Health Care Spending in the United States
BE 608
Per capita health care spending in the US and OECD countries in 2021 (source: OECD health Statistics)

Spending as % of GDP in the US and OECD countries in 2021 (source: OECD health Statistics)

Total expenditures on health care are actually pretty simple:
how much does the care cost x how much do we use or:
Where Pi is the price of service i and Qi is the amount we consume.
Differences in expenditures over time or across countries must be driven by either Q, P, or a combination of both.
Why?
What is your explanation for why expenditures in the United States are so much higher than in other wealthy countries? (Drawing from your experiences or the reading by Aaron and Ginsberg)
- Does this reflect higher "p" or high "q"?
Let's examine some specific hypotheses...
- Americans are richer, so we'd expect to spend more on all things, not just on health care. This is why health care spending is higher in the US.
- Americans are less healthy, and need more care/spending to achieve the same level of health as other countries.
Non healthcare reasons for higher spending:
Income and Spending
Source: OECD health statistics, 2021

Percent age 65 and Older (OECD Health Data, 2019)

Percent daily smokers (OECD Health Data, 2020)

Percent obese, OECD Health Stats 2016


So what do we spend money on? (From 2018 NHE Data, KFF)
NOTE: Other Personal Health Care includes, for example, dental and other professional health services, durable medical equipment, etc.
Other Health Spending includes administration and net cost of private insurance, public health activity, research, and structures and equipment, etc.
Who is doing that spending?

Source: KFF, 2017
Who is doing that spending?
Mix of private and public payers
- Medicare: everyone age 65 and older plus the disabled
- Either directly by federal government or through privately contracted insurance companies
- Medicaid: certain low income groups (low income pregnant women, children, disabled, low income adults in some states)
- Either through federal/state partnership directly or through privately contracted insurance companies
- Employer sponsored health insurance
- Individual plans
- Self-pay
Spending on Insurance Administration per Capita, 2020

Pharmaceutical Spending per Capita, 2021


Number of prescriptions taken regularly, 2014

Humira

Enbrel
Silver lining: we take far more generic drugs in US than in Europe (85% volume in US, only 50-60% in most European countries)
Price of selected drugs (monthly)
Source: Health Care Cost Institute
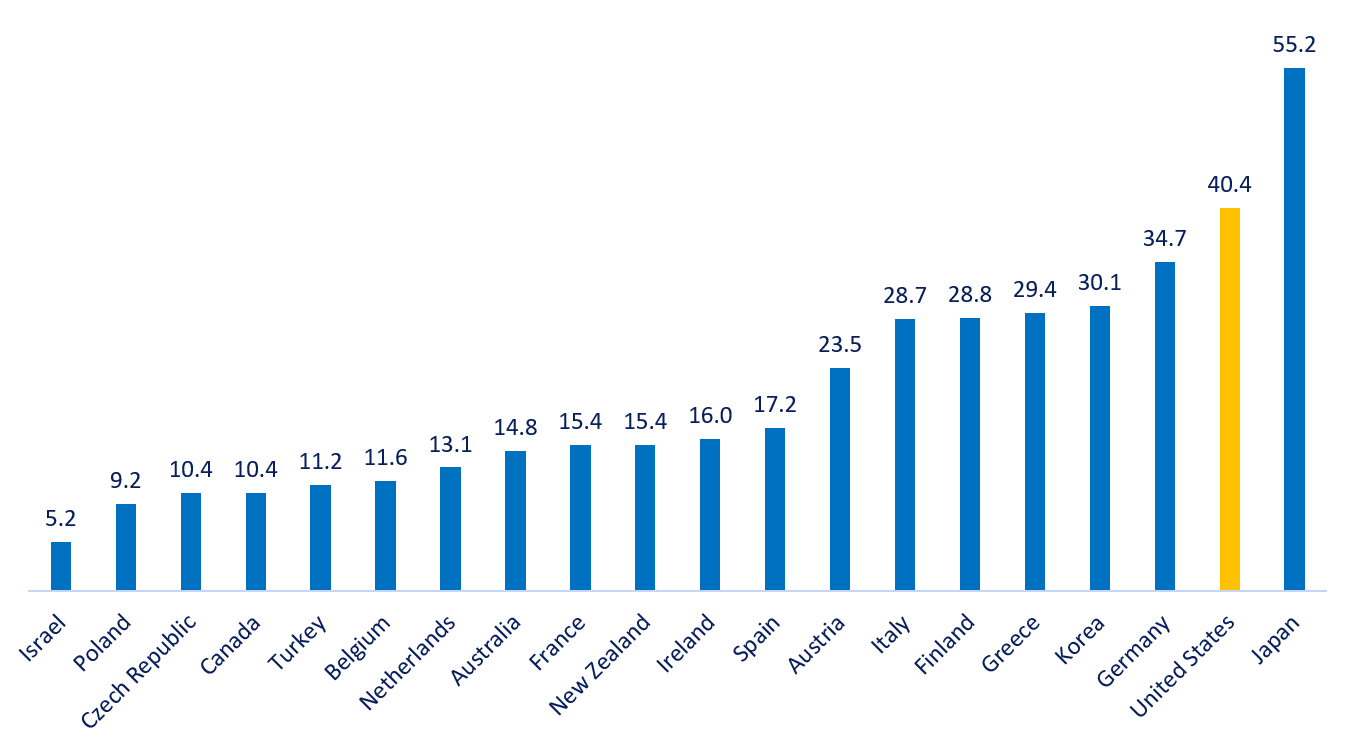
Practicing Physicians per 1000 Population, 2020 (OECD Health Statistics)

Annual physician visits per capita, 2017

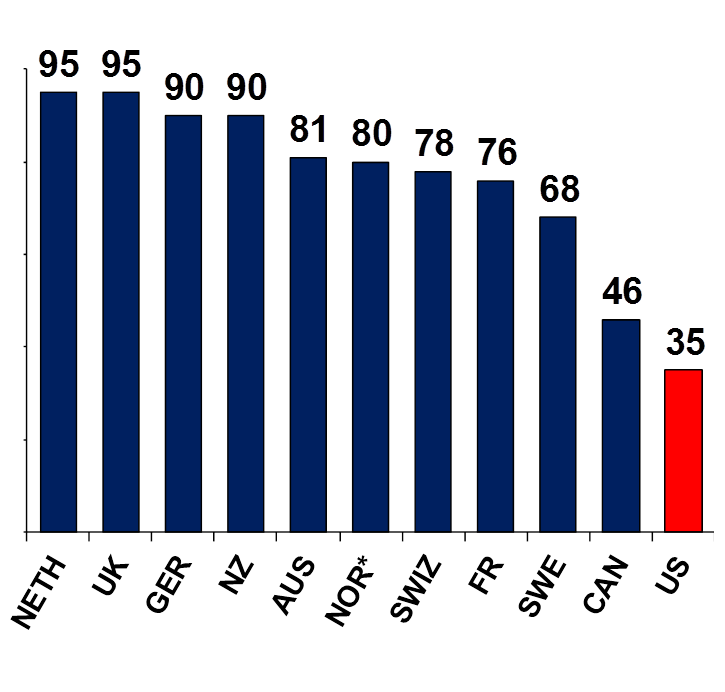
Survey of adults, 2013:
Easy getting after-hours care without
going to the ER
Source: Commonwealth Fund International Health Policy Survey

Survey of primary care physicians, 2012:
Practice has arrangement for patients’ after-hours care to see doctor or nurse
Average Physician Income by Age (includes business earnings)

Source: Gottlieb et al. NBER (2020)
Average Physician Income by Specialty (includes business earnings)

Source: Gottlieb et al. NBER (2020)

Physician Earnings (excludes business earnings), Selected Countries 2010
Cutler and Ly, Journal of Economic Perspectives (2011)

Hospital Discharges per 100,000 population, 2019

Spending per hospital discharge, 2017


Source: HCCI data/IFHP Analysis

Source: HCCI data/IFHP Analysis
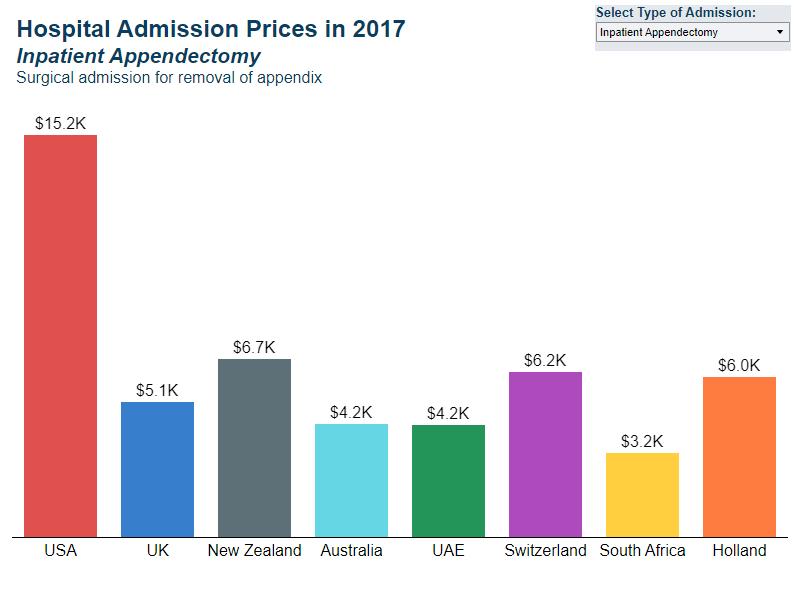
Source: HCCI data/IFHP Analysis
MRI Machines per million population, 2019
MRI exams per 1k population, 2019

CT Scans per 1000 population, 2019

Diagnostic Imaging Prices

As percent of US price, 2019 (HCCI)
| Prices | Quantities | |
|---|---|---|
| Administrative Costs | Higher | Much higher |
| Prescription drugs | Brand prices are much higher, but greater generic use | Slightly higher than average |
| Physician services (GP) | Higher | Somewhat lower |
| Physician services (specialists) | Higher | Higher for some procedures |
| Inpatient care | Higher | Similar admissions, shorter length of stay, more intensive treatment |
| Diagnostic imaging | Higher | Higher |
Summary
How does the US compare to other countries in terms of...
Geographic Variation in Spending

McAllen TX: $13,648 per Medicare beneficiary
El Paso, TX: $8,714 per Medicare beneficiary
No clear difference in health outcomes.
Geographic Variation in Spending
What is correlated with this variation within the United States?
- Historical factors: Hill Burton hospital construction, nature of tort system in state
- Physician culture ("cowboys/cowgirls" vs "comforters"/"high follow up" vs "low follow up")
- Patient preferences and characteristics are not highly correlated
Cutler, Skinner, Stern, and Wennberg AEJ: Policy 2019
Geographic Variation in Spending

Cutler, Skinner, Stern, and Wennberg AEJ: Policy 2019
Geographic Variation in Spending
- Different regions have different cultures, fixed capital, and patient populations.
- They also have different policy environments, and appetites for intervention.
What has your state done (if anything) to curb health care spending?
Spending Growth
Health Spending per Capita, 1970–2019
Source: KFF and Peterson/Kaiser Health System Tracker (based on NHE data)

Health Spending as Percent of GDP, 1970–2021
Source: Commonwealth Fund analysis of OECD Health Data

Historical growth by decade

Post 2010 Cost Slow Down: spending for those age 65+

"Bending the cost curve"
Cutler et al. Health Affairs 2019
Post 2010 Cost Slow Down
Cutler et al. Health Affairs 2019

Change in Healthcare Spending During and After COVID-19

Change in Healthcare Employment During and After COVID-19

Change in Health Care Employment During COVID-19

Change in Expenditures Since COVID-19

Change in Expenditures Since COVID-19

So: Does the US Spend "Too Much"?
Understanding Differences in Spending
•The US spends substantially more on health care than other high income countries.
•Although health care is a normal good, this higher spending cannot be explained by higher income in the US.
•Also, higher spending is not driven by greater health needs.
•Higher spending in the US is driven by higher prices and greater use of “high tech” interventions.
Challenges in the US

These Challenges are Tightly Connected

Rising costs have led to an erosion of insurance coverage
Over-utilization increases costs and harms patients
The uninsured often go without necessary care
Upcoming Topics
•Is the level of health spending in the US inefficiently high?
•If technology drives the growth in health spending, how should we think about the efficient level of technology diffusion?
•How does insurance design influence the demand for and supply of health services? How can plan benefits and provider payments be designed to improve efficiency?
•How do payment/delivery reforms address inefficiencies in the US system?
For next class
Garber and Skinner, Gawande articles:
•How can we apply the concepts of productive and allocative efficiency to health care?
State question:
Is your state a high spending or low spending state? What factors do you think explain this level of spending? Have there been trends in one direction or the other? What do you think explains these trends?
Copy of Lecture 1
By umich
Copy of Lecture 1
- 107



