How To Avoid
Pyramid Of Doom
When Designing
Bot Workflows
Alex Bunardzic
October 14, 2016
Vienna, Austria
me
- 26 years of software development
- 50% engineering, 50% process
- 50% business analysis
- fan of purity in programming (no side effects)
- intensely dislike self-serve (will be explained later)

Two Families of Bots
1. Concierge

2. Butler

Concierge
Loyal to the Corporation
Butler
Loyal to the Individual
Butler
- Focused on learning about its owner's habits
- Focused on detecting recurring behavioural patterns
- Trained to respect the owner's preferences
Butler Bot
- Stars in many Hollywood movies
- Needs heavy duty AI
Concierge
- Focused on learning about the corporate goals
- Focused on consistent customer service
- Trained to detect business opportunities (i.e. up-sell/cross-sell)
- Sets the tone of the conversation
Concierge Bot
Establishes the conversational protocol
Concierge Bot
Doesn't need beefy AI
Conversation with a narrow focus
Example: Medical Receptionist


Typical experience with a Medical Receptionist (Concierge)
- Receptionist sets the tone of the conversation
- Establishes the conversational protocol
- Asks for pertinent information (name, insurance, phone, date of birth)
- Impervious to any attempts to spark up irrelevant conversation
- If a visitor refuses to comply, receptionist may ask them to leave
Concierge Bot model requires rudimentary NLP
Self-serve
Technological advancements have ushered the era of
self-serve
High tech self-servitude => instead of human cashiers, self-serve checkouts

Consumers are duped into doing all the legwork while still paying the full price
Only businesses benefit from the self-serve model
Concierge bots are the next step in the evolution of high tech self-serve paradigm
What's the difference between self-serve and full-serve bots?
Using a self-serve bot is similar to explaining your problem to a toddler
Using a full-serve bot is similar to explaining your problem to a mathematician
Self-serve/full-serve dichotomy is similar to the imperative/functional programming dichotomy
Challenges
Challenges
- Even rudimentary NLP is a huge challenge!

Google Assistant
Challenges
- Even rudimentary NLP is a huge challenge!
- Luckily, there are commodities and neural networks to help
Challenges
- Even rudimentary NLP is a huge challenge!
- Luckily, there are commodities and neural networks to help
- One challenge remains largely unaddressed
Workflow
Workflow
- Bot workflow is an uncharted territory
Why?

Bots are Stateless
Stateless Bots are Useless Bots

How to Endow Bots with State?
Implement Workflow!
Bot Workflow persists the state of conversation
Workflow can get very complex!
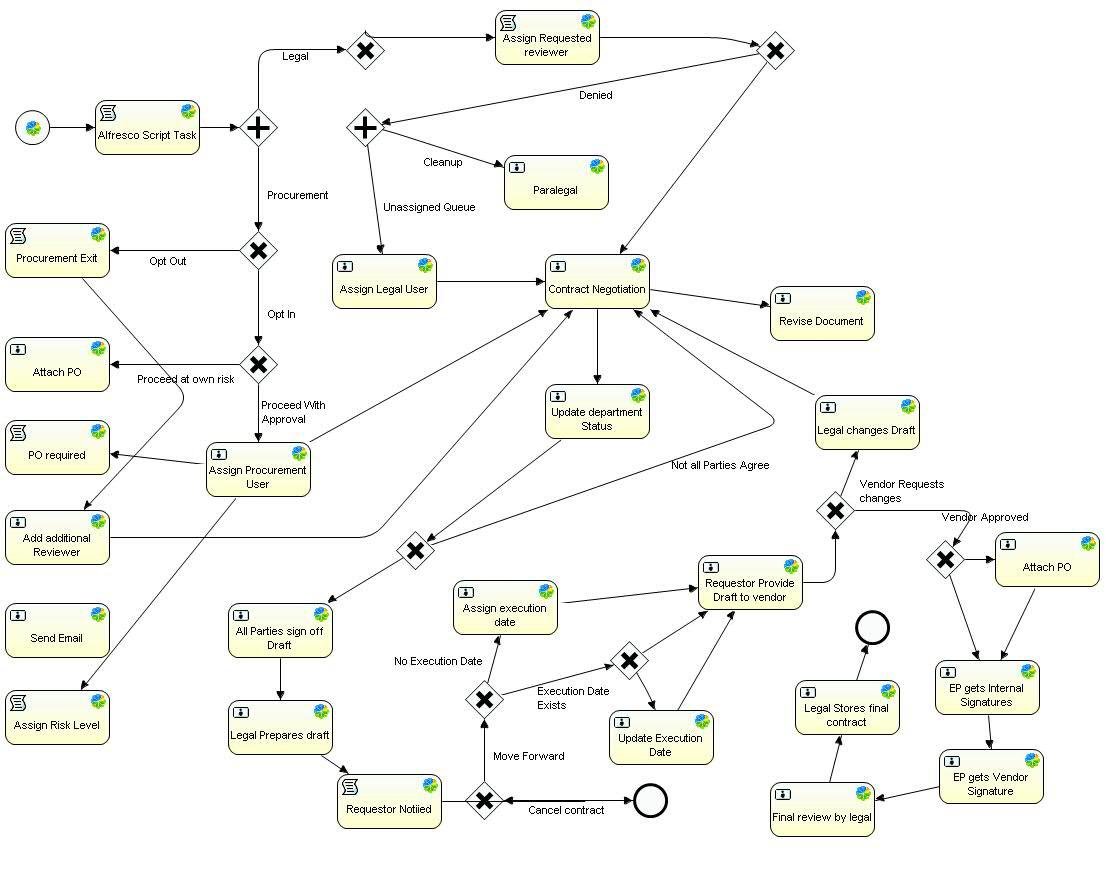
Is there a prescribed solution?
Yes, there is. It's called REST
How does REST implement workflow?
HATEOAS: Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State
Work flows through piecemeal discovery
All the information necessary to decide what's the next step is
in band
There is no need to establish the purpose of the conversation beforehand
There is no need to reach out for any additional information that's
out of band
Nice. Why don't we use REST for bot workflow then?
Unlike apps, bots have no routes
In REST, business logic is compartmentalized in routes
In bots, business logic is piled up in a big
bowl of spaghetti
Also known as the Pyramid of Doom!


So what's wrong with the Pyramid of Doom?
Difficult to read
Difficult to reason about
Very hard to modify
Extremely hard to troubleshoot
Extremely hard to debug
Almost impossible to document
Is there a solution to this?

I wasn't able to find ready made solution for bot workflows, so I rolled up my sleeves
Fight the Pyramid of Doom!

Divide and Conquer!
Bot Architecture
Two Layers
Commodity layer
Core competence layer
Commodity Layer
- Messaging channels (SMS, Messenger, WhatsApp, Slack, etc.)
- Natural Language Processing/Understanding (NLP/NLU)
- Computing infrastructure (servers, clients, message queues...)
Core Competence Layer
- Business application domain-specific code
- Business entities
- Business operation
Business Operation
- Dispatching
- Authentication/authorization
- Validation
- Business rules/processing logic
- Persistence
- Response
Business Entities
- User
- Conversation
- Context
Conversation
- Belongs to User
- Remembers messages received from the User
- Remembers replies to the User
- Declares the next step
- Drives the workflow
Next step?
Determined by the business logic
How is next step implemented?
If using imperative approach, results in Pyramid of Doom!
More desirable to implement next step using declarative approach
How to implement
declarative approach?
Compartmentalize processing logic into isolated components
Similar to REST and HATEOAS
In REST isolated components are implemented as resources
HATEOAS provides the next step
Example (simplified)
- User asks the bot to see the menu
- The bot messages back with the menu
- User is supposed to pick an item and send it to the bot as a message
- Bot checks if the user chose an existing menu item, or if the user said something unrelated
Implementation
(gory details)
Create a component ProcessMenuSelection
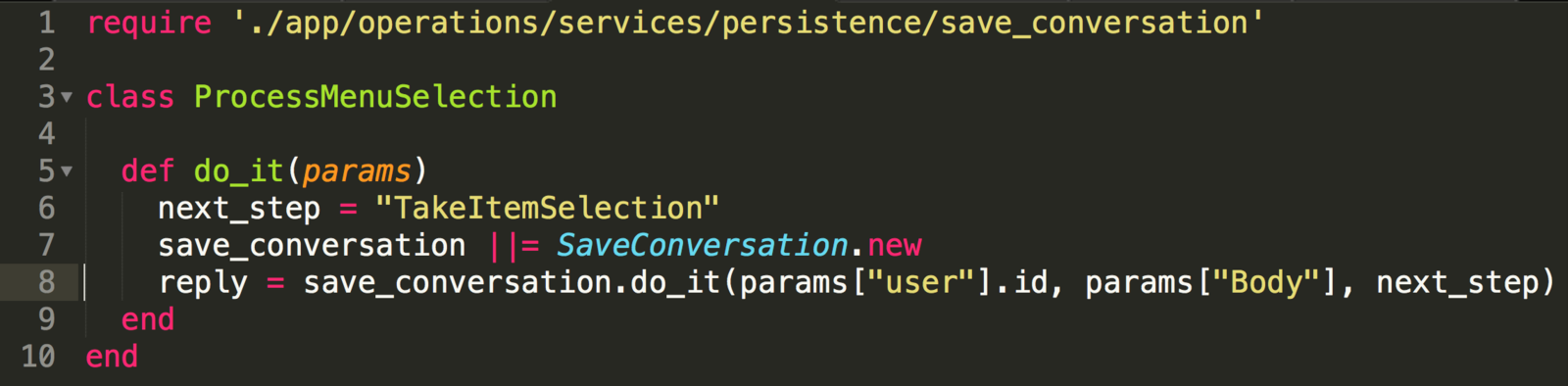
Declare next step to be "TakeItemSelection"
Create a component TakeItemSelection
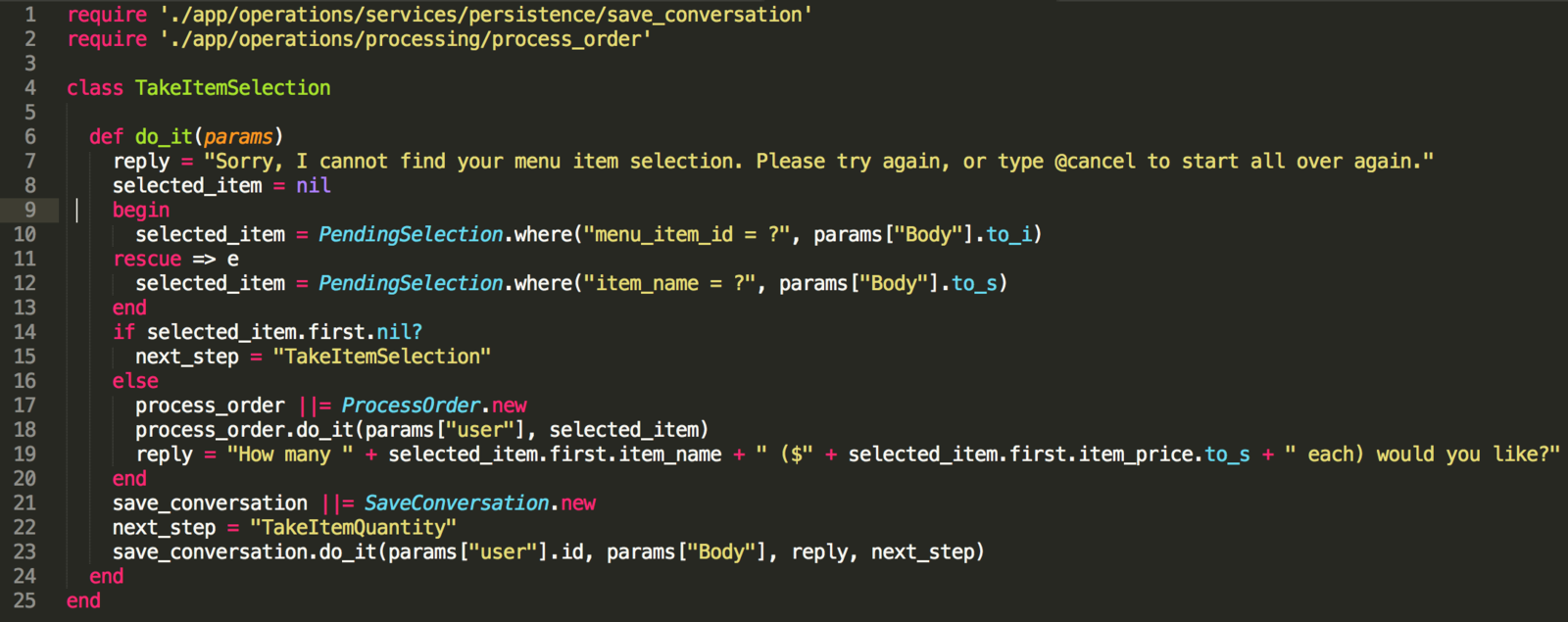
Declare next step to be "TakeItemQuantity"
And so on...
How to execute this Workflow?
Create a main diver component:
Entry with a single method: dispatch

The main engine runs on two lines of code:
-
clas = next_step.constantize
-
clas.new(params)
OK, but where is the next step coming from?
next_step = user.conversations.last.next_step
Wrap up
Bots for Business https://medium.com/bots-for-business

Welcome to Web 3.0!
Questions?
Parting is a sweet sorrow
-
https://twitter.com/alexbunardzic
-
https://medium.com/@alexbunardzic
Copy of deck
By Alex Bunardzic
Copy of deck
- 836



