Angular Worksop
Setting up Webpack
Angular Worksop
Webpack
JS build systems
Grunt

- The JavaScript Task Runner
- focus on configuration
- build around a set of commonly used tasks
- extensions using plugins
- each plugin has its own custom configuration
- each task is an array of different plugin configurations, that get executed one after another in an independent sequential fashion
Gulp
- The streaming build system.
- focus on code
- micro tasks connected to each other (agnostic about their nature)
- extensions using plugins
- plugins have an API to program them
- streams and pipelines
- support for parallel tasks

Gulp
Use Gulp to:
- run tests and merge files
- compile Saas
- minify CSS/HTML
- bundle/uglify JS
gulp.task('test:unit', () => { /* Run unit tests */});
gulp.task('test:e2e', () => { /* Run selenium tests */});
gulp.task('test', ['test:unit', 'test:e2e']);
gulp.task('build:saas', () => { /* Compile Saas */ });JS Task runners
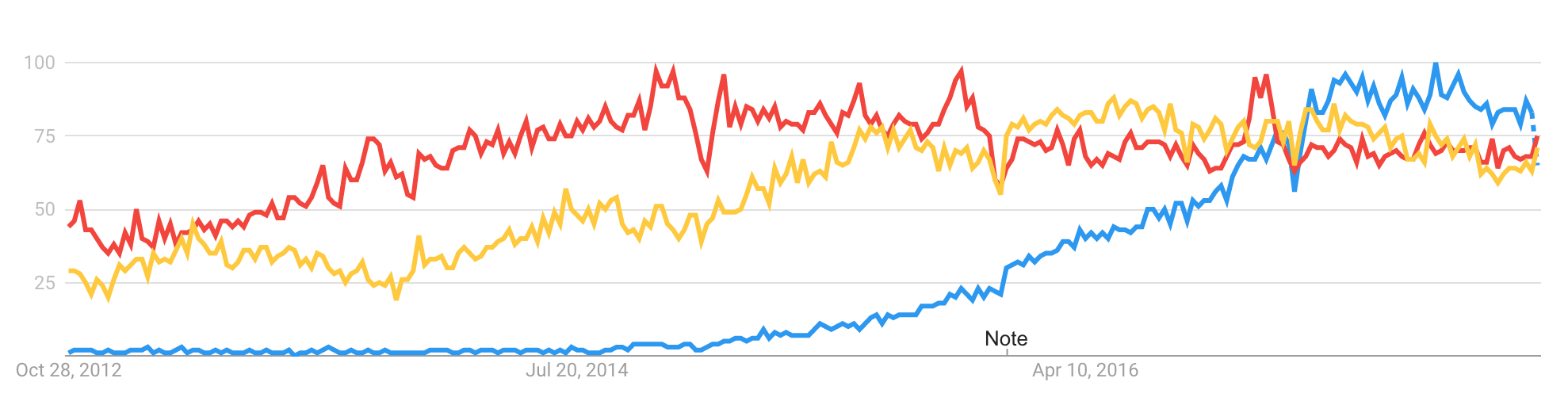
Webpack
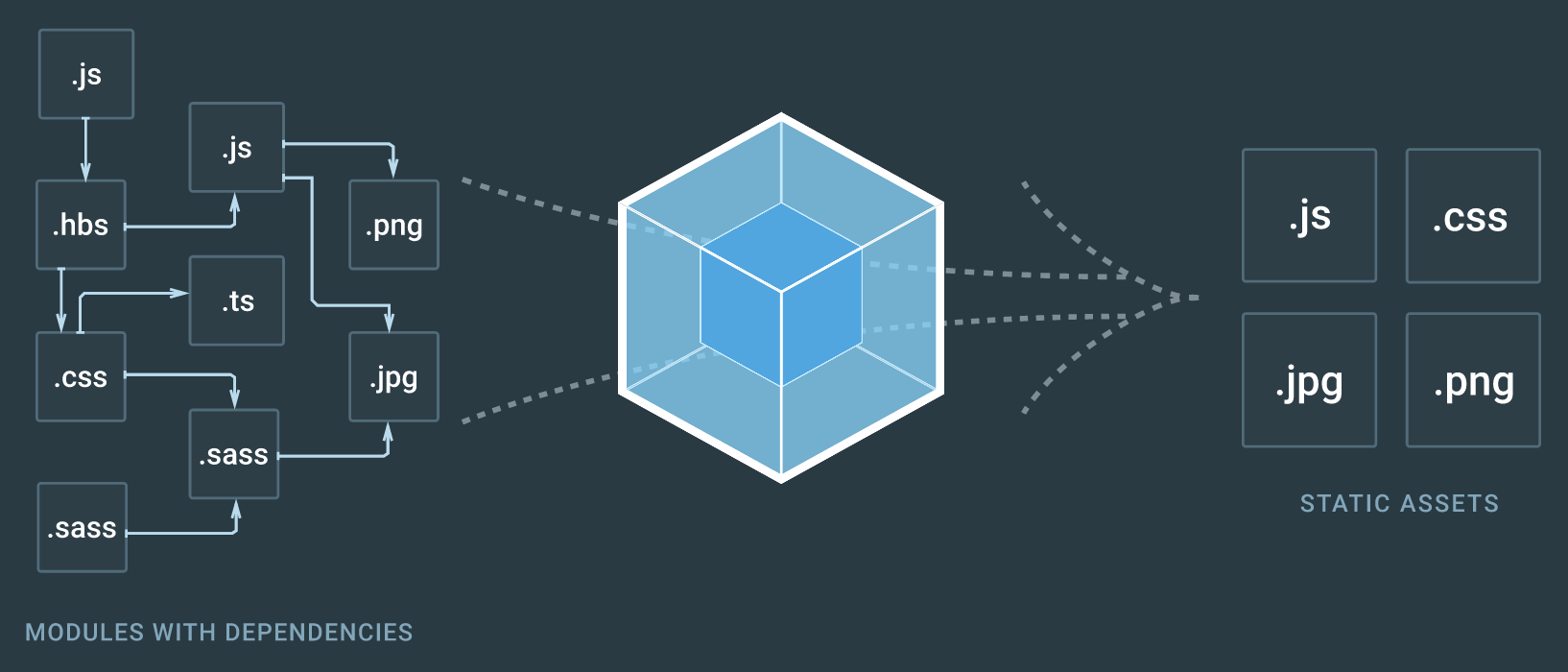
Webpack takes modules with dependencies and generates static assets representing those modules.
Webpack overview
Webpack
- Webpack is package bundler - it creates a single package for the web (Most of the time).
- It can also be called module bundler because it must understand module dependencies, and how to grab the dependencies and to bundle them together.
- Webpack is NOT a task runner
Webpack
There are 3 (main) things Webpack needs to know:
- The starting point of your application
- Which transformations to make to your code
- Where should it save the new transformed code
This is done in a file typically named webpack.config.js
npm install -g webpackWebpack
// webpack.config.js
// 1. Define the entry point in the application
const config = {
entry: ['./src/app.ts'],
// 2. Add a loader (processor for a file type)
module: {
rules:
[ {test: /\.ts?$/, use: ['ts-loader'] } ]
},// 3. Specify the output
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
}// 4. export the configuration
module.exports = config;A basic configuration:
Webpack
Webpack modules
- discrete chunks of code the application is broken into
- abstraction
- single responsibility
- reusability
- better debugging and testing
// mathFunctions.js
export function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
export function multiply(a, b) {
return a * b;
}// app.js
import {add} from './mathFunctions.js';
console.log(add(2,3));Webpack
Webpack modules
- dependencies are expressed by:
- import (es6)
- require() (commonJS)
- define() and require() (AMD)
- @import (css/sass/less)
- url() (stylesheet)
- <img src=""> (html)
Webpack
Loaders
- functions
- transform the source code of a module
- sync and async
- can be configured with options
- can be chained
- can emit additional arbitrary files
Webpack
Plugins
- "webpack backbone"
- "anything else the loader can't do"
- hooks into the webpack build process
- allows you to access, change, extend any phase of the build process from resolving a module to bundling the output
To sum up:
- loaders: tell webpack how to load a file of a certain type
- plugins: everything else
Webpack
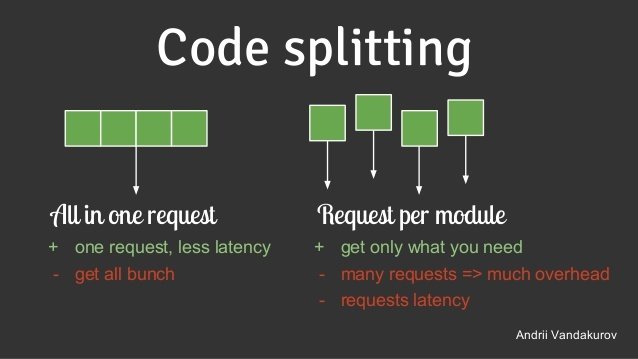
Webpack

Webpack
Code splitting
- split your code into various bundles
- smaller bundle sizes
- resource load prioritization control
- on-demand (lazy) loading
- performance impact
- build/rebuild time
- application load time
- freedom to choose which strategy suits you and your project best
Webpack
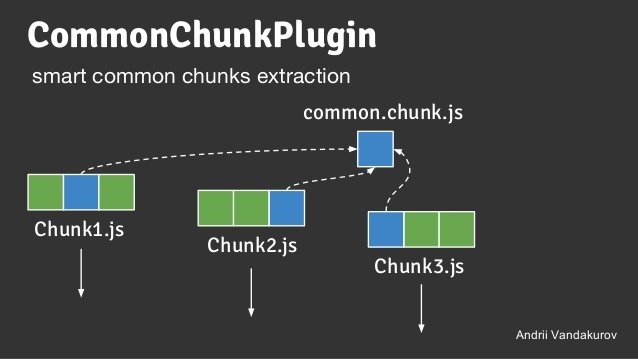
Code splitting
- css
- style-loader
- ExtractTextPlugin
- vendor
- CommonChunckPlugin
- lazy
- import()
- require.ensure()
Webpack
Webpack
Tree shaking
- positive code inclusion of actual used code (live-code)
- as opposed to exclusion of dead code (using UglifyJS)
- introduced in RollupJS
- makes sense only in module world
Limitations
- static analysis
- relies on es2015 module import/export
- cannot shake objects or inside statements
- can drop functions but not classes
Webpack
Running webpack - NPM Scripts
// package.json
{
...
"scripts": {
"start": "webpack -w",
"build": "webpack -p"
}
...
}// usage
npm start
npm run buildWebpack
Running webpack - NPM Scripts
- Run commands from local node_modules folder (update the $PATH variable)
- cross platform
- pre and post tasks (ex. prebuild )
- chain tasks using &&
- run concurrently using &
- sub tasks - run other npm scripts from a script
- namespacing (ex: test:ci )
NPM + Webpack -> best build tool
Assignment time
Angular Worksop - Webpack
By Andrei Antal
Angular Worksop - Webpack
- 1,593



