Microservice architecture patterns

About me
Alejandro Vidal Rodriguez
Director of Engineer @TribalScale
www.tribalscale.ae
we are hiring!
Agenda
- Motivation
- Prerequisites
- Inter Process Communication
- Transaction & sagas
- Event sourcing
- Querying data
The interview

The Job
Tech lead position at company that delivers food to people!
toys
The tech
At foodToGo they been developing their system in a big single solution.
yallaToyz

The Monolith
The meeting

The poll

Microservices vs Monolith
Monolith
-
simple to develop
-
easy to make radical changes to the application
-
straightforward to test
-
straightforward to deploy
-
easy to scale more instances
-
IPC speed
Pros
- Resource management (scale)
- Deployment gets harder
- Coupled with a tech stack
- Complexity grows beyond whats understandable
- Easy to miss boundaries
Cons
Microservices
- Enables the continuous delivery and deployment of large systems
- Services are small and easily maintained
- Services are independently deployable
- Services are independently scalable
- The microservice architecture enables teams to be autonomous
- Easily experiment with and adopt new technologies
- Better fault isolation
Pros
- cross-cutting concerns & responsibilities
- difficult to debug
- added overhead, network hops and complexity
- lack of transactional operations
- Finding the right set of services is challenging
- Distributed systems are complex dev, testing and deployment gets harder
- Deploying features that span multiple services requires careful coordination
- Deciding when to adopt the microservice architecture is difficult
Cons
Migrate to microservices!

You have to be this tall to ride
- Rapid provisioning
- Basic monitoring
- Rapid deployment
Expanded
- Basic Monitoring, instrumentation, health checks
- Distributed logging, tracing
- Ready to isolate not just code, but whole build
- Can define upstream/downstream/compile-time/runtime dependencies clearly for each service
- Know how to build, expose and maintain good APIs and contracts
- Ready to honour b/w and f/w compatibility
- Good unit testing skills and readiness to do more
- Aware of [micro] service vs modules vs libraries, distributed monolith, coordinated releases, etc
- Know infrastructure automation
- Have working CI/CD infrastructure
-
Have or ready to invest in development tooling, shared libraries, internal
artifact registries, etc - Have engineering methodologies and process-tools to split down features and develop/track/release them across multiple services
Inter Process Comunication

Inter Process Comunication
| one to one | one to many | |
|---|---|---|
| synchronous | Request/Response | - |
| asynchronous | Request/notification | Publish/subscribe |
Inter Process Comunication
Contract definition
API design first
Semantic versioning
Inter Process Comunication
Message formatting
JSON
XML
Protocol buffers
Avro
Text based
Binary based
Inter Process Comunication
REST
- It is simple and familiar
- You can test an HTTP API from within a browser
- It directly supports Request/reply style communication.
- HTTP is, of course, firewall friendly
- It doesn’t require an intermediate broker, which simplifies the system’s architecture.
- It only supports the request/reply style of communication.
- Reduced availability - client and server they must both be running for the duration of the exchange.
- Clients must know the locations (i.e. URL) of the service instances(s). Clients must use what is known as a service discovery
- Fetching multiple resources in a single request is challenging
- It’s sometimes difficult to map multiple update operations to HTTP verbs
Pros
Cons
Inter Process Comunication
Messaging
-
Document - a generic message that just contains data. The receiver decides how to interpret it. The reply to a command is an example of a document message.
-
Command - a message that is the equivalent of an RPC request. It specifies the operation to invoke and its parameters.
- Event - a message indicating that something notable has occurred in the sender. An event is often a domain event, which represents a state change of a domain object such as an Order, or a Customer.
Inter Process Comunication
Messaging
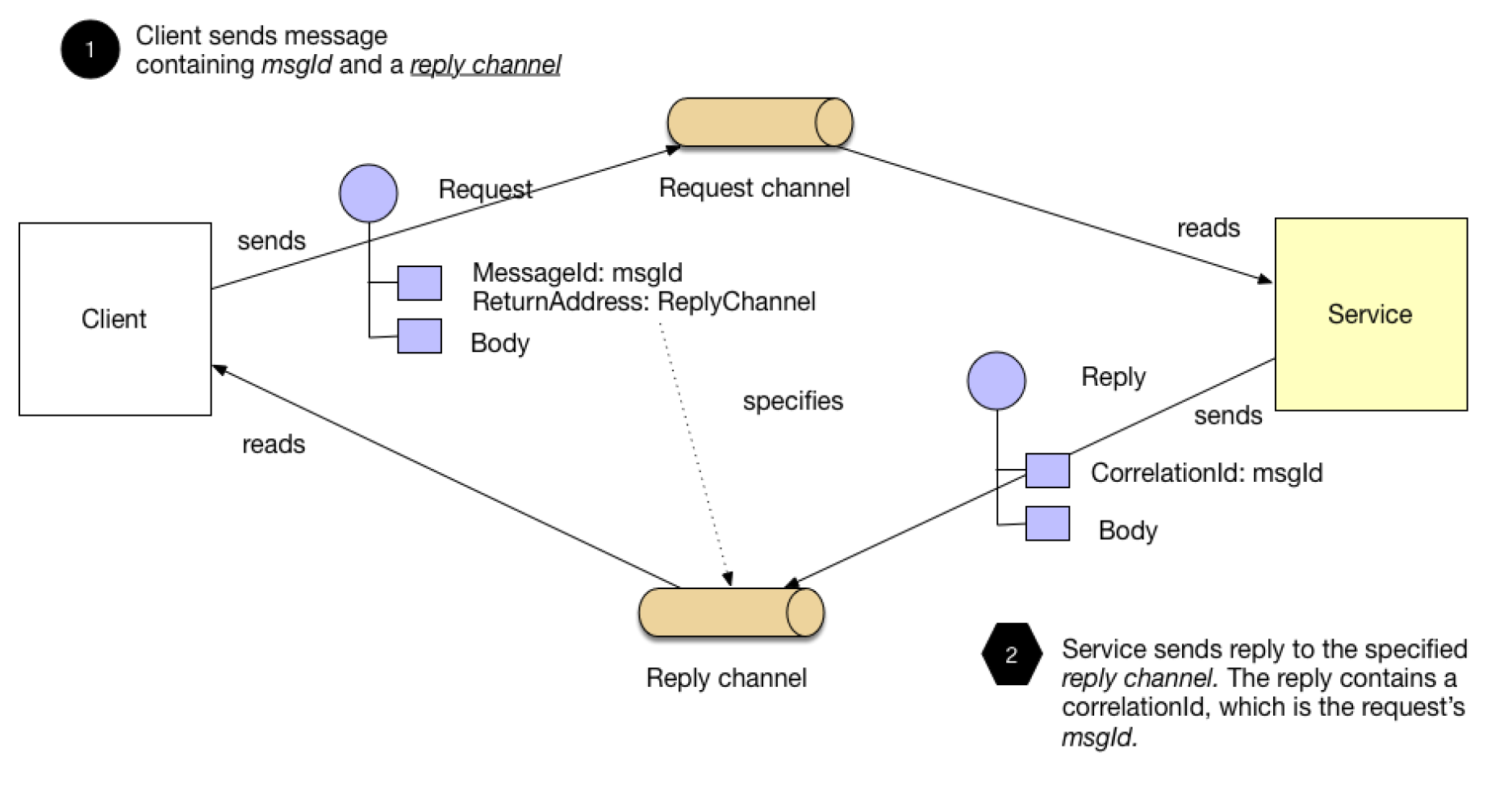
Inter Process Comunication
Message broker
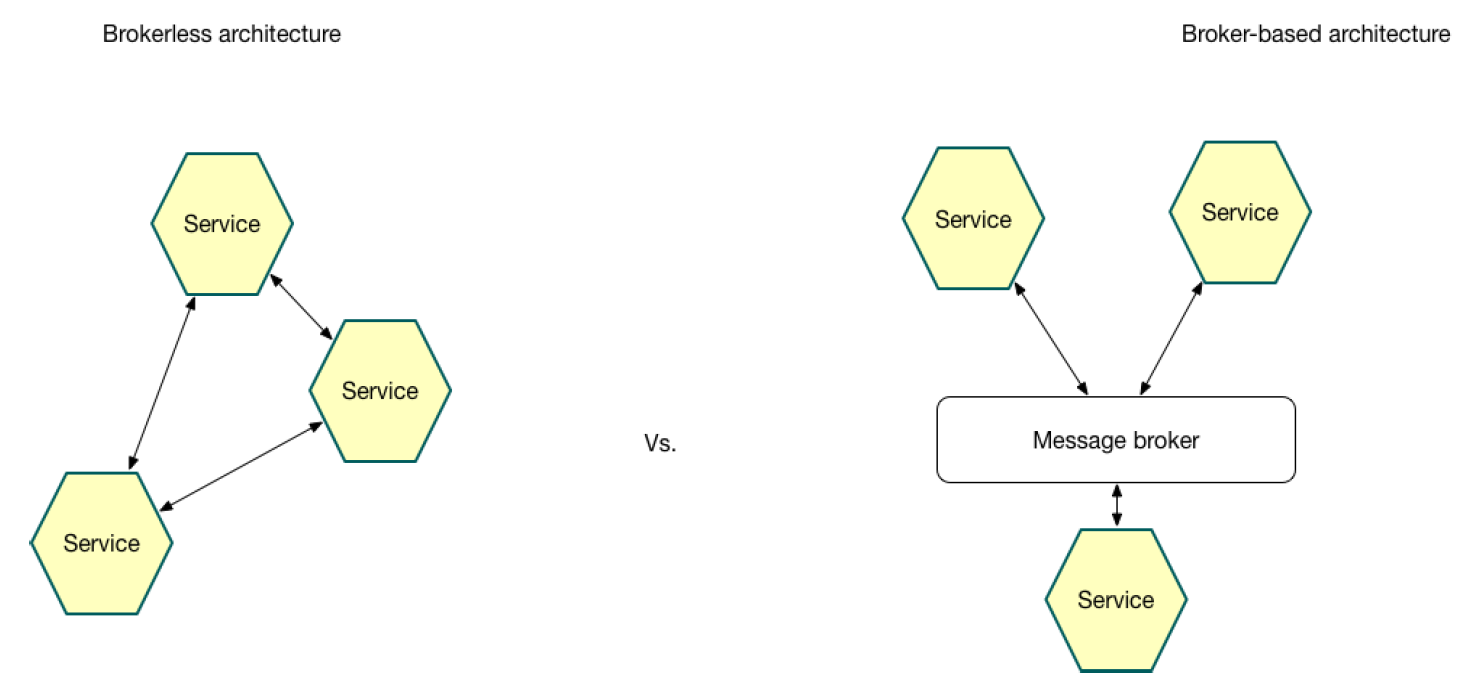
Inter Process Comunication
Message broker
- Loose coupling - a client makes a request simply sending a message to the appropriate channel.
- Message buffering - the message broker buffers messages until they can be processed.
- Flexible communication - messaging supports any defined operation
- Explicit inter-process communication - RPC-based mechanism attempt to make invoking a remote service look the same as calling a local service.
- Potential performance bottleneck - there is a risk that the message broker could be a performance bottleneck.
- Potential single-point of failure - its essential that the message broker is highly available otherwise system reliability will be impacted.
- Additional operational complexity - the messaging system is yet another system component that must be installed, configured and operated.
Pros
Cons
Inter Process Comunication
If you have to call 5 systems with an SLA of 99% uptime, what is this aggregated SLA?
99 * 99 * 99 * 99 * 99 / 10000000000 = 95%

Transactions & sagas

Problem
Someone purchases a teddy bear, how will you ensure in a monolith that the operation is saved?
and if it fails?
Solution
begin transaction
UPDATE ProductStock SET quantity = quantity - 1
WHERE id = $productId field > 0
INSERT INTO Purchases (ItemId, ProdName, Quantity, Price, Total)
VALUES (1234, 'Teddy Bear', 1, 200, 200);
commit transactionbegin catch
raiserror('Not enough teddy bears!')
rollback transaction
end catchSagas
Maintain data consistency across services using a sequence of local transactions that are coordinated using asynchronous messaging.
Sagas
- Order Service creates an order as APPROVAL_PENDING
- Stock service checks if there is enough stock
- Fullfilment service validates the order creates a ticket.
- Payment Service validates if its paid.
- Order Service sets the order to APPROVED
Sagas
| Service | Transaction | Compensating tx |
|---|---|---|
| Order Service | createOrder() | rejectOrder() |
| Stock service | verifyStock() | - |
| Fullfillment Service | createTicket() | rejectTicket() |
| Payment Service | chargeAmount() | refundAmount() / - |
| Fullfillment Service | approveTicket() | - |
| Order Service | approveOrder() | - |
Compensating transactions to achieve rollbacks
choreography

choreography
No central coordinator
participants 'simply' subscribe to each other’s events and respond accordingly
- Simplicity: service just publish events when they do something
- Loose coupling: participants subscribe to events they want to know about
- Difficult to understand: There is no single place where to look for how sagas work
- Cyclic dependencies: Services subscribe to events that might trigger other services creating loops.
- Coupling on events: Each service could be subscribe to multiple events, any change of them might generate a dependency.
Pros
Cons
Orchestration

Orchestration
define an orchestrator class whose sole responsibility is to tell the saga participants what to do
- Simpler dependencies: The orchestrator knows the participants, the services don't.
- Less coupling: Orchestrator uses the services APIs, the services do not need to know about the events or messages.
- Simpler business logic: The orchestrator just handles calls, not any logic.
- Risk of centralizing: Orchestrator can easily become a place where a lot of business logic is done becoming bloated.
Pros
Cons
Atomicity
Consistency
Isolation
Durability
Isolation RIP
- Lost updates - one saga overwrites without reading changes made by another saga
- Dirty reads - a saga reads the updates made by a saga that has not yet completed those updates
- Fuzzy/non-repeatable reads - two different steps of a saga read the same data and get different results.

Countermeasures
Semantic lock: ORDER_PENDING -> ORDER_APPROVED
Conmutative operations: credit() <---> debit()
Re read value: Check if data has change -> restart
Version: if the data has a higher version -> discard
By value: high risk? -> don't use sagas, use distributed tx
Event sourcing

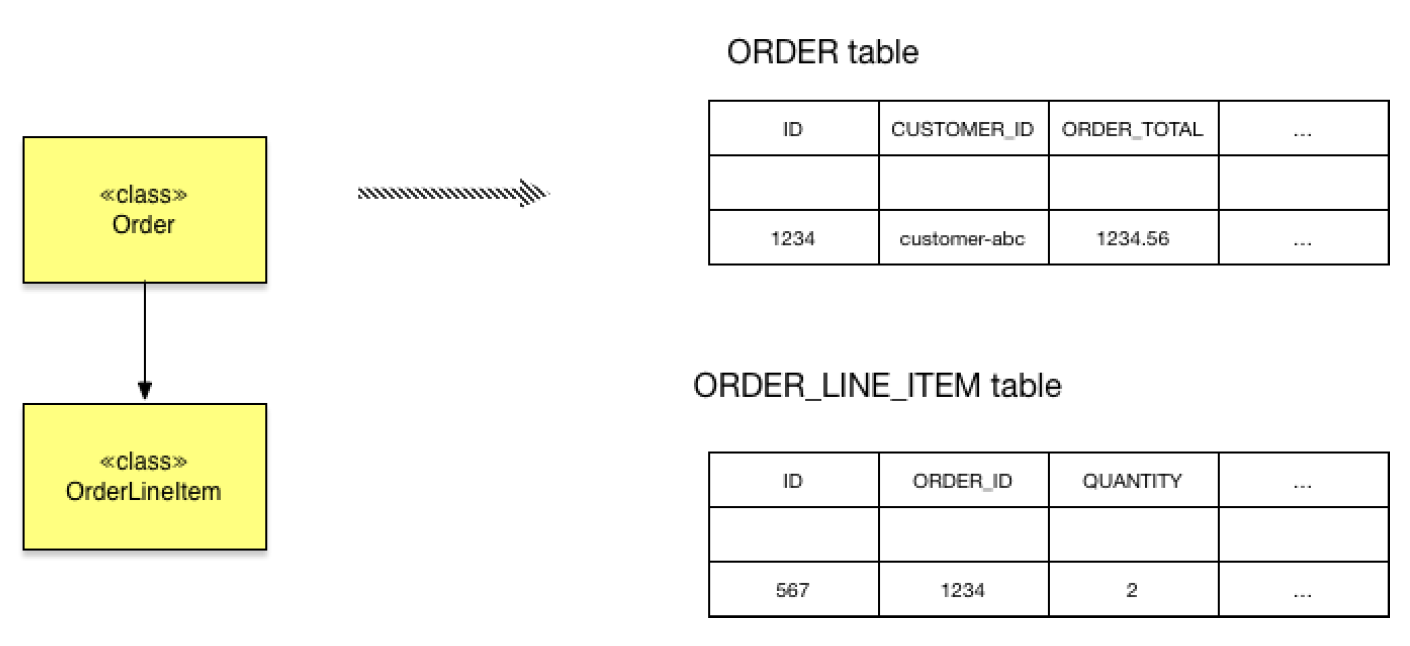
Tabular database
- Object-Relational impedance mismatch
- Lack of aggregate history
- Implementing audit logging is tedious and error-prone
- Event publishing is bolted on to the business logic
Problems
Event sourcing in microservices
Event sourcing in microservices
• Reliably publishes domain events
• Preserves the history of aggregates
• Mostly avoids the O/R impedance mismatch problem
• Provides developers with a time machine
• Different programming model that has a learning curve
• Complexity of a messaging-based application
• Evolving events can be tricky
• Deleting data is tricky
• Querying the event store is challenging
Pros
Cons
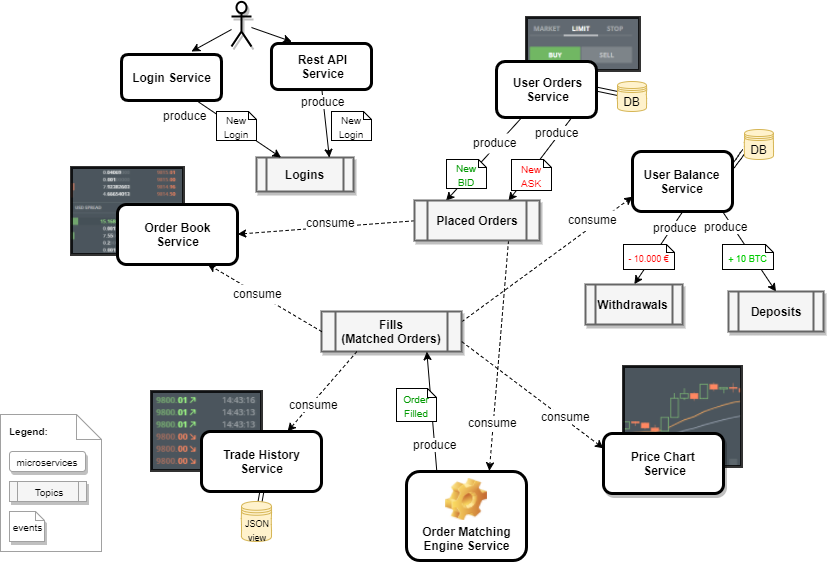
Querying data

Querying data
Your data used to be in one place, one simple query gets your data.
Can I get my previous orders given a keyword?
How many red teddy bears did I bought last year?
Querying data
Monolith
Microservices


Querying data
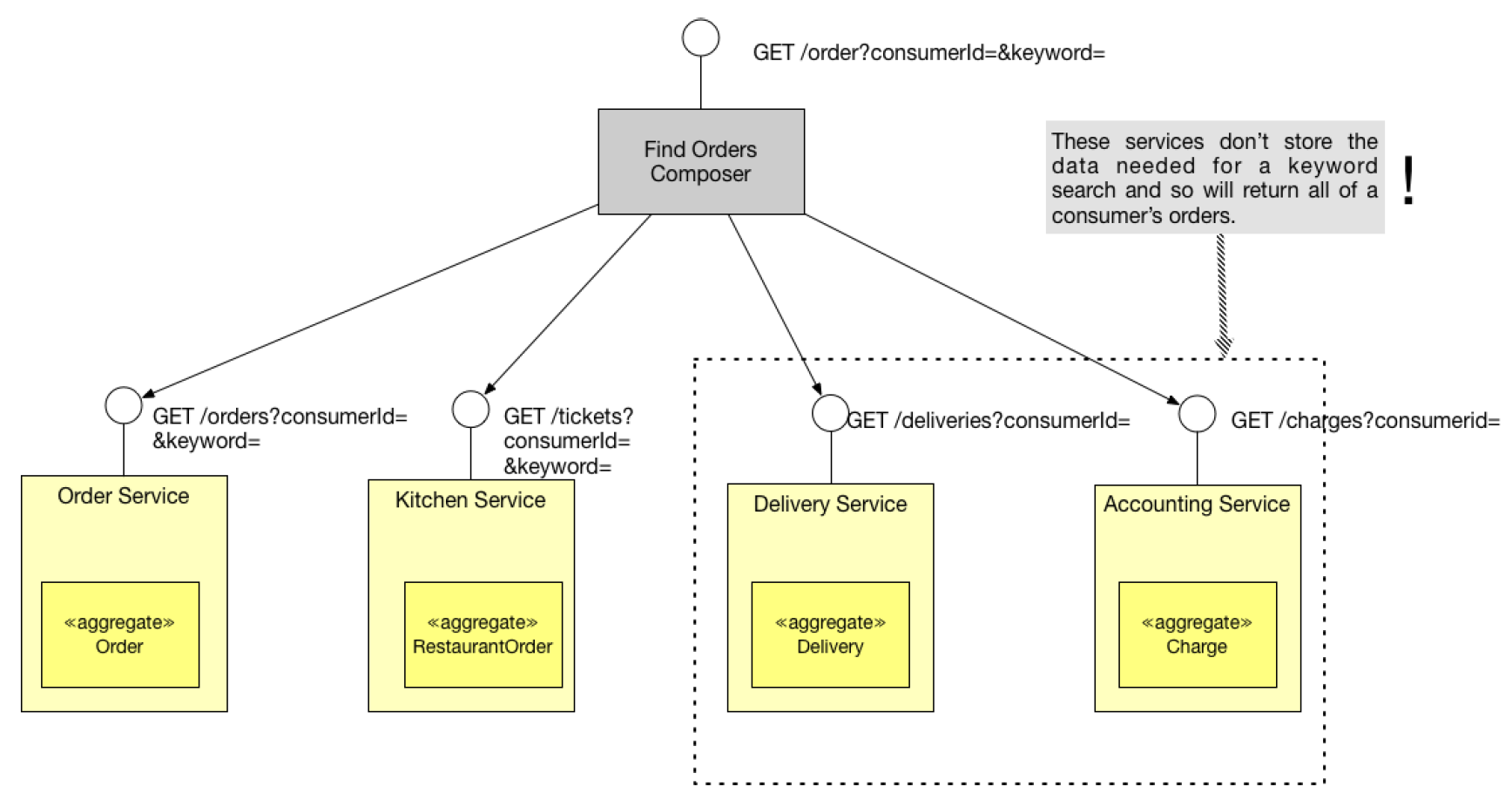
Querying data
Even simple queries get tricky:
findAvailableToyStores()
has the service the geospatial capablitity?
Its owned by the StoreService or by the PurchaseService?
Capability
Ownership
composition pattern
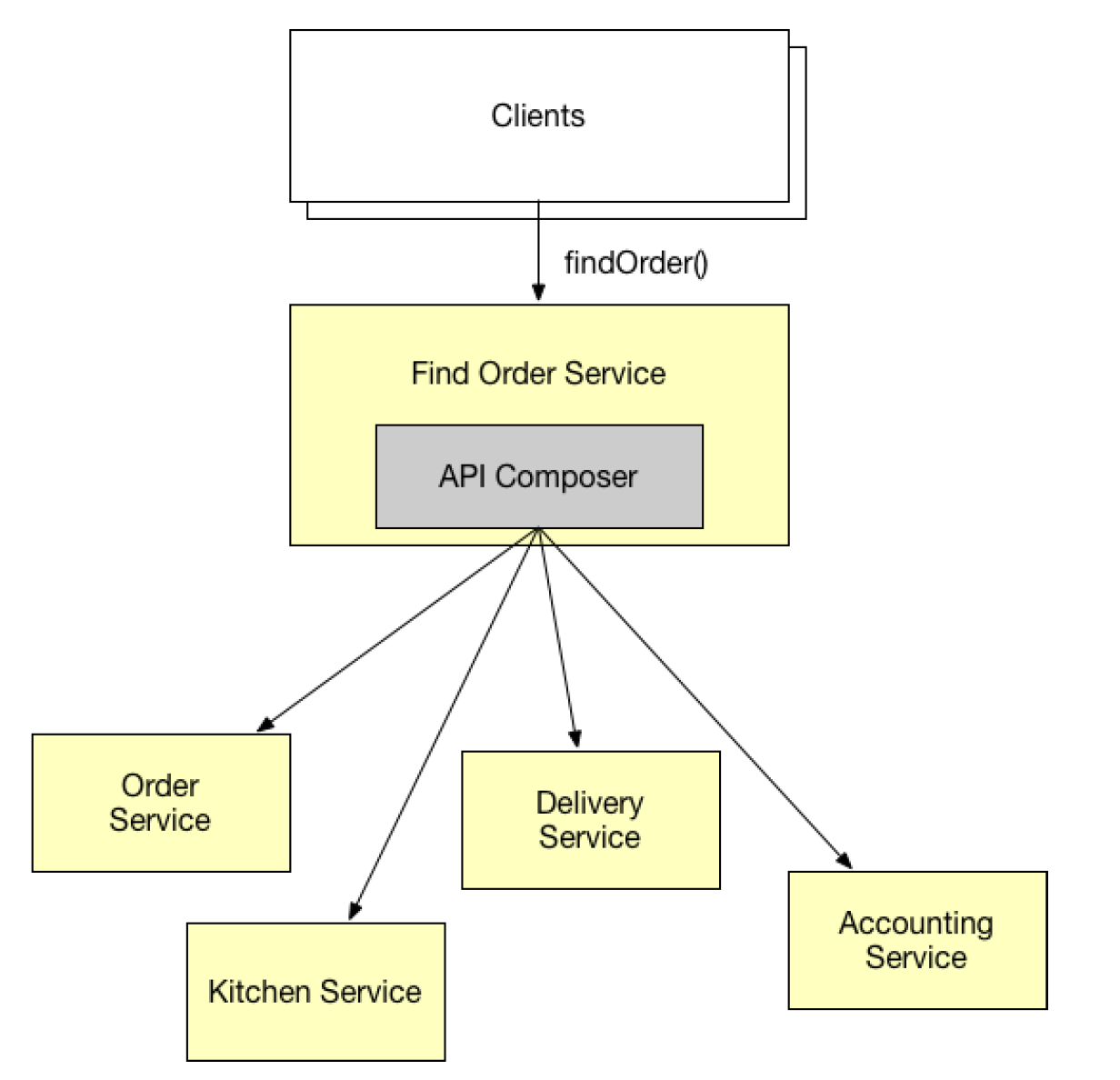
composition pattern
• Simple and intuitive
• Effective if can be paralelized
• Increased overhead
• Risk of reduced availability
• Lack of transactional data consistency
Pros
Cons
CQRS
CQRS
• Enables efficient impl of queries in a ms architecture
• Enables efficient impl of a diverse queries
• Makes querying possible in an event sourcing application
• Improves separation of concerns
• More complex architecture
• Dealing with the replication lag
• More expensive
Pros
Cons
Api patterns
Api patterns
- API gateway
- Edge services
- Security
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Rate limits
- Caching
- Metrics
- Logging
- BFF
- Legacy support
- API Querying
Deployment

Deployment
- 4 key deployment patterns
- Language specific package
- Service as VM
- Service as container
- Serverless
- Kubernetes
- Service mesh
- Deployment patterns
Production readiness

Production readiness
- Developing secure services
- Configuration pattern
- Observability pattern
- Health check API
- Log aggregation
- Distributed tracing
- Exception tracking
- Application metrics
- Audit logging
Questions?

Homework
- Go to https://microservices.io/patterns/index.html
- Play around with docker/kubernetes/istio
- Build a yalla toyz sample on the cloud

Microservice architecture patterns
By Alejandro Vidal Rodriguez
Microservice architecture patterns
Talk about microservices patterns and how to be careful when migrating to this architecture.
- 51



