Test
Software Development
Questions
Adam Lass
We have looked at some static analysis tools like StyleCop, PMD, FindBugs and SonarLint. Explain how static analysis can improve code quality. Explain how it helped you or could have helped you in your project.
1.1
-
StyleCop, PMD, FindBugs
-
Linters, SonarLint
-
Security
Static analysis
In General
Framework best practices analysis
Code styling analysis
Security linting
Error detection
UML Diagram creation
Duplicate Code Detection
Complexity Analysis
Secret detection
Comment styling analysis
Unused code detection
Tools
Linting
Code Style
Security
ESLint
Javascript & Typescript
sonarlint
Java, Javascript, PHP, Python & more
StyleCop
C# (.NET)
Checkstyle
Java
Pylint
Python
PEP8
Python
Bandit
Python
FindBugs (SpotBugs)
Java
(sonarcloud)
PMD
Python
(Bad practices)
Example
npx eslint --initESLint
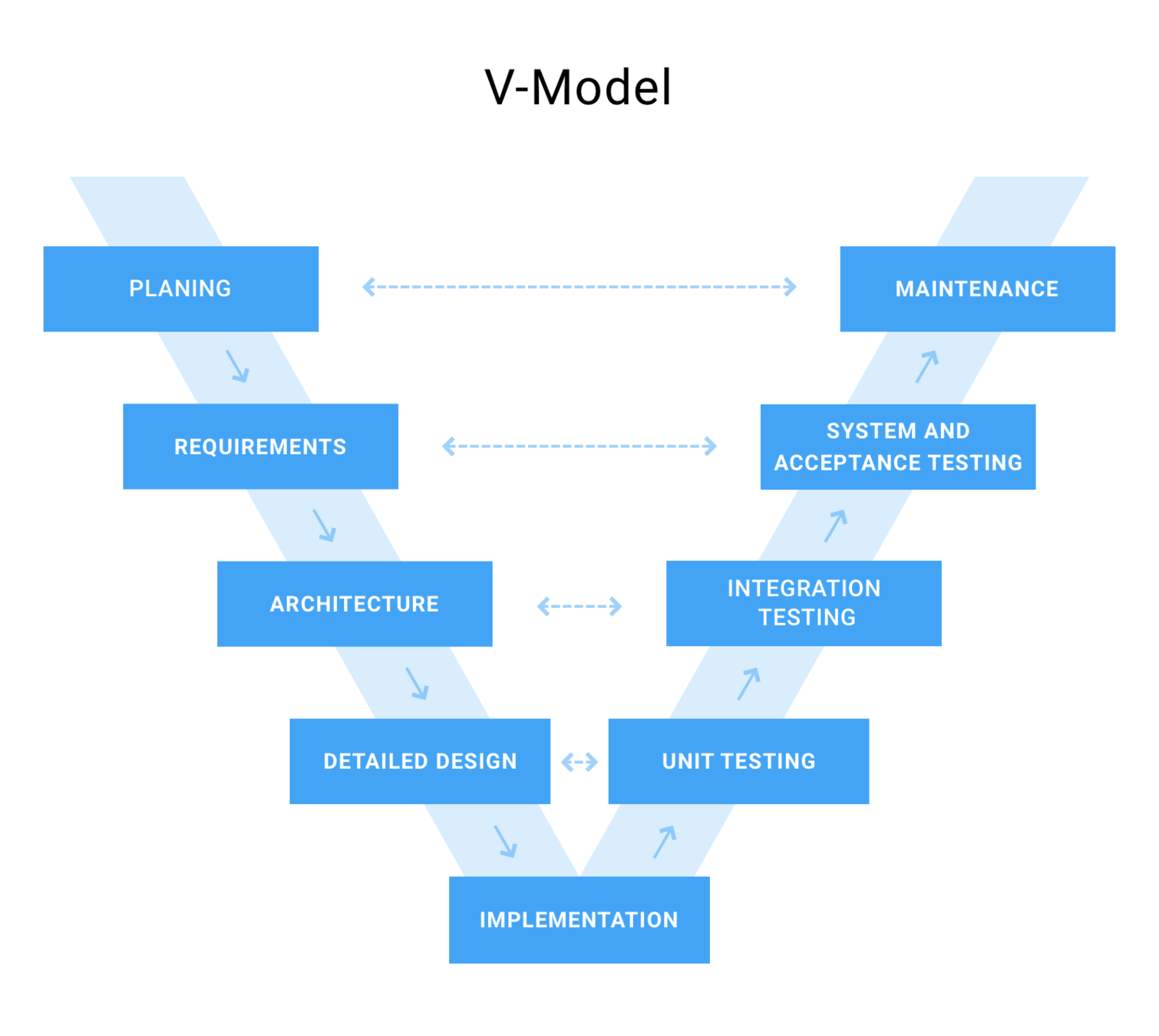
npx eslint .Explain test levels, and what characterizes the individual levels. Then, relate to your own project.
1.2
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- Load testing
- Static testing
- Acceptance testing
Unit Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Types of testing
Explain what kinds of test can be carried out without running any code. Explain how it can be used on non-code documents as well.
1.3
- Reviews
- Technical reviews
- Management reviews
- Audit
- Static analysis
- Linters
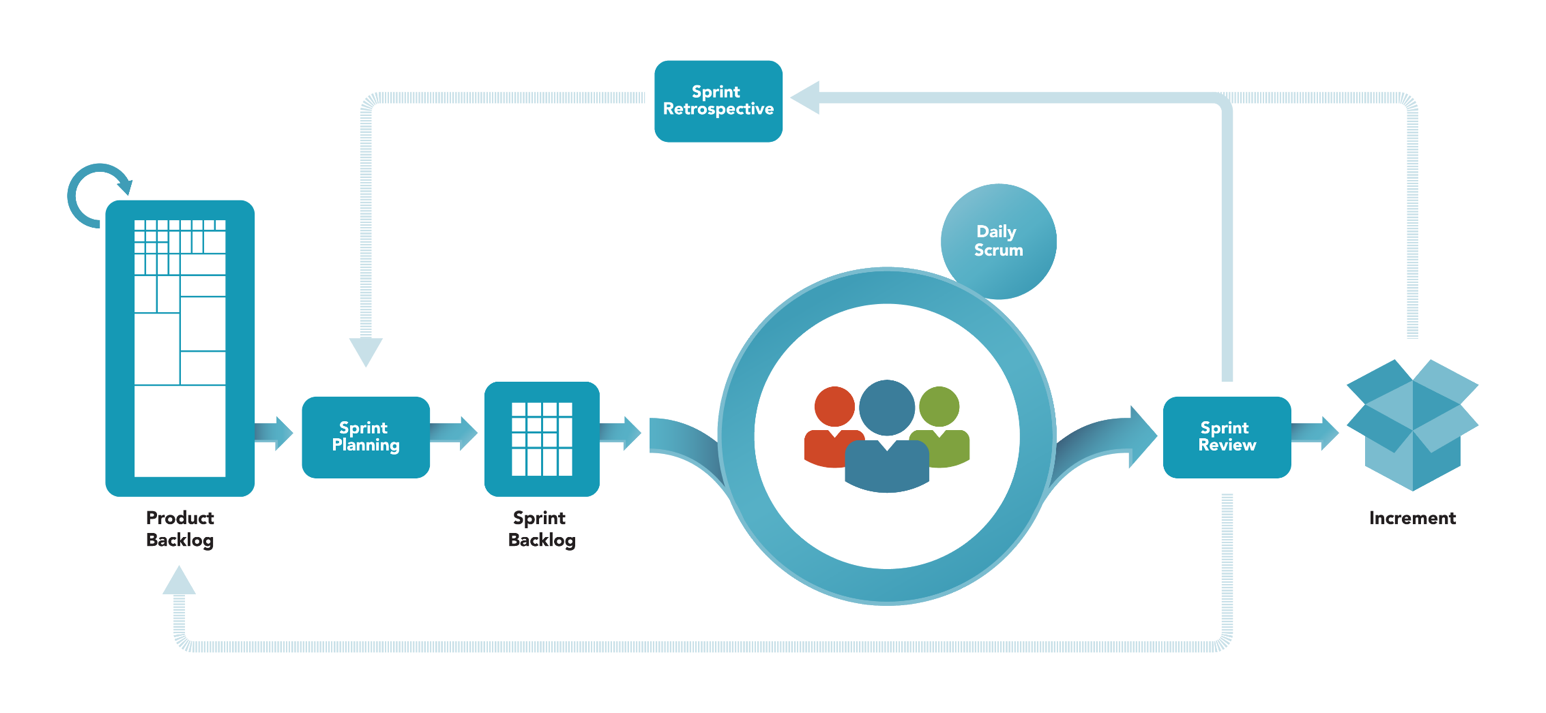
In the context of SCRUM
Example
npx eslint --initESLint
npx eslint .Explain test activities, and how they are related to each other. Then explain the test activities you carried out in your project.
1.4
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- Refactoring
- Maintenance
- Continuous Integration
- Code reviews
Unit Testing
Integration Testing
System Testing
Acceptance Testing
Types of testing

Testing is related to ensuring higher code quality. Elaborate on what characterizes high code quality, and what makes code testable.
1.5
- Testable code
- Names of tests
- “sufficient” tests of a method or class
- Assertions, defensive programming
- Dependency injection
Testable code
Single-responsibility principle
Open–closed principle
Liskov substitution principle
Interface segregation principle
Dependency injection principle
SOLID
Test design principles
test[ExpectedBehavior][StateUnderTest]
Naming
testGetAccountOnCPRInvalidCPRLength
testTransferAmountIsNegative
testTransferNotExists
Examples
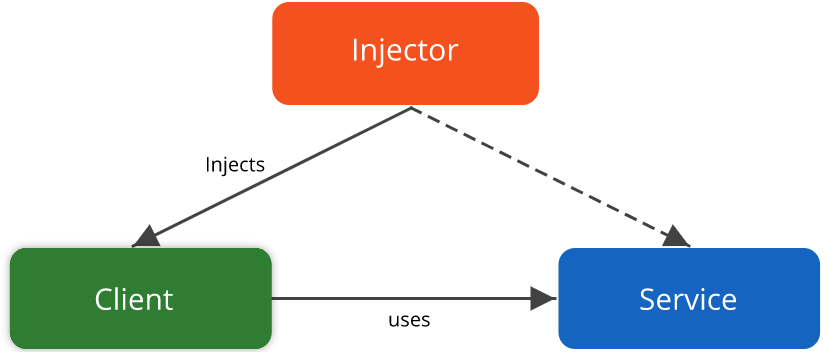
Dependency injection
Explain the concept of maintainable code, and how it’s related to test. Explain how to find out if a code base is maintainable.
1.6
- Maintainability
- Product quality
- Temporal coupling
- Continuous Integration
- Static Analysis
- Dependency injection, inversion of control
- Low coupling, high cohesion
- Cyclomatic code complexity
Temporal Coupling
Component A
Component B
Component C
Cyclomatic code complexity
if-then-else
do-until
while
for
M = E – N + 2P
Testable code
Single-responsibility principle
Open–closed principle
Liskov substitution principle
Interface segregation principle
Dependency injection principle
SOLID
Test design principles
Explain unit testing, and what characterizes it in contrast to other types of test.
1.7
- What and why
- Unit Under Test _ System Under Test_
- Unit test lifecycle(BeforeAll, AfterAll _ SetUp, TearDown)_
- Test doubles (mock, fake, stub, spy)
- Matchers(Hamcrest)
- Test Driven Development
- Dependency Injection
- Equivalence classes, boundary value analysis, equivalence partitions
Matchers
assert_that(x, equal_to(y))
assert_that(x, is_not(equal_to(y)))Example
Unit test lifecycle
Example
Explain test driven development, and how it affects the development process and code quality.
1.8
- Red, Green, Refactor
- Testable code
- Maintainable code
- Equivalence partitions
- Positive, negative tests
Testable code
Single-responsibility principle
Open–closed principle
Liskov substitution principle
Interface segregation principle
Dependency injection principle
SOLID
Test design principles
Explain about test doubles. Explain how and why mocking is useful, and in what test areas.
1.9
- JMock, mocks, spies, stubs, fakes, dummies
- Dependency injection
- Interfaces, contracts
- Black-box vs white-box

Characterize high quality software. Explain how writing tests can increase code quality.
1.10
- Defensive programming
- Black-box development
- Interfaces, contracts
- Inversion of control
- Dependency injection
- Components
Testable code
Single-responsibility principle
Open–closed principle
Liskov substitution principle
Interface segregation principle
Dependency injection principle
SOLID
Test design principles
test[ExpectedBehavior][StateUnderTest]
Naming
testGetAccountOnCPRInvalidCPRLength
testTransferAmountIsNegative
testTransferNotExists
Examples
Contract Testing
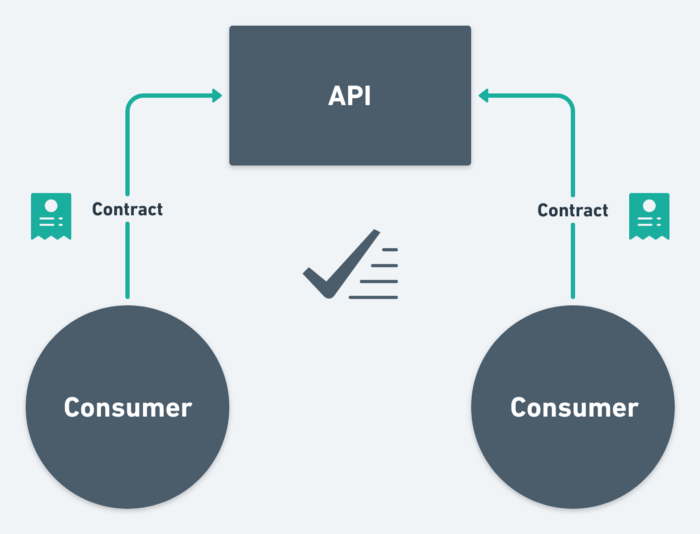

Dependency injection
Elaborate on dependencies in software, and how it’s related to the subject of test.
1.11
- Dependencies between layers
- System resources
- Relations between objects
- Dependency inversion, Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection
- Mocks
Explain problems in test automation, and how a continuous integration tool can help.
1.12
- What is Continuous Integration?
- How can a CI help regarding tests?
- What is a regression?
- What test levels can be covered by a CI system?
Explain specification-based testing, and how you can be more confident that you have written a sufficient amount of tests.
1.13
- Equivalence partitioning
- Boundary value analysis
- Edge cases
- Decision tables
- Code coverage
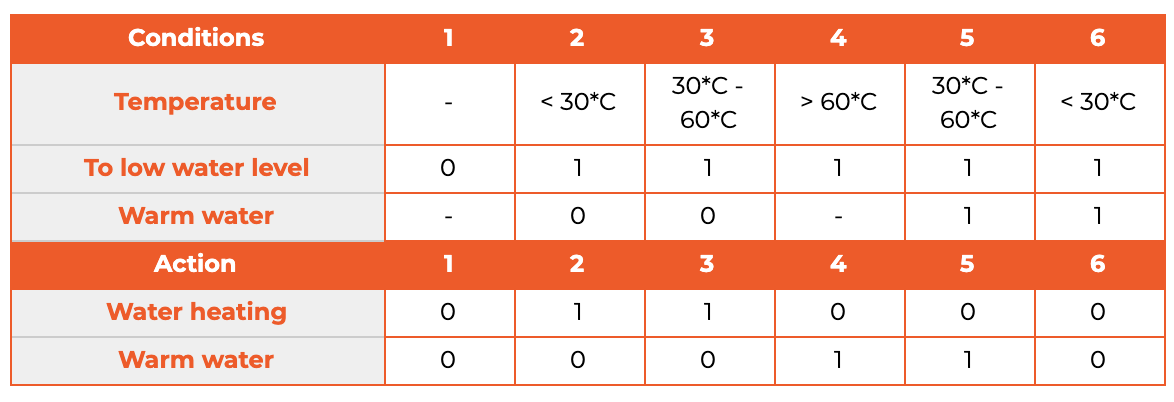
Decision Table
deck
By Adam Lass
deck
- 391



