ }V
I
\text{loop 3}
\text{loop 1}

i_1
i_2
i_3
1)\text{choose the directions of $i_1$, $i_2$ and $i_3$}
2)\text{choose the direction of the loops (clockwise)}
3)\text{draw the arrows for the potential increase}
a)\text{at emf: \textcolor{green}{towards the +}}
b)\text{at resistors: \textcolor{green}{opposit to current}}
4)\text{the sum of potentials =0: if with the chosen direction it is + if against it is -}
\underline{\text{loop 1}}
\xi-5i_1+10 i_2+15=0
\xi-4i_3=21
\Rightarrow
\underline{\text{loop 3}}
\xi-5i_1-4 i_3-15=0
\xi-5i_1+10 i_2+15=0
\xi-10 i_2=-9
\Rightarrow
i_3=i_1+i_2
\xi-4i_3=21
\Rightarrow
\documentclass{article}
\usepackage{amsmath}
\usepackage{xcolor}
\begin{document}
\begin{tabular}{rl}
\textcolor{purple}{loop 1} & \\[6pt]
$\xi - 5i_1 - 4i_3 - 15 = 0$ & $\implies \xi - 4i_3 = 21$ \quad $\implies \boxed{\xi - 4i_3 = 21}$ \\[12pt]
\textcolor{purple}{loop 3} & \\[6pt]
$\xi - 5i_1 + 10i_2 + 15 = 0$ & $\implies \xi - 10i_2 = -9$ \\[6pt]
& $i_3 = i_1 + i_2$
\end{tabular}
\end{document}



5.0 \text{ }\Omega
10 \text{ }\Omega
4.0 \text{ }\Omega
\xi



\frac{2}{3} \text{ }\Omega
6.0 \text{ }\Omega
\text{What is the equivalent resistance?}



5.0 \text{ }\Omega
10 \text{ }\Omega
2.0 \text{ }\Omega


3.0 \text{ }\Omega
\text{What is the equivalent resistance? $i_0$}
\xi_2=2.5 V
\xi_1
i_0
i=1.3 A
\mathcal{H}=-\mu\sum_i m_i \cdot(h^0+\delta h(t))
H_\text{eff}=h^0+\delta h(t)
-H^0.e_{r_p}=-(h^0+\delta h(t)).e_{r_p}=- h^0.e_{r_p}
\int_2^4\left(y^2-3 y+5\right) d y
\text{Integration in Maths - Definition, Formulas and Types
Integrntegrals in.}


6.0 \text{ }k\Omega
3.0 \text{ }k\Omega
15 \text{ }V
C=200\mu F
R_\text{eq}=\frac{6\times3}{6+3}=2k\Omega
\tau=R_\text{eq}C=2\cdot10^3\times 400\times 10^{-6}=0.8s
q=q_0(1-e^{-t/\tau})
\ln(2)=t/\tau
t=\tau\ln(2)=0.555s
\text{wrong answers:}
t=\tau\ln(2)=1.5\times0.555s=0.832s
t=\tau\ln(2)=3\times0.555s=1.664s
\text{Figure 1 shows a circuit with an initially empty capacitor. After closing the switch,}
S
\text{what time is needed to charge the capacitor half its maximum charge capacity?}
\text{$R_1$ and $R_2$ are in parallel}
R_\text{eq}=\frac{R_1R_2}{R_1+R_2}=2\Omega
\tau=R_\text{eq}C=2 \times 10^3\times 400\times 10^{-6}=0.8 s
q=q_m(1-e^{-t/\tau})
\Rightarrow
\frac{q_m}{2}=q_m(1-e^{-t/\tau})
\Rightarrow
\frac{q_m}{2}=q_m(1-e^{-t/\tau})
\Rightarrow
\frac{1}{2}=e^{-t/\tau}
\Rightarrow
t=\ln(2) \tau=0.555s
\begin{aligned}
v & =\sqrt{\frac{2 K}{m}}=\sqrt{\frac{2\left(1.6 \times 10^3 \mathrm{eV}\right)\left(\frac{1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{~J}}{\mathrm{eV}}\right)}{1.67 \times 10^{-27} \mathrm{~kg}}}=5.5 \times 10^5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s} \\
F_B & =q v B \sin \phi=\left(1.6 \times 10^{-19}\right)\left(5.5 \times 10^5\right)\left(1.2 \times 10^{-3}\right) \sin 90^{\circ}=1.1 \times 10^{-16} \mathrm{~N}
\end{aligned}
\\
\text{Direction: in the horizontal plane perpendicular to the path of proton}
\begin{aligned}
& \vec{F}_B=q \vec{v} \times \vec{B} \\
& K=\frac{1}{2} m v^2
\end{aligned}
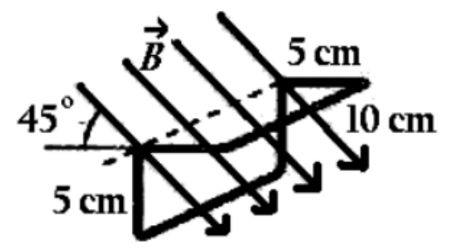
5\text{ cm}
5\text{ cm}
10\text{ cm}
\vec{E}
30^0
y
x
z
\sigma
-\sigma
\textcircled{-}
\vec{v}
deck
By smstry
deck
- 184



