Managing Kubernetes with Rancher
KSS CON'19
Adam Płaczek
Problem solving history
- Virtual machines solved problems with hardware- one OS running on one HW
- Containers solved developers problems with Virtual Machines- light image, slow boot, big OS overhead, portability ....
- Orchestrators solved operations problems with containers- managing multiple Docker Engines and application lifetime.
- Kubernetes platforms solved everyones problems with orchestrators- Difficult deployment and management
Container app development

Deployment and testing done on a laptop
No worries about HA
No worries about deployment
No worries about scaling up
Why containers need orchestration ?
Provisioning and deployment of multiple containers
Ensuring containers availability
Scaling up or down
Load Balancing
Service Discovery
Secrets management
Health monitoring
Allocation of resources between containers
External exposure of services to the outside world
...............

Container Orchestrators
Kubernetes ( aka K8s )
Docker swarm
Mesos + Marathon
Nomad

Kubernetes vs Nomad
Out of the box K8s provides collection of collaborating services which provide full container orchestration functionality.
Widely adopted -all major cloud vendors provide managed K8s clusters GKE, EKS, AKS
Nomad focus is workload scheduling and cluster management without additional stuff like Service Discovery, Secret Management etc.
Managed k8s comparision

KUBECTL
command line too to interact with K8 cluster
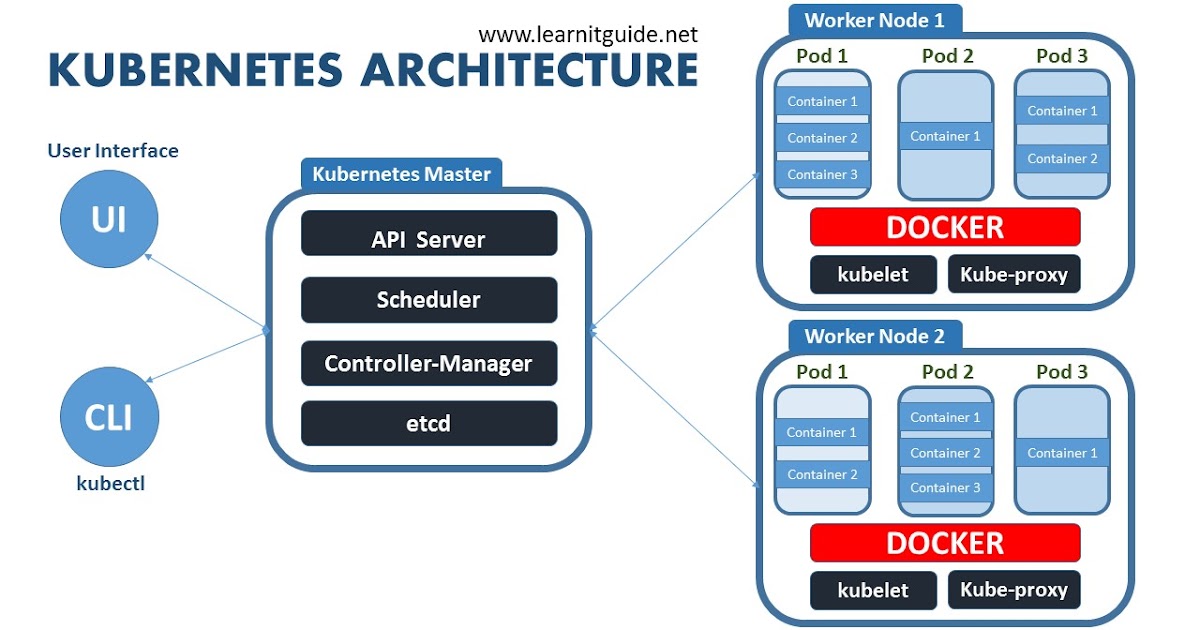
Concepts
- Pod- smallest deployable unit
- Service- DNS entry grouping multiple pods
- Deployment- Create and update multiple pods


Deployment
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: super-saiyan-app-1.0
spec:
replicas: 2
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: super-saiyan-app
version: "1.0"
spec:
containers:
- name: super-saiyan-app
image: brudnyhenry/super-saiyan-app:v1
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 8080kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
Service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: super-saiyan-app
labels:
name: super-saiyan-app
spec:
ports:
- name: http
protocol: "TCP"
port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
selector:
name: super-saiyan-app
version: "1.10"
type: LoadBalancerkubectl apply -f service.yamlkubectl expose deployment super-saiyan-app --type=LoadBalancer --name=my-service

Port Forward
kubectl port-forward deployment/demoapp 8080:8080
curl localhost:8080Access your deployments without exposing them to external network
https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/access-application-cluster/port-forward-access-application-cluster/

Rancher
multi-cluster Kubernetes manager
- One level of abstraction above Kubernetes
- User friendly UI
- Well tested app catalog
- Authentication across multiple clusters
- Connect to existing K8s or create new cluster with RKE


Rancher
Run Rancher locally
docker run -p 80:80 -p 443:443 -v /opt/rancher:/var/lib/rancher rancher/rancher:latest
Try Kubernetes locally
https://k3s.io/
Demo
Create Kubernetes cluster in AWS EC2
Deploy custom app
Upgrade
Create Rancher server AWS EC2
App Monitoring
Rancher and Kubernetes
By Adam Płaczek
Rancher and Kubernetes
Presentation about how Kubernetes clusters can be managed with Rancher
- 331
