Earthsys 144: Fundamentals of GIScience
Spatial Analytic Models
where is your data? gis.stanford.edu



Stace's Office Hours
I will be available for Open Office Hours all day, every day, next week!! Come with troubleshooting, questions, get caught up on Labs, get help with your final project, etc... etc...
(Analytic) Spatial Models
In general, analytic spatial models can be classed as:
- Cartographic Models
- Simple Spatial Models
- Spatial-temporal models
Cartographic Models

Cartographic Models

Ranking Criteria

Continuous Rank Layers
a) Sites should be far enough from a main road to offer some privacy, but not so far as to be isolated.
b) Slopes should not be too steep. Steep slopes may substantially increase costs or may preclude construction.

Relative Importance Ranking

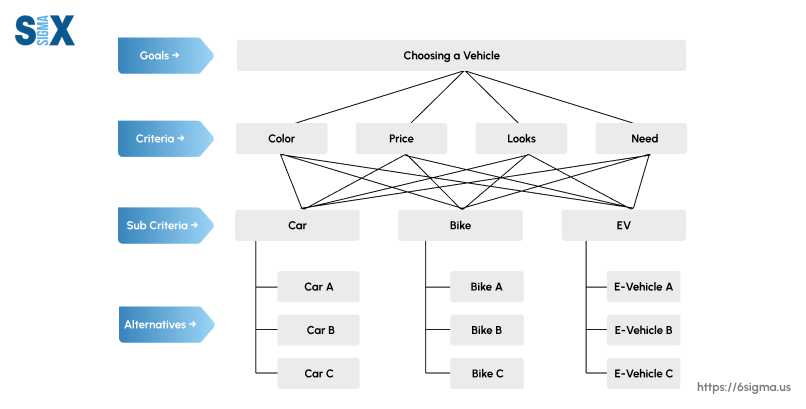
AHP - Analytic Hierarchical Process
A Relative Ranking Method
Simple Spatial Models

Simple Spatial Models

Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE)
E=R*K*C*P*L*S
- E is average annual erosion,
- R is a rainfall factor,
- K reflects soil erodibility,
- C integrates crop/veg effects,
- P accounts for management practices,
- L reflects slope length, and
- S represents steepness.
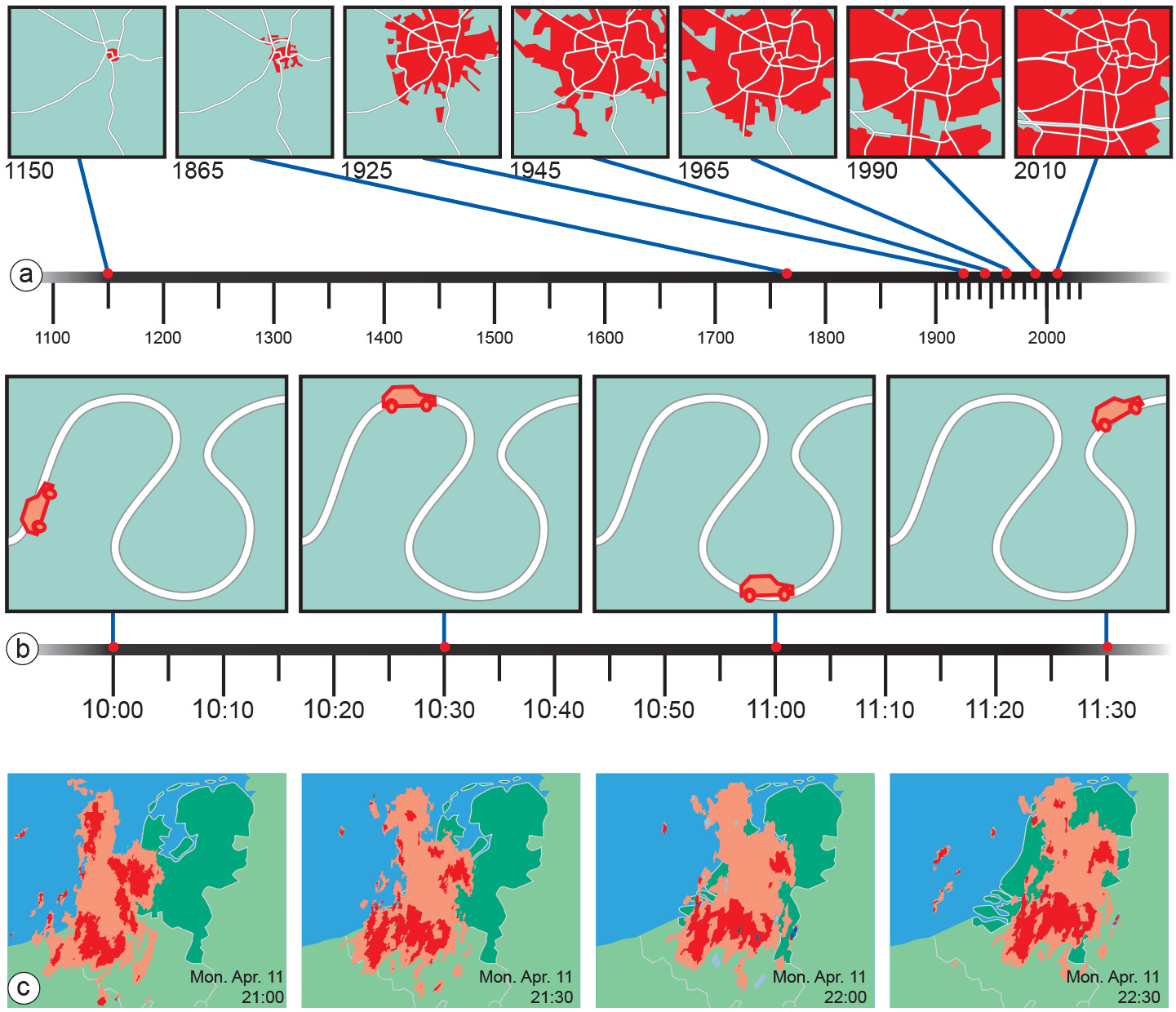
Spatio-temporal Models
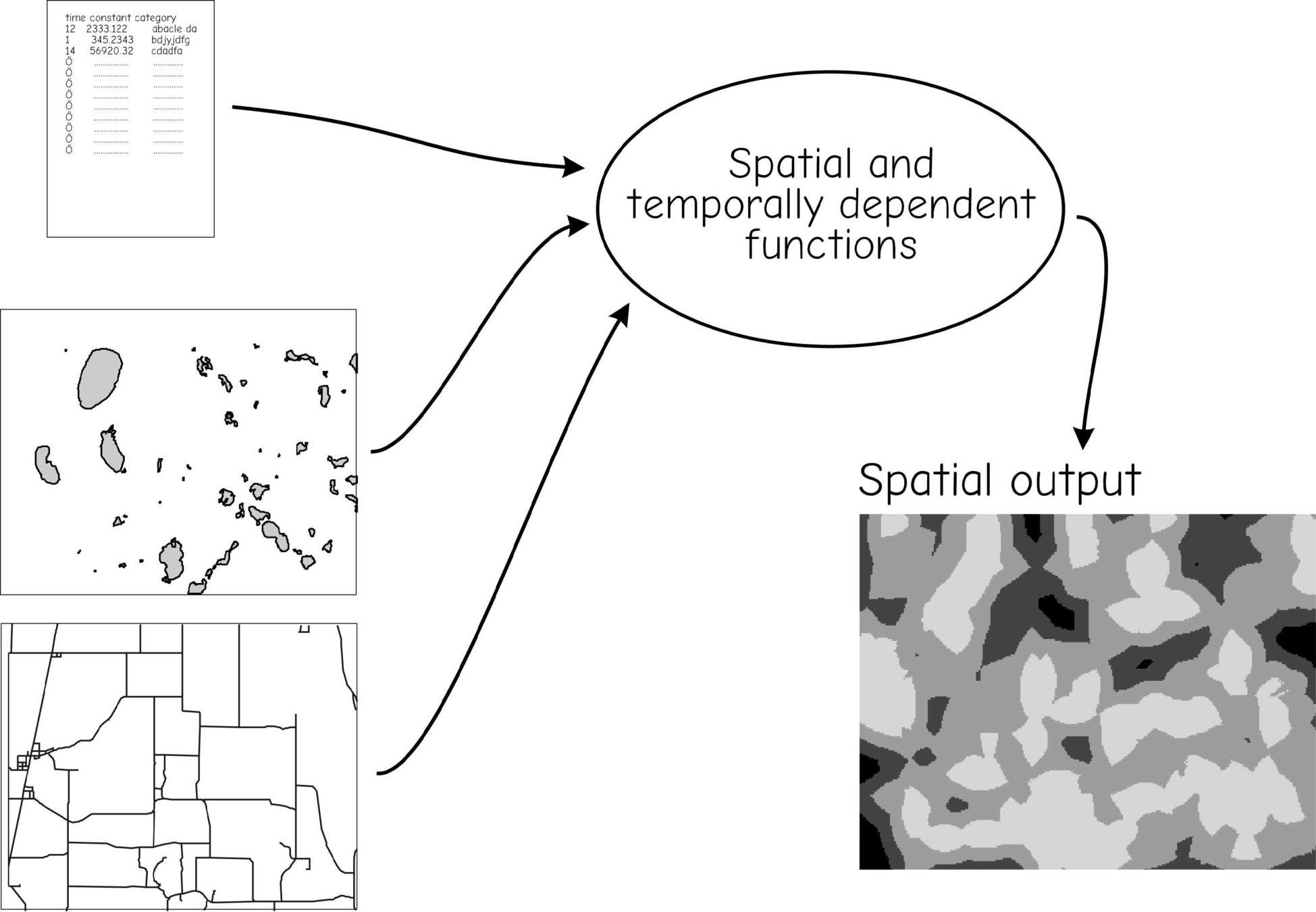
Often cell-based models

Tobler's Hiking Function

r=6exp(−3.5|S+0.05|)
r
= the walking rate in km/hr
S
= slope degrees
Tobler's Hiking Model

Tobler's Hiking Function

Models & 'Scripting'

QGIS Modeler


Earth Engine Example
https://code.earthengine.google.com/?accept_repo=users/stacemaples/SGC-EE101
Should already be in your EE101 Samples Scripts
Spatial Analytic Models
By Stace Maples
Spatial Analytic Models
- 756



