Introduction to Graph Databases & The Pacer library

Brought to you by
What Is a Graph?

Vertices
(aka nodes)
Edges
(aka relations)

- A data structure
- Used for storing and accessing data
+
Variations
Undirected


Directed
vs.
Variations
Without

With Vertex Properties
vs.

Variations
Without

With Edge Labels
vs.

Property Graph
- Directed graph
-
Vertices & Edges with properties
- Key-value pairs
- Keys are strings, values can be anything
-
Edges are labeled
- Each edge has exactly one label (a string).
- Label can be thought of as "edge type".
Property Graph
Conceptually simple,
yet extremely flexible ...
Airline's Flight Data
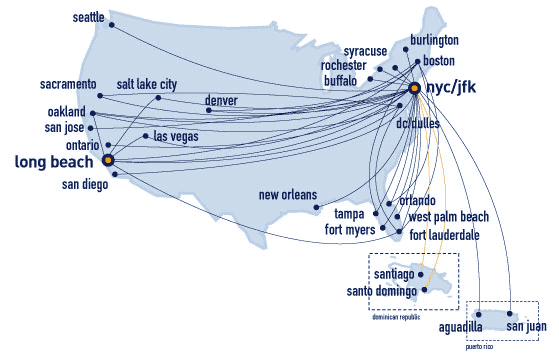
Airline's Flight Data

Social Network
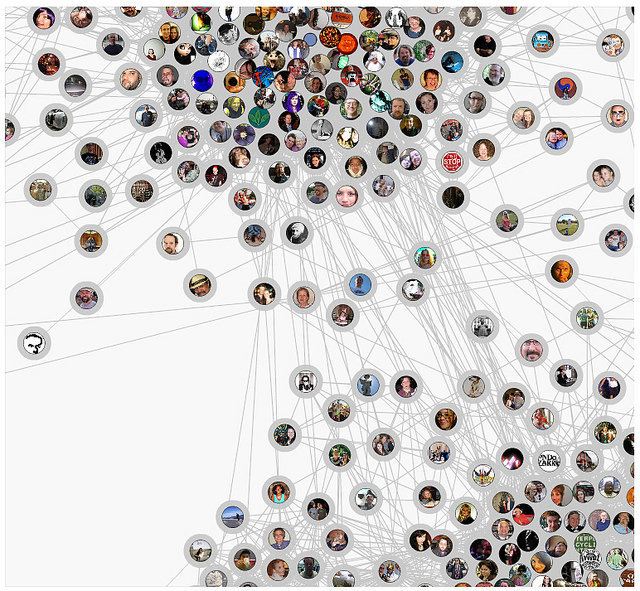
Social Network

Decision Making
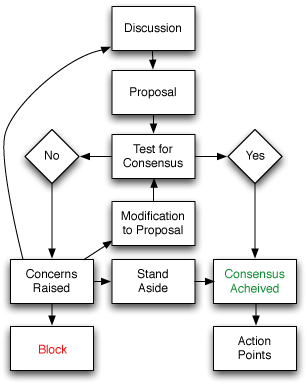

One way of representing the data in a property graph ...
Decision Making

IT Infrastructure
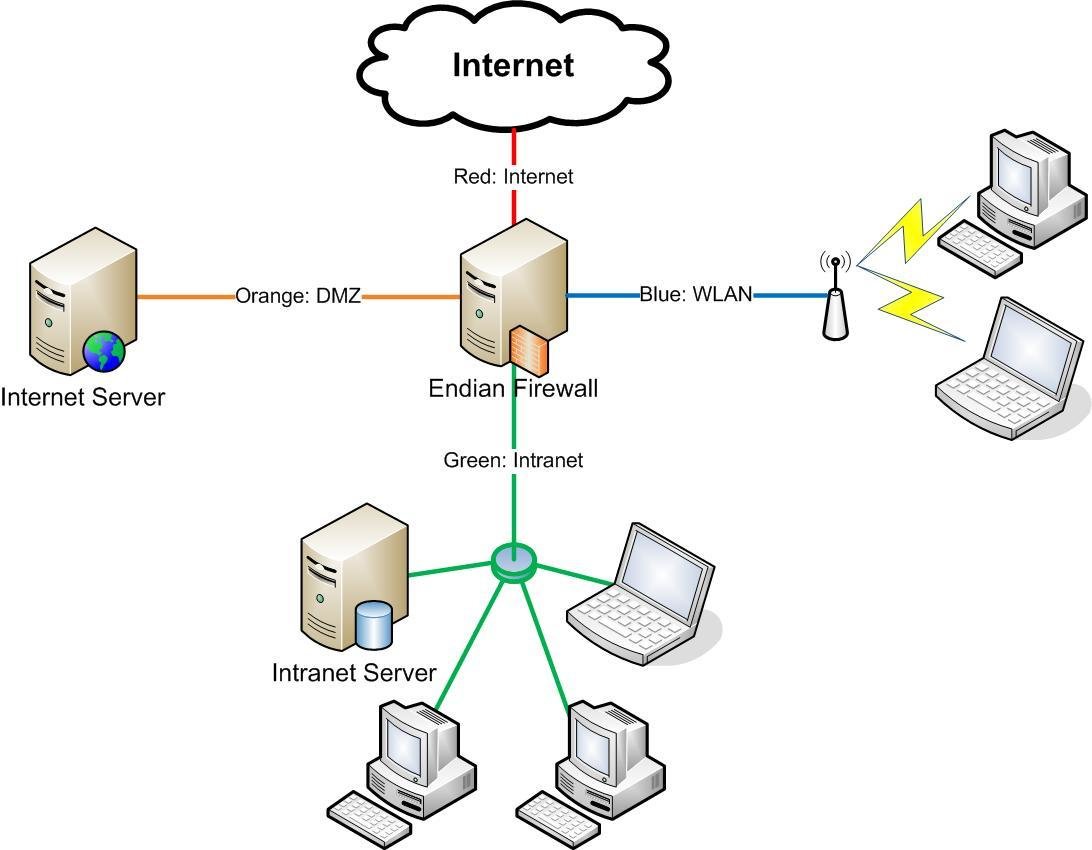
IT Infrastructure

Graph Databases
So far, we've seen an abstract model.
In practice, we will need a graph database.
A graph database is software that:
- Stores a property graph
- Supports the basic graph operations
- Given a vertex, get its edges
- Given an edge, get its vertices
- Does it efficiently!
Graph Databases
There are a number of graph databases out there:
- Neo4j
- OrientDB
- Sparksee
- TinkerGraph
- And more ...



Graph Databases
Databases differ in many aspects:
- Performance
- Persistence strategies
- Transaction management
- Supported data types
- Features
- High-Availability
- Clustering
- Integrations
- Indexing/searching (e.g. Lucene)
- Caching (e.g. Memcached)
- Licensing & Price
Choosing a Graph DB
- Your specific needs (e.g. Scalability, flexibility, ease of development and/or deployment, etc).
- Existing ecosystem.
- How difficult is it to switch to a different database?
- Can I use multiple databases together?
Things to consider ...
Which graph database is the best?
Depends on your use-case.
Luckily, we don't have to commit to one database...
Blueprints
- Blueprints
- Generic Java interfaces for property graphs
-
Adapters for all common databases
- Build your application against Blueprints, and it will support all common graph databases.
- Open-source
- Supported by XN Logic
Additional Benefits
Pacer
- Written in JRuby
- Ruby expressiveness
- Java performance
- Built on top of the Tinkerpop stack
- Well-tested
- Used in production
If you haven't done so already, you may want to install Pacer and its dependencies.
Pacer in 60 Seconds
Graph traversal
- Graphs are processed as streams of elements
- Routes = composable, lazily-loaded streams.
- Build traversals by chaining routes
Data Modeling
- Extend elements with Ruby modules
- Use extensions to create a Domain Specific Language
The Benefits
- Routes allow us to run queries efficiently.
- DSL makes it easy to define complex queries.
user.as(:me)
.out_e(:friend).in_v(type: "user").as(:my_friends)
.out_e(:friend).in_v(type: "user")
.is_not(:me).is_not(:my_friends)becomes ...
user.suggest_friendsOK, let's see Pacer in action ...
Graph Training 1
By XN Logic Corporation
Graph Training 1
A friendly introduction to the field of Graph Databases - We will answer the questions "What are graphs & graph databases, and why should we use them?", survey the current state of the ecosystem and introduce the Pacer library.
- 1,189



