HashMap

Map and Set are most important data structures we use in development
There are multiple different maps and sets that are in Java
Traverse a HashMap
# 使用迭代器
iterator = map.items().__iter__()
while True:
try:
entry = iterator.__next__()
print("Key: " + entry[0] + " Value:" + entry[1])
except StopIteration:
break
# 更加优雅的方式
for key, value in map.items():
print("Key: " + key + " Value: " + value)
# 也可以使用键迭代
for key in map.keys():
print("Key: " + key + " Value: " + map[key])Hashing
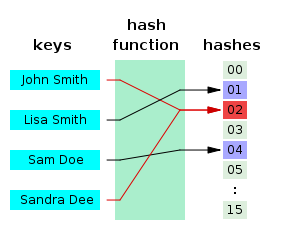
collision
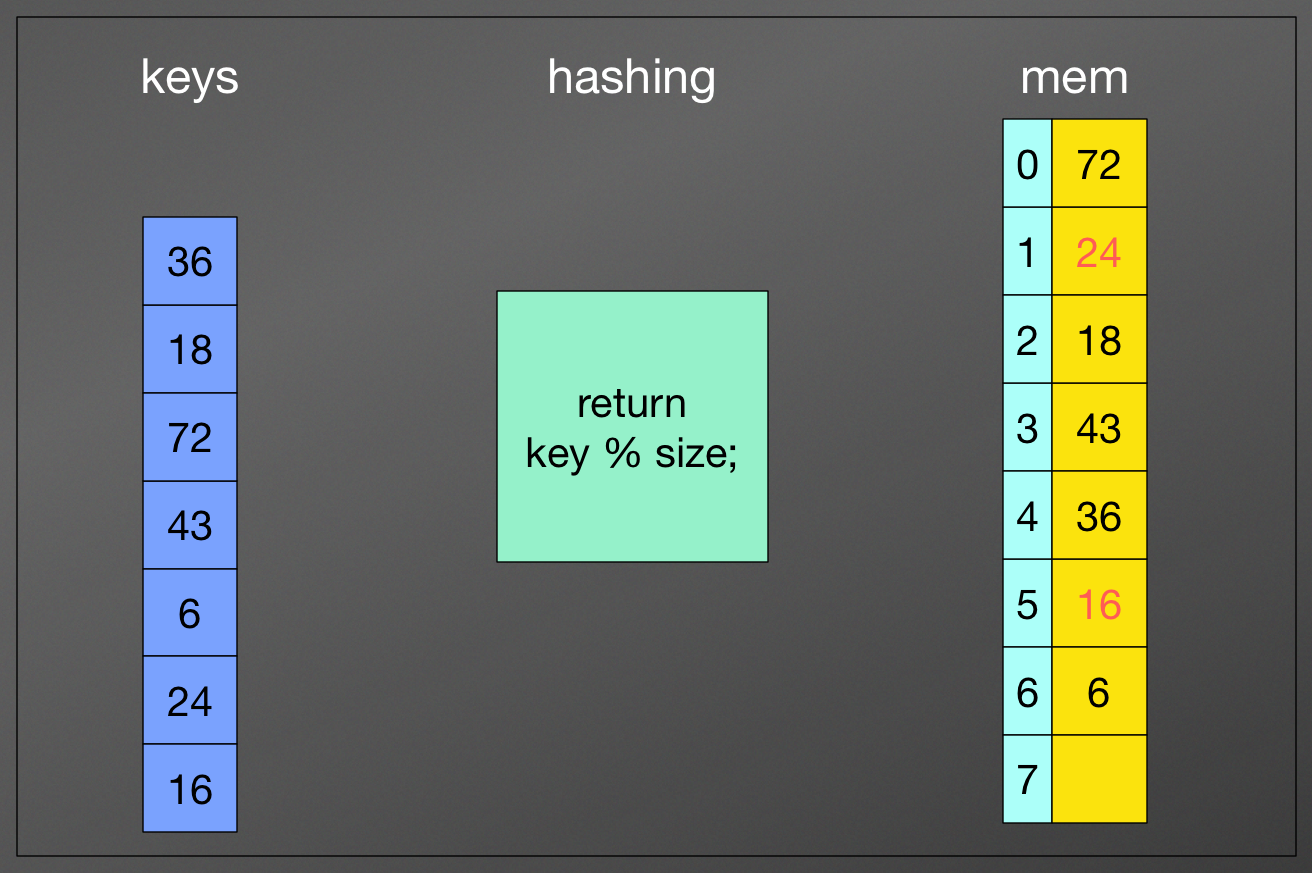
Hash Function
a function that can take a key and compute an integer (or an index in a table) for it
What really matters: How could we find a hash function that could fast compute the index without collisions
Collision
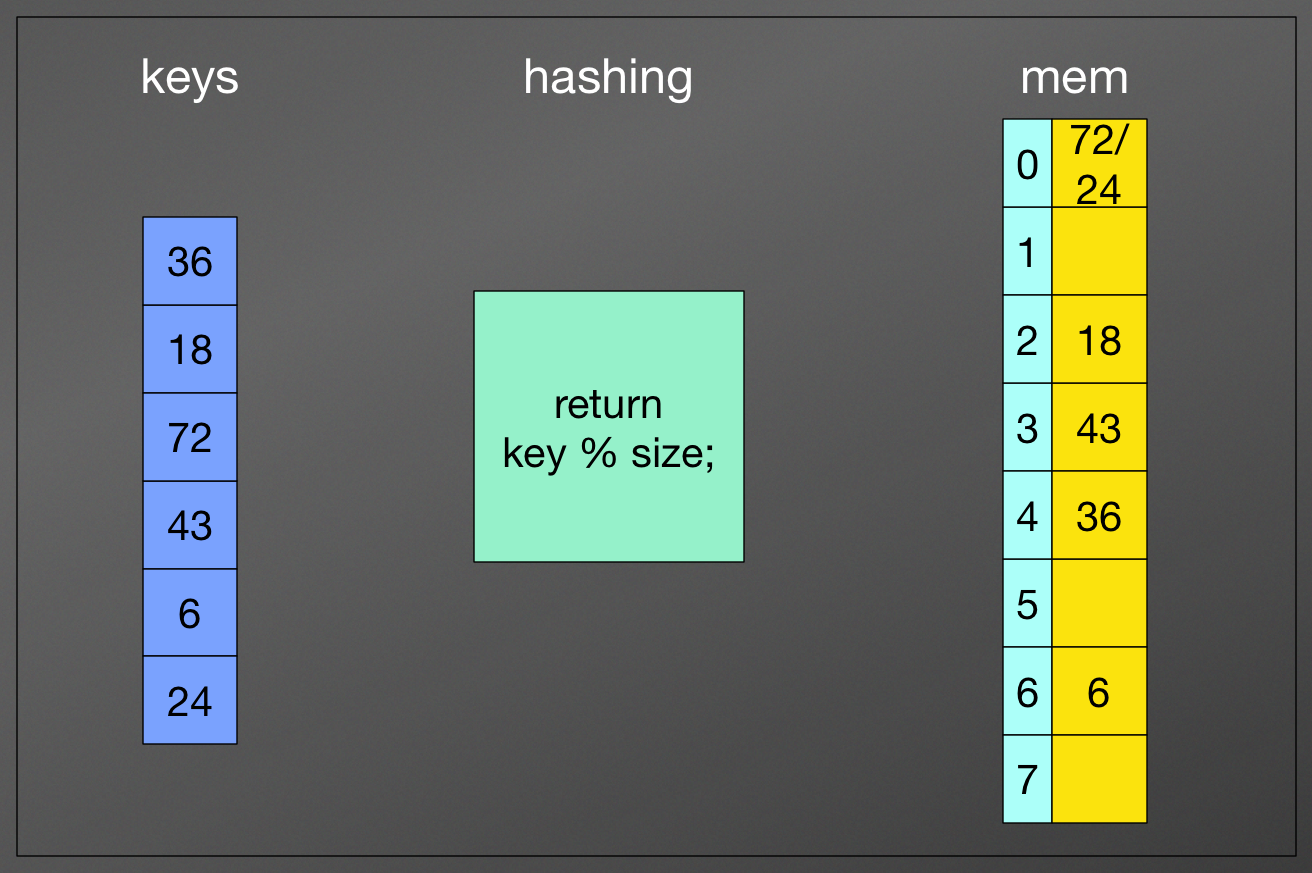
Collision
No matter which function, you are using, you have to deal with collision
reason that there is collision:
- some keys just happen to map to the same index
- keys > slots
Collision
How to solve them:
- We cannot, just try to find a better algo
- Open hashing
- Closed hashing
- Expand the space (Load Factor)
Load factor: size/capacity
Normally if (LF > 0.75), we double the space.
Collision
Open hashing:
for each collision, we use a linked list to store them
Closed hashing:
we store them in somewhere else in the table
Open hashing
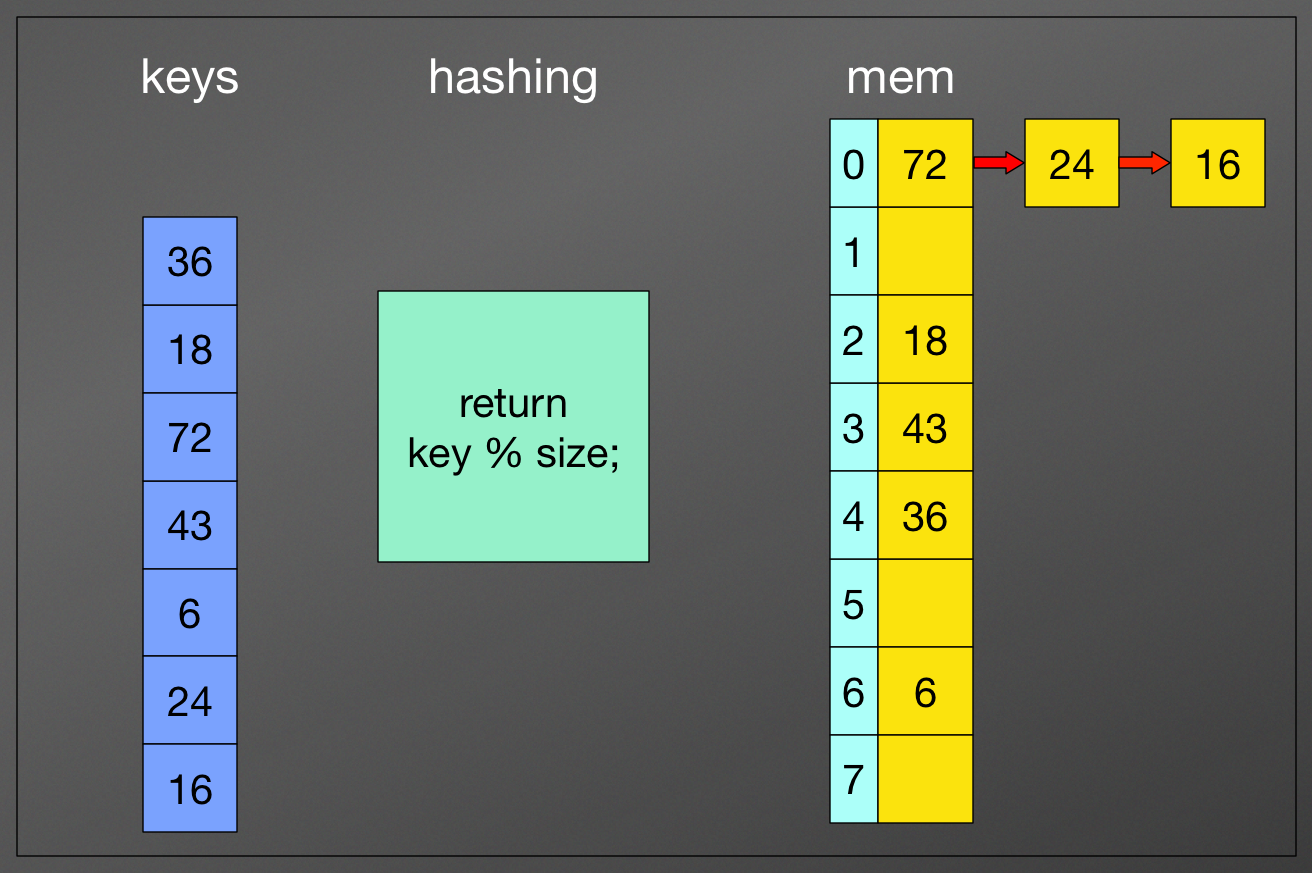
Closed hashing
Hash Function Key Points
- Hash function is not random, given the same key, you can always find the corresponding hashing value.
- Easy and quick to compute.
- Distribution as even as possible
Two Sum
Given an array of integers nums and an integer target, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
You can return the answer in any order.
Two Sum
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,7,11,15], target = 9
Output: [0,1]
Explanation: Because nums[0] + nums[1] == 9, we return [0, 1].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,4], target = 6
Output: [1,2]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [3,3], target = 6
Output: [0,1]
Two Sum
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
cache = {}
for i, x in enumerate(nums):
if target - x in cache:
return [cache[target - x], i]
cache[x] = i
# TC, SC:O(N)
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k, return the total number of subarrays whose sum equals to k.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,1], k = 2 Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], k = 3 Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000-107 <= k <= 107
Solution 1
Sum[end] - sum[start] = k
class Solution:
def subarraySum(self, nums, k):
count = 0
n = len(nums)
prefix_sum = [0] * (n + 1)
prefix_sum[0] = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
prefix_sum[i] = prefix_sum[i - 1] + nums[i - 1]
for start in range(n):
for end in range(start + 1, n + 1):
if prefix_sum[end] - prefix_sum[start] == k:
count += 1
return count
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
nums = [1, 2, 3]
k = 3
print(solution.subarraySum(nums, k)) # 输出:2Time & Space ?
Solution 2
HashMap:
key: sum
value: number of occurrences of sum
class Solution:
def subarraySum(self, nums, k):
count = 0
sum_val = 0
hashmap = {0: 1}
for num in nums:
sum_val += num
if sum_val - k in hashmap:
count += hashmap[sum_val - k]
hashmap[sum_val] = hashmap.get(sum_val, 0) + 1
return count
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
nums = [1, 2, 3]
k = 3
print(solution.subarraySum(nums, k)) # 输出:2Time & Space ?
Word Pattern II
Given a pattern and a string str, find if str follows the same pattern.
Here follow means a full match, such that there is a bijection between a letter in pattern and a non-empty substring in str.
Examples:
1. pattern = "abab", str = "redblueredblue" should return true.
2. pattern = "aaaa", str = "asdasdasdasd" should return true.
3. pattern = "aabb", str = "xyzabcxzyabc" should return false.
Word Pattern II
Example 1:
Input: pattern = "abab", s = "redblueredblue"
Output: true
Explanation: One possible mapping is as follows:
'a' -> "red", 'b' -> "blue"
Example 2:
Input: pattern = "aaaa", s = "asdasdasdasd"
Output: true
Explanation: One possible mapping is as follows:
'a' -> "asd"
Example 3:
Input: pattern = "aabb", s = "xyzabcxzyabc"
Output: false
Word Pattern II
So apart from using HashMap to store the words to Character mapping, we also need to know what the words are.
So besides HashMap, we need to use recursion to go through all the possible split cases to find right words for the Map.
Word Pattern II
def wordPatternMatch(pattern, str):
map = {}
set = set()
return isMatch(str, 0, pattern, 0, map, set)
def isMatch(str, i, pattern, j, map, set):
if i == len(str) and j == len(pattern):
return True
if i == len(str) or j == len(pattern):
return False
c = pattern[j]
if c in map:
s = map[c]
if not str.startswith(s, i):
return False
else:
return isMatch(str, i + len(s), pattern, j + 1, map, set)
for k in range(i, len(str)):
p = str[i:k + 1]
if p in set:
continue
map[c] = p
set.add(p)
if isMatch(str, k + 1, pattern, j + 1, map, set):
return True
map.pop(c, None)
set.remove(p)
return False
Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] Output: 9
Constraints:
0 <= nums.length <= 105-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
Solution 1: sorting
class Solution:
def longestConsecutive(self, nums):
if len(nums) == 0:
return 0
nums.sort()
cnt = 1
res = 1
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
if nums[i] - nums[i - 1] == 1:
cnt += 1
elif nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
continue
else:
res = max(res, cnt)
cnt = 1
res = max(res, cnt)
return res
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
nums = [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2]
print(solution.longestConsecutive(nums)) # 输出:4Time & Space?
Solution 2: HashSet
class Solution:
def longestConsecutive(self, nums):
num_set = set(nums)
longest_streak = 0
for num in num_set:
if num - 1 not in num_set:
current_num = num
current_streak = 1
while current_num + 1 in num_set:
current_num += 1
current_streak += 1
longest_streak = max(longest_streak, current_streak)
return longest_streak
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
nums = [100, 4, 200, 1, 3, 2]
print(solution.longestConsecutive(nums)) # 输出:4Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Examples:
Given "abcabcbb", the answer is "abc", which the length is 3.
Given "bbbbb", the answer is "b", with the length of 1.
Given "pwwkew", the answer is "wke", with the length of 3. Note that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring.
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Examples:
Given "abbcdefdgh", the answer is "bcdef", which the length is 5.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
a b b c d e f d g h
_ _ j _ _ _ i _ _ _
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
a b b c d e f d g h
_ _ _ _ _ j _ i _ _
// Sliding Window
// Two Pointersclass Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
result = 0
if not s:
return result
hm = {}
j = 0
for i, c in enumerate(s):
if c in hm:
# move j to next available position
j = max(j, hm[c] + 1)
hm[c] = i
result = max(result, i - j + 1)
return result
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
s = "abcabcbb"
print(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s)) # 输出:3The idea of Hashing -> Array
AsciiCode -> hashcode
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
result = 0
cache = [0] * 256
j = 0
for i, c in enumerate(s):
if cache[ord(c)] > 0:
j = max(j, cache[ord(c)])
cache[ord(c)] = i + 1
result = max(result, i - j + 1)
return result
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
s = "abcabcbb"
print(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s)) # 输出:3class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s):
result = 0
cache = [0] * 256
j = 0
for i in range(len(s)):
j = max(j, cache[ord(s[i])])
cache[ord(s[i])] = i + 1
result = max(result, i - j + 1)
return result
# 测试示例
solution = Solution()
s = "abcabcbb"
print(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring(s)) # 输出:3Given a string S and a string T, find the minimum window in S which will contain all the characters in T in complexity O(n).
For example,
S = "ADOBECODEBANC"
T = "ABC"
Minimum window is "BANC".
Minimum Window Substring
S
t
S'
End pointer:
keep including characters to find a feasible substring
Minimum Window Substring
S
t
S'
Start pointer:
keep excluding characters to make the feasible substring shorter
from collections import Counter
class Solution:
def minWindow(self, s: str, t: str) -> str:
l, r = 0, 0
counts = Counter(t)
required_chars = len(t)
formed_chars = 0
ans = [-1, len(s)]
m = len(s)
while r < m:
# Add the right character to the window
char_r = s[r]
if char_r in counts:
counts[char_r] -= 1
if counts[char_r] >= 0:
formed_chars += 1
# Try to contract the window till it's no longer valid
while formed_chars == required_chars:
# Update the answer if this window is smaller
if (ans[1] - ans[0]) > r - l:
ans = [l, r]
# Remove the left character from the window
char_l = s[l]
if char_l in counts:
counts[char_l] += 1
if counts[char_l] > 0:
formed_chars -= 1
l += 1
r += 1
# Return the minimum window or an empty string if not found
return "" if ans[0] == -1 else s[ans[0]: ans[1] + 1]Word Break II
Given a string s and a dictionary of strings wordDict, add spaces in s to construct a sentence where each word is a valid dictionary word. Return all such possible sentences in any order.
Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.
Example 1:
Input: s = "catsanddog", wordDict = ["cat","cats","and","sand","dog"] Output: ["cats and dog","cat sand dog"]
Word Break II
DFS + hash map
def wordBreak(self, s: str, wordDict: List[str]) -> List[str]:
wordSet = set(wordDict)
cache = {}
def dfs(s, wordSet, cache):
if not s:
return []
if s in cache:
return cache[s]
ans = []
if s in wordSet:
ans.append(s)
for i in range(len(s)):
pre = s[:i]
if pre in wordSet:
rest = dfs(s[i:], wordSet, cache)
for x in rest:
ans.append(pre + " " + x)
cache[s] = ans
return ans
return dfs(s, wordSet, cache)
Python [GoValley-Jo]Hashmap 7
By ZhiTongGuiGu
Python [GoValley-Jo]Hashmap 7
- 54



