Angular
Change detection (CD)

What is CD?

The basic mechanism of the change detection is to perform checks against two states, one is the current state, the other is the new state. If one of these states is different of the other, then something has changed, meaning we need to update (or re-render) the view.


How CD flows?

Change detection goes through every components in the component tree (from top to bottom) to check if the model it depends on changed;
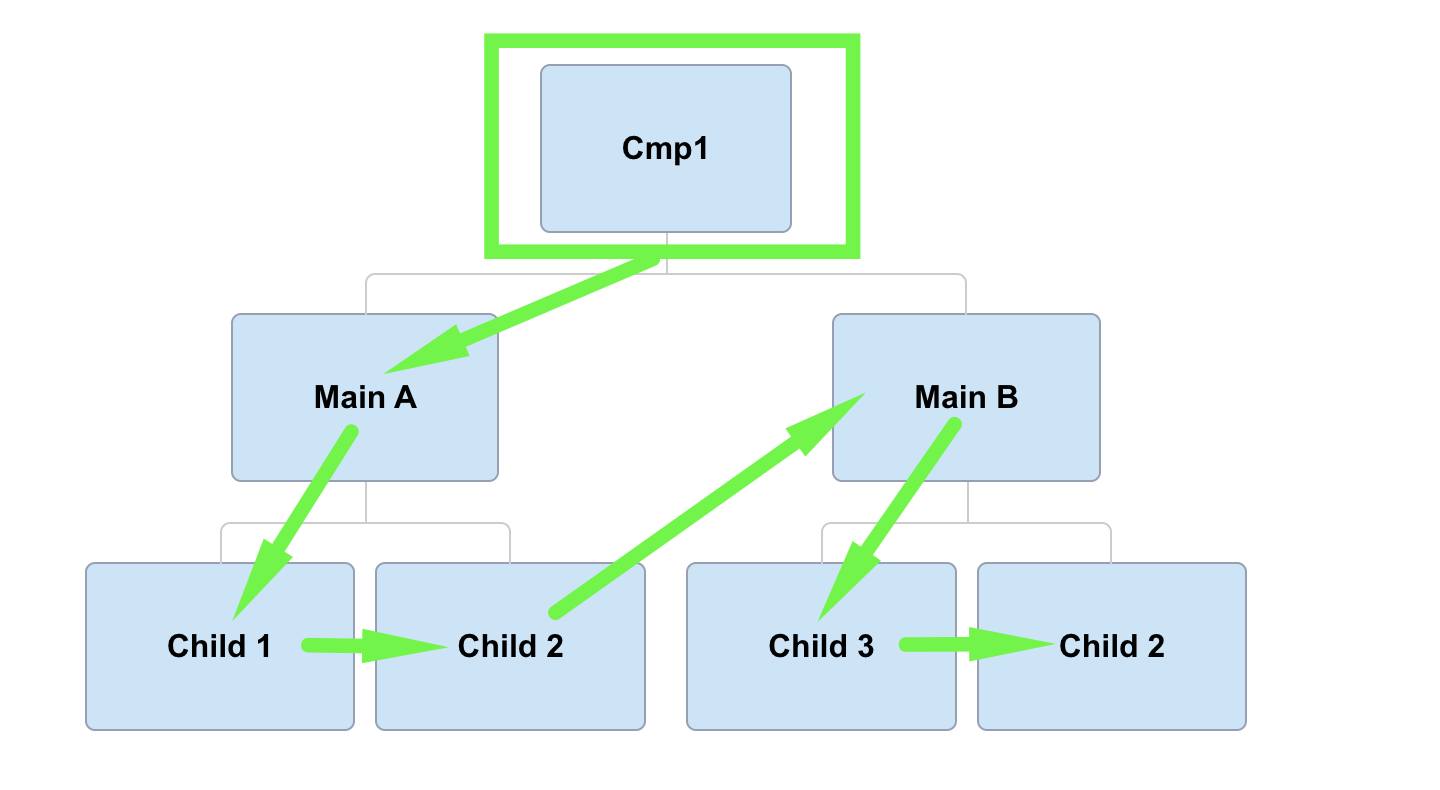
What difference between CD strategies?

Note:
Examples in further slides will contain either all components as ChangeDetectionStrategy.Default (Default)
or all as
ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush (OnPush)
Components that have been re-rendered will be highlighted with green
CD propagation

Change detection will be propagated to the root parent component and call changed detection in child components. Note that event handler is required for CD
Default
OnPush
What triggers CD?

- macrotasks like:
- events like (click) (focus)
- setTimeout/setInterval - microtasks like:
- Promise.resolve / reject - Observable.subscribe
- changeDetectorRef (markForCheck, detectChanges)
- | async (call markForCheck in the background)
Default
- events on components like (click) (focus) (someCustomEvent)
- @Input property changed
- changeDetectorRef (markForCheck, detectChanges)
- | async (call markForCheck in the background)
OnPush
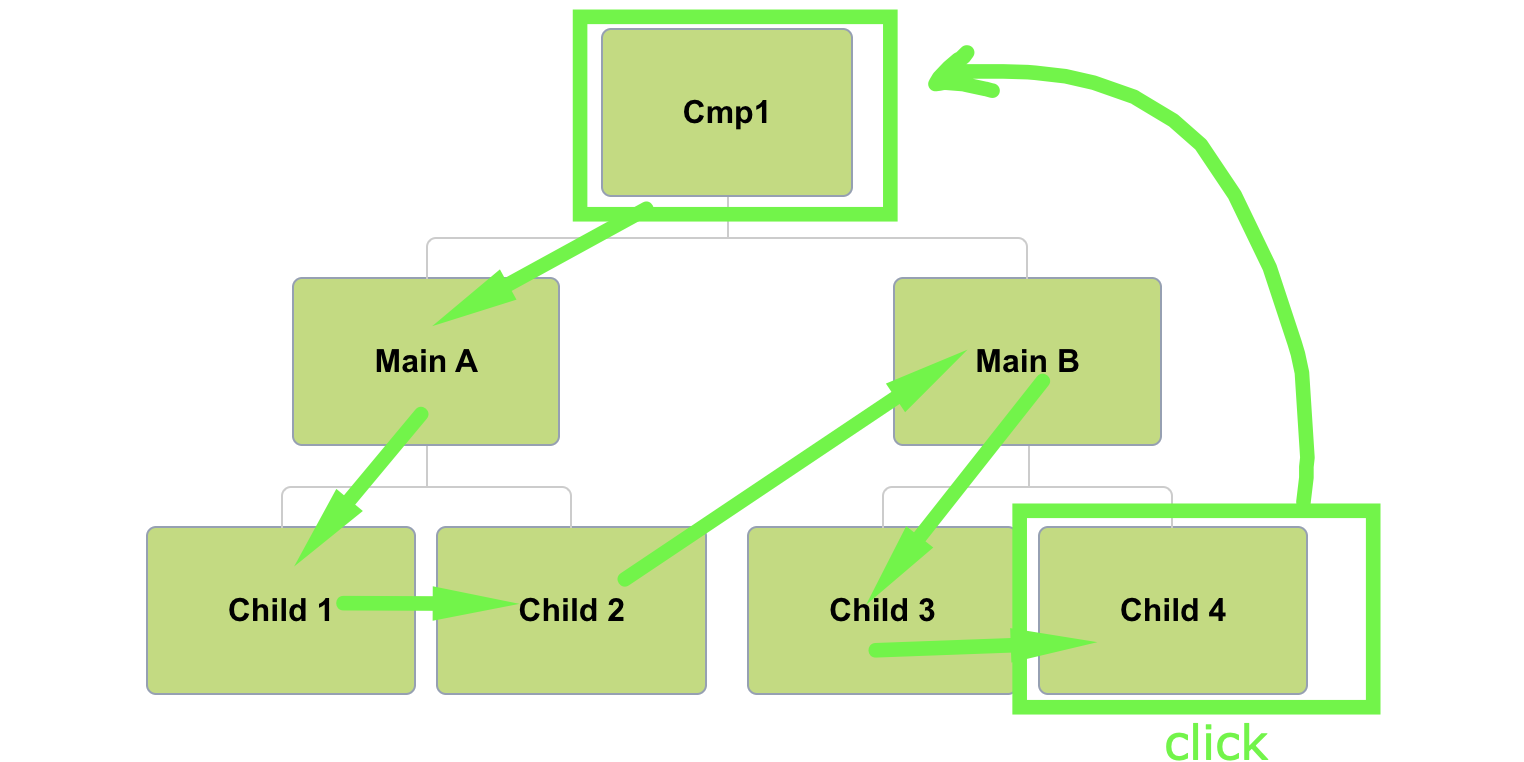
CD of events
(child4)


Default

OnPush
Note that child 4 has a click handler
CD of timeout/interval
(any component)

Default
OnPush
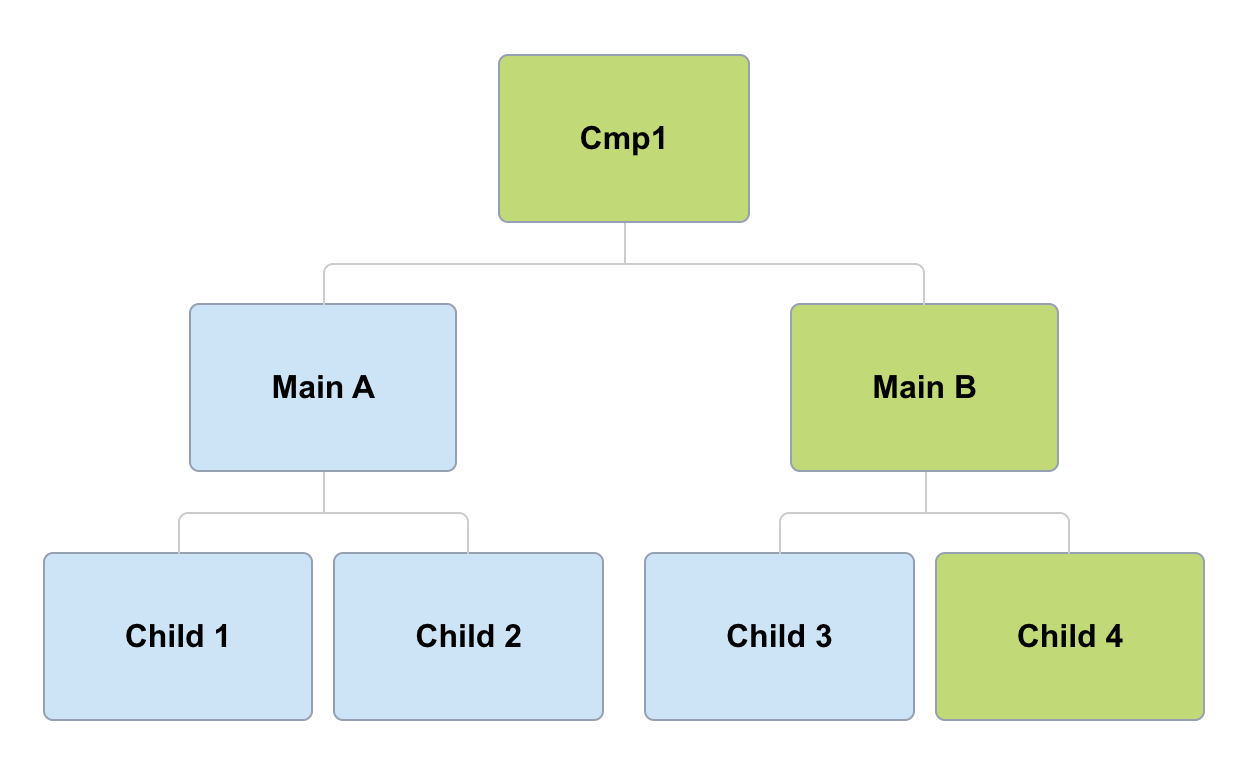
markForCheck OR | async (child4)

Default

OnPush
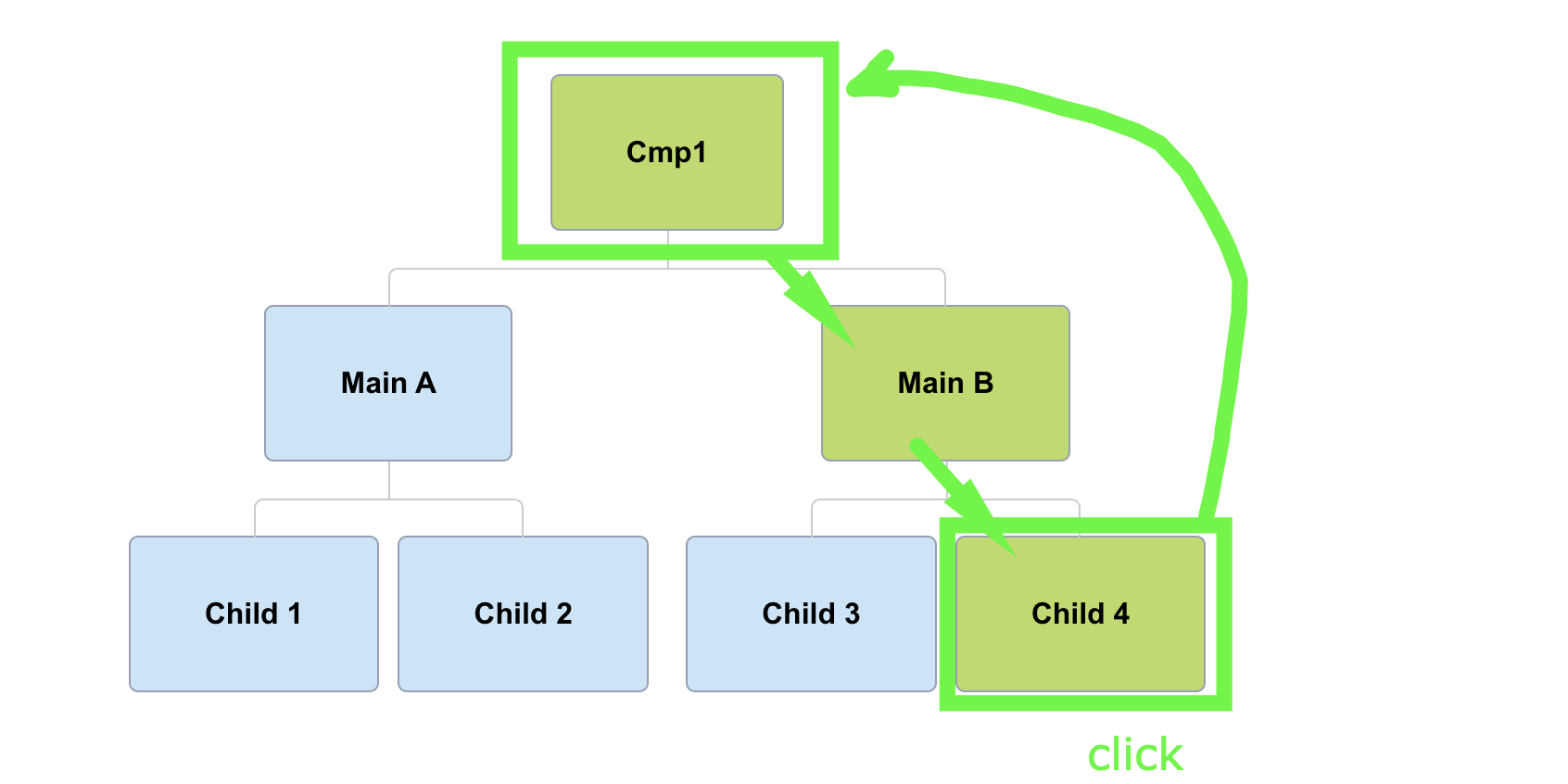
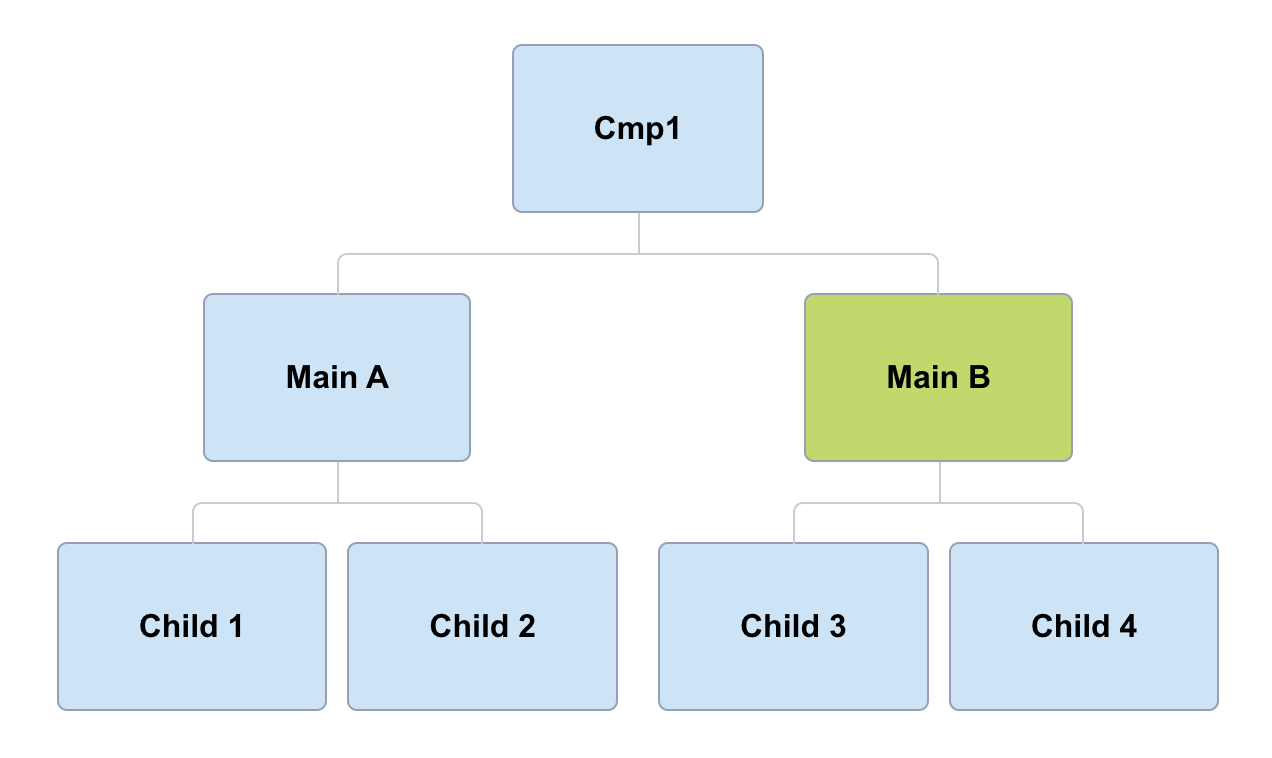
detectChanges
(Main B)

Default

OnPush
detectChanges and @Input
(Main B and child3 @Input)

Default

OnPush
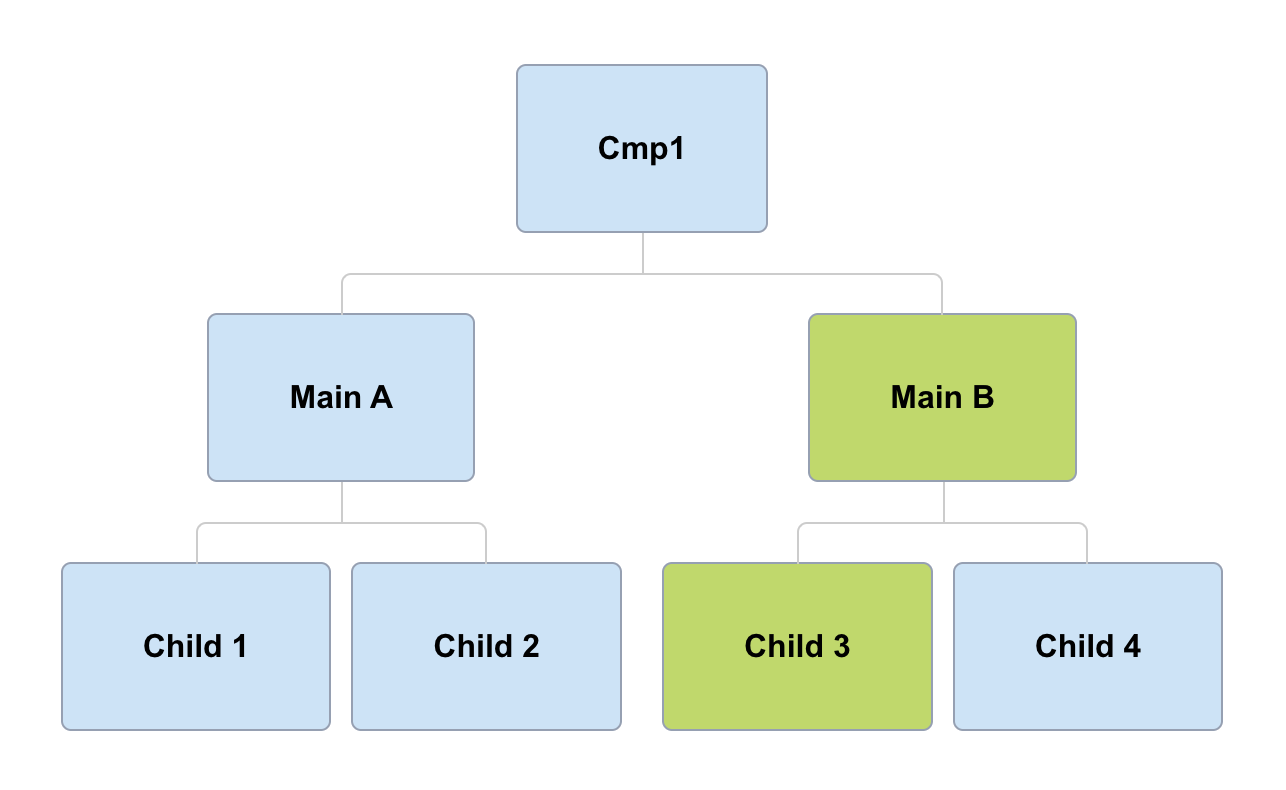
Note child 3 @Input should be changed to trigger CD
Demos

Thanks for your attention

Angular. Change detection
By TenantCloud
Angular. Change detection
Some useful feature of TS without proper attention to them
- 477



