How to use Git
Introduction to Git and Git commands
Hi.
Sanjeev Yadav
Software Engineer @mindfires

Most Important Thing
🧐
My Username 🤦♂️
✔️ alex aka sanjeev
❌ alexa ka sanjeev
Version Control System(VCS)
-
Record changes to your file
-
Revert back to any version
-
Basically lets you do Time Travel
What is GIT?
🤔
🗂️ Repository 🗂️
a.k.a.
repo
Four Fundamental
elements in Git Workflow
💨 Wind
🔥 Fire
🌎 Earth
🌊 Water
🙅♂️
Four Fundamental
elements in Git Workflow
✨ Working Directory
✨ Staging Area
✨ Local Repo (HEAD)
✨ Remote repo (MASTER)
Working
Directory
Staging
Area
Local Repo
(HEAD)
Remote Repo
(MASTER)
Git Add

Git Commit

Git Push

Git Fetch

Git Merge

Git Pull

git init
git init
- Create an empty Git repository
- Creates .git folder inside the repo
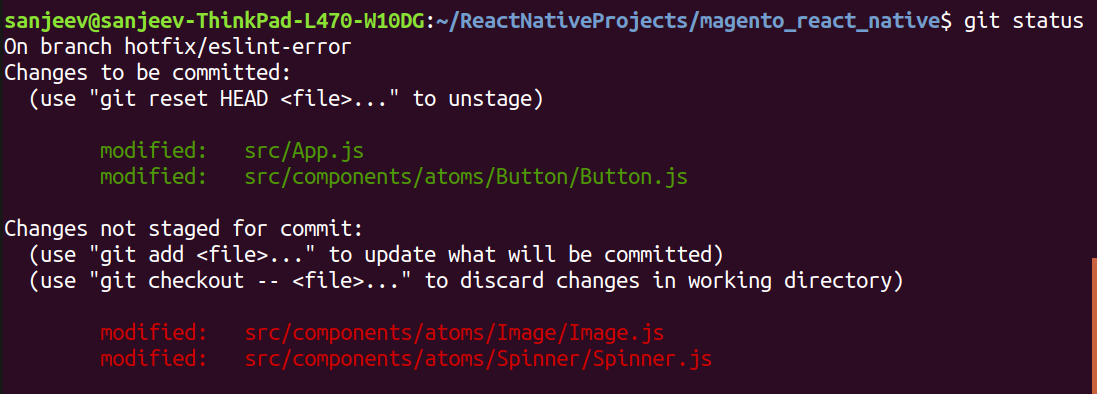
git status
git status
Current State of the repository
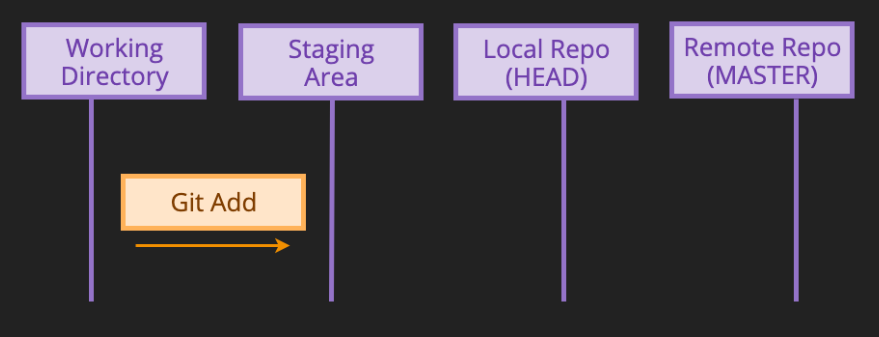
git add
git add <file_name>
- adds a file to "staging area"
- tells git to include the file in the next revision to the repository
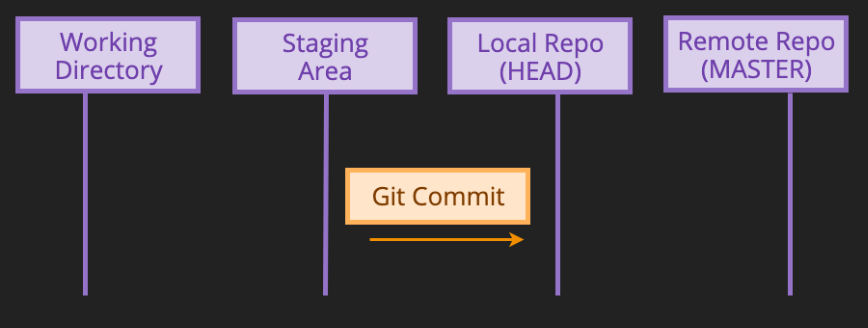
git commit
git commit -m "message"
- saves the changes to repository as a new revision
- git commit -am "message" adds and commits in same step
git log
git log
- shows a history of commits and messages

git log
commit 6aa24bb96658ce2541f69f9eccfc3d65826c726b
Author: Sanjeev Yadav<sanjeev@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Apr 22 22:39:20 2019 -0300
Added a line
commit c861cb6c8d0f3c78b24004cfe23df55934cd3ca4
Author: Robin Thicc <thicc@gmail.com>
Date: Mon Apr 8 18:20:20 2019 -0300
Created file
Demo

git remote
git remote
- Manage set of tracked repositories
- git remote add <name> <url> Adds a remote named <name> for the repository at <url>
git remote add myrepo
https://github.com/user/repo.git
git push
git push

- sends committed changes to remote repository
- more explicitly, could write git push myrepo master
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;
git push
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;add line
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;server
local
git pull
git pull

- retrieves changes from remote repository
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;
git pull
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;server
local
int a = 1;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;int a = 1;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;git clone
git clone <url>
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;

- downloads a copy of the repo in your computer
git clone <url>
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;Demo

git reset
git reset

- git reset --hard <commit> reverts code back to a previous commit
git reset --hard
edfe30cc
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;add line edfe30cc
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;remove line 51ej004
git branch
int a = 1;
int b = 2;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;int a = 1;
int c = 3;int a = 1;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;master branch
int a = 1;
int b = 2;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;master branch
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
String sanjeev = "handsome";int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
// No you are not :(feature branch
bugfix branch
git branch

- shows all branches of code
- git branch <branch_name> creates new git branch
- git checkout <branch_name> switch to or ("checkout") to new branch
git branch
feature
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;master branch
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;feature branch
git merge
git merge
- Join two or more development histories together
- git merge <branch_name> merges feature branch to current branch
int b = 2;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;master branch
feature branch
Demo

Merge Conflicts
Merge Conflicts

- when two different commits can't be automatically merged
- need to be restored
git pull
int a = 1;
<<<<<<< HEAD
int b = 2;
=======
int b = 0;
>>>>>>> c861cb6c8d0f3c78b2
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;{
your changes
{
remote changes
conflicting commit
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
int c = 3;
int d = 4;
int e = 5;git merge
- git merge --abort can only be run after the merge has resulted in conflicts
- git merge --continue can only be run after the merge has resulted in conflicts
Demo

git commit -m "I know git"

Reference
git add ask_question.txt

FeedBack

git commit -m
"The End"

How to use Git @Js_lovers
By Sanjeev Yadav
How to use Git @Js_lovers
Talk is basically aimed at beginners, introducing them about GIT and GIT command.
- 580





