Recurrent Neural Network
By INFOR 28th 李睦樂、洪啟勳、王冠人
What is
Machine Learning?
What is Machine Learning?
- getting computer to learning
- mimic human brain learn

How can Machine Learning do?
- speech recognition
- email anti-spam
- handwriting recognition
- Natural Language Process(NLP)
- Computer Vision
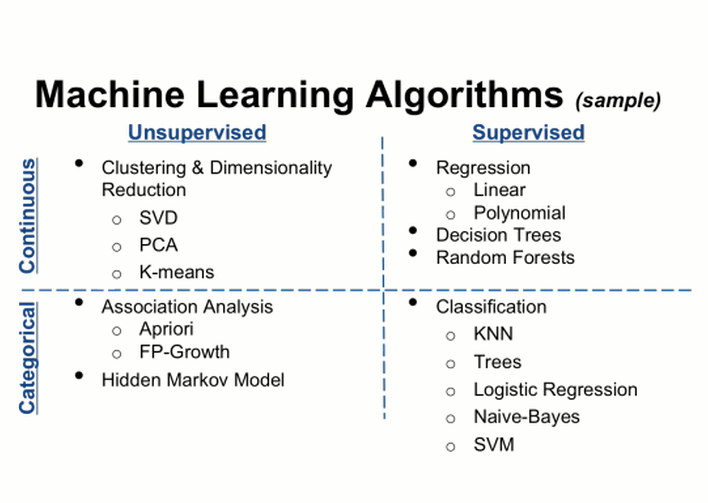
Basic Machine Learning Categories
- Supervised Learning
- Unsupervised Learning
Supervised Learning
We give the algorithm a data set in which the "right answers" were given, which means in supervised learning the examples must be labeled.
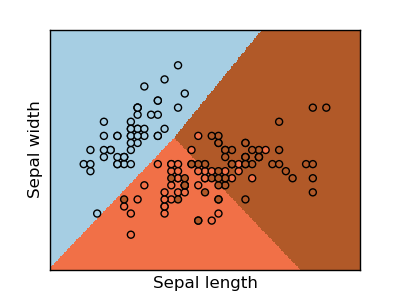
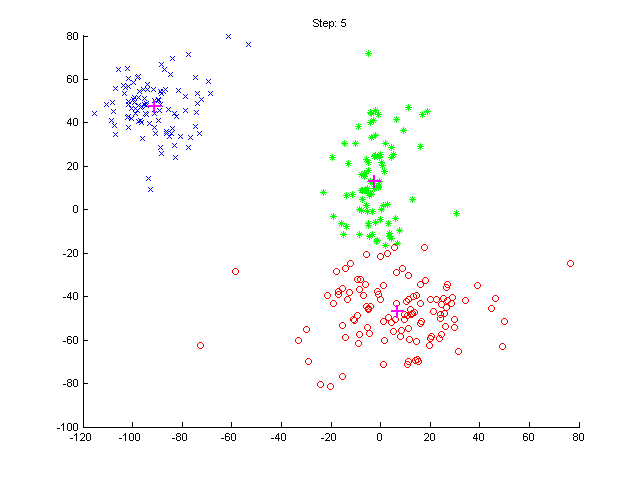
Unsupervised Learning
In unsupervised learning the examples are not labeled. That is, you don't say anything. And the algorithm will cluster the data into different group.
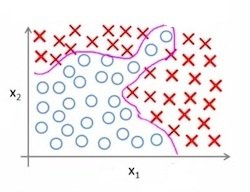
Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
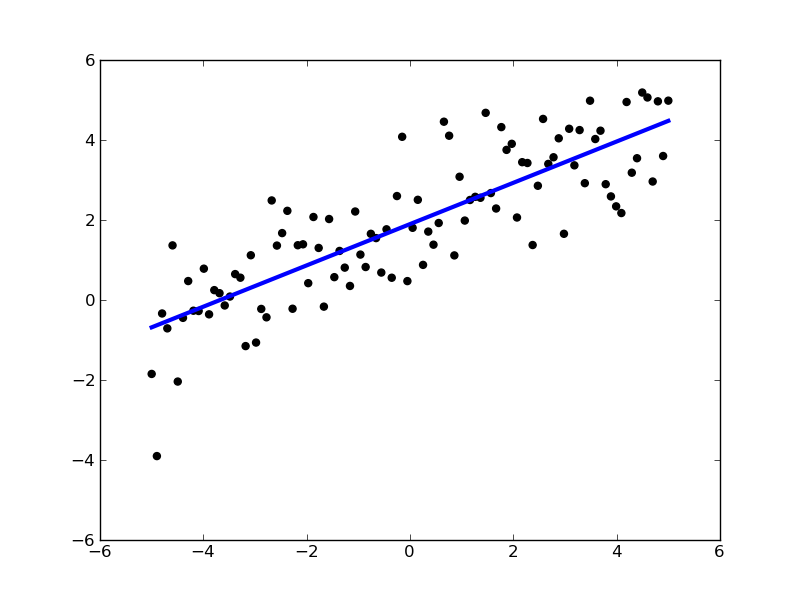
Regression Analysis
- Linear regression
- Least squares
- cost function
- minimize
- Logistic regression
- Sigmoid function
- cost function
- minimize

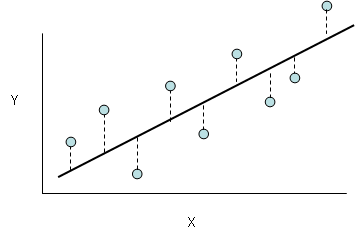
Linear Regression
Linear Regression predicts a real-valued output based on an input value. For example, predict the housing price prediction

Least Squares
Least Squares means that overall solution minimizes the sum of the square of the errors made in the result of every single equation.
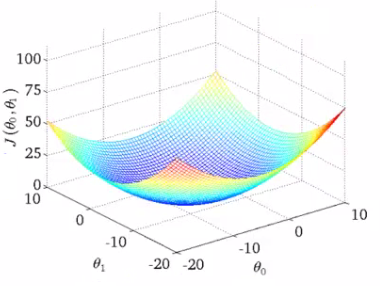
Cost Function
A cost function (or loss function) that maps events or values of one or more variables onto a real number intuitively representing some "cost" associated the event. Optimize problem seeks to minimize a cost function.
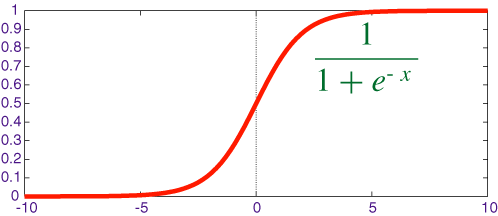
Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is a method for classifying data discrete outcomes. We would like our classifier to output value that between 0 and 1. So the hypothesis we use is "logistic function" (sigmoid function).


Minimize--
Gradient Descent
We keep change parameters to reduce cost function. Until we end up at minimum. So we can find the best line to our data.
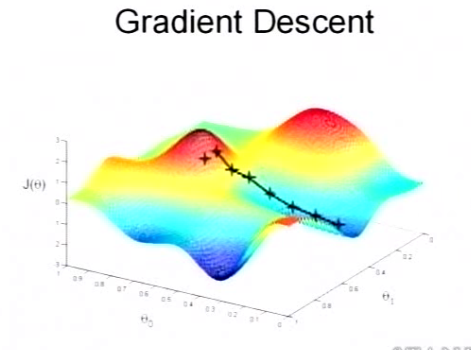
repeat until convergence {
}
Neural Network
Non-linear Hypothesis
When doing classification, sometimes we have to fit a more sophisticated hypothesis, and neural network provides a great idea of how to do that.
How Brains Work
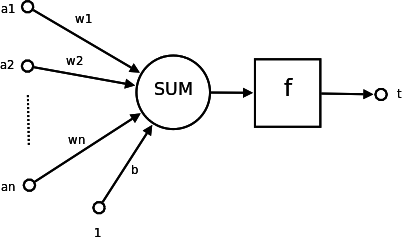
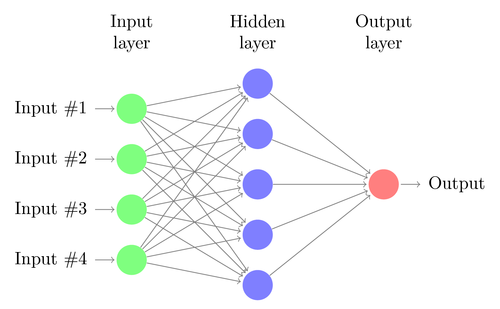
The Model
- Multi-layer
- Neurons
- Connected Architecture
Recurrent Neural Network
- Sequence Learning
- speech recognition
- handwriting recognition
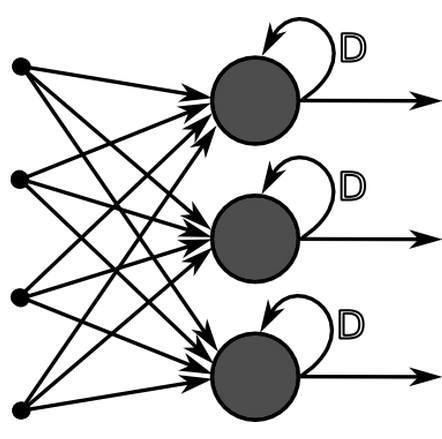
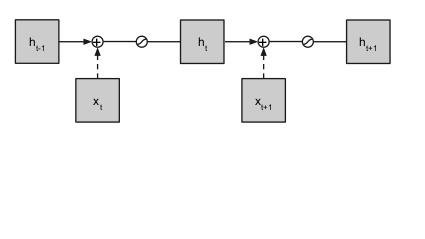
A Simple RNN

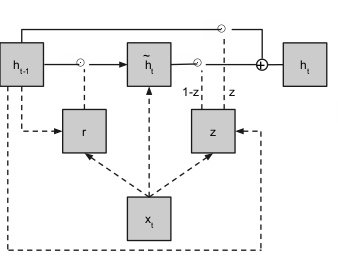
Gated Recurrent Unit
- gates:
r: scales input to cell
z: scales output from cell
Theano
- Python
- Machine Learning
- GPU
Define a function in a mathematical way.
import theano
from theano import tensor as T
X = T.scalar()
w = T.scalar()
y = X*w
power = theano.function(inputs=[X, w], outputs=y)Linear Regression
import theano
from theano import tensor as T
import numpy as np
X = T.scalar()
Y = T.scalar()
def model(X, w):
return X*w
w = theano.shared(np.asarray(0., dtype = theano.config.floatX))
y = model(X, w)
cost = T.mean(T.sqr(y - Y))
grad = T.grad(cost = cost, wrt = w)
updates = [[w, w - grad*0.01]]
train = theano.function(inputs = [X, Y], outputs = cost, updates = updates, allow_input_downcast = True)
predict = theano.function(inputs = [X], outputs = pred_y, allow_input_downcast = True)Logistic Regression
import os
def floatX(X):
return np.asarray(X, dtype = theano.config.floatX)
def init_weights(shape):
return theano.shared(floatX(np.random.randn(*shape)*0.01))
def model(x, w):
return T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(x, w))
X = T.fmatrix()
Y = T.fmatrix()
w = init_weights((784, 10))
py_x = model(X, w)
pred_y = T.argmax(py_x, axis = 1)#find the maximum
cost = T.mean(T.nnet.categorical_crossentropy(py_x, Y))
grad = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=w)
updates = [[w, w - grad*0.05]] #update weights
train = theano.function(inputs = [X, Y], outputs = cost, updates = updates, allow_input_downcast = True)
predict = theano.function(inputs = [X], outputs = pred_y, allow_input_downcast = True)Neural Network
from foxhound.utils.vis import grayscale_grid_vis, unit_scale
from scipy.misc import imsave
def floatX(X):
return np.asarray(X, dtype = theano.config.floatX)
def init_weights(shape):
return theano.shared(floatX(np.random.randn(*shape)*0.01))
def model(x, w):
return T.nnet.softmax(T.dot(x, w))
X = T.fmatrix()
Y = T.fmatrix()
w = init_weights((784, 10))
py_x = model(X, w)
pred_y = T.argmax(py_x, axis = 1)#find the maximum
cost = T.mean(T.nnet.categorical_crossentropy(py_x, Y))
grad = T.grad(cost=cost, wrt=w)
updates = [[w, w - grad*0.05]] #update weights
train = theano.function(inputs = [X, Y], outputs = cost, updates = updates, allow_input_downcast = True)
predict = theano.function(inputs = [X], outputs = pred_y, allow_input_downcast = True)Recurrent Neural Network
class GRU(object):
def __init__(self, n_u, n_h):
self.n_u = int(n_u)
self.n_h = int(n_h)
# W_xz : n_h x n_u
# W_hz : n_h x n_h
# W_xr : n_h x n_u
# W_hr : n_h x n_h
# W_xh : n_h x n_h
# W_hh : n_h x n_h
#
# b_z : n_h x 1
# b_r : n_h x 1
# b_h : n_h x 1
# Update gate weights
self.W_xz = theano.shared(value = np.asarray(
np.random.uniform(
size = (n_h, n_u),
low = -.01, high = .01),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'W_xz')
self.W_hz = theano.shared(value = np.asarray(
np.random.uniform(
size = (n_h, n_h),
low = -.01, high = .01),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'W_hz')
# Reset gate weights
self.W_xr = theano.shared(value = np.asarray(
np.random.uniform(
size = (n_h, n_u),
low = -.01, high = .01),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'W_xr')
self.W_hr = theano.shared(value = np.asarray(
np.random.uniform(
size = (n_h, n_h),
low = -.01, high = .01),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'W_hr')
# Other weights :-)
self.W_xh = theano.shared(value = np.asarray(
np.random.uniform(
size = (n_h, n_u),
low = -.01, high = .01),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'W_xh')
self.W_hh = theano.shared(value = np.asarray(
np.random.uniform(
size = (n_h, n_h),
low = -.01, high = .01),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'W_hh')
# Update gate bias
self.b_z = theano.shared(value = np.zeros(
(n_h, ),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'b_z')
# Reset gate bias
self.b_r = theano.shared(value = np.zeros(
(n_h, ),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'b_r')
# Hidden layer bias
self.b_h = theano.shared(value = np.zeros(
(n_h, ),
dtype = theano.config.floatX),
name = 'b_h')
self.params = [self.W_xz, self.W_hz, self.W_xr, self.W_hr,
self.W_xh, self.W_hh, self.b_z, self.b_r,
self.b_h]
def gru_as_activation_function(self, x_t, h_tm1):
# update gate
z_t = T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(self.W_xz, x_t) + \
T.dot(self.W_hz, h_tm1) + \
self.b_z)
# reset gate
r_t = T.nnet.sigmoid(T.dot(self.W_xr, x_t) + \
T.dot(self.W_hr, h_tm1) + \
self.b_r)
# candidate h_t
can_h_t = T.tanh(T.dot(self.W_xh, x_t) + \
r_t * T.dot(self.W_hh, h_tm1) + \
self.b_h)
# h_t
h_t = (1 - z_t) * h_tm1 + z_t * can_h_t
return h_tReference
-
K-Means clustering http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/cmp/courses/recognition/Labs/kmeans/index_en.html
-
Supervised learning: predicting an output variable from high-dimensional observations http://gaelvaroquaux.github.io/scikit-learn-tutorial/supervised_learning.html -
Supervised vs unsupervised learning https://medium.com/@RobinCRLee/supervised-vs-unsupervised-learning-36d5106c7b0b
Thanks for listening
Recurrent Neural Network 20150531
By a136489
Recurrent Neural Network 20150531
INFOR 27x28 Presentation, Recurrent Neural Network
- 1,337



