Service Workers
the gotchas in your path to production.
Hi, I'm Antoni
@GatMesquer
MrFrontend






Agenda
- Why is caching important ?
- Overview of cache technologies.
- HTTP cache best practices.
- Service Worker cache strategies.
"53% of mobile site visits are abandoned if pages take longer than 3 seconds to load."
- Alex Shellhammer, Double click
3s network round-trip on average 2G
(bit.ly/network-costs)
320ms to load 1MB
(bit.ly/network-costs)
"Used correctly, caching is a massive performance enhancement and bandwidth saver"
- Jake Archibald, dev advocate for Google Chrome
"Used correctly, caching is a massive performance enhancement and bandwidth saver"
- Jake Archibald, dev advocate for Google Chrome
The goal is to avoid requesting resources from the network as much as possible.
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
Browser built in mechanism
- Memory cache
- HTTP headers + HTTP cache
- HTTP/2 push cache
- ...
🏎 repeat visits
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
Optimized browser cache
Load resources before they are required
<link rel="import"...>
requestIdleCallback
<script src="~.js"... defer>
Some proactive page load improvements
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
Optimized browser cache
Content caching
Proactive page load improvements

IndexedDB
Structured Data
Cache Storage
URL addressable
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
Optimized browser cache
🚀 Service Workers + Cache Storage
Content caching
Full cache control
Proactive page load improvements
+ Offline available
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
🕗
🕗🕗
🕗🕗🕗🕗
Optimized browser cache
Content caching
Full cache control
0
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
🕗
Optimized browser cache
Content caching
Full cache control
0
Unpredictable
~ Content predictability
Fully predictable
🕗🕗
🕗🕗🕗🕗
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
🕗
Optimized browser cache
Content caching
Full cache control
0
Unpredictable
~ Content predictability
Fully predictable
Coarse granularity
~ Content granularity
Content granularity
🕗🕗
🕗🕗🕗🕗
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
🕗
Optimized browser cache
Content caching
Full cache control
0
Unpredictable
~ Content predictability
Fully predictable
Coarse granularity
~ Content granularity
Content granularity
Network response only
All response types
🕗🕗
🕗🕗🕗🕗
Spectrum of cache technologies:
Browser cache
🕗
Optimized browser cache
Content caching
Full cache control
0
Unpredictable
~ Content predictability
Fully predictable
Coarse granularity
~ Content granularity
Content granularity
Network response only
All response types
Best return on your time invested
🕗🕗
🕗🕗🕗🕗
How much space do we get ?
50 MB of persistent storage on all devices and browsers
chrome dev summit 2016

How reliable is it ?
chrome dev summit 2016

What is coming ?
chrome dev summit 2016

HTTP cache best practices
Pattern 1: Immutable content per URL
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable
The content for an specific URL never changes
- The browser, CDN,... can cache this resource for long time
- Cached content younger than max-age seconds can be used without consulting the server
- If the content changes you must update the url.
<script src="/script-v1.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/styles-Fs837mq1c.css">
<img src="/img/banner-02-01-2017.jpg" alt="…">Pattern 1: Immutable content per URL
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable
Use the immutable Cache-Control extension.
- The browser must find out which resources may change on page reload.
- For smaller objects, the work of this revalidation via a 304 HTTP response code can be almost as much work as just transferring the response fully !!!
Pattern 1: Immutable content per URL
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable
"This change effectively eliminated revalidation requests to us from up-to-date versions of Firefox which, in many cases, can improve load times by seconds"
- Nathan Schloss, Software Engineer, Facebook
Pattern 1: Immutable content per URL
- Does not work with often updated content with a fixed URL (blog posts, articles, ...)
Pattern 2: Mutable content must be server-revalidated
Cache-Control: no-cache
The content for an specific URL may change so it always must be revalidated with the server.
Pattern 2: Mutable content must be server-revalidated
Important notes:
| doesn't mean | it means | |
|---|---|---|
| no-cache | don't cache | must be revalidated with the server before using a cached version |
| no-store | can not be cached at all | |
| must-revalidate | must revalidate | the cached version can be used if it's younger than the provided max-age, otherwise revalidate |
Pattern 2: Mutable content must be server-revalidated
Important notes:
no-cache !== max-age=0
no-cache: the browser MUST revalidate with the server before using a cached copy.
max-age=0: the time of the cache expired so the browser SHOULD (but might not) revalidate with the server before using a cached copy.
Pattern 2: Mutable content must be server-revalidated
- Requires always a network fetch for each resource.
Combine pattern 1 and pattern 2
Remember:
- Changes into the HTML might have CSS and JS changes as a dependency
- Specific user information should be served with Cache-control: private
What's a Service Worker ?
- An event-driven web worker registered against an origin and a path.
- Can intercept and modify navigation and resource requests.
- Runs in a different thread, so not blocking.
- It is designed to be fully async.
- Access to IndexedDB.
What's a Service Worker ?
Remember:
- Works only over HTTPS.
- No access to DOM
- No access to synchronous (XHR, localStorage, ...)
- Not available on private mode browsing on Firefox
Your first Service Worker
Lifecycle events:
- install
- activate
- fetch
<script>
'use strict';
self.addEventListener('install', function(event) {
console.log('install');
});
self.addEventListener('activate', function(event) {
console.log('activate');
});
self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
console.log('fetch:', event.request.url);
});
</script>Your first Service Worker
Service Worker cache strategies
When to store resources ?
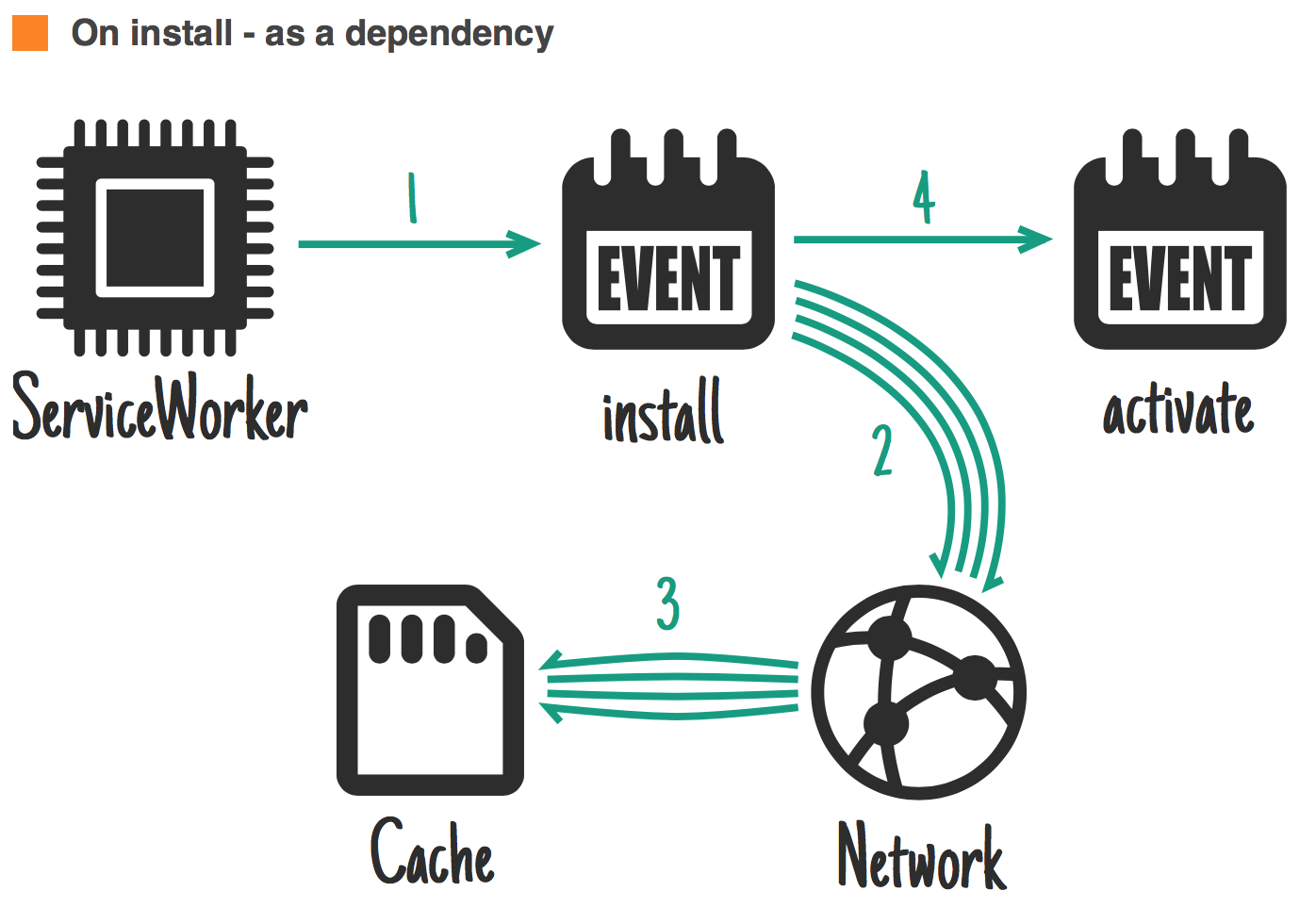
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: all the static files for this version.
When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: bigger resources that are not needed straight away.
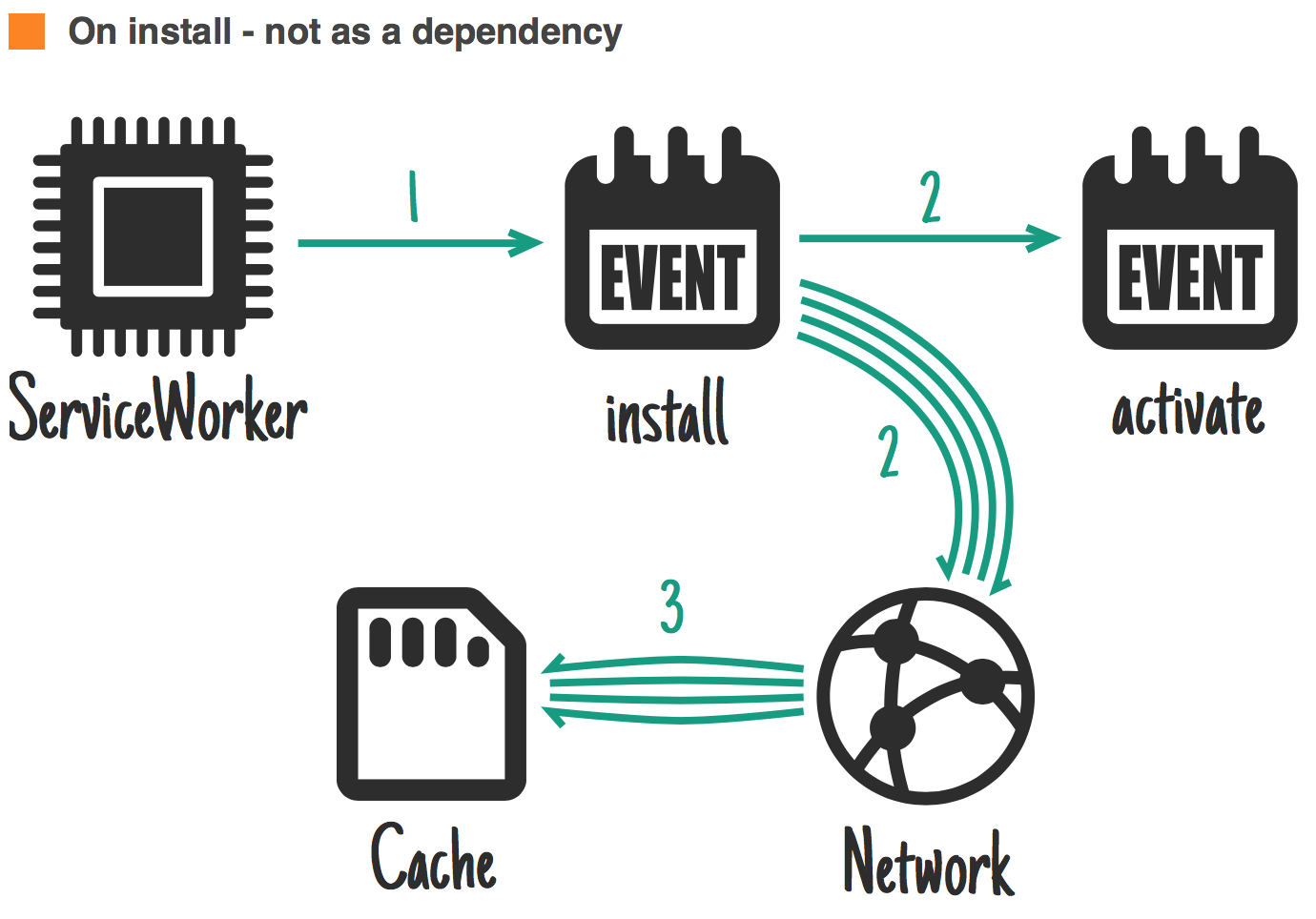
HTTP cache and Service Workers
Ideal for: not reloading from the network static assets.
Work together
Ideal for: want to be sure to fetch the most fresh data and we don't mind the network overload.
Cache busting in the Service Worker
let request = new Request(url, {cache: 'no-cache'});When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: Clean-up & migration.

"With great power comes great responsibility"
Nicolas Hoizey
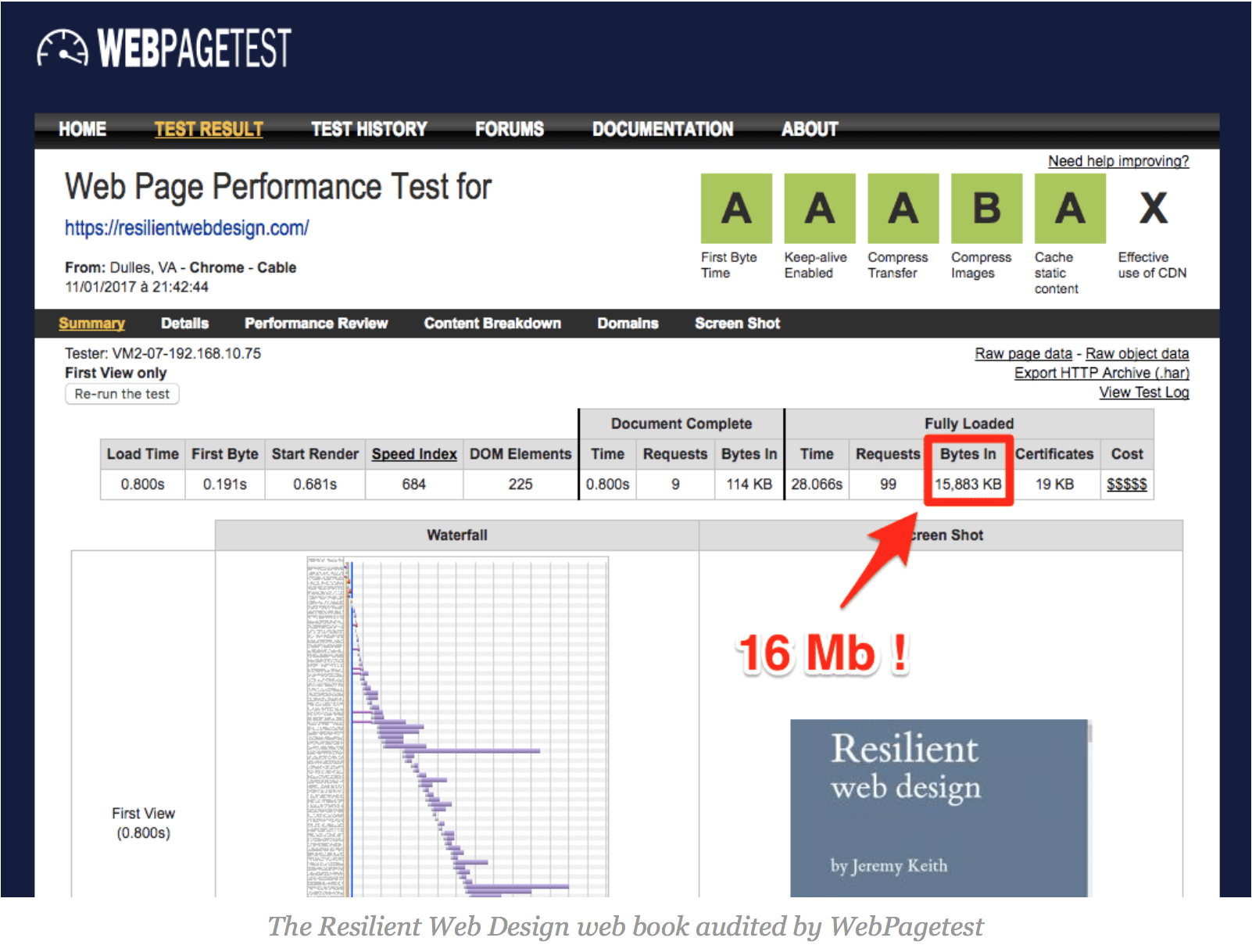
When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: let the user pick what should be available offline.
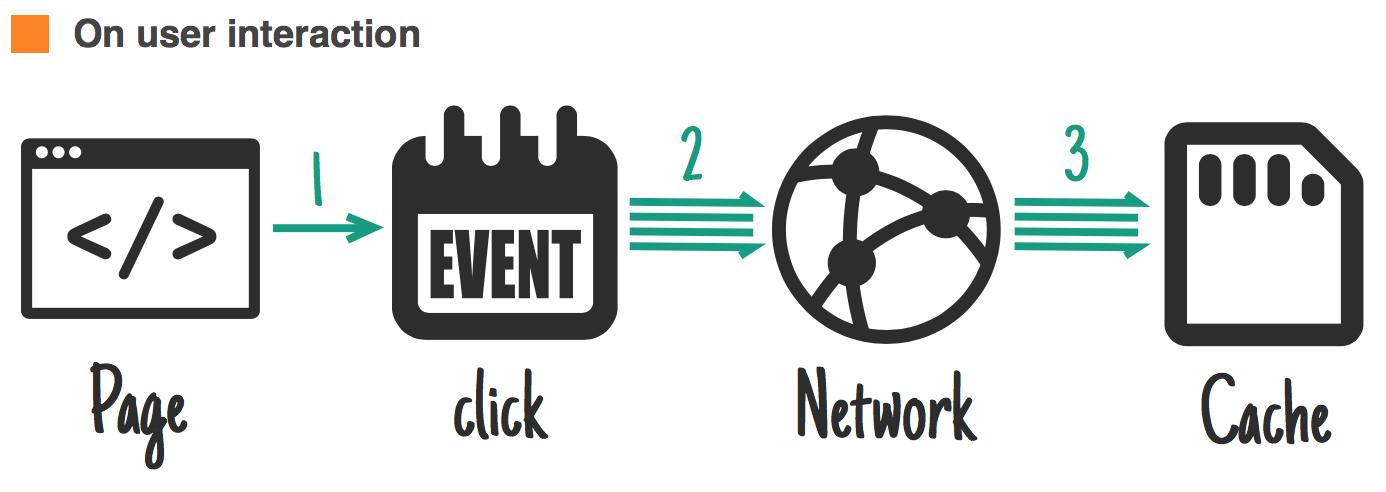
Share caches
Ideal for: reuse cached resources managed by someone else.

Is possible to share resources that were cached by another service worker or script.

When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: frequently updated resources.
When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: frequently updated resources.
<script>
self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.open('mysite-dynamic').then(function(cache) {
return cache.match(event.request).then(function (response) {
return response || fetch(event.request).then(function(response) {
cache.put(event.request, response.clone());
return response;
});
});
})
);
});
</script>When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
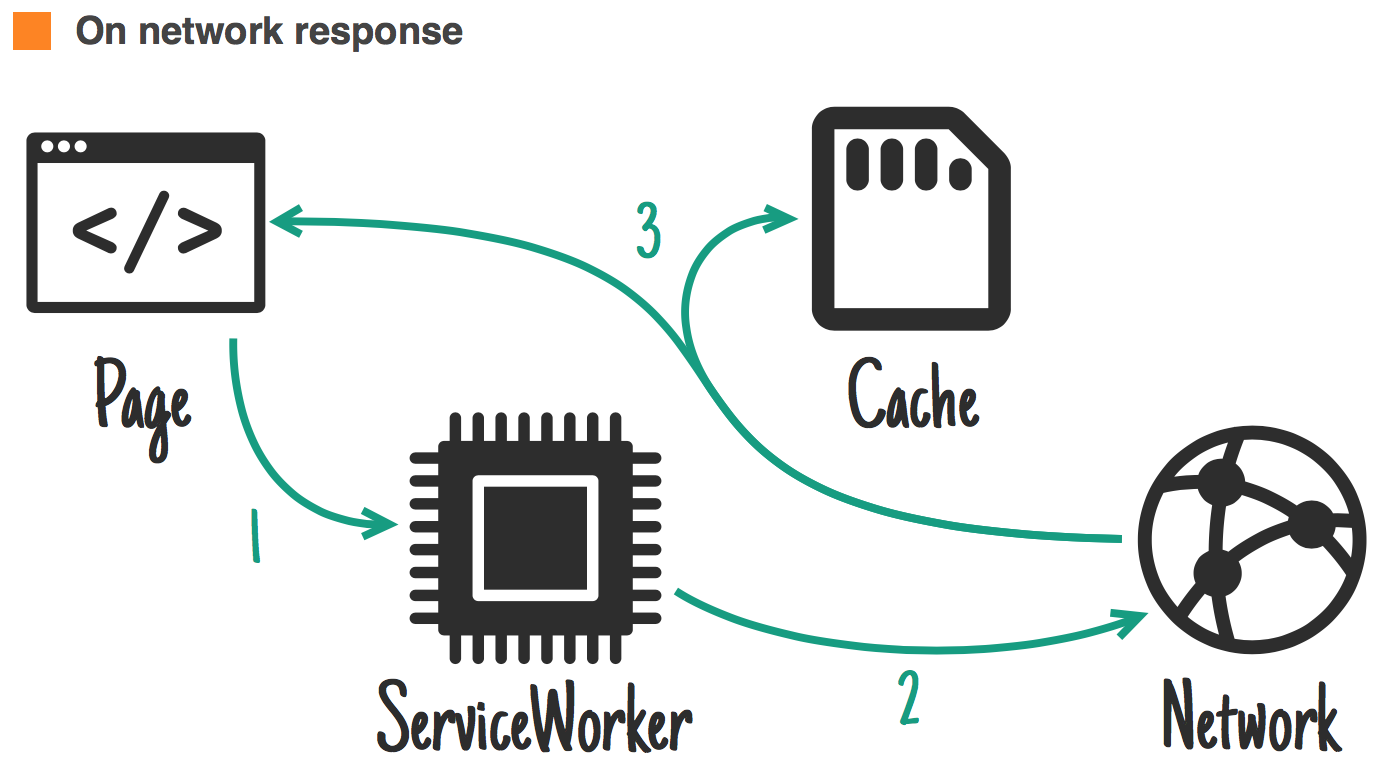
Ideal for: frequently updated resources when having the latest version is non-essential.
When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: frequently updated resources when having the latest version is non-essential.
self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.open('mysite-dynamic').then(function(cache) {
return cache.match(event.request).then(function(response) {
var fetchPromise = fetch(event.request).then(function(networkResponse) {
cache.put(event.request, networkResponse.clone());
return networkResponse;
})
return response || fetchPromise;
})
})
);
});When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: content related to a notification.
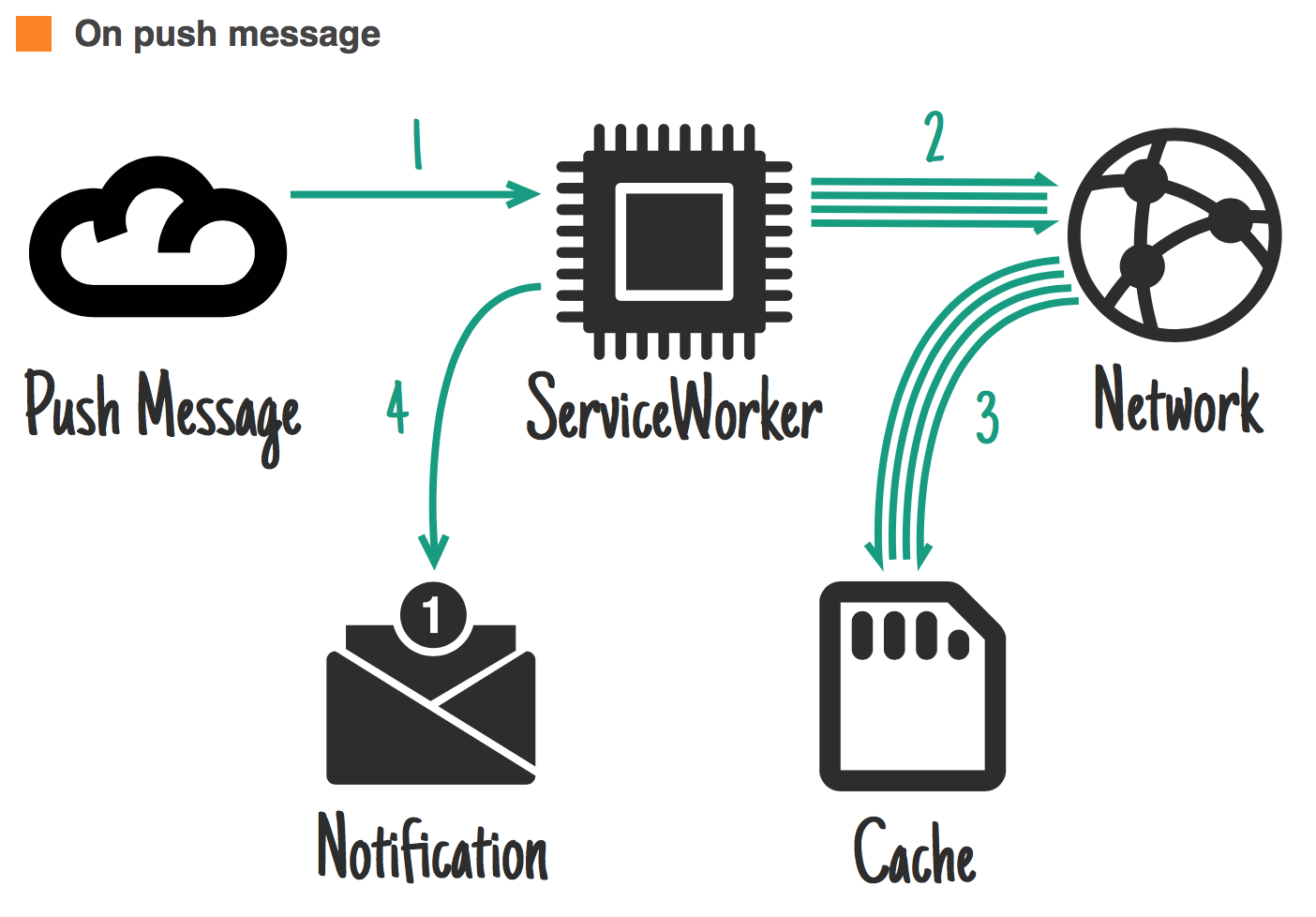
When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: content related to a notification.
self.addEventListener('push', function(event) {
if (event.data.text() == 'new-email') {
event.waitUntil(
caches.open('mysite-dynamic').then(function(cache) {
return fetch('/inbox.json').then(function(response) {
cache.put('/inbox.json', response.clone());
return response.json();
});
}).then(function(emails) {
registration.showNotification("New email", {
body: "From " + emails[0].from.name
tag: "new-email"
});
})
);
}
});
self.addEventListener('notificationclick', function(event) {
if (event.notification.tag == 'new-email') {
new WindowClient('/inbox/');
}
});When to store resources ?
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: non urgent updates.
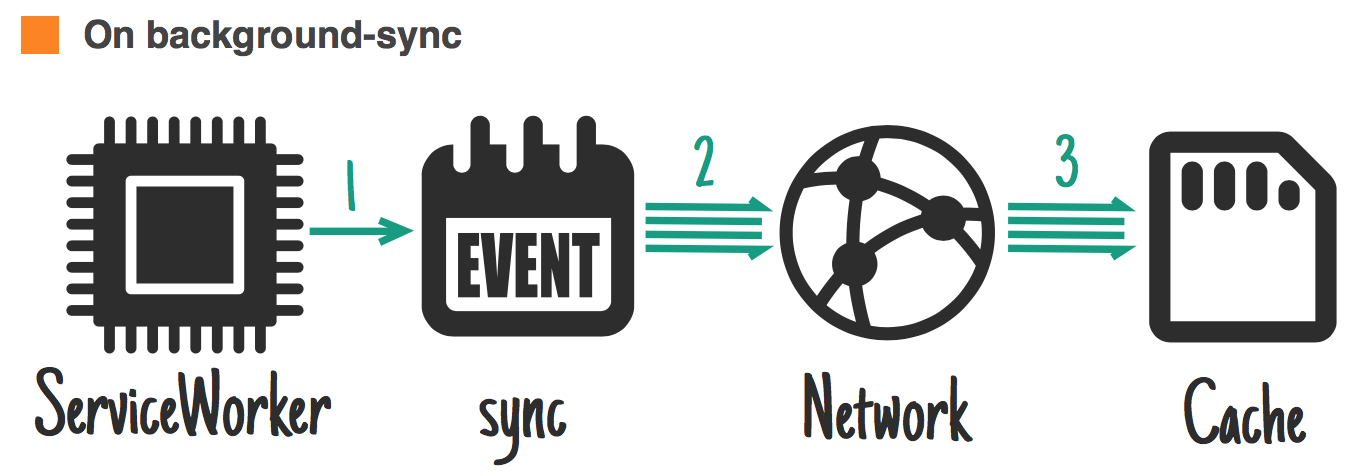
self.addEventListener('sync', function(event) {
if (event.id == 'update-leaderboard') {
event.waitUntil(
caches.open('mygame-dynamic').then(function(cache) {
return cache.add('/leaderboard.json');
})
);
}
});Common response strategies
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: common requests for offline-first.
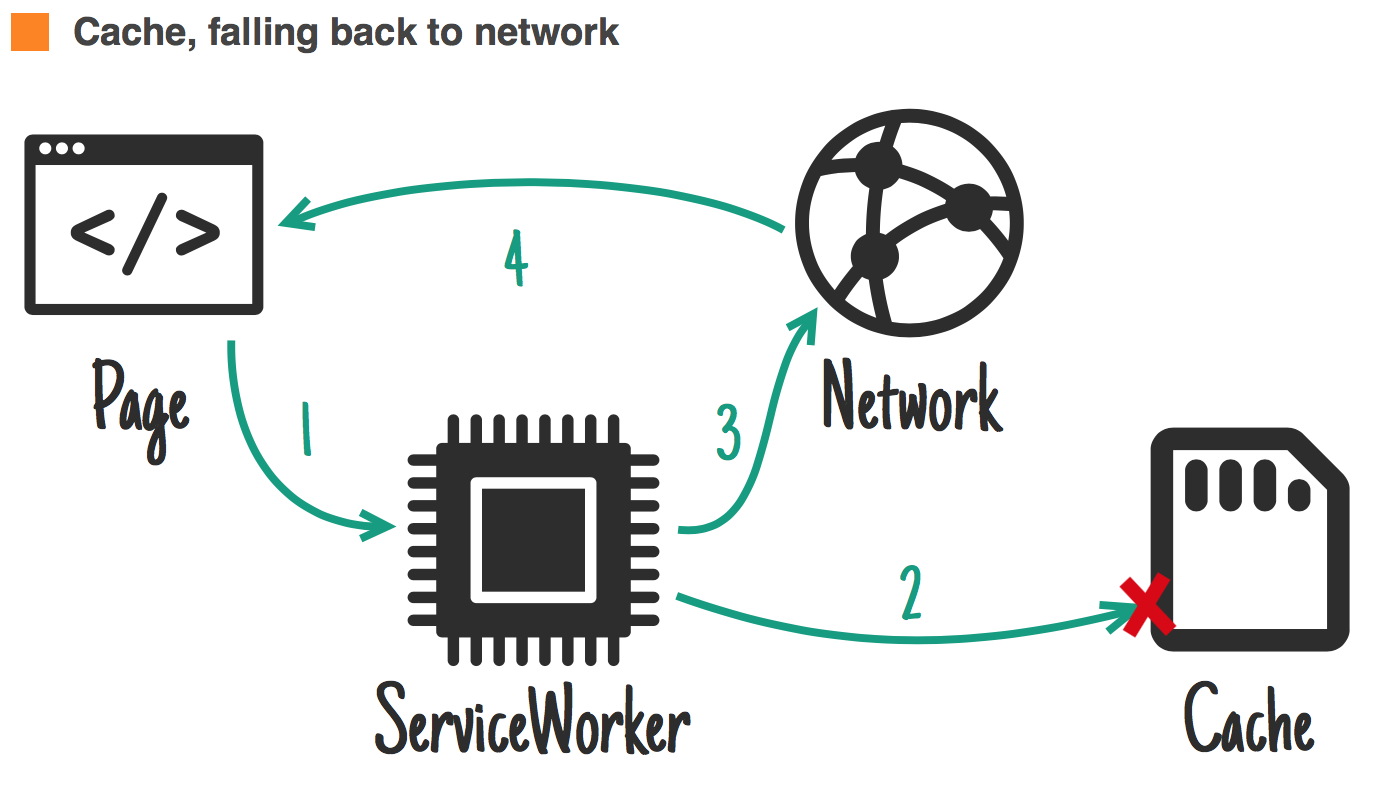
self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request).then(function(response) {
return response || fetch(event.request);
})
);
});Common response strategies
jakearchibald.com
Ideal for: quick fix for frequently updated resources when offline
self.addEventListener('fetch', function(event) {
event.respondWith(
fetch(event.request).catch(function() {
return caches.match(event.request);
})
);
});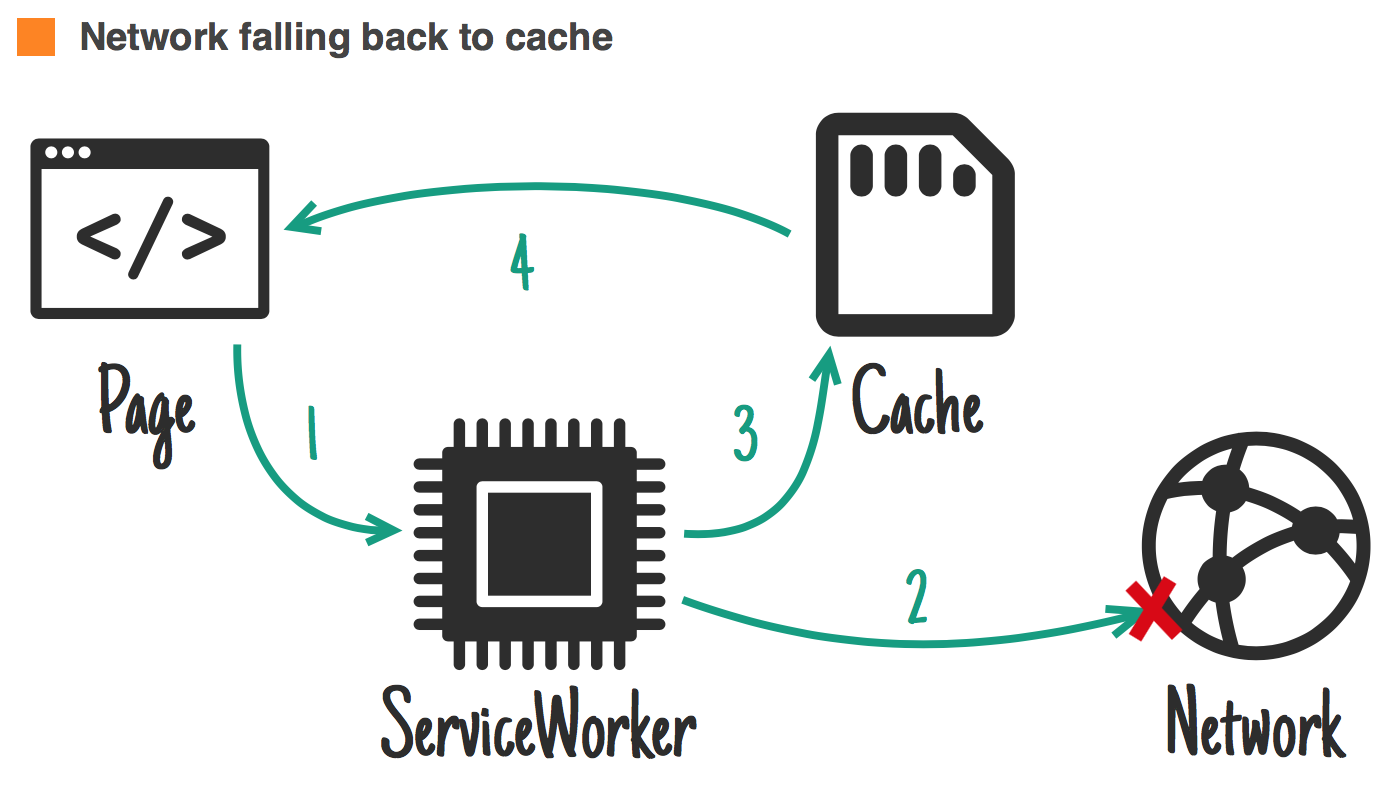
Common response strategies
jakearchibald.com
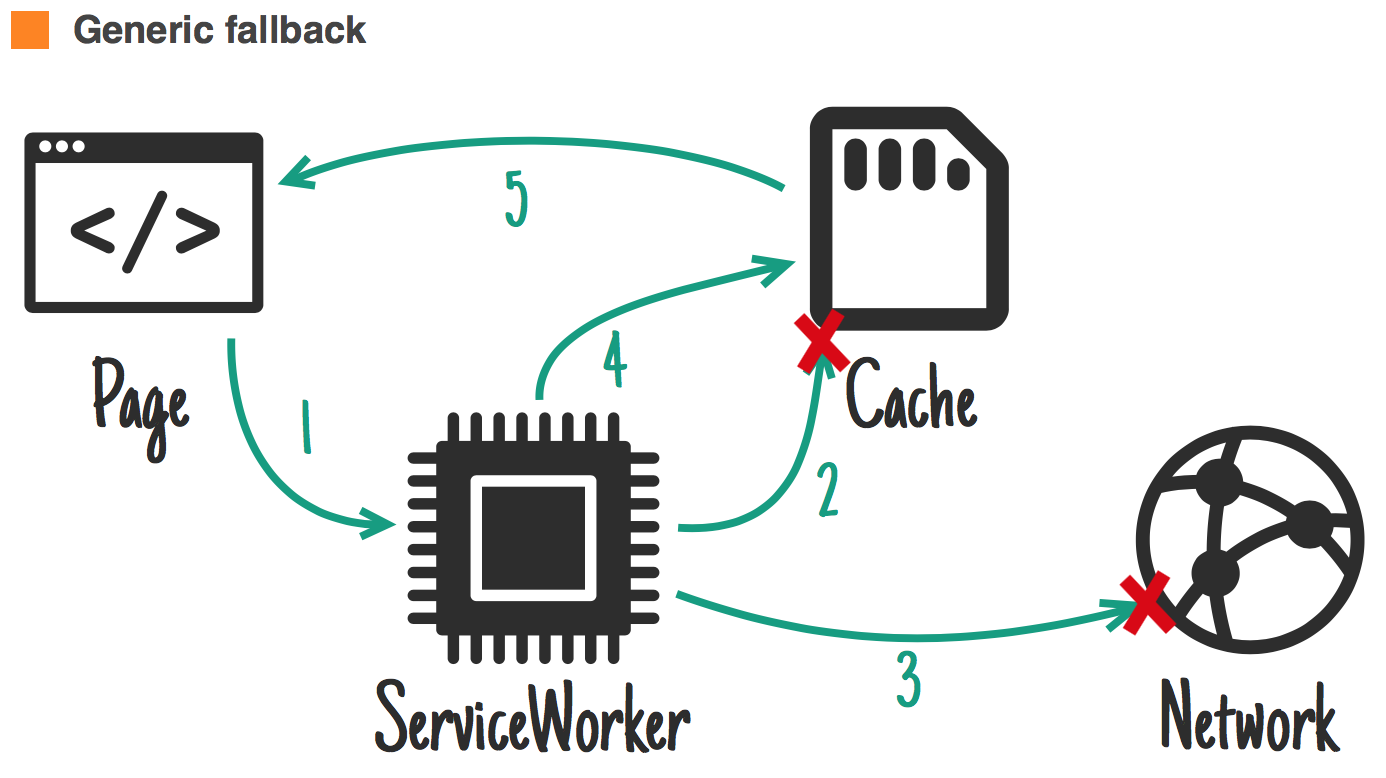
Ideal for: consistent generic fallback for not found resources.
Panic time !
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable
For your service-worker.js file !!!

Panic time !
Cache-Control: max-age=31536000, immutable
For your service-worker.js file !!!
Service Workers must be downloaded after 24 hours of the first download.
Useful resources
Follow
- https://serviceworke.rs/
- github.com/mozilla/serviceworker-cookbook
- jakearchibald.com
- github.com/cezaraugusto/curated-service-worker-list
Libraries
- sw-precache (static assets, app-shell)
- Webpack offline-plugin
Questions ?
@GatMesquer
MrFrontend


Thank you !
❤️ Margherita Farina
Service workers to production
By ajrkemp
Service workers to production
- 980


