Arrays in
Ahmed Murtaza 😎
ahmedgmurtaza

ahmedgmurtaza

slides.com/ahmedmurtaza


codepen.io/ahmedgmurtaza
https://medium.com/@ahmedgmurtaza

It is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements, Each identified by at least one array index or key
Applications of Array
Array of Donuts

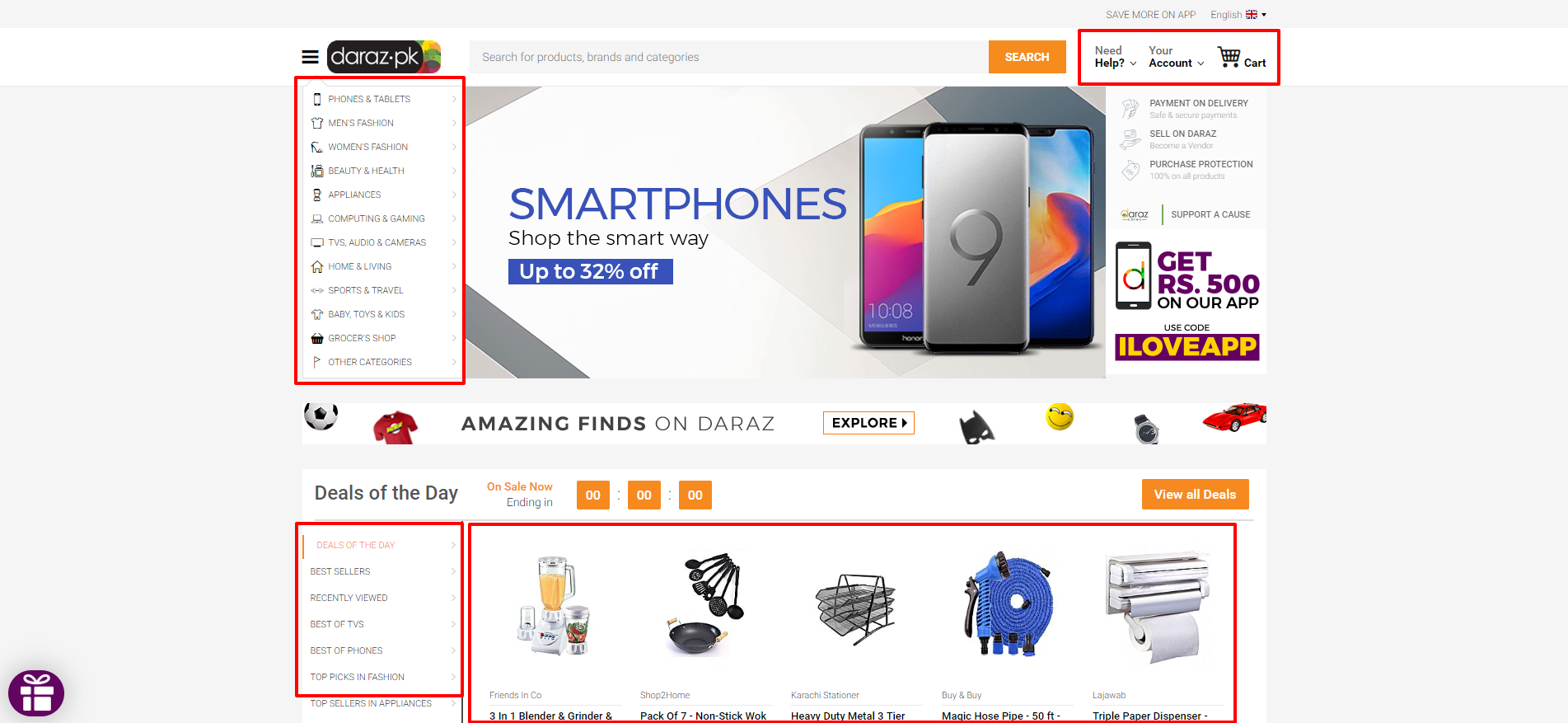
Array of links, icons and thumbnails
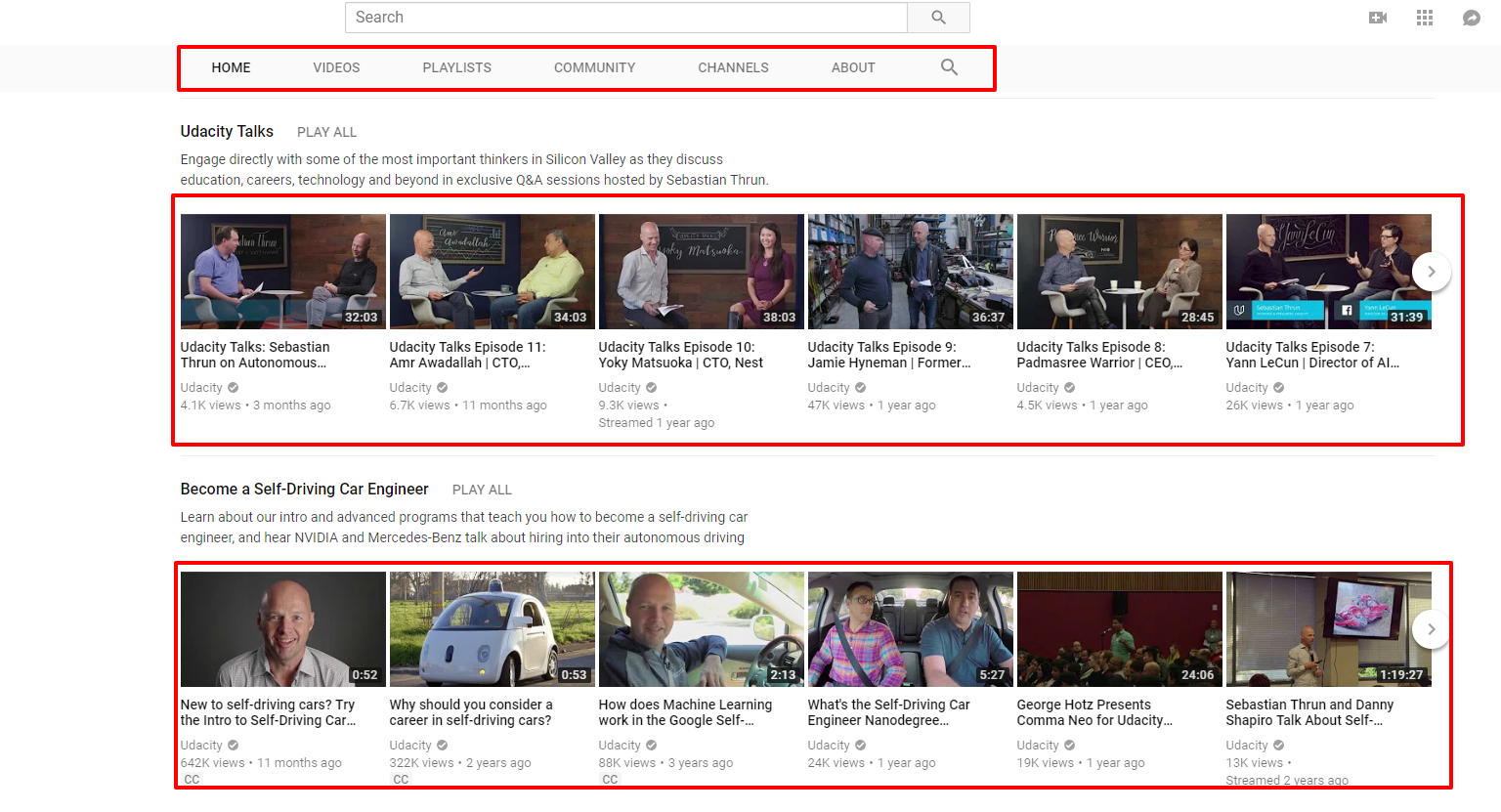
Array of links, icons and thumbnails
Declaration
let arr = new Array(1,2,3);
let arr = Array(1,2,3);
let arr = [1,2,3];In most languages, the elements of an array required to be of same type. JavaScript allows an array to contain any type of values:
var arr = [ 'string', 42.0, true, false, null,
undefined, ['sub', 'array'],
{object: true}, NaN
];Accessing & Assigning in Array
var arr = [27,"Karachi",true];
arr[0]; // 27var arr = [27,"Karachi",true];
arr[3] = 72;
arr; // [27, "Karachi", true, 72]
Accessing
Assigning
.length
var colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Yellow'];
console.log(colors.length); // 3
var arr = Array(10); // Creates an array
//with no element, but with arr.length set to 10
// The above code is equivalent to
var arr = [];
arr.length = 10;example
var colors = ['Red', 'Blue', 'Yellow'];
console.log(colors.length); // 3
colors.length = 2;
console.log(colors); // ["Red","Blue"] - Yellow has been removed
colors.length = 0;
console.log(colors); // [] the colors array is empty
colors.length = 3;
console.log(colors); // [undefined, undefined, undefined]Iterating Array values
let colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue'];
for (let i = 0; i < colors.length; i++) {
console.log(`Color is ${colors[i]}`);
}Array Built-in Methods
concat
pop
push
shift
unshift
.concat()
let myArray = new Array("33", "44", "55");
myArray = myArray.concat("3", "2", "1");
console.log(myArray); // ["33", "44", "55", "3", "2", "1"] The concat() method joins two arrays and returns a new array:
.pop()
let myArray = new Array("1", "2", "3");
let last = myArray.pop(); // "3"
myArray // ["1", "2"] The pop() method removes the last element from an array and returns that element
.push()
let myArray = new Array("1", "2");
myArray.push("3"); // 3
myArray // ["1", "2", "3"]The push() method adds elements to the end of an array and returns the resulting length of the array
.shift()
let myArray = new Array ("1", "2", "3");
let first = myArray.shift(); // "1"
myArray // ["2", "3"]The shift() method removes the first element from an array and returns that element
.unshift()
let myArray = new Array ("1", "2", "3");
myArray.unshift("4", "5"); // 5
myArray // ["4", "5", "1", "2", "3"] The unshift() add elements to the Front of an array and returns the new length of it
Thank You
ahmedgmurtaza

Array basics in JavaScript
By Ahmed Murtaza
Array basics in JavaScript
overview of Arrays in JavaScript, Array length and other properties, array applications, array methods: reverse, pop,push,shift, unshift, join.
- 345



