Hyper-Text Markup Language.


HTML - Introduction and History
HyperText - Text connected to a link.
Any text available on the internet is inevitably connected to a “link” that is the “address” of that “document” that contains that text, on the network called the “internet”.
Markup - A way to describe a text’s formatting.
When you add any extra property/properties to a piece of text, it gets marked up.
“Markdown” is a library implementing markup, created by John Gruber - 2004
Language - A set of rules to write in a particular manner for a particular purpose.
HTML’s Timeline
First written in 1993, by Sir Tim Berners-Lee
(also the creator of the Web), for scientific documents.
Was based on SGML - Standard Generalized Mark-up Language.
By 2000s, it’s 4th (4.0) version came.
Current - HTML 5 - released in 2012.
Ref: History of HTML


HTML Today
- We’re working with HTML 5.
- An HTML file is also called a “document” because of historical reasons.
- And is called a “page” in modern times.
- One HTML file = one page on the web (webpage).



Document - Structure, Tags and Attributes
HTML Doc Structure

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<!--- Code not visible on browser --->
</head>
<body>
<!--- Visible UI code--->
</body>
</html>

D.I.Y
- Added on top of every HTML file.
- If present, the browser executes the code in standards mode (new),
- if not present browser executes the code in quirks mode (old).
- It’s not an HTML element. It's a special kind of node called "doctype".
- Ref: Quirks and Standards mode.
<!DOCTYPE html>
OR
<!doctype html>
HTML Tags and Attributes
- Root element,
- Not required, if not given will be implied.
- Has “lang” attribute, that defines default language of the document.
<html lang="attribute">
</html>Lang attribute:
- It’s value is a two- or three-letter ISO language code (en, fr, hi) followed by the region (CA, US, UK, IN).
- The region is optional.
- Language declaration enables screen readers, search engines, and translation services (like Google Translate) to know the document language.
- Can be used with any html tag.

Contains all the visible UI (user interface) elements of the document.
Contains all the metadata about the document - everything that’s not visible to the user (UI).
The information here is super important for SEO and
<body>
</body><head>
</head>
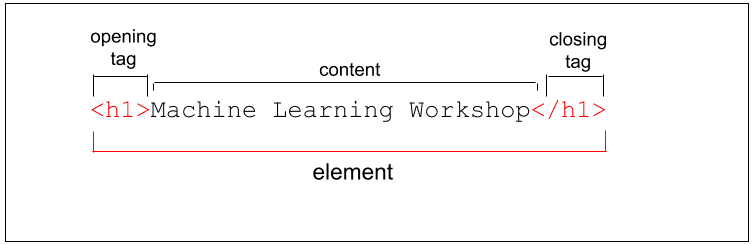
Difference between HTML Tag and HTML Element ?

<body>
<div>
This is a div tag
<span>
Inside div 1
</span>
</div>
<p>
This is another div tag
</p>
<p>
div 1
<span>This is a div tag</span>
</p>
</body>div, p and span tags
**Note::
- Check Element Inspector for UI structure.
- Check console for any errors and warnings.
-
<p>tags cannot be nested.

D.I.Y

HTML Attributes
Key-values added in opening tag.
Global
Enumerated
Boolean
can appear on any tag:
-
id, class,style,role,contenteditabledata etc.
values can only be true or false:
-
disabled, checked,autocompletereadonly etc.
a set of predefined values
-
type etc.
**Note:
-
Some attribute values are case sensitive, eg:
id, class

class, and id attributes

D.I.Y
<div class="container">
- I'm <span class="name-span">
Yash Priyam
</span>
<p class="para1 info" id="one">
- I am a software developer.
</p>
<p class="para2 info" id="two">
- And I love basketball.
</p>
</div><div class="container">
- I'm <span class="name-span">
Yash Priyam
</span>
<p class="para1 info" id="one">
- I am a software developer.
</p>
<p class="para2 info" id="two">
- And I love basketball.
</p>
</div>Connecting CSS and HTML


D.I.Y
/* index.css */
.name-span {
/* class based styling */
}
span {
/* tag based styling */
}
#one {
/* id based styling */
}
<div class="container">
- I'm <span class="name-span">
Yash Priyam
</span>
<p class="para1 info" id="one">
- I am a software developer.
</p>
<p class="para2 info" id="two">
- And I love basketball.
</p>
</div>Starting with CSS:


D.I.Y
/* index.css */
.name-span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
#one {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
width, height
** can be set on any element
background-colors

.rebecca-purple {
background-color: purple;
}
.gray {
/* hsl(144, 3%, 77%) */
background-color: #c3c6c432;
}
.green {
background-color: hsl(180deg, 70%, 18%);
}
.red {
/* hsl(0deg, 70%, 18%);*/
background-color: #4e0e0e;
}
.yellow {
/*hsl(60deg, 70%, 80%);*/
background-color: rgb(240, 240, 168);
}
.blue {
/* hsl(210,70.6%,80%) */
background-color: rgb(65.9%, 80%, 94.1%);
}
<div class="wrapper">
<div id="box1" class="demo-box rebecca-purple"></div>
<div id="box2" class="demo-box green"></div>
<div id="box3" class="demo-box red"></div>
<div id="box5" class="demo-box blue"></div>
<div id="box6" class="demo-box gray"></div>
</div><div class="container">
- I'm <span class="name-span">
Yash Priyam
</span>
<p class="para1 info" id="one">
- I am a software developer.
</p>
<p class="para2 info" id="two">
- And I love basketball.
</p>
</div>

D.I.Y
/* index.css */
.name-span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
span {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
#one {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
Add random background-colors to each of the selectors in css


D.I.Y
Add background color on the entire background (page)
W1_D1
By Yash Priyam
W1_D1
- 274



