Array & ArrayList



数组是一组元素(数值或者变量)的集合,每一个元素都被数组索引(array index)或者键值(key)所标识.
什么是数组(Array)?



数组是一组元素(数值或者变量)的集合,每一个元素都被数组索引(array index)或者键值(key)所标识.
什么是数组(Array)?
| ... |
|---|
| ... |
Memory



A data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key.
What is Array?
| ... |
|---|
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| ... |
Memory
Array



A data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key.
What is Array?
| ... |
|---|
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| ... |
Memory
Array
| ... |
|---|
| 5 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| ... |
| ... |
|---|
| 'c' |
| 'b' |
| 'r' |
| ... |
| ... |
|---|
| true |
| false |
| false |
| ... |



A data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key.
What is Array?
| ... |
|---|
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| ... |
Memory
Array
This could be 1D array, or 2D array, or even 3D array, etc.



数组是一组元素(数值或者变量)的集合,每一个元素都被数组索引(array index)或者键值(key)所标识.
什么是数组(Array)?
| ... |
|---|
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| ... |
Memory



数组是一组元素(数值或者变量)的集合,每一个元素都被数组索引(array index)或者键值(key)所标识.
什么是数组(Array)?
| ... |
|---|
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| ... |
Memory



| ... |
|---|
| 5 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| ... |
| ... |
|---|
| true |
| false |
| false |
| ... |
| ... |
|---|
| 'c' |
| 'b' |
| 'r' |
| ... |
Array
数组是一组元素(数值或者变量)的集合,每一个元素都被数组索引(array index)或者键值(key)所标识.
什么是数组(Array)?
| ... |
|---|
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| Element |
| ... |
Memory



可以是1维数组, 2维数组或者3维数组等
Array
如何表示数组(Array)
- C/C++
- int a[5], char c[3][6], etc.
- C语言中无法获取数组的长度.
- Java
- int[] a = new int[5];
- char[][] c= new char[3][];
- a.length = 5
- Library
- ArrayList<Integer> a = new ArrayList<Integer>(5);
- vector<int> a;



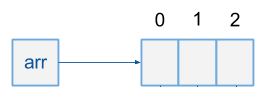
How to represent Array
int[] arr = new int[3]
int[][] arr = new int[3][]
arr[0] = new int[3]
arr[1] = new int[5]
arr[2] = new int[4]




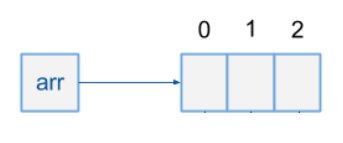
How to represent Array
int[] arr = new int[3]

| length |
|---|
Object Header



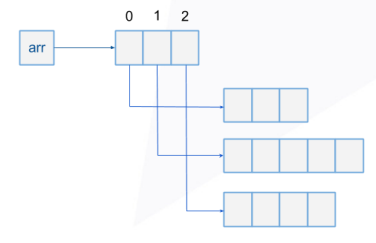
如何表示数组(Array)



int[] arr = new int[3]
int[][] arr = new int[3][]
arr[0] = new int[3]
arr[1] = new int[5]
arr[2] = new int[4]
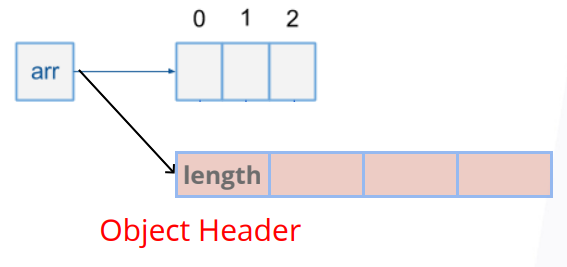
如何表示数组(Array)



int[] arr = new int[3]
数组(Array)的性质
- 地址空间连续
- addr = base_addr + offset (=index * sizeof(elem))
- 元素地址=数组基地址+元素偏移量
- 元素类型相同
- int[] arr = new int[10];
- 可以用下标表示
- a[2], a[10]
- 访问数组中任何元素的时间复杂度均为 O(1)



Array是其他数据结构的基础
- 空间连续
- 元素类型相同
- 可以用索引表示
Linked List
Tree
String
Set
HashMap
Stack/Queue
Heap
Graph



为什么要使用数组呢(Array)?
可以是代码简单并且整洁



从键盘输入10个数字并且反向打印
int a, b, c, ..., j;
cin >> a;
cin >> b;
cin >> d;
....
cout << j << endl;
cout << i << endl;
...
cout << a << endl;
int a[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--)
cout << a[i];


- 数组求和
- 求数组的最小值
- 求数组的次小值
- 交换数组中的两个元素
热身练习



- Sum of the array numbers
Warmup Questions
int sum(int[] nums) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
result += nums[i];
}
return result;
}


- Minimum element of the array
Warmup Questions
int minimum(int a, int b) {
if (a < b) {
return a;
}
return b;
}
int minimum(int[] nums) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < min) {
min = nums[i];
}
}
return min;
}


- Second minimum element of the array
Warmup Questions
int secondMinimum(int[] nums) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < min) {
min = nums[i];
}
}
int secondMin = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == min) {
continue;
}
if (nums[i] < secondMin) {
secondMin = nums[i]
}
}
return secondMin;
}There are at least two numbers in the array and all numbers are distinct.



- Second minimum element of the array
Warmup Questions
int secondMinimum(int[] nums) {
int min = Math.min(nums[0], nums[1]);
int secondMin = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < min) {
secondMin = min;
min = nums[i];
} else if (nums[i] == min) {
secondMin = min;
} else if (nums[i] > min && nums[i] < secondMin) {
secondMin = nums[i];
} else if (nums[i] == secondMin) {
continue;
} else {
continue;
}
}
return secondMin;
}


- Second minimum element of the array
Warmup Questions
int secondMinimum(int[] nums) {
int min = Math.min(nums[0], nums[1]);
int secondMin = Math.max(nums[0], nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] < min) {
secondMin = min;
min = nums[i];
} else if (nums[i] < secondMin) {
secondMin = nums[i];
}
}
return secondMin;
}


- Swap two elements in an array
Warmup Questions
{
int a = 5, b = 3;
int c = a;
a = b;
b = c;
// a = 3, b = 5;
}
void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}


两数之和
在一个没有重复数字的整数数组中, 找出两个数字, 使得它们的和等于给定的数字
函数twoSum返回两个数字且它们的和等于给定的数字, 其中第1个数字小于第2个数字.
假定每组输入都有解.
例如:
Input: numbers={2, 7, 11, 15}, target=9
Output: {2, 7}
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// TODO: implement this function.
}



Always ASK before you write code.



两数之和
在一个没有重复数字的整数数组中, 找出两个数字, 使得它们的和等于给定的数字.
函数twoSum返回两个数字使得它们的和等于给定的数字, 其中第1个数字小于第2个数字.
假定每组输入都只有唯一解.
Examples:
Input: numbers={2, 7, 11, 15}, target=9
Output: {2, 7}
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// TODO: implement this function.
}



解决方案-1
- 取出一个数字, 分别计算它与其他每个数字的和,看是否等于给定的数字.
- 依次对所有数字进行上述尝试, 最后一定可以找到满足条件的两个数字.



int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
if (numbers.length < 2) {
return result;
}
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j < numbers.length; j++) {
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) {
if (numbers[i] < numbers[j]) {
result[0] = numbers[i];
result[1] = numbers[j];
} else {
result[0] = numbers[j];
result[1] = numbers[i];
}
return result;
}
}
}
return result;
}解决方案-1



解决方案-1-总结
- 直接, 简单
- 时间复杂度为O(n^2).
- 执行效率低
- Numbers : {1, 4, 20, 15, 8, 6, 3 }, Target = 10.
- 第1轮: 1 + 20 > 10
- 第2轮: 4 + 20, NO NEED!
- 很多不必要的操作
- Numbers : {1, 4, 20, 15, 8, 6, 3 }, Target = 10.
- 排序



解决方案-2
- 首先对数组进行排序操作
- 从数组开头位置取出数字i, 从数组结尾位置取出数字j.
- if sum == target, RESOLVED.
- if sum > target, j--.
- if sum < target, i++.
-
Numbers : {1, 4, 20, 15, 8, 6, 3 }, Target = 10.
- 排序后 {1, 3, 4, 6, 8, 15, 20}.
- 不会出现类似于 4+20 ? 10这样没有意义的比较操作
- 时间复杂度: O(nlogn) + O(n) = O(nlogn).



解决方案-2
int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
Arrays.sort(numbers);
int first = 0, second = numbers.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
if (numbers[first] + numbers[second] == target) {
result[0] = numbers[first];
result[1] = numbers[second];
return result;
}
if (numbers[first] + numbers[second] > target) {
second--;
}
if (numbers[first] + numbers[second] < target) {
first++;
}
}
return result;
}


双指针
利用两个指针按照相同或相反遍历数组



双指针
-
大多数情况下,数组已排序.
- 按照数字顺序.
- 按照数组顺序.
- 按照链表顺序.
- 查找满足某些条件的两个数字或者两组数字.



3个数之和
在一个没有重复数字的整数数组中, 找出3个数字, 使得它们的和等于给定的数字.
函数threeSum 返回3个数字使得它们的和等于给定的数字, 返回结果按照升序排列.
假定每组输入都只有唯一解.
Examples:
Input: numbers={-1, 0, 1, 2, -4}, target=0
Output: {-1, 0, 1}
public int[] threeSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// TODO: implement this function.
}
COMMUNICATION!!!



解决方案
- 枚举前两个数字
- 在剩余元素中尝试查找第3个数字使得它们的和等于给定值 (target-num1-num2)



解决方案
-
枚举前两个数字在剩余元素中尝试查找第3个数字使得它们的和等于给定值 (target-num1-num2).
- 枚举第一个数字,
- 在剩余元素中尝试查找另外两个数字使得它们的和等于给定值 (target-num1).



Solution
-
枚举前两个数字在剩余元素中尝试查找第3个数字使得它们的和等于给定值 (target-num1-num2).
- 枚举第一个数字
- 在剩余元素中尝试查找另外两个数字使得它们的和等于给定值 (target-num1).
- 时间复杂度
- 首先进行一次Sort, 再对n个不同的第一个数字分别进行 twoSum操作.
- O(nlogn) + n*O(n) = O(n^2)
twoSum



解决方案
// pseudo code.
int[] threeSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[3];
if (nums.length < 3) {
return nums;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-2; i++) {
twoSum(nums[i+1..], target-nums[i]);
if (twoSum has results) {
result = {nums[i], (twoSum result)}
}
}
return result;
}


解决方案
int[] threeSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] result = new int[3];
if (nums.length < 3) {
return nums;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-2; i++) {
int first = i+1, second = nums.length-1, new_target = target-nums[i];
while (first < second) {
if (nums[first] + nums[second] == new_target) {
result[0] = nums[i];
result[1] = nums[first];
result[2] = nums[second];
return result;
}
if (nums[first] + nums[second] > new_target) {
second--;
}
if (nums[first] + nums[second] < new_target) {
first++;
}
}
}
return result;
}


K个数之和(k-Sum)
- 排序.
- 枚举第一个数, 然后执行(k-1)-Sum.
- 时间复杂度
- 2-Sum: O(nlogn) + O(n) = O(nlogn)
- 3-Sum: O(nlogn) + O(n^2) = O(n^2)
- 4-Sum: O(nlogn) + O(n^3) = O(n^3)
- k-Sum: O(nlogn) + O(n^(k-1)) = O(n^(k-1))



转置数组(Reverse Array)
把一个数组的元素反向排列.
Examples:
Input: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Output: {7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}
public void reverseArray(int[] nums) {
// TODO: implement this function.
}



Reverse Array
Given an array, reverse all the numbers in the array.
Examples:
Input: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Output: {7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}
public void reverseArray(int[] nums) {
// TODO: implement this function.
int first = 0, end = nums.length - 1;
while (first < end) {
swap(nums, first++, end--);
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int first, int second) {
int temp = nums[first];
nums[first] = nums[second];
nums[second] = temp;
}


Reverse Array
Given an array, reverse all the numbers in the array.
Examples:
Input: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
Output: {7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1}
Follow up:
- Reverse Number (1234 -> 4321)
- Palindrome Number/String ('abcd' -> false; 343 -> true)
- Odd Even Sort, Pivot Sort
- etc.



奇偶排列(Odd Even Sort)
把一个数组中的所有奇数排列到所有偶数的前面.
排序之后奇数部分或偶数部分各自的元素不需要保持原有的顺序,也不要求按序排列.
Examples:
Input: {4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 11, 0, 8, 6, 9}
Output: {9, 3, 5, 11, 1, 2, 0, 8 , 6, 4}
public void oddEvenSort(int[] nums) {
// TODO: implement this function. After sorting,
// nums should start with odd numbers and then
// even numbers.
}



Odd Even Sort
Given an array of integers, sort them so that all odd integers come before even integers.
The order of elements can be changed. The order of sorted odd numbers and even numbers doesn't matter.
Examples:
Input: {4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 11, 0, 8, 6, 9}
Output: {9, 3, 5, 11, 1, 2, 0, 8 , 6, 4}
public void oddEvenSort(int[] nums) {
int first = 0, second = nums.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
while (first < second && nums[first] % 2 == 1) {
first++;
}
while (first < second && nums[second] % 2 == 0) {
second--;
}
if (first < second) {
swap(nums, first++, second--);
}
}
}


轴排序(Pivot Sort)
给定一个数字, 把数组中所有小于该数字的元素排列到大于该数字的元素的前面.
排序之后元素之间原有的相对顺序可以改变.
Examples:
Input: {4, 9, 5, 2, 1, 11, 0, 8, 6, 3}, 7
Output: {4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 6, 0, 8, 11, 9}
public void pivotSort(int[] nums, int pivot) {
// TODO: implement this function.
}



Pivot Sort
Given an array of integers and a target number, sort them so that all numbers that are smaller than the target always come before the numbers that are larger than the target.
The order of elements can be changed.
Examples:
Input: {4, 9, 5, 2, 1, 11, 0, 8, 6, 3}, 7
Output: {4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 6, 0, 8, 11, 9}
public void pivotSort(int[] nums, int pivot) {
// TODO: implement this function.
}
void pivotSort(int[] nums, int pivot) {
int first = 0, second = nums.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
while (first < second && nums[first] <= pivot) {
first++;
}
while (first < second && nums[second] > pivot) {
second--;
}
if (first < second) {
swap(nums, first++, second--);
}
}
}
void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}


Pivot Sort
Given an array of integers and a target number, sort them so that all numbers that are smaller than the target always come before the numbers that are larger than the target.
The order of elements can be changed.
Examples:
Input: {4, 9, 5, 2, 1, 11, 0, 8, 6, 3}, 7
Output: {4, 3, 5, 2, 1, 6, 0, 8, 11, 9}
follow up: Quicksort



删除元素(Remove Element)
给定一个数组和一个数字,在原数组中将等于该数字的元素原地删除,并且返回删除元素之后的数组长度.
删除元素之后数组元素的顺序可以改变. 删除元素之后留下的位置可以是任意值.
Examples:
Input: {10, 9, 5, 3, 9, 9, 8, 6, 7}, 9
Output: {10, 5, 3, 8, 6, 7, X, X, X}, 6
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
// TODO: implement this function. After removing,
// nums should contain only instances which
// is not equal to val (from 0 to new length).
}


Remove Element
Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in place and return the new length.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int first = 0, second = nums.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
while (first < second && nums[first] != val) {
first++;
}
while (first < second && nums[second] == val) {
second--;
}
if (first < second) {
swap(nums, first++, second--);
}
}
return first;
}


Remove Element
Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in place and return the new length.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int first = 0, second = nums.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
while (first < second && nums[first] != val) {
first++;
}
while (first < second && nums[second] == val) {
second--;
}
if (first < second) {
swap(nums, first++, second--);
}
}
return first;
}[3, 2, 2, 3], 3



Remove Element
Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in place and return the new length.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int first = 0, second = nums.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
while (first < second && nums[first] != val) {
first++;
}
while (first < second && nums[second] == val) {
second--;
}
if (first < second) {
swap(nums, first++, second--);
}
}
return first;
}[2, 2, 3, 3], 3



Remove Element
Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in place and return the new length.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int first = 0, second = nums.length - 1;
while (first < second) {
while (first < second && nums[first] != val) {
first++;
}
while (first < second && nums[second] == val) {
second--;
}
if (first < second) {
swap(nums, first++, second--);
}
}
return nums[first] != val ? first+1 : first;
}


Remove Element
Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in place and return the new length.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int index = 0, len = nums.length;
// len is the valid length of remaining array.
while (index < len) {
if (nums[index] == val) {
len--; // remove one element.
// Keep the possible valid element.
nums[index] = nums[len];
} else {
index++;
}
}
return len;
}


Remove Element
Given an array and a value, remove all instances of that value in place and return the new length.
The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int index = 0, len = nums.length;
while (index < len) {
nums[index] = nums[index] == val ?
nums[--len] : nums[index++];
}
return len;
}


归并两个有序数组(Merge Two Sorted Array)
给定两个升序排列的数组,将它们归成一个升序数组.
Examples:
Input: {1, 3, 5}, {2, 4, 6}
Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Solution:
Iterate two arrays at the same time, and always pick the smaller element from two numbers to put into the result array.



Merge Two Sorted Array
Given two sorted arrays of integer, both with increasing order. Please merge them into one sorted array, with increasing order.
Examples:
Input: {1, 3, 5}, {2, 4, 6}
Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Solution:
Iterate two arrays at the same time, and always pick the smaller element from two numbers to put into the result array.
public int[] removeElement(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
int[] result = new int[arr1.length + arr2.length];
int index = 0, index1 = 0, index2 = 0;
while (index1 < arr1.length && index2 < arr2.length) {
if (arr1[index1] < arr2[index2]) {
result[index++] = arr1[index1++];
} else {
result[index++] = arr2[index2++];
}
}
for (int i = index1; i < arr1.length; i++) {
result[index++] = arr1[i];
}
for (int i = index2; i < arr2.length; i++) {
result[index++] = arr2[i];
}
}


Merge Two Sorted Array
Given two sorted arrays of integer, both with increasing order. Please merge them into one sorted array, with increasing order.
Examples:
Input: {1, 3, 5}, {2, 4, 6}
Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Follow up:
- Merge Two Sorted Linked List
- Merge K Sorted Array
- etc.



有限的数组操作
- 按数组下标取值 & 获取数组长度
- 我们还需要其它数组操作
- 在数组中增加一个数字
- 从数组中和删除一个数字
- 在数组中查找一个给定数字
- 等等.
这些操作都很常见但是却需要额外写很多行的代码 !



ArrayList



ArrayList
Array
ArrayList





基本操作
| Operation | Input | Output | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Get | index | value | O(1) |
| Set | index, value | void | O(1) |
| Add | [index], value | void | O(n) |
| Remove | index/value | void | O(n) |
| Find | value | boolean | O(n) |



ArrayList是一个对象
- 字段(Fields)
- 存储对象的数据和信息
- 函数(Functions)
- 访问或者修改字段(fields)



ArrayList实现
- 定义字段(fields)
- 定义函数(functions)
- 构造函数(constructor function): new ArrayList();
- 其它函数



ArrayList实现 - Fields
public class ArrayList{
private int capacity;
private int size;
private int[] data;
}


ArrayList Implementation - Functions
public class ArrayList{
public ArrayList(int capacity_) {
capacity = capacity_;
size = 0;
data = new int[capacity];
}
}



ArrayList Implementation - Functions
public class ArrayList{
// TODO: implement this class.
public int get(int index) {
// TODO: implement this method.
}
public void set(int index, int value) {
// TODO: implement this method.
}
public void add(int value) {
}
public void add(int index, int value) {
// TODO: implement this method.
}
public void remove(int index) {
// TODO: implement this method.
}
public void remove(int value) {
}
}


ArrayList Implementation - Get
public class ArrayList{
public int get(int index) {
return data[index];
}
}


ArrayList Implementation - Get
public class ArrayList{
public int get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
// throw Exception
}
return data[index];
}
}


ArrayList Implementation - Set
public class ArrayList{
public void set(int index, int value) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
// throw Exception
}
data[index] = value;
}
}


ArrayList Implementation - Add
public class ArrayList{
public void add(int index, int value) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
// throw Exception
}
size++;
for (int i = size-1; i >= index+1; i--) {
data[i] = data[i-1];
}
data[index] = value;
}
}


ArrayList Implementation - Add
public class ArrayList{
public void add(int index, int value) {
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
// throw Exception
}
if (size == capacity) {
resize();
}
size++;
for (int i = size-1; i >= index+1; i--) {
data[i] = data[i-1];
}
data[index] = value;
}
private void resize() {
capacity *= 2;
int[] new_data = new int[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
new_data[i] = data[i];
}
data = new_data;
}
}


ArrayList Implementation - Remove
public class ArrayList{
public void remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
// throw Exception
}
size--;
for (int i = index; i < size; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
}
}


very very very important!!!
ArrayList实现 - Keys
- 数据的存储(storage), data[]
- 初始化时指定容量(capacity)
- 始终进行边界检查(Check Bound)
- Resize



课后作业



两数之和(Two Sum) - follow up
在一个(没有重复数字)的整数数组中, 找出两个数字, 使得它们的和等于给定的数字.
函数twoSum返回两个数字使得它们的和等于给定的数字, 其中第1个数字小于第2个数字.
假定每组输入都只有唯一解.
Java:
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> twoSum(int[] nums, int target);
C++:
vector<vector<int>> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target);



课后作业(Optional)



基础班 02 Array & ArrayList CN
By ZhiTongGuiGu
基础班 02 Array & ArrayList CN
Array & ArrayList, Charlie
- 326



