Dependencies Management

in
An Empirical Study of

Open source platform
Built on Chrome’s Javascript runtime V8
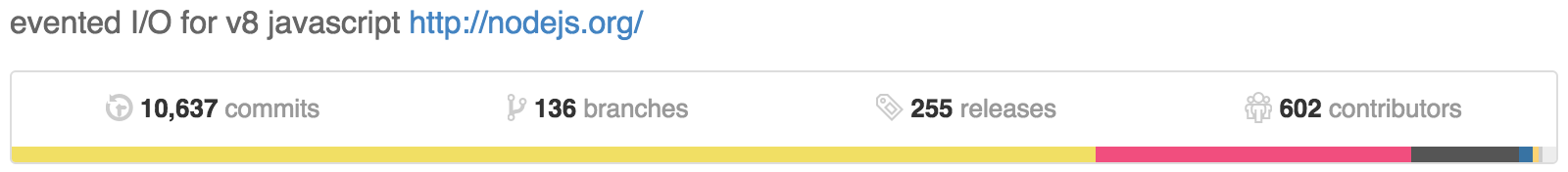
written in javascript & using CLI

$ npm install <package-name>
vs
Flat
Nested
A@1.0.0
|
+-- B@1.0.0
| |
| `-- D@1.0.0
|
`-- C@1.0.0
|
`-- D@1.0.0
A@1.0.0 | +-- B@1.0.0 | +-- C@1.0.0 | `-- D@1.0.0
A@1.0.0
|
+-- B@1.0.0
| |
| `-- D@1.0.0 \
| \
`-- C@1.0.0 > Conflict?
| /
`-- D@2.0.0 /
Semantic Versioning 2
MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH
Package.json
"dependencies": {
"primus": "*",
"async": "~0.8.0", // >= 0.8.0 < 0.9.0
"express": "4.2.x", // >=4.2.0 < 5.0.0
"vows": "^0.7.0", // >=0.7.0 < 1.0.0
"assume": "<1.0.0 || >=2.3.1 <2.4.5 || >=2.5.2 <3.0.0",
"winston": "git://github.com/flatiron/winston#master",
"bigpipe": "bigpipe/pagelet",
"plates": "https://github.com/flatiron/plates/tarball/master"
}
Dependency Tree
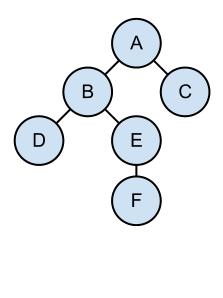
Dependency Tree
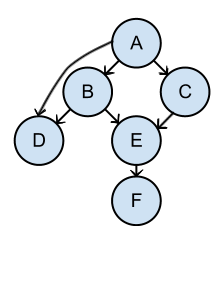
Dependency Tree
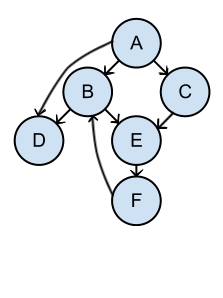
Dependency Tree
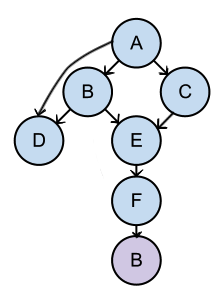
Model
Get the graph
by a Breadth First Search
Used 10 most starred modules, 10 most depended upon modules and 10 random modules as roots.
We explored over 90% of the packages in NPM registry.
http://registry.npmjs.org/MOD_NAME/VERSION

RQ1
What is the redundancy percentage in each node?
A@1.0.0
|
+-- B@1.0.0
| |
| `-- D@1.0.0 \
| \
`-- C@1.0.0 > Redundancy
| /
`-- D@1.0.0 /
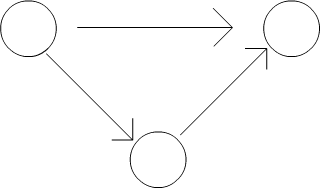
Find multiple routes
Using DFS
A@0.1
C@0.3
B@0.9
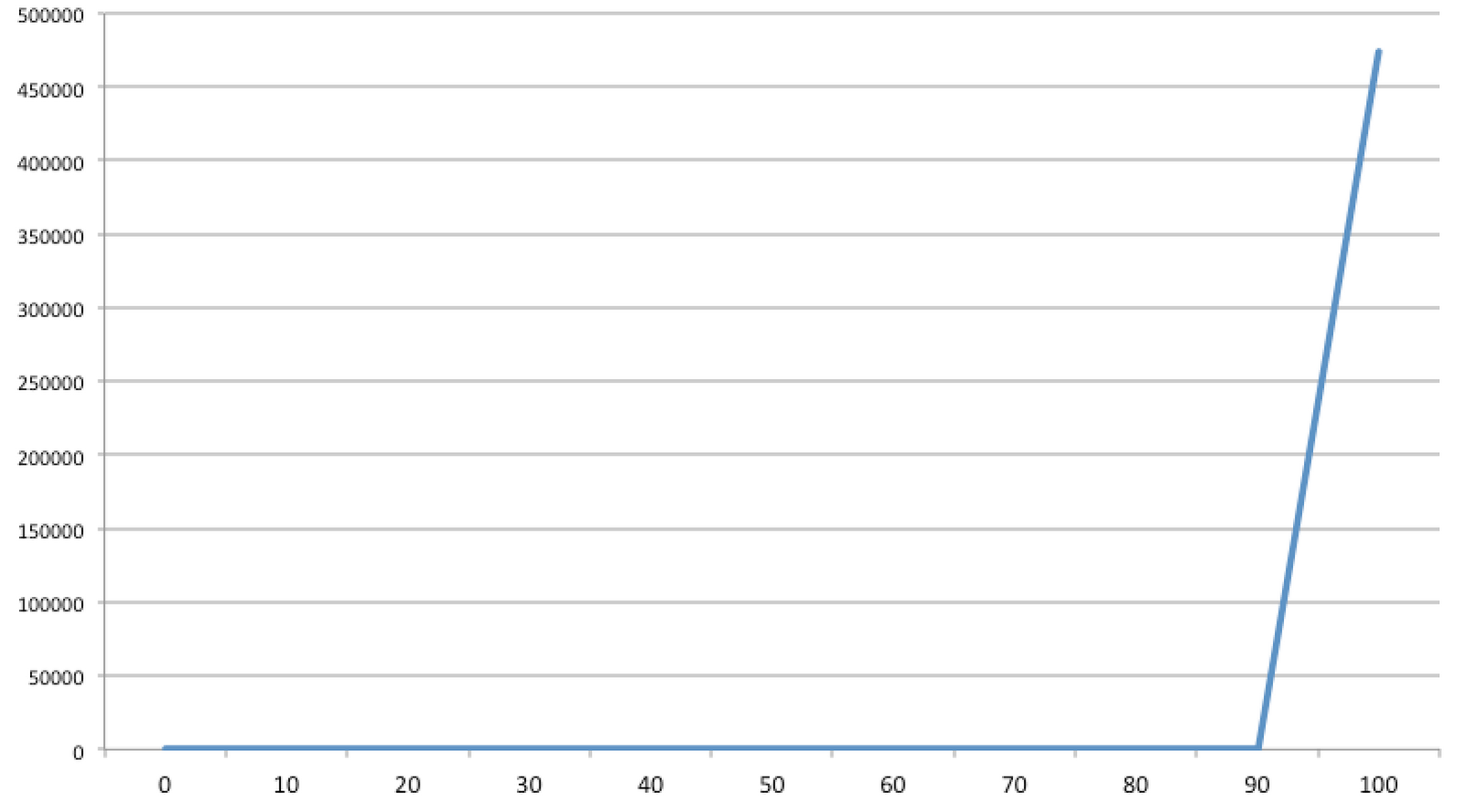
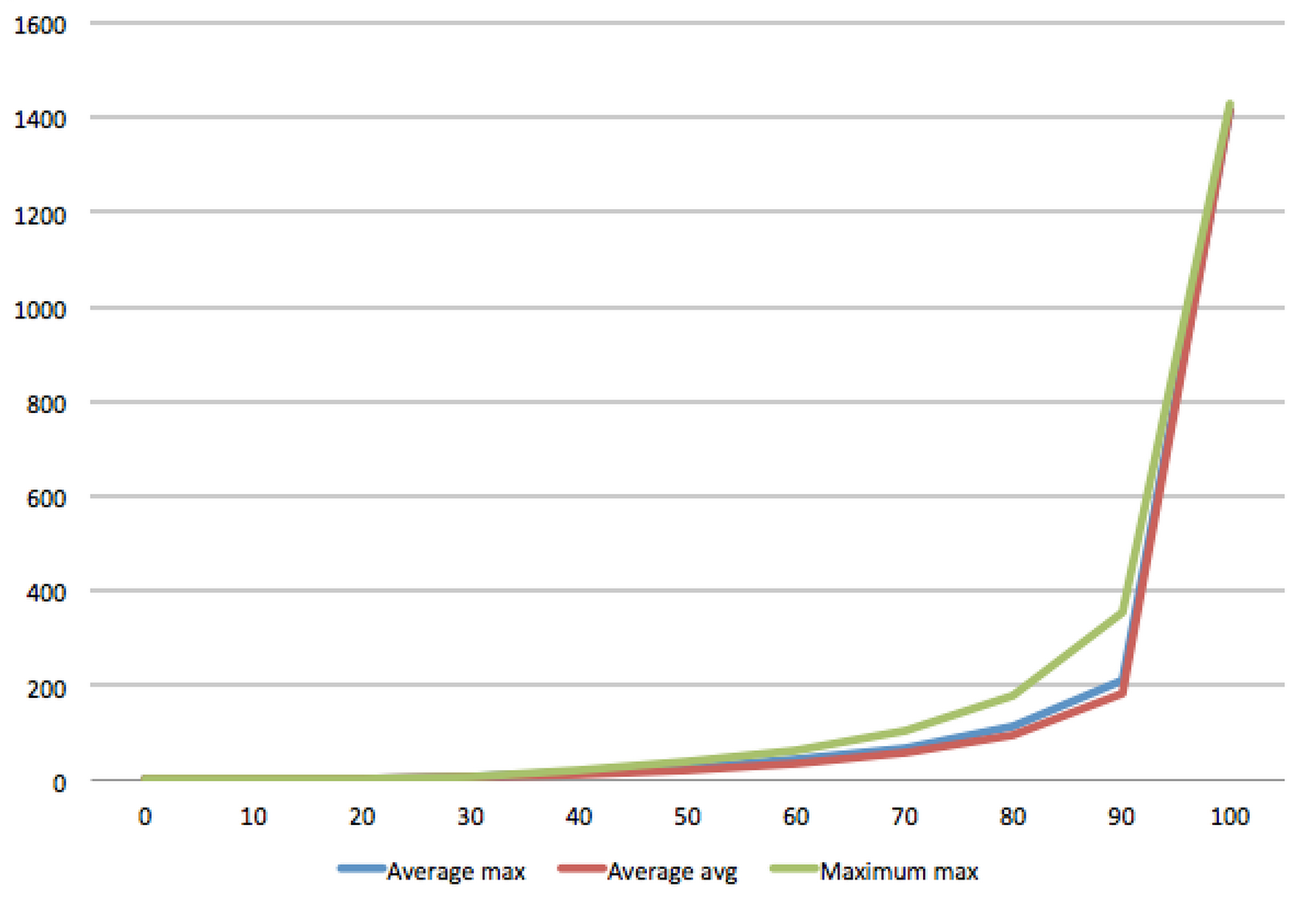
According to the results, about 52% of the NPM modules
have zero duplicate and roughly 90% of the packages have
less than a hundred duplicates. 75% of the modules have less
than 15 duplicates in their sub-tree.
RQ2
How long it takes for each module to update their
dependencies after an update in one of the dependencies?
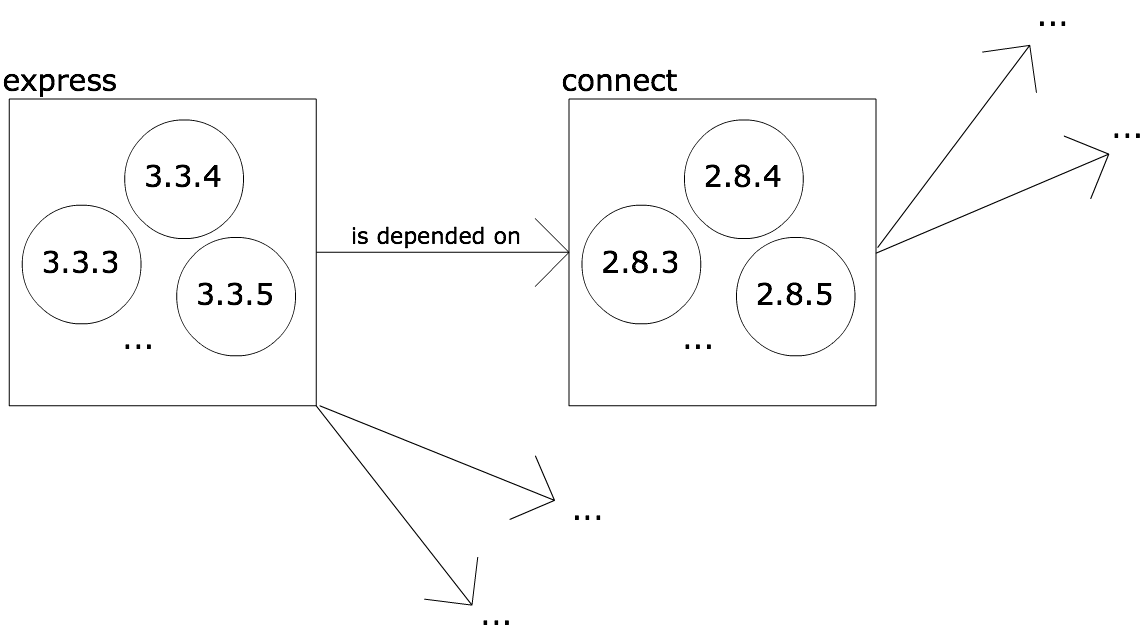
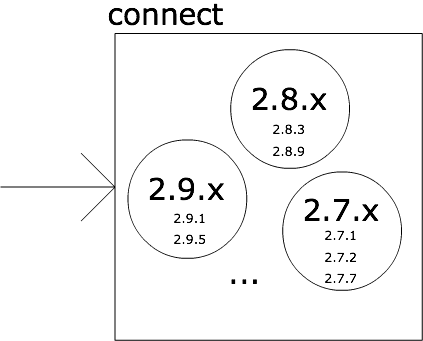
Group the versions
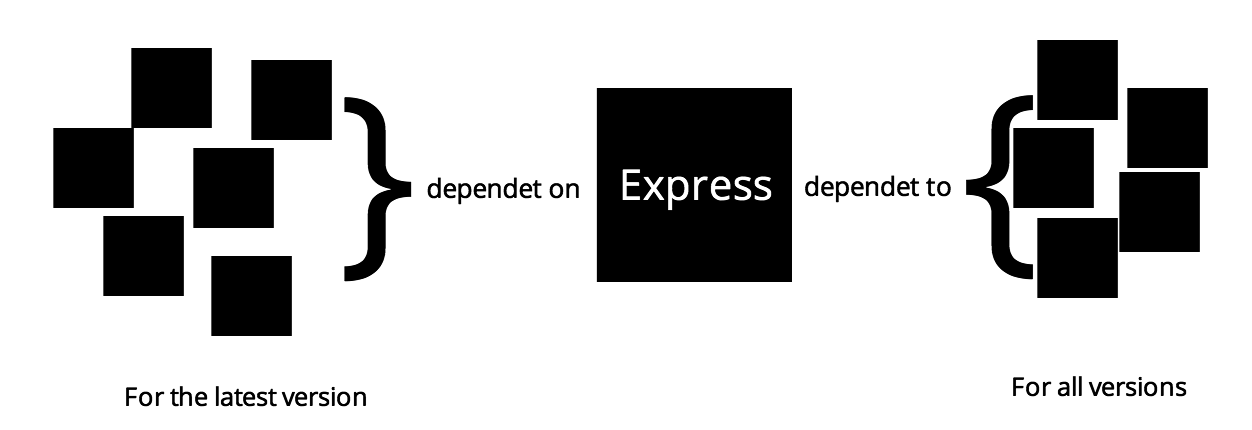
Express

For each release of each module
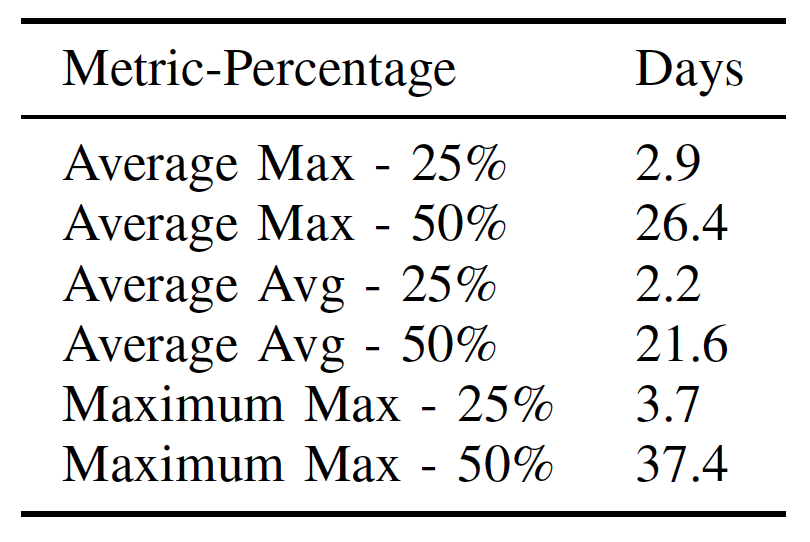
Average of propagation time
71.6
days
Average of maximum propagation time
82.4
days
RQ3
What are the common patterns in dependency tree
evolution and which changes have more contribution
in future bugs?
150 packages
based on the number dependents and availability of their git repository
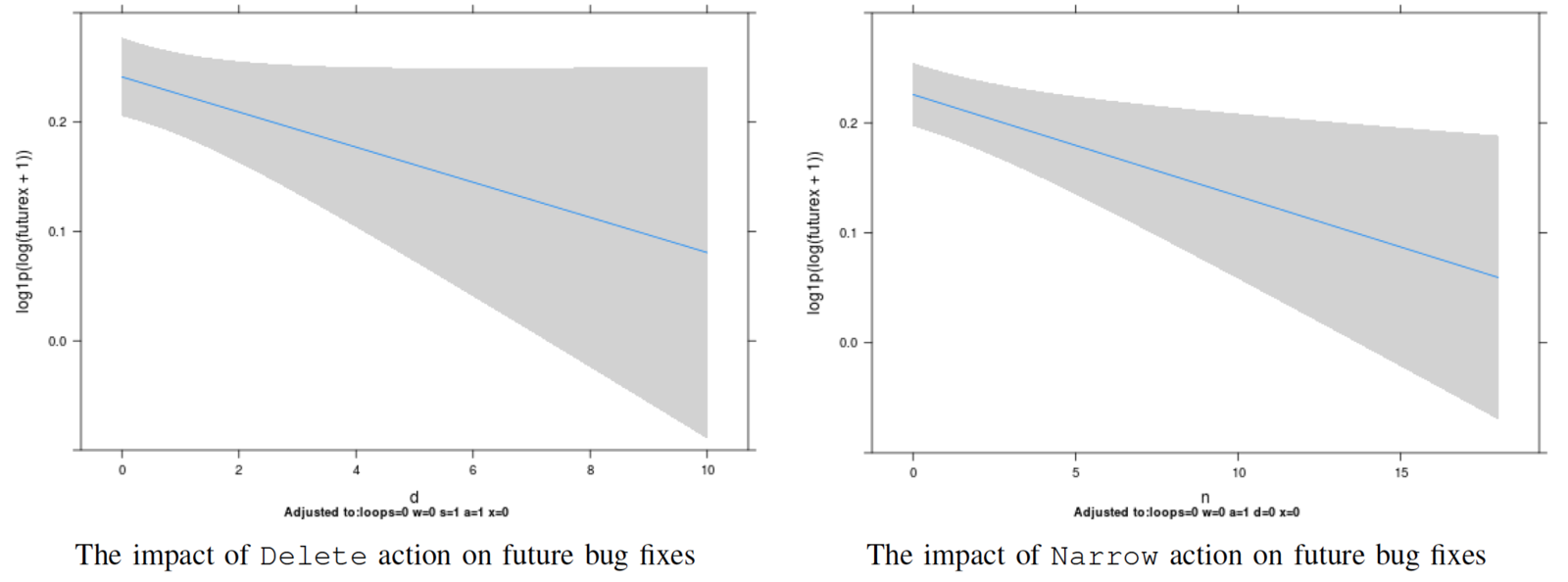
- A- add action – Shows if a dependency has been added to the package’s direct dependencies
- D- delete action – Shows if a dependency has been deleted from the package’s direct dependencies
- W- wide action – Shows if a dependency required version range became wider
- N- narrow action – Shows if a dependency required version range became narrower
- S- skip action – Shows if a dependency release has skipped (one or more releases of the dependency never adopted by the module)
- R- release action – Shows if the current change, includes a new minor release
- X- fix action – Shows if the current commit is a bug fixing commit
For Each release
the number of each action -> future bugs
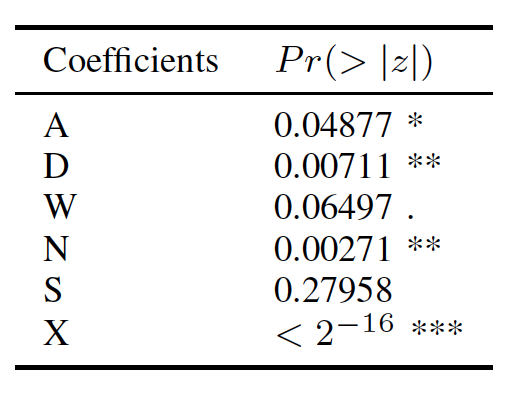
logistic regression model
Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) multiple regression
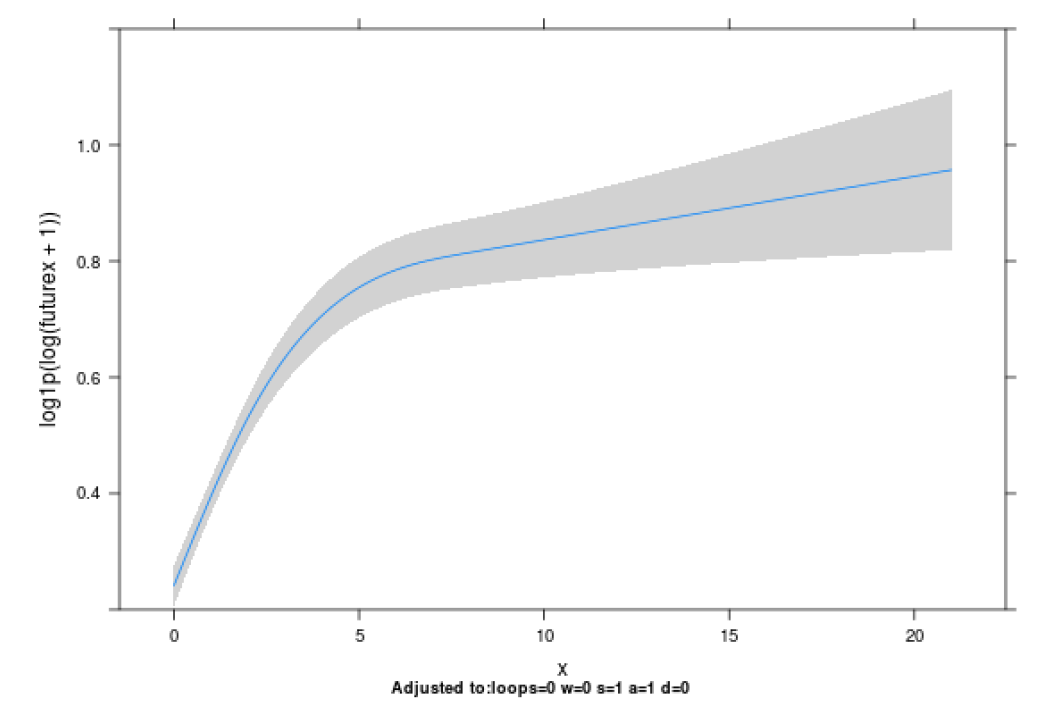
RQ4
How NPM Packages follow semantic versioning
rules?
npm view <package-name> versions
npm install <package-name>@<version>
- At least one function was present in the previous release and it is not in the new release
- The number of parameters of at least one function is less than the number of parameters of the same function in the previous release
Breaking changes
Naive approach
Limitations
- Global state and behavior
- Return type
- Object parameter
- Variable number of parameters
var f = function (options) {
// options.name
// options.age
}
f({
name: 'Amir',
age: 25
})
Object parameter
var f = function () {
// arguments.length
// argument[0], argument[1], ...
}
Variable number of args
25
random packages
from the most dependent upon packages
semver-breaking vs naive-breaking
naive-breaking covered 50% of semver-breaking
In average
43%
of releases of package were breaking within the same major number.
Conclusion
Duplicate in dependency tree
Big portion of the packages have small amount of duplicates
More than half of the packages have zero duplicates
Update ripple effect
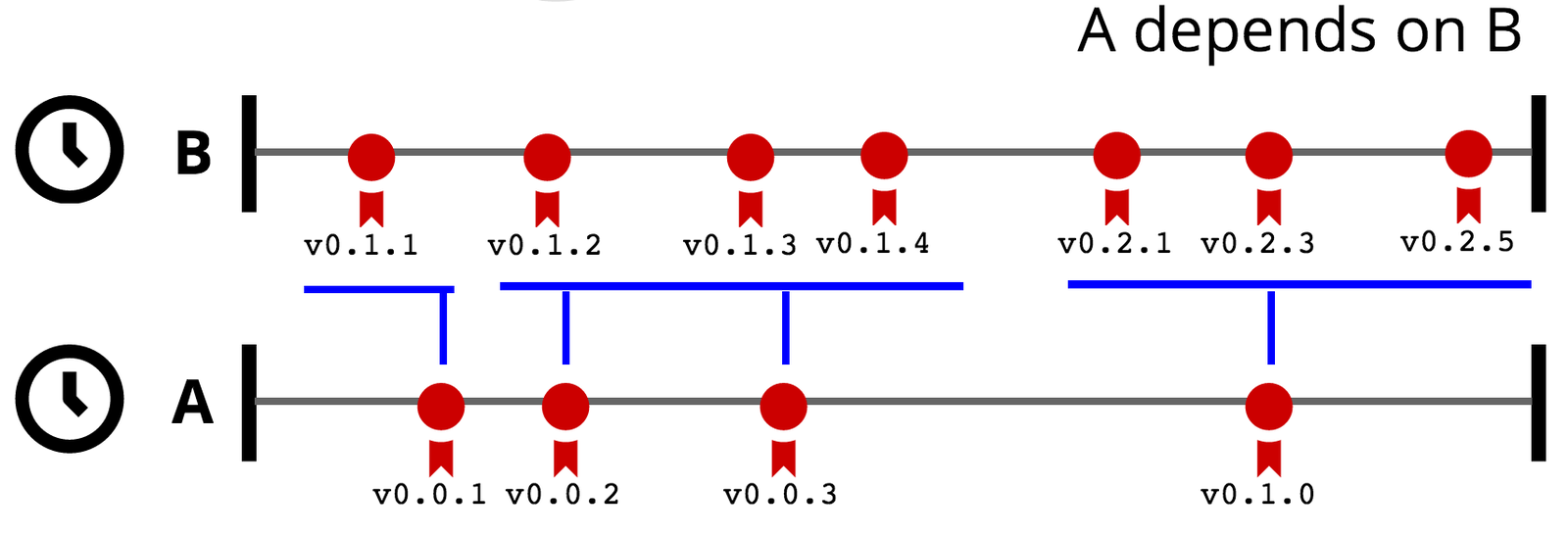
Three metrics. Distribution of the propagation time in each metric.
measured how many days it takes to a package update after one of its direct dependencies updated.
Common evolutionary patterns
categorized the changes at commit level.
Seven types of changes.
Contribution of each type in fixing future bugs.
Misusing of semantic versioning
Automated naive approach to detect breaking changes
to find a lower-bound for misusing semantic versioning in NPM.
npm
By amir
npm
- 1,263



