STL 基礎
Standard Template Library
10th Sep 2019 by Sean Liu
暖身題 (CF 1076C)

今天會學到什麼?
基本資料結構
- 堆疊 (Stack)
- 佇列 (Queue)
- 雙向佇列 (Double-Ended Queue)
- 鏈狀數組 (Linked List)
這些要會自己實作!雖然有模板可以用,但是還是強烈建議要自己會寫一個。
稍微進階一點的資料結構
- 堆積 (Heap)
- 平衡樹雙兄弟 (Balanced Binary Tree - Map & Set)
以上的Heap如果可以自己實作出來會很好!至於平衡樹現在還不急學,會用就好了。
概念
實作
回家寫題
Stack (堆疊)
基本題目
Bndrew Zang 是盤子大師!他有一堆盤子,每一個都有自己的顏色。他每次可以將一個顏色的盤子疊在最上面,拿掉最上面的盤子,或回答你最上面的盤子是什麼顏色。

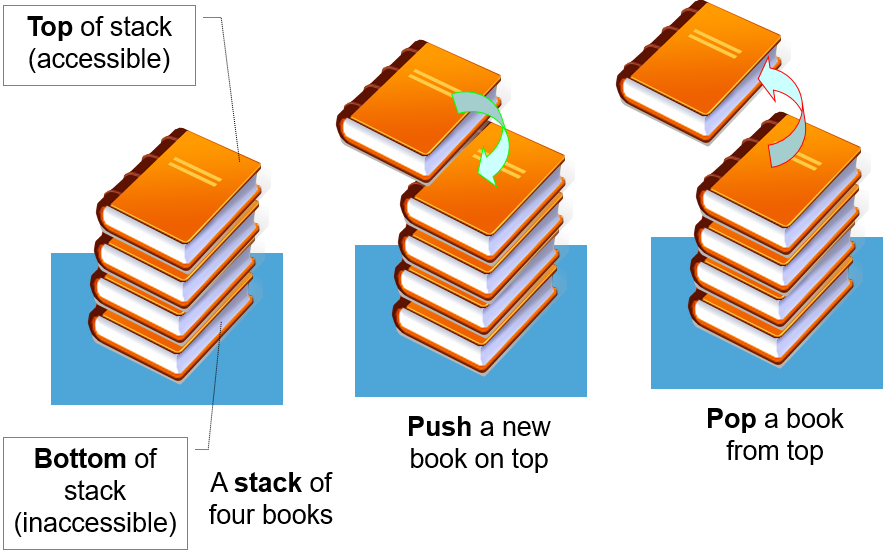
要怎麼實作?
只需要知道最上面的元素!
存有幾個元素就好了,然後每次都去戳最後一個
const int maxN = 1e5;
int stack[maxN], head = 0;
void push(int x){
if(head == maxN){
cout << "Stack is full!" << endl;
return;
} else {
stack[head] = x;
head++:
}
}
int pop(){
if(!head){ //if(head == 0)
cout << "Stack is empty!" << endl;
return -1; //代表沒有東西了!
} else {
int t = stack[head - 1];
head--;
}
}題目
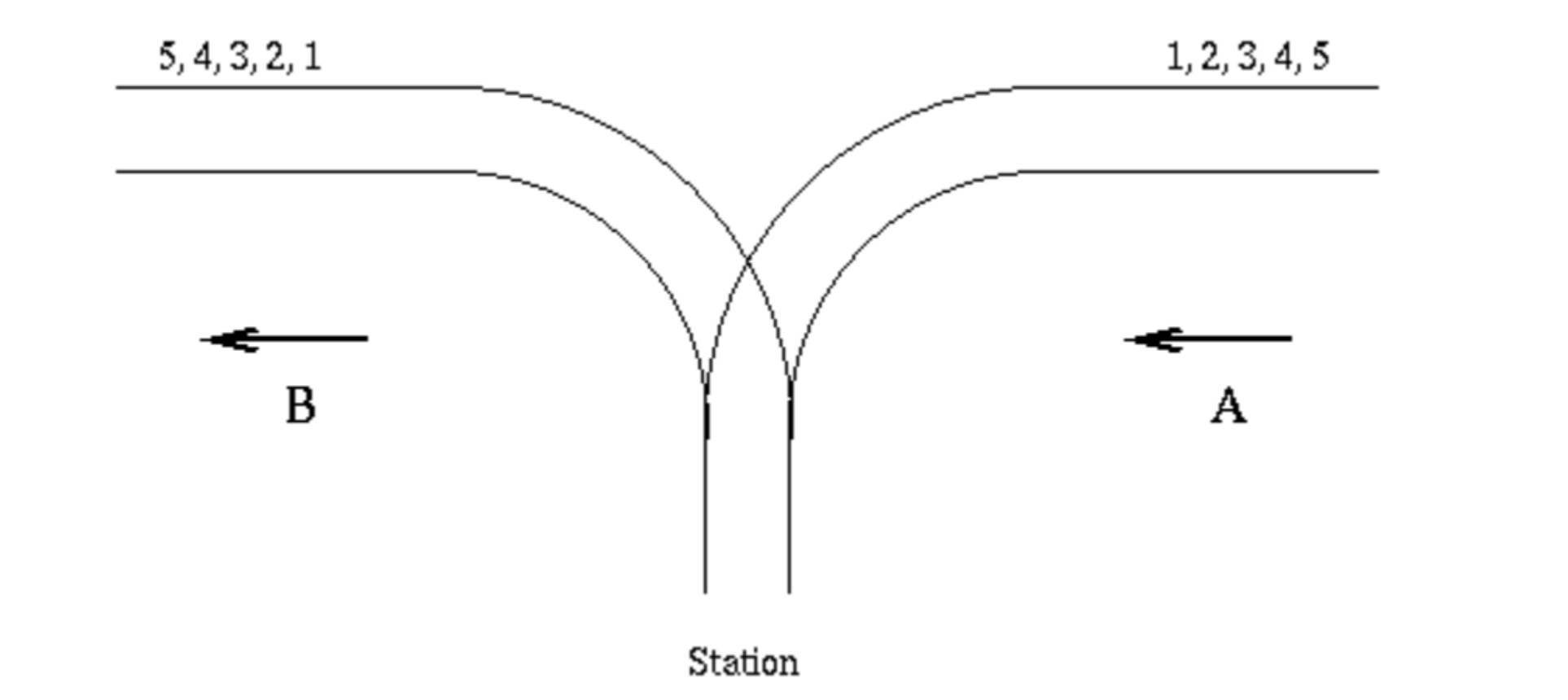
UVa 514 - Rails

(挑戰)NEOJ 22 - 檸檬汽水傳說

Queue (佇列)
基本題
Fric Yiao 是排隊大師!他在觀察一堆人排隊,每次可能有一個人排在隊伍的最後面,或者有人從隊伍的最前面離開,當離開的時候,他要回答離開的人的衣服顏色(假設大家都有穿衣服)

Queue
要怎麼實作?
只要知道目前最前面是誰和最後面是誰就好了!
Title Text
const int maxN = 1e5;
int queue[maxN], head = 0, tail = 0; //含head, 不含tail
void enqueue(int x){ //push()
if(tail == maxN){
cout << "Queue Full!" << endl;
return;
} else {
queue[tail] = x;
tail++;
}
}
int dequeue(){ //pop()
if(head == tail){
cout << "Queue Empty!" << endl;
return -1;
} else {
int t = queue[head];
head++;
return t;
}
}這樣會有什麼問題?
只能push maxN次!
Cyclic Queue
const int maxN = 1e5;
bool isFull = false;
int queue[maxN], head = 0, tail = 0; //含head, 不含tail
void enqueue(int x){ //push()
if(tail == head){
cout << "Queue Full!" << endl;
return;
} else {
queue[tail] = x;
tail = (tail + 1) % maxN;
if(tail == head){
isFull = true;
}
}
}
int dequeue(){ //pop()
if(head == tail && !isFull){
cout << "Queue Empty!" << endl;
return -1;
} else {
int t = queue[head];
head++;
return t;
}
}習題嘍
UVa 540 - Team Queue

UVa 10935 - Throwing cards away I

Deque(雙向佇列)
「Deque」怎麼念?

不用基本題了啦
反正就是兩邊都可以進入,推出!
也不給code了,好煩哦 = =
為什麼不全部都用deque
既然deque兩個功能都有,為什麼還要有stack和queue?寫題目為什麼不全部都用deque?

可讀性!
也就是,雖然是可以什麼都用deque,但是如果你用stack或queue,別人(包括以後的你)比較能看出你用這個資料結構想要做什麼,不論是競賽中debug或日後寫project需要維護都很有用!
超級挑戰:APIO 2010 pA - Commandos

鏈狀串列 (Linked List)
1. 我不知道中文是什麼
2. 這個很好用!
3. 一半了加油
基本題
Uhomas Xang 是尋寶大師!他在他所在的地方找到了一塊石板,上面寫了下一個石板的位置和一個的數字。他必須找完石板——最後一個石板指向的位置就是寶物——紀錄長高秘訣的十陰真經!請幫他紀錄密碼吧!
一個指向下一個
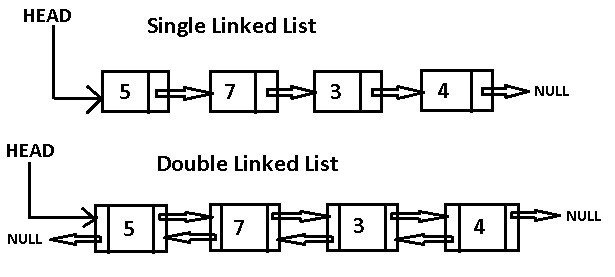
如果不止知道要知道下一個是誰,
還要知道前一個是誰的話,就得變成雙向!
需要支持的操作:
- Next: 詢問一個節點下一個是什麼節點
- Prev: 詢問一個節點前一個是什麼節點
- Insert: 將一個節點插入在一個節點後面
- Delete: 將一個節點刪除
要怎麼實作?
struct node {
node *prev, *next;
int id;
node(): prev(NULL), next(NULL){}
};
vector<node*> List;
// list[x] 儲存指向 id = x 的指標
void Init(){ //初始化
List[0] = new node; // 起始空節點
List[0]->id = 0;
}
int prev(int x){ // 查詢前一項的 id
if(List[x] && List[x]->prev)
return List[x]->prev->id;
return -1;
}
int next(int x){ // 查詢下一項的 id
if(List[x] && List[x]->next)
return List[x]->next->id;
return -1;
}
bool Insert(int x, int id) {
// 在 id = x 的節點之後插入 id = id 的節點
if(!List[x]) return false;
node *n = new node;
List[id] = n;
n->next = List[x]->next;
if(n->next) n->next->prev = n;
List[x]->next = n;
n->prev = List[x];
n->id = id;
return true;
}
bool Delete(int x){
// 刪除 id = x 的節點
if(!List[x]) return false;
if(List[x]->next)
List[x]->next->prev = List[x]->prev;
List[x]->prev->next = List[x]->next;
delete List[x];
List[x] = NULL;
return true;
}
void travel(){ // 依序尋訪所有節點
node *s = List[0]->next; // start
while(s){
printf("%d ",s->id);
s = s->next;
}
puts("");
}
基本的功能
bool Insert(int x, int id) {
// 在 id = x 的節點之後插入 id = id 的節點
if(!List[x]) return false;
node *n = new node;
List[id] = n;
n->next = List[x]->next;
if(n->next) n->next->prev = n;
List[x]->next = n;
n->prev = List[x];
n->id = id;
return true;
}
bool Delete(int x){
// 刪除 id = x 的節點
if(!List[x]) return false;
if(List[x]->next)
List[x]->next->prev = List[x]->prev;
List[x]->prev->next = List[x]->next;
delete List[x];
List[x] = NULL;
return true;
}
void travel(){ // 依序尋訪所有節點
node *s = List[0]->next; // start
while(s){
printf("%d ",s->id);
s = s->next;
}
puts("");
}
進階功能 —— 插入和刪除
寫的時候自己畫圖!很重要!
xiti
NEOJ 21 - 陸行鳥大賽車

UVa 11988 - Broken Keyboard (a.k.a. Beiju Text)

中場休息!
去想題目或發呆或問問題吧!
Heap (堆疊)
這裡誰最大?
基本題
Dasper Xang 是主考官!他的考場會一直來、離開人,各有各自的能力值。每次詢問他,他都可以告訴你這裡能力最大是多少
為什麼叫做 Heap?
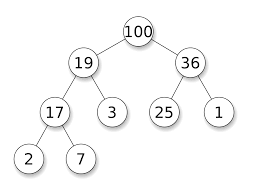
符合 Max Heap Property
也就是對於一個節點,他的值會不比其子樹的所有數字小(反過來的話,稱為Min Heap Property)
每一個數字都存成一個樹上的節點!
根節點(最上面的)是最大/小值!
Heap 的一些性質、操作

他是一個平衡二元樹,即他可能除了最後一層之外,每一層都是填滿的!而且,最後一層會從左邊填到右邊。這個性質讓我們可以用一個array來存他,一個位於 i 的節點的左、右子節點位於 2i, 2i + 1。(1base的話;否則是2i + 1, 2i + 2)
要支援的操作
-
查詢最大值
-
插入一個值為 的節點
-
刪除根節點
要支援的操作
-
查詢最大值 - 直接看根
-
插入一個值為 的節點
-
刪除根節點
插入節點

先把節點插入最後的位置,然後只要目前的節點比他的前一個節點還大,就交換兩者
刪除根節點
先刪除根節點,然後將目前最後的節點換上去,再開始:其子節點大,若比目前大就換上來,然後遞迴下去;否則停止。
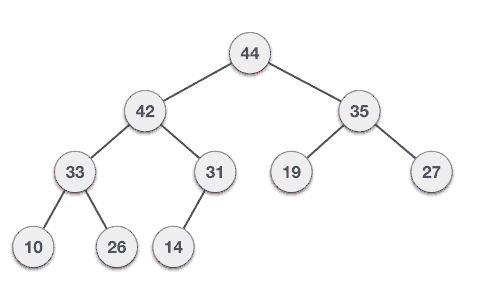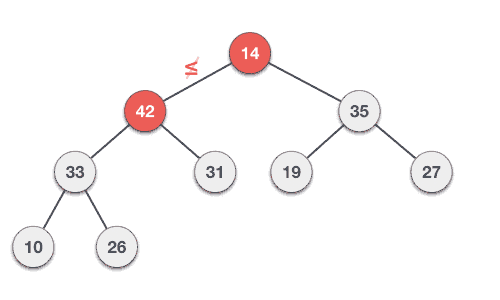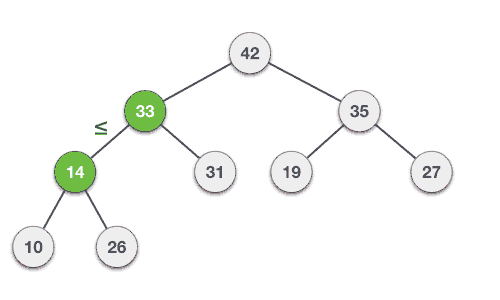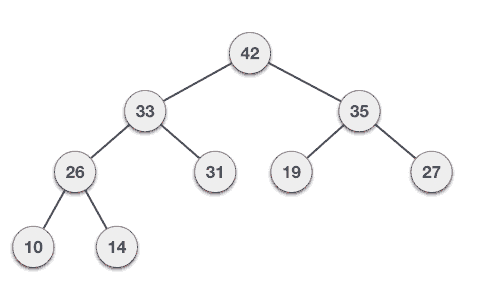
怎麼實作?
這是講師第一次實作Heap qwq
const int maxN = 1e5;
int heap[maxN], sz = 1; //一開始所有的數字都是無限大
int getMax(){
return heap[1];
}
void Insert(int x){
heap[sz] = x;
int ind = sz;
sz++;
while(heap[ind] > heap[ind/2]){
swap(heap[ind], heap[ind/2]);
ind /= 2;
}
}
void Delete(){
swap(heap[sz], heap[0]);
sz--;
int ind = 1;
while(max(heap[2*ind, 2 * ind + 1]) > heap[ind]){
if(heap[2 * ind] > heap[2 * ind + 1]){
swap(heap[ind], heap[2 * ind]);
ind = 2 * ind;
} else {
swap(heap[ind], heap[2 * ind + 1]);
ind = 2 * ind + 1;
}
}
}void Delete(){
swap(heap[sz], heap[0]);
sz--;
int ind = 1;
while(max(heap[2*ind, 2 * ind + 1]) > heap[ind]){
if(heap[2 * ind] > heap[2 * ind + 1]){
swap(heap[ind], heap[2 * ind]);
ind = 2 * ind;
} else {
swap(heap[ind], heap[2 * ind + 1]);
ind = 2 * ind + 1;
}
}
}題目
UVa 10954 - Add All

TIOJ 1999 - 排隊買飲料

延伸閱讀:霍夫曼編碼
平衡二元樹雙胞胎
Map & Set (映射 & 集合)
Set (集合)
基本題
Uim Min 是找東西大師!他有一個大箱子,會一直放進去東西或拿東西出來。保證每一個東西都相異,詢問是:一個東西到底在不在箱子裡面?
原理
簡單來說,裡面是用一個自動平衡的二分樹來儲存所有的東西,然後再每次二分搜,看有沒有搜尋到。實作通常非常複雜(資料結構除外還要加許多優化,隨便就上百、甚至或許上千行!)。有興趣的人可以去維基百科上看:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Self-balancing_binary_search_tree
實作
AVL Tree
Source (222 Lines)
/* AVL Tree Implementation in C++ */
/* Harish R */
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class BST
{
struct node
{
int data;
node* left;
node* right;
int height;
};
node* root;
void makeEmpty(node* t)
{
if(t == NULL)
return;
makeEmpty(t->left);
makeEmpty(t->right);
delete t;
}
node* insert(int x, node* t)
{
if(t == NULL)
{
t = new node;
t->data = x;
t->height = 0;
t->left = t->right = NULL;
}
else if(x < t->data)
{
t->left = insert(x, t->left);
if(height(t->left) - height(t->right) == 2)
{
if(x < t->left->data)
t = singleRightRotate(t);
else
t = doubleRightRotate(t);
}
}
else if(x > t->data)
{
t->right = insert(x, t->right);
if(height(t->right) - height(t->left) == 2)
{
if(x > t->right->data)
t = singleLeftRotate(t);
else
t = doubleLeftRotate(t);
}
}
t->height = max(height(t->left), height(t->right))+1;
return t;
}
node* singleRightRotate(node* &t)
{
node* u = t->left;
t->left = u->right;
u->right = t;
t->height = max(height(t->left), height(t->right))+1;
u->height = max(height(u->left), t->height)+1;
return u;
}
node* singleLeftRotate(node* &t)
{
node* u = t->right;
t->right = u->left;
u->left = t;
t->height = max(height(t->left), height(t->right))+1;
u->height = max(height(t->right), t->height)+1 ;
return u;
}
node* doubleLeftRotate(node* &t)
{
t->right = singleRightRotate(t->right);
return singleLeftRotate(t);
}
node* doubleRightRotate(node* &t)
{
t->left = singleLeftRotate(t->left);
return singleRightRotate(t);
}
node* findMin(node* t)
{
if(t == NULL)
return NULL;
else if(t->left == NULL)
return t;
else
return findMin(t->left);
}
node* findMax(node* t)
{
if(t == NULL)
return NULL;
else if(t->right == NULL)
return t;
else
return findMax(t->right);
}
node* remove(int x, node* t)
{
node* temp;
// Element not found
if(t == NULL)
return NULL;
// Searching for element
else if(x < t->data)
t->left = remove(x, t->left);
else if(x > t->data)
t->right = remove(x, t->right);
// Element found
// With 2 children
else if(t->left && t->right)
{
temp = findMin(t->right);
t->data = temp->data;
t->right = remove(t->data, t->right);
}
// With one or zero child
else
{
temp = t;
if(t->left == NULL)
t = t->right;
else if(t->right == NULL)
t = t->left;
delete temp;
}
if(t == NULL)
return t;
t->height = max(height(t->left), height(t->right))+1;
// If node is unbalanced
// If left node is deleted, right case
if(height(t->left) - height(t->right) == 2)
{
// right right case
if(height(t->left->left) - height(t->left->right) == 1)
return singleLeftRotate(t);
// right left case
else
return doubleLeftRotate(t);
}
// If right node is deleted, left case
else if(height(t->right) - height(t->left) == 2)
{
// left left case
if(height(t->right->right) - height(t->right->left) == 1)
return singleRightRotate(t);
// left right case
else
return doubleRightRotate(t);
}
return t;
}
int height(node* t)
{
return (t == NULL ? -1 : t->height);
}
int getBalance(node* t)
{
if(t == NULL)
return 0;
else
return height(t->left) - height(t->right);
}
void inorder(node* t)
{
if(t == NULL)
return;
inorder(t->left);
cout << t->data << " ";
inorder(t->right);
}
public:
BST()
{
root = NULL;
}
void insert(int x)
{
root = insert(x, root);
}
void remove(int x)
{
root = remove(x, root);
}
void display()
{
inorder(root);
cout << endl;
}
};
註:set裡面的東西不能重複,如果要重複的話就得用另外一個叫做multiset的東西。
習題
ZJ a091 - 今晚打老虎

TIOJ 1513 - 好多燈泡

Map (映射)
Set 的小老弟

基礎題
Uim Min 是找東西大師!他有一個大箱子,會一直放進去東西或拿東西出來。每一個東西都有自己的值,且保證每一個東西都相異,詢問是:
1. 一個東西到底在不在箱子裡面
2. 如果一個東西在箱子裡面,那他的值是什麼?
很類似一個陣列,只是索引值是任意的東西!
當然,查詢就變成了
實作
就是一個塞了pair的set,不過是依照索引值排序而已!
習題
UVa 10226 - Hardwood Species

STL - Standard Template Library
爽啦!都不用自己寫
Stack
#include <stack> //引用stack
stack<int> stk; //這個stack裡面裝的是int
int main(){
stk.push(5); //放進去一個值為5的數字
cout << stk.top() << endl; //stk.top()代表最上面的數字, 5
stk.pop(); //拿出來
}Queue
#include <queue> //引用queue
queue<int> que; //這個queue裡面裝的是int
int main(){
que.push(5); //放進去一個值為5的數字
que.push(7);
cout << que.front() << endl; //que.top()代表最前面的數字, 5
que.pop(); //拿出來
cout << que.front() << endl; //7
}Dequeue
#include <deque> //引用deque
deque<int> dq; //這個dequeue裡面裝的是int
int main(){
dq.push_front(3); //將3放在deque最前面
dq.push_back(7); //將7放在deque最後面
dq.push_front(5);
cout << dq.front() << endl; //最前面的數字, 5
cout << dq.back() << endl; //最後面的數字, 7
dq.pop_back(); //將最前面的數字拿出來
dq.pop_front(); //將最後面的數字拿出來
cout << dq[0] << endl; //可以隨機存取!, 3
}
Heap (Priority Queue)
#include <queue> //引用queue - priority_queue在queue裡面
#include <vector>
priority_queue<int> pq; //這個priority_queue裡面裝int
int main(){
pq.push(5); //將一個數字放進去
pq.push(7);
pq.push(3);
pq.push(2);
cout << pq.top() << endl; //拿出最大值,7
pq.pop(); //刪除最大值
cout << pq.top() << endl; //拿出最大值,5
}
Heap (Priority Queue)
#include <queue> //引用queue - priority_queue在queue裡面
#include <vector>
class Cmp{
public:
bool operator()(int a, int b){ //a < b
return a < b;
}
}
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, Cmp > pq; //型別, 容器, 比較
Set
#include <set> //引用set
set<int> st;
int main(){
st.insert(5); //放入5
cout << st.count(5) << endl; //有沒有 5?
cout << st.size() << endl; //st裡面有幾個元素
st.erase(5); //將5刪除
}Map
#include <map> //引用map
map<int, int> mp; //key, value
int main(){
mp.insert({2, 1}); //用大括弧包起來就行了
cout << mp[2] << endl; //2所對應到的值:1
cout << mp.count(3) << endl; //有沒有索引值為3的? 0
}據說Linked List還有一個叫做std::list
不過我不熟qq沒有用過
謝謝大家!
可能有點超時了?有問題記得問,可以去密學長!

Copy of STL 基礎
By ycsh1519
Copy of STL 基礎
- 135



