
Uvindu Perera
Mozilla NSBM
https://www.linkedin.com/in/uvindu-perera
im@uvinduperera.me
Introduction to Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is renting resources, like storage space or CPU cycles, on another company's computers.
You only pay for what you use. The company providing these services is referred to as a cloud provider. Some example providers are Microsoft, Amazon, and Google.
The computing services offered tend to vary by the cloud provider. However, typically they include:
-
Compute power - such as Linux servers or web applications
-
Storage - such as files and databases
-
Networking - such as secure connections between the cloud provider and your company
-
Analytics - such as visualizing telemetry and performance data
Cloud computing services
There are two most common services that all cloud providers offer
– compute power
– storage.
What are the containers?
Containers provide a consistent, isolated execution environment for applications. They're similar to VMs except they don't require a guest operating system.
The open-source project, Docker, is one of the leading platforms for managing containers.
What is serverless computing?
Serverless computing lets you run application code without creating, configuring, or maintaining a server.
Compute Power
we're all dependent on the computing services provided by the various cloud providers that make up the Internet.
When you build solutions using cloud computing, you can choose how you want to work to be done based on your resources and needs. If you want to have more control and responsibility for maintenance, you could create a virtual machine (VM).
A VM is an emulation of a computer - just like your desktop or laptop, you're using now.
VMs aren't the only computing choice - there are two other popular options: containers and serverless computing.
Storage
Cloud providers typically offer services that can handle all of these types of data. For example, if you wanted to store text or a movie clip, you could use a file on disk. If you had a set of relationships such as an address book, you could take a more structured approach like using a database.
The advantage of using cloud-based data storage is you can scale to meet your needs. If you find that you need more space to store your movie clips, you can pay a little more and add to your available space. In some cases, the storage can even expand and contract automatically - so you pay for exactly what you need at any given point in time.
Benefits of cloud computing
Cloud computing isn't an all-or-nothing service approach. Companies can choose to use the cloud to store their data and execute logic as much, or as little, as necessary to fulfill their business requirements.
There are some of the top benefits of cloud computing.
- It's cost-effective
- It's scalable
- It's elastic
- It's current
- It's reliable
- It's global
- It's secure
This means you're able to spend more time on what matters and less time managing the underlying details.
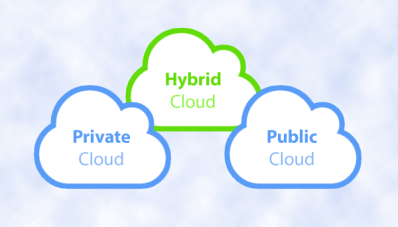
Cloud deployment models
There are three different cloud deployment models. A cloud deployment model defines where your data is stored and how your customers interact with it – how do they get to it, and where do the applications run? It also depends on how much of your own infrastructure you want or needs to manage.
~Public Cloud
~Private Cloud
~Hybrid Cloud
Public cloud
This is the most common deployment model. In this case, you have no local hardware to manage or keep up-to-date – everything runs on your cloud provider's hardware. In some cases, you can save additional costs by sharing computing resources with other cloud users.
Businesses can use multiple public cloud providers of varying scale. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud provider.

Private cloud
In a private cloud, you create a cloud environment in your own datacenter and provide self-service access to compute resources to users in your organization. This offers a simulation of a public cloud to your users, but you remain completely responsible for the purchase and maintenance of the hardware and software services you provide.

Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, allowing you to run your applications in the most appropriate location. For example, you could host a website in the public cloud and link it to a highly secure database hosted in your private cloud (or on-premises datacenter).
This is helpful when you have some things that cannot be put in the cloud, maybe for legal reasons. For example, you may have some specific pieces of data that cannot be exposed publicly (such as medical data) which needs to be held in your private datacenter. Another example is one or more applications that run on old hardware that can't be updated. In this case, you can keep the old system running locally, and connect it to the public cloud for authorization or storage.

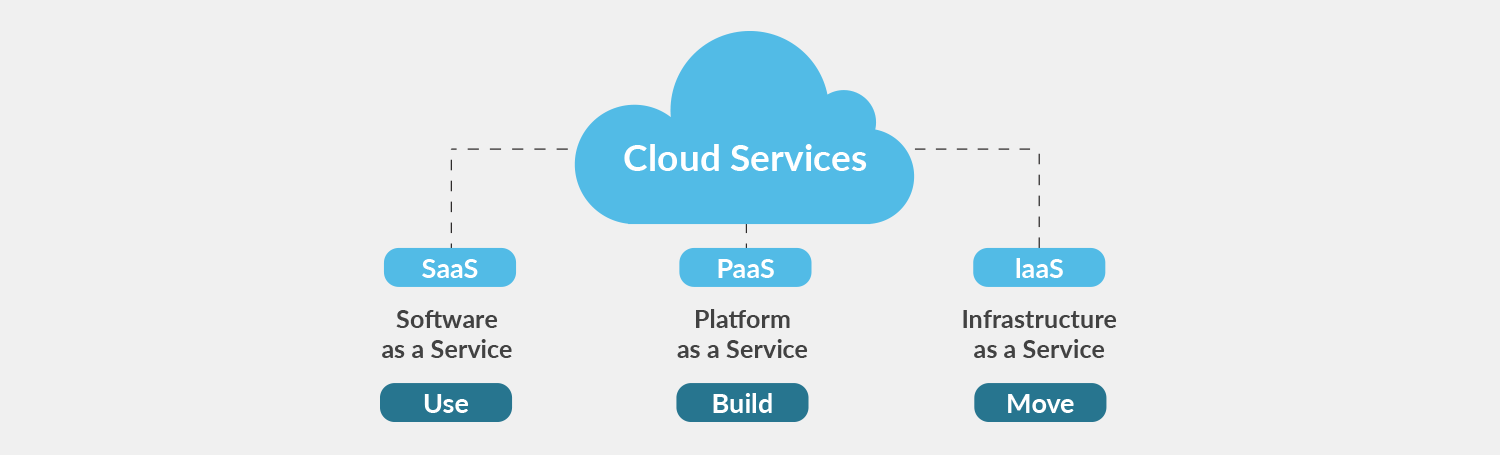
Types of cloud services

When talking about cloud computing, there are three major categories. It's important to understand them because they are used in conversation, documentation, and training.
There are three categories of cloud computing
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS)

Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service is the most flexible category of cloud services. It aims to give you complete control over the hardware that runs your application (IT infrastructure servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, and operating systems). Instead of buying hardware, with IaaS, you rent it. It's an instant computing infrastructure, provisioned and managed over the internet.
IaaS is commonly used in the following scenarios:
Migrating workloads.
Test and development.
Storage, backup, and recovery.


Platform as a service (PaaS)
PaaS provides an environment for building, testing, and deploying software applications. The goal of PaaS is to help you create an application quickly without managing the underlying infrastructure. For example, when deploying a web application using PaaS, you don't have to install an operating system, web server, or even system updates.
IaaS is commonly used in the following scenarios:
Development framework.
Analytics or business intelligence.


Software as a service (SaaS)

SaaS is software that is centrally hosted and managed for the end customer. It is usually based on an architecture where one version of the application is used for all customers, and licensed through a monthly or annual subscription. Office 365, Skype, and Dynamics CRM Online are perfect examples of SaaS software.

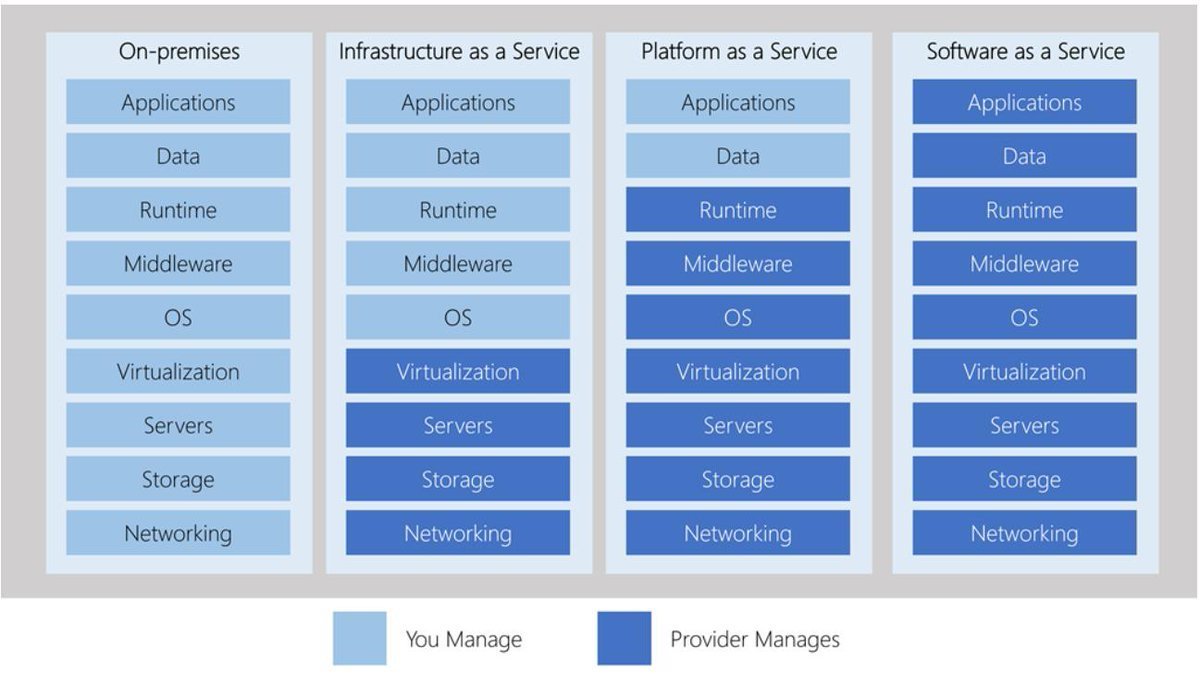
Management responsibilities
One thing to understand is that these categories are layers on top of each other.The following illustration shows a list of resources that you manage and that your service provider manages in each cloud service category.
Conclusion
In this session, we've discussed about cloud computing, what it is and what its key characteristics are. Here are some of the things we covered.
- Different types of cloud models that are available and the considerations of using those different models.
- The different cloud services available, the benefits of using the different types, and the management responsibilities under each service type.
- Cloud models such as public, private and hybrid, and what the key characteristics of each model are.
- The different types of cloud service available: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS; what the key characteristics of each service are and when you would choose one over the other.


Too many theories?
Let's start the hands on session !
OpenVPN
wget http://swupdate.openvpn.org/as/openvpn-as-2.1.12-Ubuntu16.amd_64.deb
dpkg -i openvpn-as-2.1.12-Ubuntu16.amd_64.deb
Thank You !
Cloud Computing
By Uvindu Perera
Cloud Computing
- 125



