Functions
JavaScript Workshop
Hello!
My name is Alex Bardanov
I'm a front-end developer at GlobalLogic / AVID
GitHub: dnbard
Skype: dnbard
Contents
- Function
- A step into the Functional Programming:
- First Class Functions
- Closures
- Pure Functions
- Immediately-invoked function expression
Function
function sum(a, b){
return a + b;
}Function
Always return some value ( undefined or something else )
//this function will return undefined
function logMe(data){
console.log(data);
}
//this function will return the timestamp
function getNow(){
return new Date();
}
Function
The parameters of a function call are the function's arguments
function example(){
console.log(arguments);
}
example(1, 2); //[1, 2]
Function
Arguments are passed to functions by value
(except for Objects)
var a, b;
function increment(a){
return a + 1;
}
a = 1; // a = 1; b = undefined
b = increment(a); // a = 1; b = 2
Function
If the function changes the referred object's properties, that change is visible outside the function
var myCat = {
color: '#000000',
nickname: 'Vasiliy'
};
function recolorMyCat(cat){
cat.color = '#FFFFFF';
}
recolorMyCat(myCat);
/* {
color: '#FFFFFF',
nickname: 'Vasiliy'
} */Function
function [name]([param] [, param] [..., param]) {
statements
}Defining
Function
param1 => //statements
(param1, param2) => //statements
param1 => {
//statements
}
(param1, param2) => {
//statements
}Arrow Functions
Function
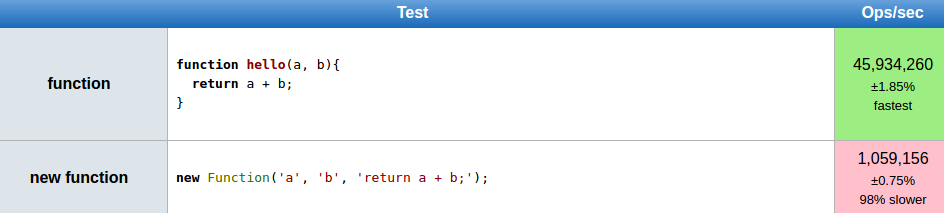
new Function (arg1, arg2, ... argN, functionBody)Function constructor
Not recommended!
Function
function Hero(){
this.id = this.generateId();
this.name = "Default name";
this.health = 100;
this.class = "Warrior";
}
Hero.prototype = {
generateId: function(){
// return unique Id
}
}
var myHero = new Hero();Constructor
Function
function logContext(){
console.log(this);
}
logContext.bind({ key: 'value' })();
// { key: 'value' }
logContext(); // Window { ... }
logContext.bind(1)(); // Window { ... }
logContext.bind(function(){ })();
// Window { ... }Bind (ECMAScript 5)
Function
var user = {
showData: function(){
return this.name + ' ' + this.age;
}
}
var cars = [
{name:"Honda Accord", age:14},
{name:"Tesla Model S", age:2}
]
var showFirstCarData = user.showData.bind (cars[0]);
showFirstCarData(); // Honda Accord 14Bind () Allows us to Borrow Methods
Function
function logContext(){
console.log(this);
console.log(arguments);
}
logContext.apply({ key: 'value' }, [1, 2]);
// Object {key: "value"}
// [1, 2]
logContext.call({ key: 'value' }, 1, 2);
// Object {key: "value"}
// [1, 2]Apply & Call (ECMAScript 3)
First class Functions
Constructing new functions during the execution of a program
function sum(a, b){
return a + b;
}
sum instanceof Object; // true
typeof sum; // 'function'First class Functions
Passing functions as arguments to other functions
function sum(a, b, callback){
callback(a + b);
}
sum(1, 2, function(result){
console.log(result); // 3
});
CLOsUREs
function init(){
var name = "Alex";
function printName(){
console.log(name);
}
printName(); // Alex
}
init();The function defined in the closure 'remembers' the environment in which it was created
CLOsUREs
function makeAddFunction(adder){
return function(value){
return adder + value;
}
}
var adder5 = makeAdderFunction(5);
adder5(10); // 15CLOsUREs
function createUser(name){
return {
setName: function(newName){
name = newName;
},
getName: function(){
return name;
}
}
}
var user = createUser("Alex");
user.getName(); // Alex
user.setName('Michael');
user.getName(); // MichaelCLOsUREs
function init(){
var counter = 0,
button = document.querySelector('#button');
button.onclick = function(){
counter ++;
}
}
init();CLOsUREs
function getUser(request, response, next){
var id = request.params.id;
database.users.find(id, function(err, user){
if (err){
return next(err);
}
response.send(user);
});
}PURE FUNCTION
The function always evaluates the same result value given the same argument values. The function result value cannot depend on any hidden information or state that may change while program execution proceeds or between different executions of the program, nor can it depend on any external input from I/O devices.
Evaluation of the result does not cause any semantically observable side effect or output
PURE FUNCTION
function Sum(a, b){
return a + b;
}var a = 5;
function AddsFive(b){
return a + b;
}Unpure function:
Pure function:
Iife
JavaScript design pattern which produces a lexical scope using JavaScript's function scoping.
Immediately-invoked function expressions can be used:
protect against polluting the global environment
allow public access to methods while retaining privacy for variables defined within the function
Immediately-invoked function expression
(self-executing anonymous function)
Iife
(function() {
// the code here is executed
// in its own scope
})();Iife
(function($, _) {
$(function(){
$('#label').text('Hello, World!');
})
})(window.jQuery, window.lodash);Passing the variables
Iife
a = b + c
(function() {
// code
})();"Defensive" semicolon
Won't work
a = b + c
;(function() {
// code
})();OK
Iife
var counter = (function(){
var i = 0;
return {
get: function(){
return i;
},
set: function( val ){
i = val;
},
increment: function() {
return ++i;
}
};
})();
counter.get(); // 0
counter.set( 3 );
counter.increment(); // 4
counter.increment(); // 5Private variables
thanks
Functions
By Alex Bardanov
Functions
"Functions" slides for JavaScript Workshop in the GlobalLogic
- 2,419



