A1: Specifying and Using Abstraction
CPSC 210






Learning Goals
- Specify the methods in a data abstraction using appropriate REQUIRES, MODIFIES & EFFECTS clauses
-
Once the methods of a data abstraction have been specified, demonstrate how those methods could be used
- i.e. write examples of calls to those methods

Abstraction Concepts

Visibility
Objects of a different class (type) can access/use it
Only objects of the same class (type) can use/access it
Private
Public


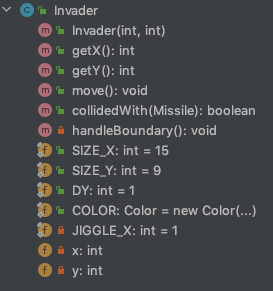
public class Dog {
private String name;
public Dog(String name) { this.name = name; }
private void makeOtherDogBark(Dog otherDog) {
otherDog.bark();
}
public void bark() {
System.out.println("BAARRRRK");
}
public void barkAndMakeOtherDogBark(Dog otherDog) {
this.bark();
this.makeOtherDogBark(otherDog);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog peter = new Dog("Peter");
Dog paul = new Dog("Paul");
peter.bark();
peter.barkAndMakeOtherDogBark(paul);
peter.makeOtherDogBark(paul);
}
}
Visibility

Parts of a Method
private void makeOtherDogBark(Dog otherDog) {
System.out.println("Woof Woof Woof Woof Woof"):
}Visibility
Return Type
Method Name
Parameter List
Method body
}
the body goes between { ... }
Specification
// Requires// Modifies// Effects- Conditions that MUST be true when the call to the method is made.
-
Does the object itself change? (this)
-
Does some other object change? (name the object)
-
No internal implementation details
- Externally visible effects
- No internal details or variable names
- No description for how you accomplish these effects
- No description of algorithm in detail
Lecture Ticket Review
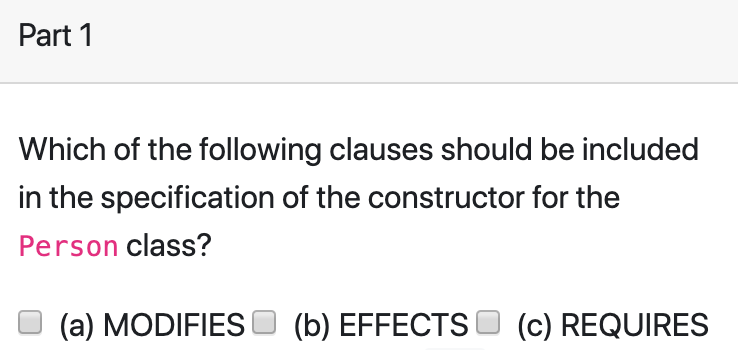
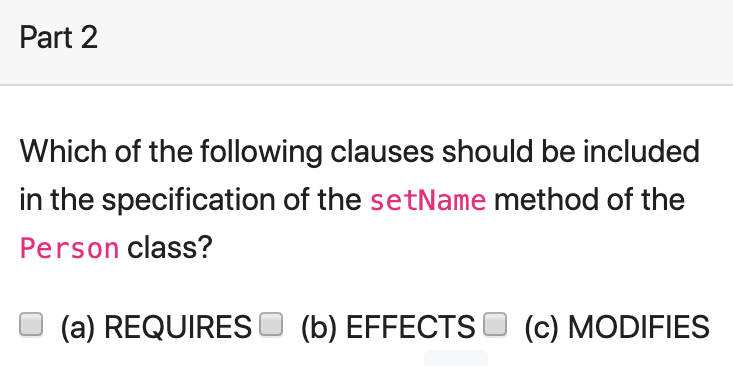
public class Person {
private int age;
private String status;
private String name;
public Person() {
this.status = "young";
this.age = 0;
this.name = "Unnamed Person";
}
public int getAge() { return age; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void getOlderByYears(int years) {
this.age = this.age + years;
if (age > 10) { this.status = "old"; }
}
}
🏗️ Lecture Lab
A1: Specifying and Using Abstraction
The End - Thank You!
CPSC210 - A1 Specifying and Using Abstraction
By Steven Wolfman
CPSC210 - A1 Specifying and Using Abstraction
- 361




