{kubernetes}
Open source containerization orchestration

# What is Docker?
Docker allows us to package an application as an image which can then be distributed and deployed as needed
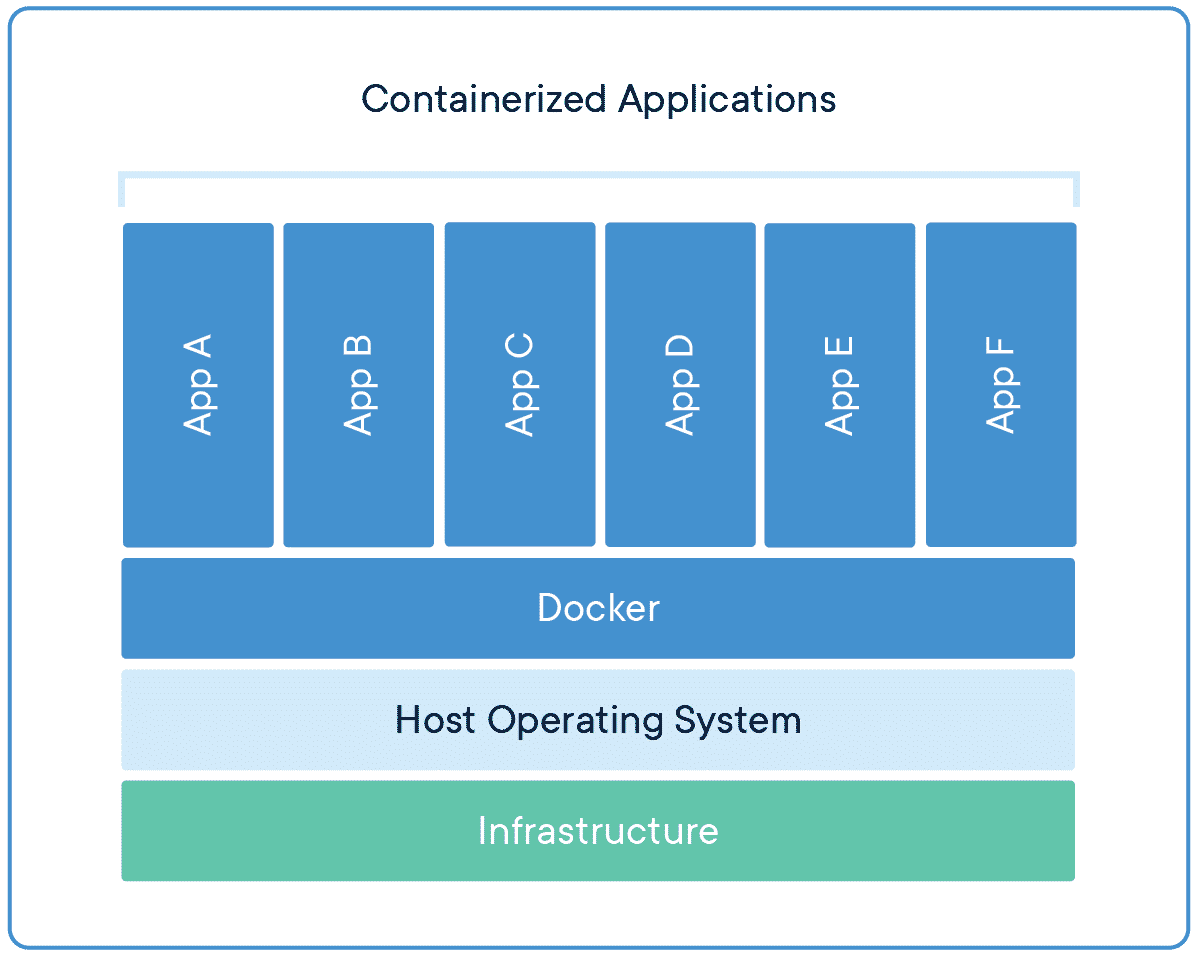
Previously...
# Service Orchestration?
Problem Statement
A containerized app needs
- Configuration
- Replication
- Secret management
- Load Balancing
- Service Discovery
- Other dependencies

X Number of instances
# What is Service orchestration
Service Orchestration
Service orchestration allows us to configure applications with automated configuration, deployments





# What is K8
Kubernetes
- Open source orchestration tool for containers
- Used for managing docker containers or any other supported container runtime
- Helps manage development which includes physical, cloud, hybrid environment
- This helps applications to have
- High Availability
- Scalability
- Disaster recovery

# K8 Components
K8 Components
- Node
- Pod
- Service
- Ingress
- ConfigMap
- Secret
- Volume
- Replication
# POD
Pod
- Pod is an abstraction over a container (dockerized)
- The smallest unit of K8
- Create an env on top of the container
- 1 pod -> 1 container
- Or 1 pod -> multiple with some side loaded
- Pod gets an IP address, its an internal address
- Pods are ephemeral
Pod
App

Pod
Database

Pod
App

Sideloaded apps
# NODE
Node
A worker machine that runs containerized workloads. This can be a VM or a bare metal machine
- Kubelet - agents that inform nodes on availability
- Kube Proxy - receives traffic
Node
Kubelet
Kube Proxy

Pod
App

Pod
Database

Pod
App

Sideloaded apps
# SERVICE
Service
- A permanent IP address that is attached to a POD
- Pod(s) can die, but the service and IP will live, so like having a static IP
- External service or Internal service

Pod
App

Pod
Database
Service (E)
Service (I)
# INGRESS
Ingress
Acts as a forwarder so you can have a DNS name attached to a service instead of a static IP Address. Can also perform load balancing

Pod
App
Service (E)
Ingress
# CONFIGMAP
ConfigMap
- Configuration for dependency service
- K8 pod uses the configmap to get information
- ConfigSet can contain URLs and other metadata
- Passwords is not recommended


Pod
App
Service (E)
Ingress

Pod
Database
Service (I)
ConfigMap
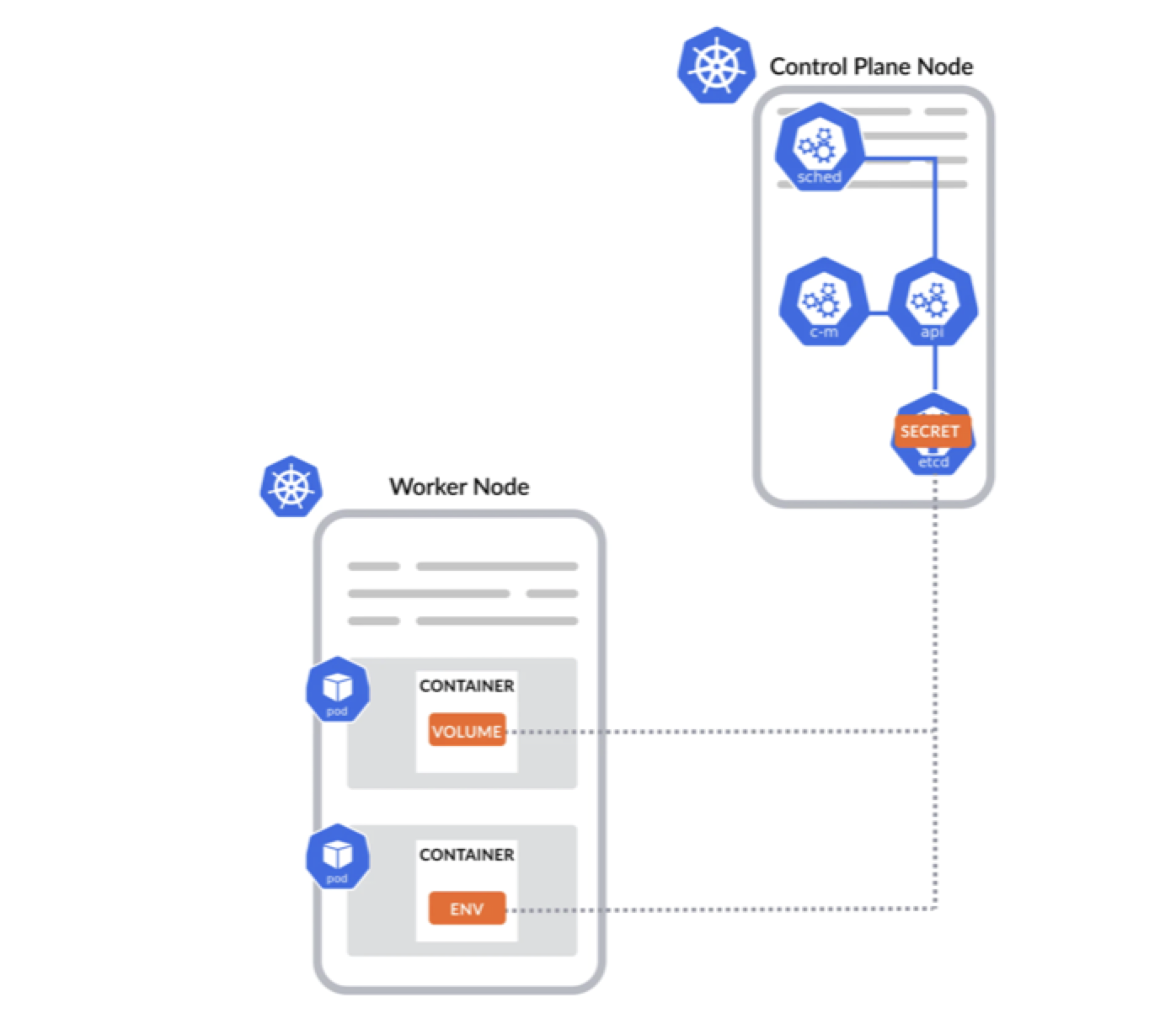
# SECRET MANAGEMENT
Secret Management
- Secrets is an object that is used to store sensitive information as unencrypted base64-encoded strings.
- Secrets can be mounted as a file on containers, made available as environment variables in the Pod, or retrieved when the image is pulled for the Pod.
- Secrets are stored on etcd which is a central key-value store for K8 cluster data
- It allows users to create one Secret that can then be referenced by any number of Pods.
- K8 secrets are static as they are generated in preparation for an application by users, not dynamically when the Pod initializes
# VOLUMES
Volumes
- Files in a container are transient in nature
- Loss of files when a container crashes or restarts
- Issues while sharing files between containers running together in a Pod.
-
Kubernetes volume abstraction solves the above problems.
- Kubernetes does not destroys persistent volumes
- Data is preserved across container restarts
-
Usage
- To use a volume, specify the volumes to provide for the Pod in .spec.volumes and declare where to mount those volumes into containers in .spec.containers[*].volumeMounts
- A process in a container sees a filesystem view composed from the initial contents of the container image.
- The process sees a root filesystem that initially matches the contents of the container image. Any writes to within that filesystem hierarchy, if allowed, affect what that process views when it performs a subsequent filesystem access.
- Volumes cannot mount within other volumes.
- Volume cannot contain a hard link to anything in a different volume
# REPLICATION
Replication
- ReplicationController makes sure that a pod or a homogeneous set of pods is always up and available.
- If there are too many pods —> ReplicationController terminates the extra pods.
- If there are too few pods —> ReplicationController starts more pods.
- Unlike manually created pods, the pods maintained by a ReplicationController are automatically replaced if they fail, are deleted, or are terminated.
- It supervises multiple pods across multiple nodes

# K8 Architecture
K8 Architecture
Node
Kubelet
Kube Proxy


Pod
Database
Pod

ConfigMap
Service (E)
Ingress
Service (I)
Control Plane
etcd
API server
👩🏽💻
Application
Ops

User

{demo}
Minikube with a single node cluster
Introduction to K8
By Ahmed Bhaila
Introduction to K8
- 35



