Blockchain Technolgy & Decentralized Finance Part 1
Instructors: Andreas Park & Zissis Poulos
Rotman – MBA


5-minute version:
What is a blockchain?
blockchain=
an infrastructure for digital resource transfers


5-minute version:
What is a cryptocurrency?
cryptocurrency =
internal payment mechanism to pay for operation of a blockchain

5-minute version:
What is Decentralized Finance?
decentralized finance =
provision of financial services without the necessary involvement of a traditional financial intermediary based on blockchain technology
Why should you care?
Verbal Overview: Origins of Financial Institutions
- Money
- Safekeeping
- Deposit certificates and lending
- Trade facilitation & finance
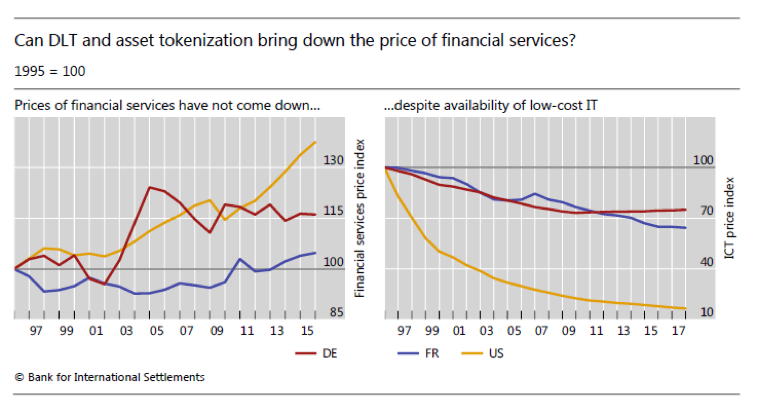
in practice: new financial infrastructure that will be a common resource

payments
stocks, bonds, and options
swaps, CDS, MBS, CDOs
insurance contracts

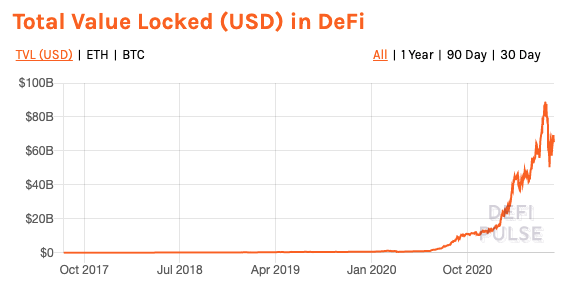
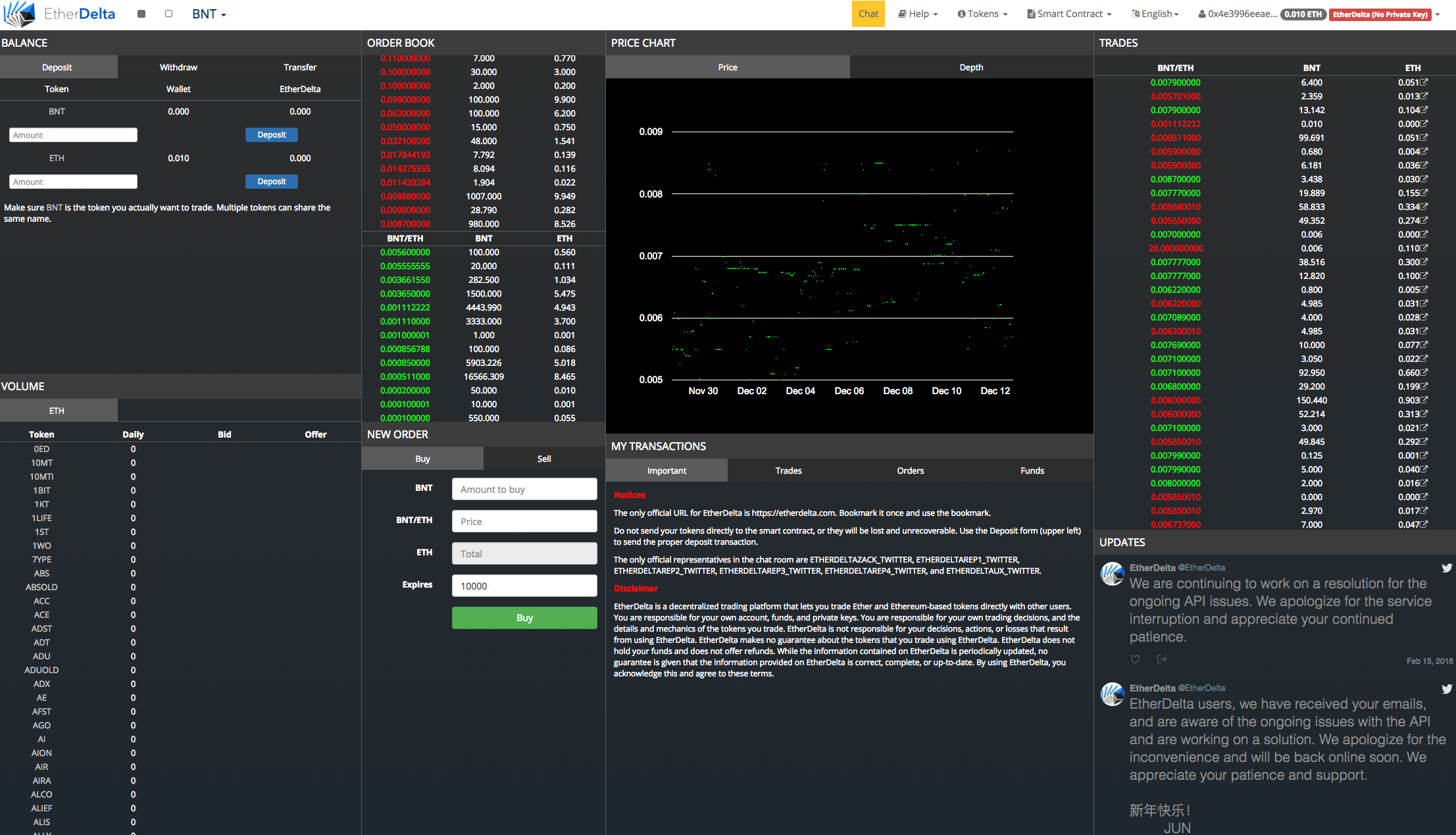
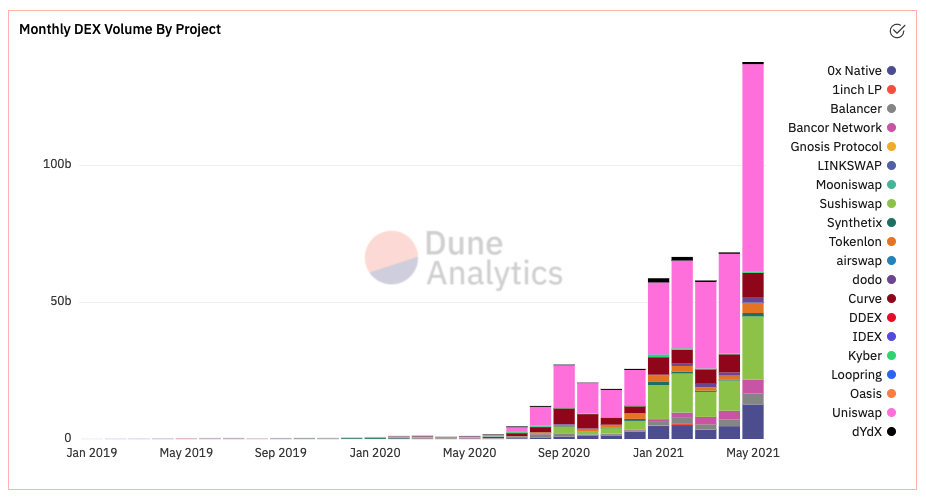
Application: decentralized trading












Application: Decentralized Lending















\(\vdots\)
dapp-linking, Defi-Legos and flash loans
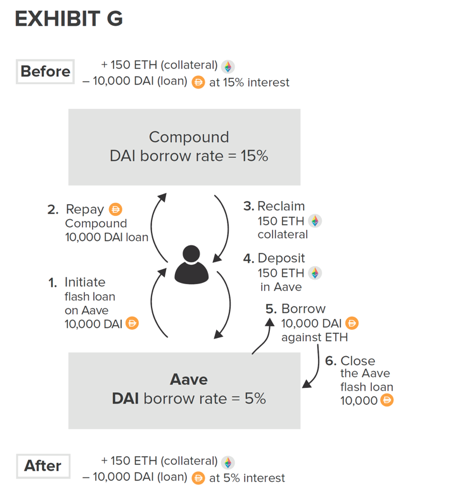
Source: Harvey, Ramachandran, and Santoro (2020)

quick comparison
FinTech vs. Defi
FinTech
DeFi
- more user-friendly UX
- more customer-oriented
- less squeezing/rent-extraction
- more competive services
- more innovative services
- currently: horribly user-unfriendly
- "blowing up the banks"
- fundamental re-thinking of financial services
- lots of scams, cowboy-attitude towards laws
innovation vs. salesmanship
main focus
Silos vs Common Infrastructures

Illustration of Infrastructure Frictions: money transfers

Version 1: They use the same bank
Change ledger entry locally

Version 2: They use different banks but the banks have a direct relationship
Sue's bank transfers from Sue's account to Bob's bank's account
Bob's bank transfers from its account to Bob's account

Version 3: They use different banks that have no direct relationship
Sue's bank transfers from Sue's account to its own account
Bob's bank transfers from its account to Bob's account
Central Bank
Central bank transfers from Sue's bank's account to Bob's bank's account

International transfers
Sue's bank transfers from Sue's account to its own account
Bob's bank transfers from its account to Bob's account

use the Swift network of correspondent banks

Bottom Line

very complex
many parties
lots of frictions and points of failure
very expensive
Crazy thought: Wouldn't it be nice if there was a single ledger?



Existing solutions
Problem:
power concentration/Monopoly

Distributed Ledger/Blockchain Technology
- A "joint, single system"
- Features:
- secure storage of information and transfer of value
- guaranteed execution of code
- Promise
- open platform
- global reach
- frictionless finance

How does it all work and why?
How do we establish trust in commerce?
trustworthy People
long-term Relationships
reputation
contract law





institutions
What's needed for trust in anonymous deals?
Authority
Execution
Continuity

Authority
Do you have the item?
Do you have power over it?
Tool: "key" cryptography

Execution
Can we agree that it happened?
Tool:
consensus algorithm

Security and Continuity
Are the records immutable?
restricted permissions
really difficult to hack

premise of blockchain
no trusted parties needed
everything
in code
open to
anyone
platform or network
commerce thrives
How?



@financeUTM
andreas.park@rotman.utoronto.ca

slides.com/ap248
sites.google.com/site/parkandreas/
youtube.com/user/andreaspark2812/
Copy of Topic 1: Introduction to Decentralized Finance
By zpoulos
Copy of Topic 1: Introduction to Decentralized Finance
This is the slide deck that I use for a quick introduction to the Decentralized Finance class.
- 529



