Introduction to
Web Development
bit.ly/2CWVlZi
Hello

Andrei Antal
@andrei_antal
Bucharest, Romania

- frontend engineer (since i can remember)
- web & JS technologies enthusiast
- perpetual learner
organizer for ngBucharest



@ngBucharest
groups/angularjs.bucharest
Course contents
Day 1
- Intro to web development
- HTML
- CSS Basics
Day 2
- CSS Layouts with Flexbox
- JavaScript Essentials
Day 3
- Advanced JavaScript (& jQuery ?)
- Responsive web design
Intro to web dev

...and then there was light


- The World Wide Web was invented by Tim Berners-Lee and developed at CERN in 1989-1990
- The first web browser was released to the public on August 1991
1991
- First Linux kernel released by Linus Torvald
- Intel 486 chip released
- Creative Labs releases first sound card
- Street Fighter 2 released
- Symantec releases Norton Anti Virus
- Terminator 2: Judgment Day released
- The Soviet Union dissolved - end of Cold War
- Start of Gulf War and Balkan War
- Nirvana releases Nevermind album
- Freddie Mercury died
The web close to day 10.000

The car at day 10.000

The TV at day 10.000
The phone at day 10.000
The human at day 10.000

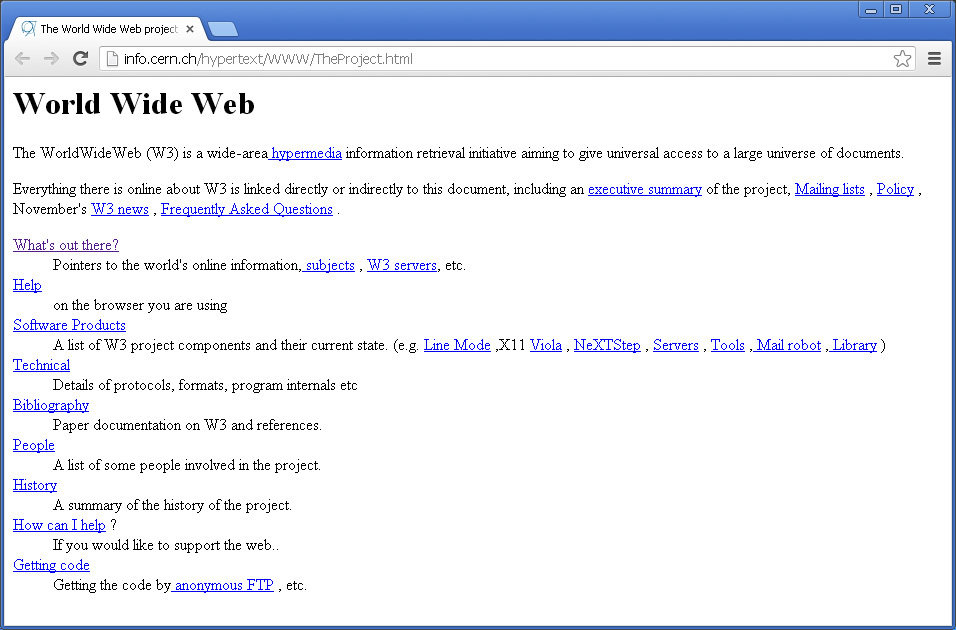
The first web page
First browsers


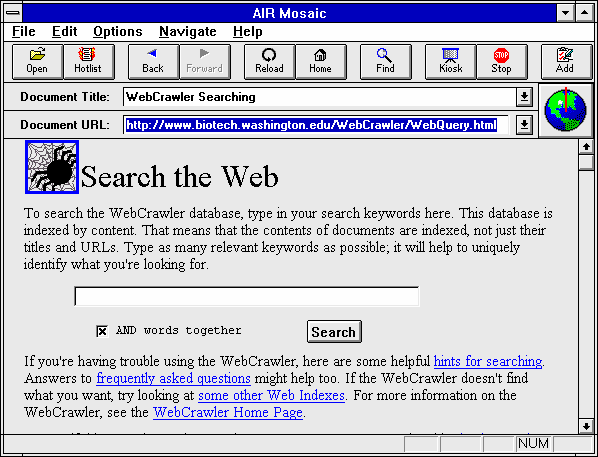
1993 - Mosaic browser - first commercial browser
1995 - Netscape and Internet Explorer
Early days
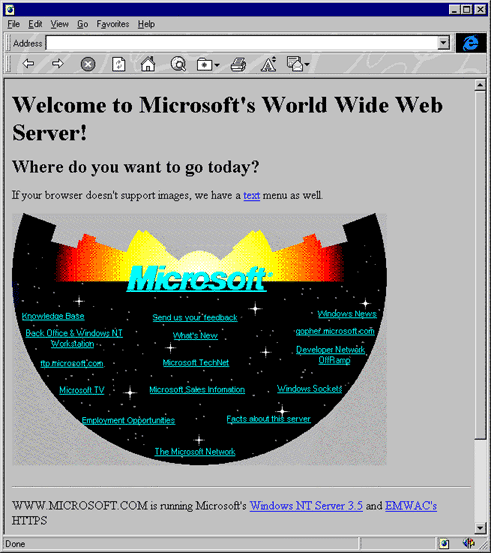
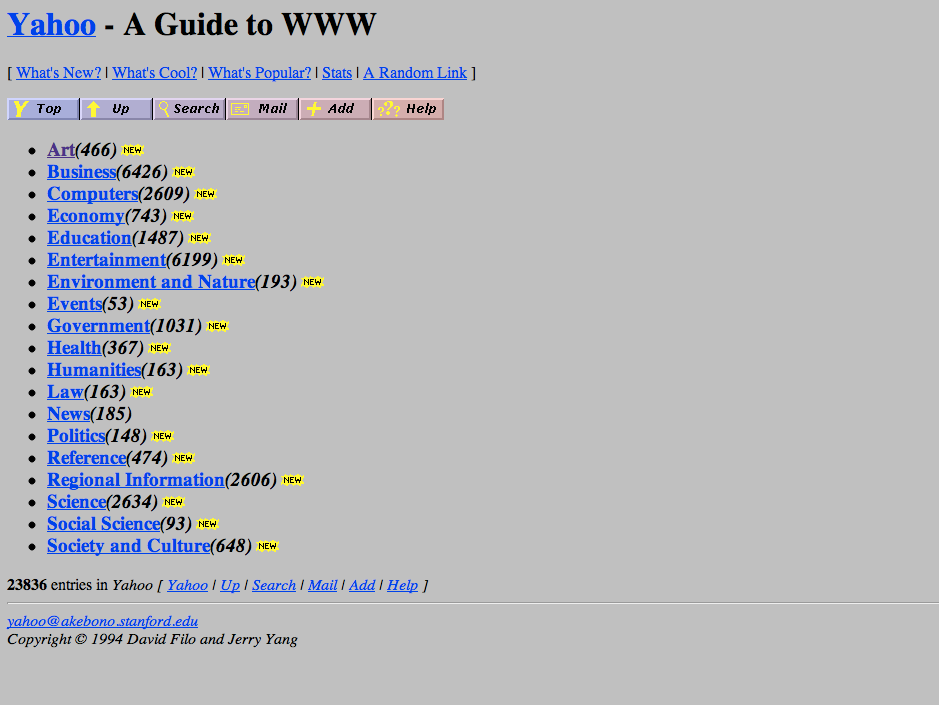
Second generation webistes
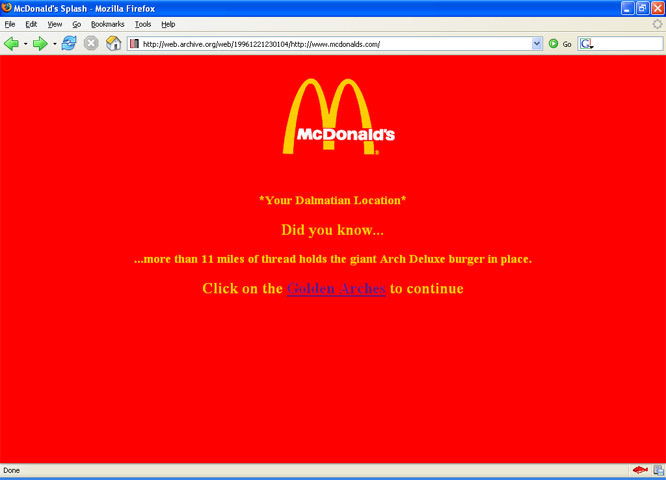
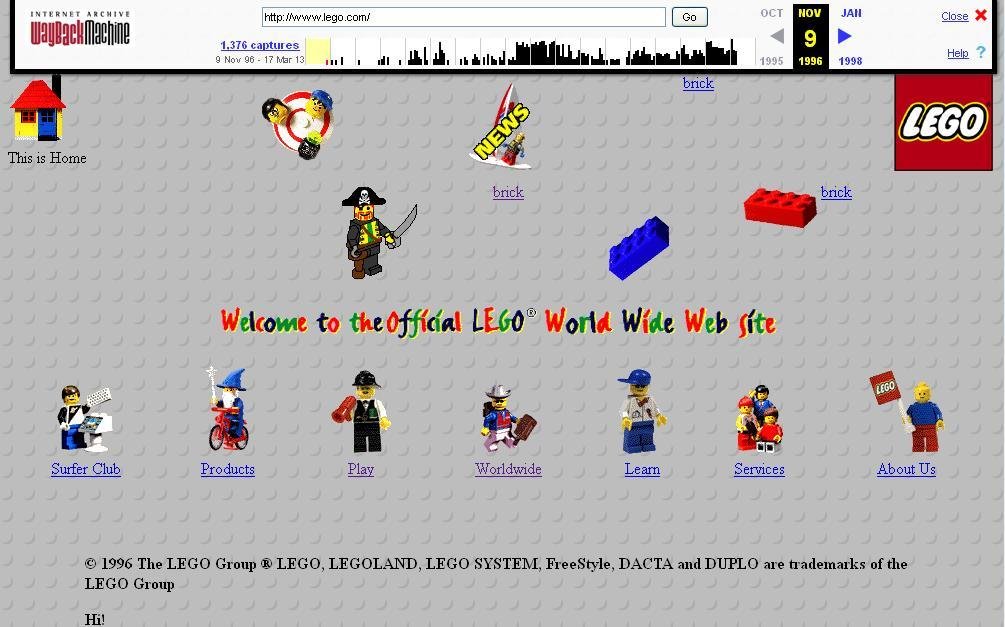
Design revolution

Table based layouts
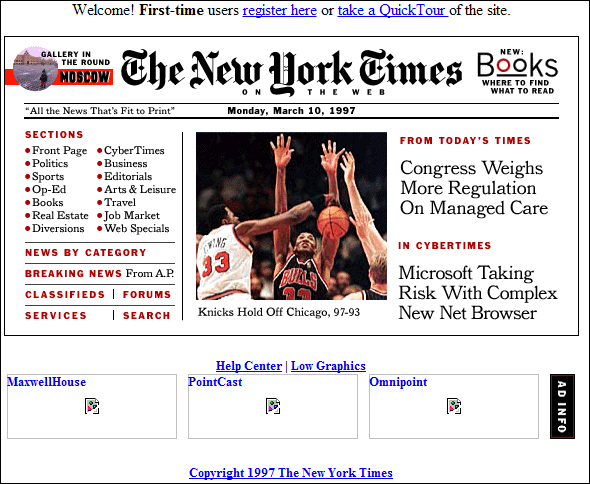

Spacer gif
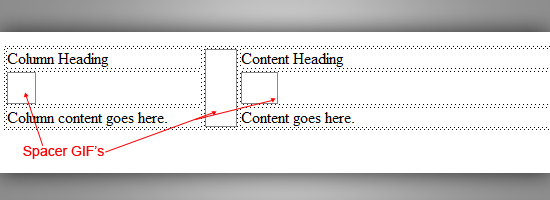
Table based layouts

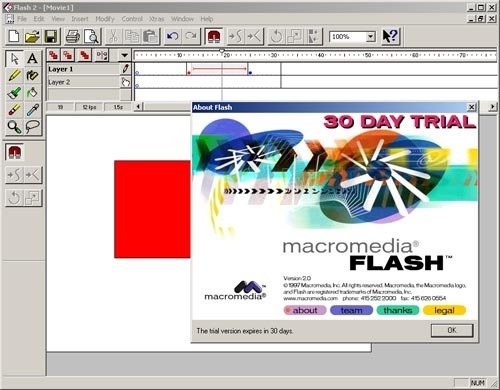
Macromedia Flash
Web tech timeline
- 1991 - HTML
- 1994 - HTML 2
- 1996 - CSS 1 + Javascript
- 1997 - HTML 4
- 1998 - CSS 2
- 2000 - XHTML 1
- 2002 - Tableless Web design
- 2005 - AJAX
- 2009 - HTML 5
- 2012 - CSS 3
The browser

Building blocks

Process
HTML
HTML

HTML
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a markup language used to tell your browser how to structure the web pages you visit.
<p> My name is Andrei </p>opening tag
closing tag
content
the emelement
- tag names are case-insensitive
HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello world</p>
</body>
</html>
- Basic HTML page
HTML
- Types of elements (main):
- Headings - h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6
- Paragraph - p
- Anchor - a
- Block container (division) - div
- Text container - span, em strong
- Lists - ol, ul, li
- Button - button
- Image - img
- Forms - form, input, textarea, select
- Table - table, th, tr, td
HTML
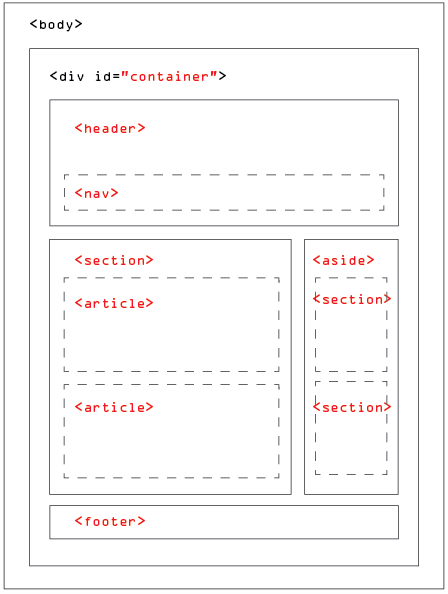
- Semantic elements
- header
- nav
- main
- section
- article
- aside
- footer
- figure
HTML
- Attributes
<div id="container"> ... </div>
<p class="details"> ... </div>
<a href="http://example.com"> link </a>
<input type="checkbox" checked>
<button disabled> Click </button>HTML
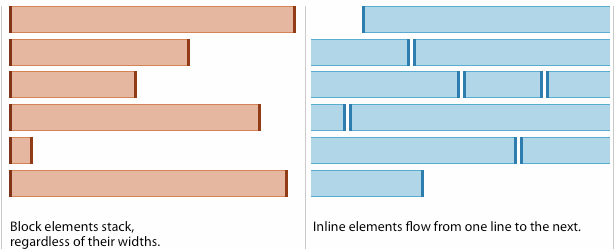
- Block vs inline elements

HTML
- Unordered list
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
...
</ul>- Ordered list
<ol>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
...
</ol>

HTML
- Images
<img src="image.png" alt="What the picture is about">- Anchors
<a href="http://example.com" target="_blank">link</a>- Video
<video controls width="250" height="300" src="vide.mp4">
Video not supported
</video>HTML
- Table
<table border>
<thead>
<tr>
<th colspan="2">The table header</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>row 1 column 1</td>
<td>row 1 column 2</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>HTML
- Forms
<form action="script.php" method="POST">
<label for="name"> user name: </label>
<input type="text" name="user-name" id="name">
<label for="user-password" id="password"> password </label>
<input type="password" name="user-password" id="password">
<label for="remember"> Remember me </label>
<input type="checkbox" name="remember-me" id="remember" checked>
<input type="submit" value="Log in">
</form>Aria and accesibility
- Roles (element type: menu, tab etc.)
- Properties (label etc.)
- States (hidden or selected)
CSS Basics
Intro
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a declarative language that controls how web pages look in the browser.
- a set of rules that describe the visual properties of elements look on a page; rules are organized in stylesheets
- the rules are targeted to DOM elements through selectors
- the style cascade and specificity decides which rules apply when multiple selectors match an element
Intro

CSS RULES
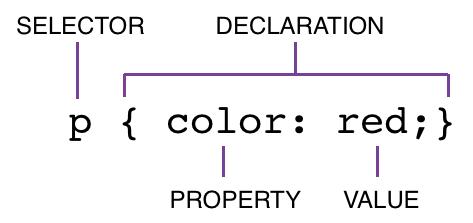
Including CSS
- Inline
- style tag
- external file
<p style="color:red;">Hello world</p><head>
<style>
p {
color: red;
}
</style>
</head><link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">CSS Selectors
- tag
- class
- id
div {
color: red;
}#main {
color: red;
}p {
color: red;
}.content {
color: red;
}.green {
color: green;
}CSS Selectors
- Chaining Selectors
h1 {
color: red;
}
h1.myHeading {
color: blue
}<h1>First Title</h1>
<h1 class="myHeading">Second Title<h1>
<h1>Third Title<h1> 
CSS Selectors
- Nesting Selectors
.myList li {
color: red
}<ul class="myList">
<li>Colored element</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>element</li>
<ol>
Specificity

Specificity
h1 {
color: red;
}
.headline {
color: blue;
}
#myText {
color: green
}<h1 class="headline">Title 1</h1>
<h1 class="headline" id="myText">Title 2</h1>
!important
- Nesting Selectors
.myClass {
color: red !important;
}
#special {
color: blue;
}<p class="myClass">
Some text goes here
</p>
<p class="myClass" id="special">
Some other text
</p>
CSS selectors
- Multiple selectors
body {
font-size: 40px;
}
h1, p {
color: red;
}<h1>
Some title
</h1>
<p>
Some text
</p>
Styling text 1
- Basic text properties
p {
color: red;
font-family: Arial;
/* font-family: "Courier New"; */
font-size: 24px;
font-weight: bold;
/* font-weight: 700; */
}
Styling text 1
- Centering
div {
text-align: center; /* left | right */
}
Color
- text-color
p {
color: red;
}- background-color
p {
background-color: red;
}
Color
- Hexadecimal
p {
color: #0000FF; /* blue */
}- RGB(A)
p {
color: rgb(0,0,255); /* blue */
color: rgba(0,0,255, 0.5);
/* blue + 0.5 transaprency */
}

Color
- HSL (Hue-Saturation-Light)

p {
color: hsl(240, 100%, 50%);
/* blue */
color: hsla(240, 100%, 50%);
/* blue + 0.5 transaprency */
}Opacity
p {
opacity: 0.33;
}
Background
div {
background: red;
background: no-repeat center/80% url("image.png");
background: url("test.jpg") repeat-y;
}Box-model

Box-model
- width/height
div {
width: 200px;
min-width: 100px;
max-width: 400px;
height: 400px;
min-height: 100px;
max-height: 600px;
}Box-model
- border
div {
border: 1px solid red;
border-radius: 16px;
}
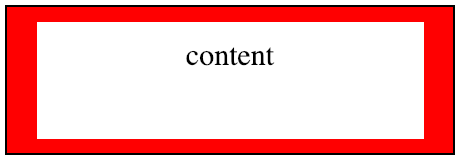
Box-model
- padding
div {
padding-top: 10px;
padding-right: 20px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
padding-left: 20px;
/* shorthand versions */
padding: 10px 20px 10px 20px;
padding: 10px 20px;
}
Box-model
- margin
div {
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 20px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
margin-left: 20px;
/* shorthand versions */
margin: 10px 20px 10px 20px;
margin: 10px 20px;
}
Box-model
- margin-collapse

Box-model
- overflow
- visibility
div {
display: none; /* not rendered, not visible */
visibility: hidden; /* rendered, not visible */
}div {
overflow: scroll-y;
}Box-model

Box-sizing

div {
box-sizing: border-box;
}Document flow
- Element positioning
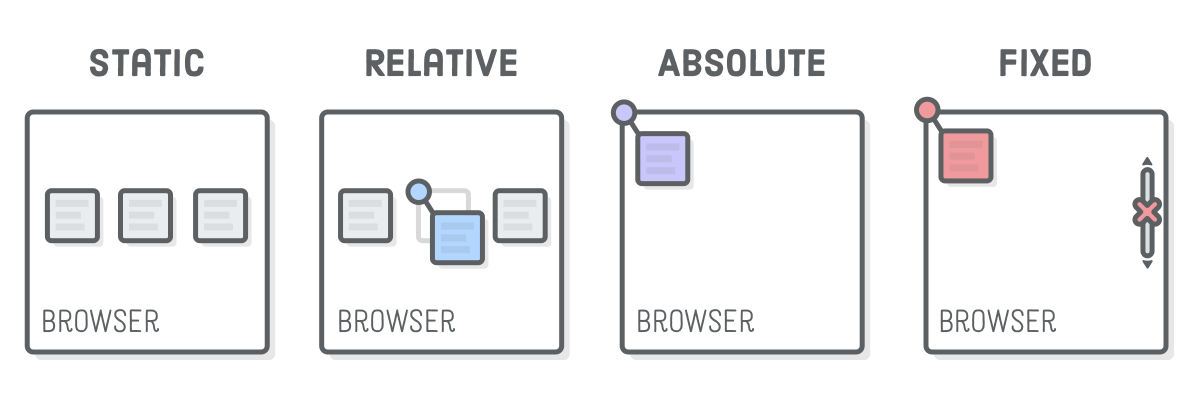
div {
position: relative;
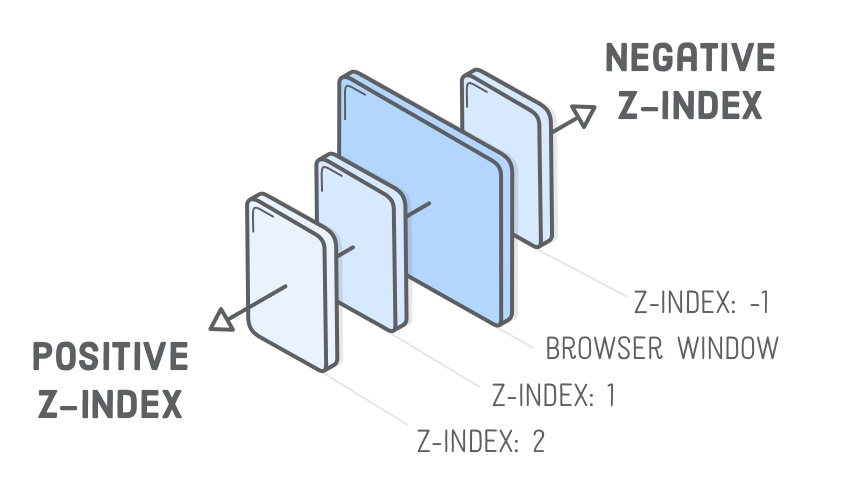
}Document flow
- Z-index
div {
z-index: 2
}
Document flow
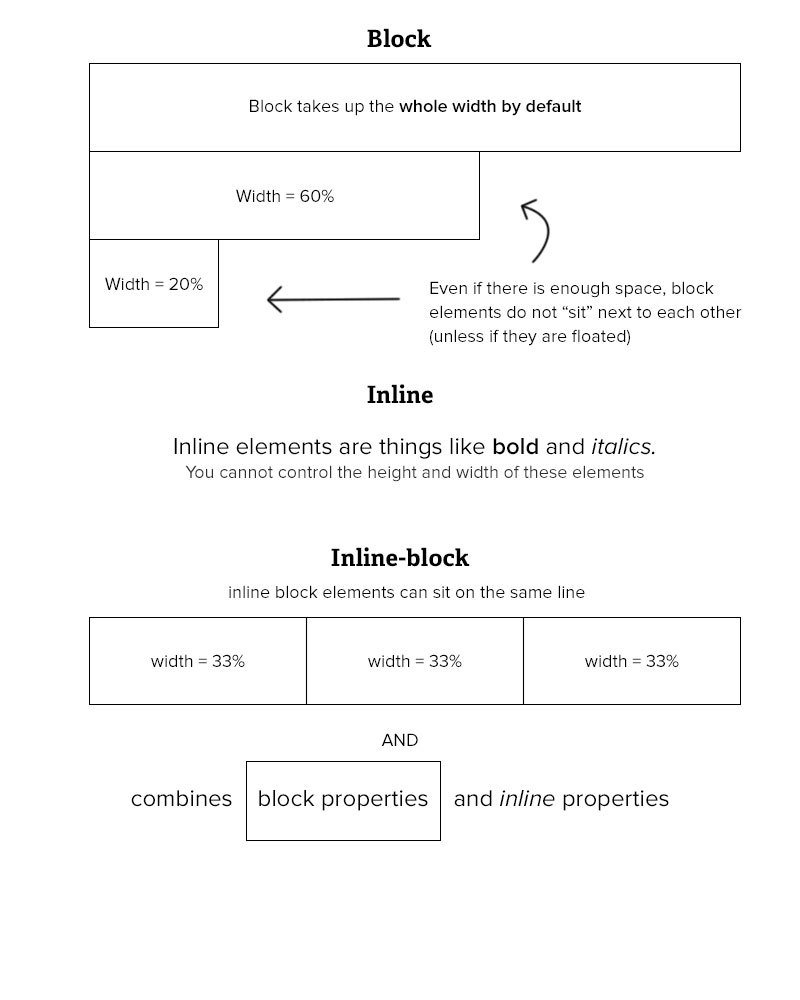
- Display
div {
display: inline-block
}
Document flow
- Float
div {
float: right;
}
div {
clear: left;
}
CSS Measurements

CSS Measurements

CSS Measurements
div {
/* property: calc(expression) */
width: calc(100% - 80px);
}Styling text 2
- font-family
- font-weight
- font-style
- word-spacing
- letter-spacing
- text-transform
Styling text 2

Styling text 2

Other stylings
ul {
list-style: none;
}- Styling lists
button:hover {
color: blue;
}- Mouse over behaviour
a {
text-decoration: underline;
}- Styling anchors
a:visited {
color: green;
}Pseudo-classes
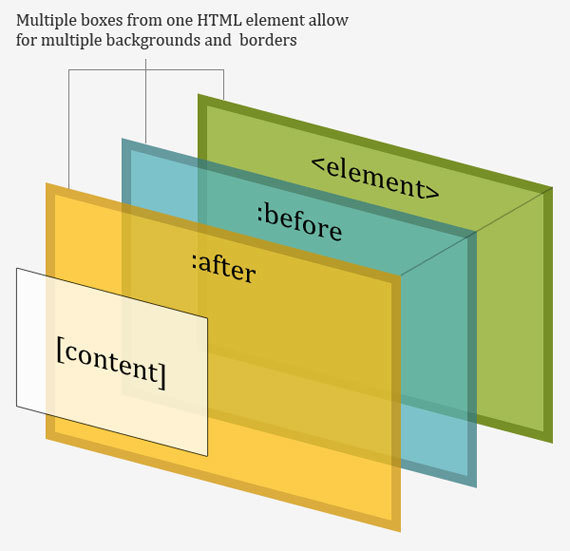
a::after {
content: "→";
}
a::before {
content: "♥";
}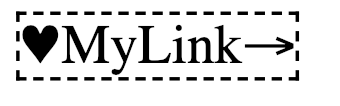
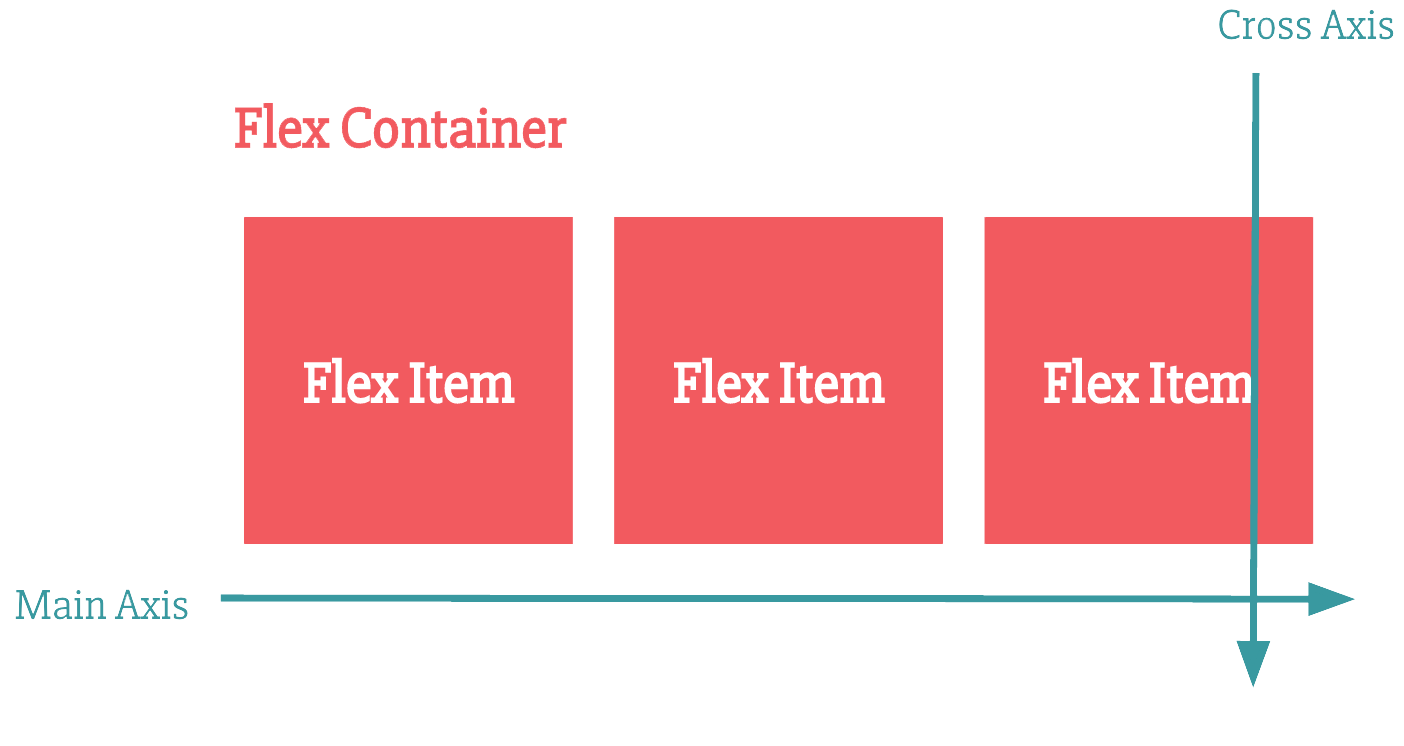
CSS Layout
Flexbox
Basis of layout
Float

img {
float: right;
margin: 0 0 1em 1em;
}Basis of layout
Clearfix
.clearfix {
overflow: auto;
}

Basis of layout
Float layout
nav {
float: left;
width: 200px;
}
section {
margin-left: 200px;
}nav.clearfix
section
section
Basis of layout
Inline-block layout
.nav
section
section
.nav {
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: top;
width: 25%;
}
.column {
display: inline-block;
vertical-align: top;
width: 75%;
}.column
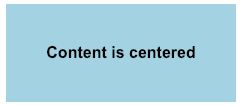
Centring content
Using padding
div {
padding: 20px;
display: inline-block;
}Vertical centring - fixed size
div {
width: 100px;
height:100px;
}
.center {
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
text-align: center;
}

Color codes:
- #3a3a3a
- #717171
- #e8e9e8
- #ee8f3c
- #d8a77a
Flexbox

Flexbox
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Red</div>
<div class="item">Orange</div>
<div class="item">Yellow</div>
<div class="item">Green</div>
<div class="item">Blue</div>
</div>
Flexbox
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Red</div>
<div class="item">Orange</div>
<div class="item">Yellow</div>
<div class="item">Green</div>
<div class="item">Blue</div>
</div>.container {
display: flex;
}
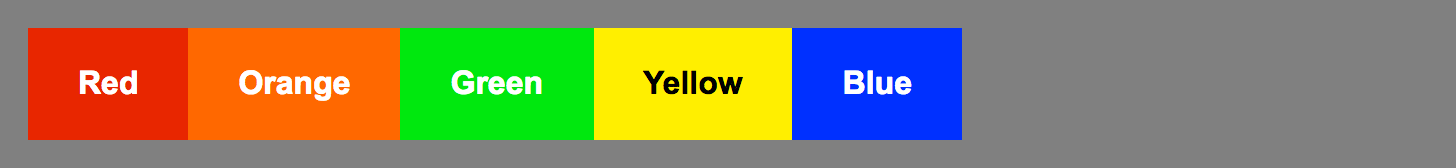
Flexbox
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Red</div>
<div class="item">Orange</div>
<div class="item">Yellow</div>
<div class="item">Green</div>
<div class="item">Blue</div>
</div>.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column; // row is the default
}

Flexbox
Flexbox
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Red</div>
<div class="item">Orange</div>
<div class="item">Yellow</div>
<div class="item">Green</div>
<div class="item">Blue</div>
</div>.container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row-reverse;
}

Flexbox

Flexbox
.item:nth-child(5) {
order: -1;
}
.item:nth-child(2) {
order: 1; /* default is 0 */
}
Flexbox
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Red</div>
<div class="item">Orange</div>
<div class="item">Yellow</div>
<div class="item">Green</div>
<div class="item">Blue</div>
</div>.container {
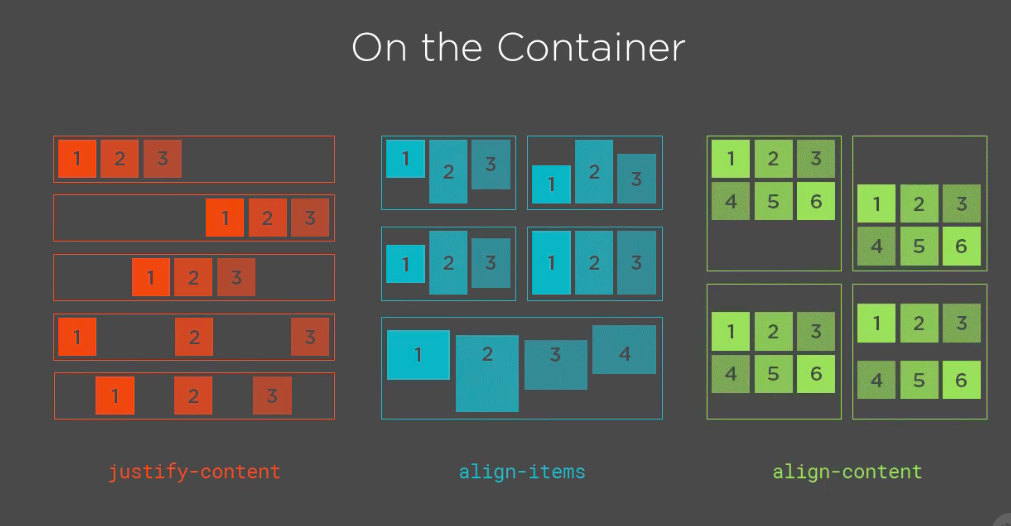
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}

Flexbox
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Red</div>
<div class="item">Orange</div>
<div class="item">Yellow</div>
<div class="item">Green</div>
<div class="item">Blue</div>
</div>.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
}

Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
height: 200px;
align-items: stretch; /* default */
}
Flexbox

Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
height: 200px;
align-items: flex-end;
}
.item:nth-child(3) {
align-self: stretch;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
height: 200px;
}
.item {
margin: auto;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item:nth-child(1) {
margin: auto;
}
.item:nth-child(2) {
margin: auto;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item:nth-child(4) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item:nth-child(4) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
.item:nth-child(5) {
flex-grow: 2;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.item:nth-child(7) {
flex-shrink: 4;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-basis: 60px;
}
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-basis: 60px;
}
.item:nth-child(1) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
}
.item {
flex-basis: 60px;
}
.item:nth-child(1) {
flex-grow: 1;
}
Flexbox
Flexbox
.item {
flex-grow: 1;
flex-shrink: 1;
flex-basis: auto;
}
/* equivalent to */
.item {
flex: 1 1 auto;
}Flexbox

Flexbox
.container {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
}
.item {
flex: 1 0 150px;
}
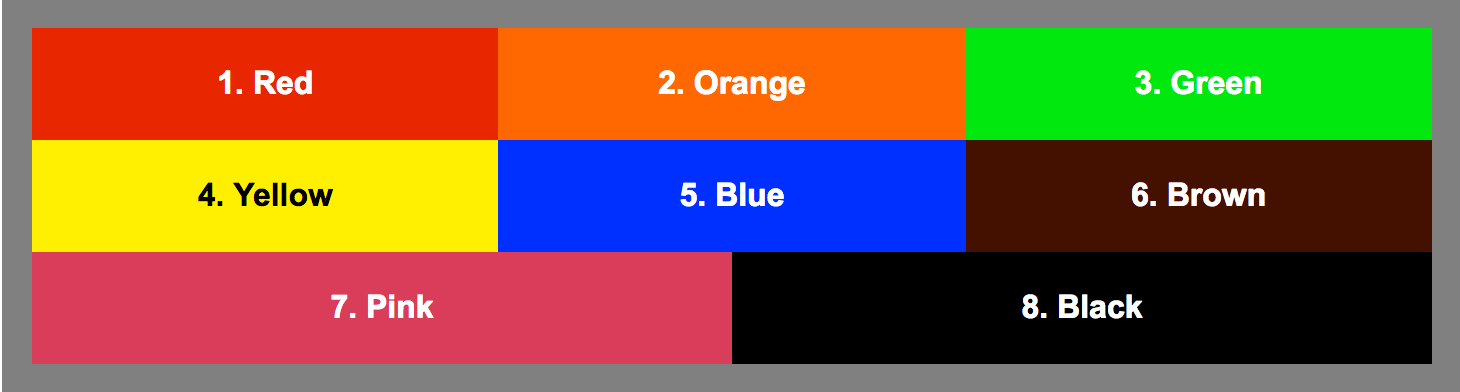
Flexbox

Flexbox
Flexbox

Let's play a game

JavaScript Essentials
History lesson
Including JS in your Webpage
1. In HTML, within a <script> tag
2. Linking to an external file
<script>
// JS Code
</script><script src="path/to/my/script.js"></script>// script.js
// JS CODEIncluding JS in your Webpage
-
Handling browsers that don’t support JavaScript
<noscript>
Your browser does not support JavaScript so page
functionality will be significantly reduced.
</noscript>-
Controlling loading style of script files:
- async - script is executed asynchronously while the page continues the parsing.
- defer - script is executed after the page has finished parsing.
Myth:
JavaScript is a scripting, interpreted language
Reality:
JavaScript engine compiles and immediately runs the code
Statements
x = y + 10;literal
value
addition
operator
variable
(identifier)
assignment
operator
expression
Expressions
3 + 4 * 53 + (4 * 5)(3 + (4 * 5))Statements
1. var a = 2;
2. var b = 3;
3. a = b * 2;
4. b = b / 4;
5. var c = a + b;- List of statements - executed in order
1. {
2. var a = 1;
3. var b = 2;
4. a = a + b;
5. }- Grouping statements using { } - blocks
Primitive data types
1. Numbers
-
4, 24, 1034032, 4.56 etc.
- up to 2^53
- Special types of numbers:
-
NaN, -Infinity, Infinity
-

Primitive data types
2. Strings
- A collection of characters used to represent text
- Enclosed by single (') or double (") quotes
"This is some string"
'This is another string'
"And they're both great!"
"And then she said: \" Whoaaa! \"."Operators
1. Addition ( + )
3 + 2 // => 5
'I am ' + 'the one!' // => 'I am the one'
1 + '2' // => 12
"I'm number " + 1 // => "I'm number 1"
Operators
2. Multiplication (*), Substraction (-) and Division ( / )
3 * 2 // => 6
4 / 2 // => 2
8 - 5 // => 3
'3' * 2 // => 6 , same for 3 * '2'
'a' * 2 // => NaN - conversion failed
'a' - 'a' // => NaN
Primitive data types
3. Booleans
- A True/False value using the true and false keywords
- Falsey values
var myTrueVar = true;
var aFalseVar = false;false
0 (zero)
'' or "" (empty string)
null
undefined
NaNOperators
3. Equality (==, === and !=, !==)
1 == 1 // => true
'abc' === 'abc' // => true
1 == '1' // true
1 === '1' // false
1 !== '1' // true
1 < 2 // true
2 >= 3 // false
Operators
3. Logical operators: and (&&), or (||), and not (!).
'Apples' == 'Oranges' && 5 > 3 //
5 > 10 || 4 < 2 //
3 < 10 && 10 > 8 //
7 > 5 || 1 > 2 //
!(7 > 5 || 1 > 2) // Comments
// Single line comment
var a = 1; // inline comment
/*
This is a
multiline comment
*/
var b /* inserted comment */ = a + 1;Declarations and variables
var myVariable; // value is undefined- Declaring a variable
var myVariable;
myVariable = 42;- Assigning a value to a variable
var myVariable = 42;
var myOtherVariable = myVariable / 2;- Using a variable
var myNumber = 42;
myNumber = 'forty two';- Variables are dynamic
Naming variables
Variable names:
- Can contain numbers, but they cannot begin with a number
-
Must not contain mathematical or logical operators.
-
Must not contain any punctuation marks of any kind other than the underscore (_) and dollar sign ($).
-
Must not contain any spaces
-
Must not be JavaScript keywords, but they can contain keywords
-
Are case-sensitive
Blocks
{
statement_1;
statement_2;
.
.
.
statement_n;
}Block statements are used to group statements together
Conditionals - if
if (condition) {
// code block if contition evaluates to true
}The else clause
if (condition) {
// contition is true
} else {
// condition is false
}Multiple conditions
if (condition1) {
// contition1 is true
} else if(condition2) {
// contition2 is true
} else { // condition1 AND condition2 is false }Conditional programming
-
Determining whether a variable has a value
var myVar = someOtherVar || 'Default value';-
Default value for potentially uninitialised variable
if (myVar) {
// myVar has a valuse set
}
else {
// myVar has no value or the value is falsey
}Loops - while
while (condition) {
// code gets executed as long as
// condition evaluates to true
}- do...while - code gets executed at least once
do {
// code runs once
// and then gets executed as long as
// condition evaluates to true
} while (condition)Breaking out of loops
var a = 0;
while (true) {
if( a >= 5 ) {
break;
}
a = a+1;
}Loops - for
for ([initialExpression]; [condition]; [incrementExpression]) {
// code gets executed as long as
// condition evaluates to true
}for (var variable=startvalue; variable < endvalue; variable = variable + increment) {
// code to be executed
}for (var i=0; i<5; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
// 0 1 2 3 4Using the for loop for iterations
Handling errors
try {
var a = 2 / b; // b is not defined
}
catch(e) {
alert('The following error occurred: ' + e.message)
}
finally {
alert('Finally block executed')
}- Catching code errors
throw 'Error2'; // String type
throw 42; // Number type
throw new Error('something happened') // Error object- Throwing custom errors
Functions
- Declaring a function
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}declaration
keyword
function name
function parameters
function return value
- Using (invoking) a function
var a = 1;
var b = 2;
var myVar = add(a, b);arguments
assignment to function return value
Block scoped variables
condition = false;
if( condition ) { // block code not run
var a = 10;
}
console.log(a); // 10- Block scoping variable declarations - let
condition = true;
if( condition ) { // block of code is executed
let a = 10;
}
console.log(a); // Error: a is not definedBlock scoped variables
- Block scoped constant variables - const
const a = 1;
a = 2; // TypeError: Assignment to constant variable.
const b; // SyntaxError: Missing initializer in declarationFunction scope
var addition = 10; // defined in global scope
function processNumber(num) {
var multiply = 2; // function scoped variable
// available only in function
// block - {}
// OK: use external scoped variable 'addition'
return (num * multiply) + addition;
}
var res = processNumber(5); // 20
console.log(multiply); // ReferenceError: num is not defined
Clojure
function foo() {
var a = 10; // variable in scope of 'foo'
function bar() {
// use outer variable 'a'
console.log(a);
}
// return another function
return bar;
}
var funct = foo(); // function expression
funct(); // 10 - actually calling bar() that uses 'a'
Callbacks
function callback() {
console.log('callback')
}
function caller(cb) {
cb();
}
caller(callback); // 'callback'Functions can be passed as arguments to other functions
goo.gl/MLfPsw
Objects
var basicObject = {};A collection of key/value pair data (similar to a dictionary)
Can contain primitives, functions, arrays and/or other objects:
const anObject = {
key1: 'value1',
key2: 'value2',
key3: 'value3'
// ...
}keys
values
properties
Objects
Literal notation
var person = {
sex: 'male', // string
age: 31, // number
name: { // nested object
'first': 'Andrei',
'last': 'Antal'
},
skills: ['HTML', 'CSS', 'JavaScript'], // array
sayHello: function() { // method
console.log('Hello, friends!')
},
favoriteFood: null // null value
};Objects
person.age; // 31
person.age = 32; // change the value
person.skills[0]; // 'HTML'
person.sayHello(); // call the function -> 'Hello, friends!'
person.name.first; // 'Andrei'
person.isStudent = false; // add a new property to the object
delete person.isStudent; // remove property from the object- Dot notation
person.nameobject
property name
dot operator
Objects
person['age']; // 31
person[age] // ReferenceError: age is not defined
var ageProp = 'age';
person[ageProp]; // 31
person['age'] = 32; // change the value
person['name'].first; // 'Andrei'
person['isStudent'] = false; // add a new prop to the object- Bracket notation
person['name']object
property name
Objects
// declare method
var person = {
sayHello: function() {
console.log('Hello, friends!')
},
};
// use method
person.sayHello();- Methods
Objects
var person = {
name: {
first: 'Andrei',
last: 'Antal'
},
education: {
schoolName: 'UPB',
degree: 'CS',
yearGraduated: 2010
}
};
person.name.first; // 'Andrei'
person.education.yearGraduated; // 2010- Nested objects
Objects
var user = { name: 'Andrei' };
function changeName(person, newName) {
person.name = newName;
}
changeName(user, 'Mihai');
user.name; // 'Mihai'- Passing object into functions - objects are always passed in by reference
Objects
- Testing if objects have properties
var person = { name: 'Andrei' };
if ('name' in person || person.name !== undefined) {
// is true
}
if ('age' in person || person.age) {
// is false
}- Getting all the object keys
var person = {
name: 'Andrei',
age: 32,
sex: 'male'
};
var keys = Object.keys(person) // [ 'name', 'age', 'sex' ]for(var key in person) {
console.log(person[key]);
}- Iterating object keys
this
- this is used in functions refer to the object the function is being called from
var person1 = {
age: 30,
printAge: function() {
console.log( 'My age is ' + this.age );
}
};
person1.printAge(); // 30 - this will refer to person1
var person2 = { age: 25 };
person2.printAge = person1.printAge;
person2.printAge(); // 25 - this will refer to person2
person3 = { age: 20 }
var bindedFunction = person2.printAge.bind(person3) // chenge this
bindedFunction();Creating objects
// create empty object
var person = new Object(); // -> {}
// create object from description
var person = new Object({
name: 'Andrei',
sex: 'male',
age: 31,
});- Object constructor
Creating objects
function Person(name, sex, age) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
return this;
}
var user = new Person('Andrei', 'male', 31);- Constructor function
Prototypes
// not optimal way
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
this.printName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
}
}// recommended way
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.printName = function() {
console.log(this.name);
};
var p1 = new Person('Andrei');
var p2 = new Person('Maria');
p1.printName(); // Andrei
p2.printName(); // MariaClasses (es2015)
class Person {
constructor(name, age, sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
printName() {
console.log('Hello, my name is ' + this.name);
}
}
var p = new Person('Andrei', 31, 'male');
p.age; // 31
p.printName(); // 'Hello, my name is Andrei'
p.age = 'thirty one'; // asign new value of new typeJSON
{
"name": "Andrei Antal",
"age": 45,
"skills": [
{ "name": "HTML", "level": 7 },
{ "name": "CSS", "level": 8 }
]
}
- A language agnostic data exchange format
- Contains only data (primitives, arrays, other objects), no methods
var person = JSON.parse(paersonJSON); // decode JSON
var json = JSON.stringify(paerson); // encode JSONBuilt-in Objects
- Date
Math.PI; // 3.141592653589793
Math.round(4.7); // 5
Math.ceil(4.4); // 5
Math.floor(4.4); // 4
Math.random(); // [0,1)- Math
var myDate = new Date(1995, 11, 17);
myDate.getFullYear(); // 1995
myDate.getMonth(); // 10 - months represented 0-11
myDate.getTime(); // 819151200000 - milliseconds since January 1, 1970Arrays
- A collection object that has a sequence of items you can access and modify
var skills = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
var fibonacci = [ 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13 ];
var array = [ 'string', 42, {name: 'Andrei'}, [1, 2, 3] ];- Access items using bracket nottaion and index for item position in collection
fibonacci[4] // 5 - array is 0 indexed
skills[1] = 'Python' // directly change a value
array[3][1]; // 2 - multidimensional arrayArrays
- Obtaining the length of the array
var skills = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
skills.length; // 3
skills[3] = 'Python';
skills; // [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python' ];
skills.length; // 4
skills [9] = 'C++';
skills; // [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python', , , , , , 'C++' ]
skills.length; // 10
skills[6]; // undefinedArrays
- Creating arrays
// most common way
var array = [];
// using the constructor
var array = Array(1, 2, 3); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
var array = Array(3) // [ , , ]
// using the of function
var array = Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
var array = Array.of(3); // [ 3 ]
// using the from function
var skills = {
0: 'HTML', 1: 'CSS', 2: 'JS', length: 3
};
var array = Array.from(skills); // [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ]
var array = Array.from('Andrei'); // [ 'A', 'n', 'd', 'r', 'e', 'i' ]Iterating Arrays
var fibbonacci = [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21];
//for loop
for (var i = 0; i < fibbonacci.length; i++) {
console.log(fibbonacci[i]); // 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
}
// for...in loop
for (var index in fibbonacci) {
console.log(fibbonacci[index]) // 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
}
// for...of loop
for (var number of fibbonacci) {
console.log(number) // 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21
}- for...in loop - iterate enumerable properties
// on objects
var object = {
a: 1,
b: 2,
c: 3,
d: 4
}
for (var key in object) {
if (object.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
console.log(key) // 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'
console.log(object[key]); // 1, 2, 3, 4
}
}
// on strings
var string = 'Andrei Antal';
for (var index in string) {
console.log(string[index]) // A, n, d, r, e, i, , A, n, t, a, l
}
Iterating Arrays
Array methods
- Concatenating 2 arrays
var skills1 = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
var skills2 = ['Python', 'Java'];
var skills = skills1.concat(skills2);
// [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python', 'Java' ]- Finding items
var skills = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
skills.indexOf('JS') // 2
skills.indexOf('Python') // -1
skills.includes('HTML') // true
skills.includes(123) // falseArray methods
- Modifying an array
var skills = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
// add at the end
skills.push('Python'); // [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python' ]
// remove from end
skills.pop(); // [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ]
// remove from start
skills.shift(); // [ 'CSS', 'JS' ]
// add to start
skills.unshift('Java'); // [ 'Java', 'CSS', 'JS' ]Array methods
- Working with strings
var names = 'Andrei George Elena Maria';
names.split(' ') // [ 'Andrei', 'George', 'Elena', 'Maria' ]
var skills = ['HTML', 'CSS', 'JS'];
skills.join(', ') // 'HTML, CSS, JS'- Working with strings
var name = 'Andrei Antal';
name.charAt(2) // d
name[2] // dArray methods
- Extracting parts of an array
var skills = ['HTML', 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python', 'Java', 'C++'];
// start/end index -> no mutation
skills.slice(1,4); // [ 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python' ]
skills; // [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python', 'Java', 'C++' ]
// start index, delete count -> mutation
skills.splice(1,4); // [ 'CSS', 'JS', 'Python', 'Java' ]
skills; // [ 'HTML', 'C++' ]Array methods
- Finding elements in arrays ( find and includes )
var people = [
{ name: 'Andrei', age: 31 },
{ name: 'Maria', age: 25 },
{ name: 'George', age: 28 }
];
var findAndrei = people.find(function(person) {
return person.name === 'Andrei';
});
findAndrei; // { name: 'Andrei', age: 31 }
var skills = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
var hasHTML = skills.includes('HTML');
hasHTML; // trueArray methods
- Sorting arrays
var numbers = [7, 2, 6, 4];
var names = ['George', 'Andrei', 'Maria'];
numbers.sort(); // [2, 6, 4, 7];
names.sort(); // ['Andrei', 'George', 'Maria'];
var people = [
{ name: 'Andrei', age: 31 },
{ name: 'Maria', age: 25 },
{ name: 'George', age: 28 }
];
people.sort(function(pers1, pers2) {
return pers1.age - pers2.age;
});
// [{ name: 'Maria', age: 25 },
// { name: 'George', age: 28 },
// { name: 'Andrei', age: 31 }]Array methods - forEach
- executes a provided function once for each array element, without changing the array.
var skills = ['HTML', 'CSS', 'JS'];
skills.forEach(function(skill) {
console.log(skill);
});
// HTML
// CSS
// JS
skills.forEach(function(skill, index) {
console.log(
'Skill ' + (index + 1) + ': ' + skill.toLowerCase()
);
});
// Skill 1: html
// Skill 2: css
// Skill 3: jsArray methods - filter
- creates a NEW array with all elements that pass the test implemented by the provided callback function
var names = ['Andrei', 'Mihai', 'Maria', 'Ioana']
var namesContainingR = names.filter(function (name){
return name.includes('r');
});
// [ 'Andrei', 'Maria' ]
var namesContainingRAndNotFirst = names.filter(function(name, index){
return index !== 0 && name.includes('r');
});
// [ 'Maria' ]
var names2 = ['Andrei', null, 'Mihai', 'Maria', 'Ioana', null];
var validNames = names2.filter(function(name){
return name != null;
})
// [ 'Andrei', 'Mihai', 'Maria', 'Ioana' ]Array methods - map
- creates a NEW array with the results of calling a provided callback function on every element in the calling array.
var numbers = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
var doubeledNumbers = numbers.map(function(number){
return number * 2
});
// [ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 ]
var skills = [ 'HTML', 'CSS', 'JS' ];
var lowercaseSkills = skills.map(function (skill) {
return skill.toLowerCase();
})
// [ 'html', 'css', 'js' ]Array methods - map
- data projection - turning a collection of one data type into another
var people = [
{name: 'Andrei', age: 30},
{name: 'Maria', age: 25},
{name: 'George', age: 28}
]
var names = people.map( function(person) {
return person.name;
});
// [ 'Andrei', 'Maria', 'George' ]
var capitalNamesWithIds = people.map( function(person, index){
return {
name: person.name.toUpperCase(), id: index
};
});
// [ { name: 'ANDREI', id: 0 },
// { name: 'MARIA', id: 1 },
// { name: 'GEORGE', id: 2 } ]Array methods - reduce
- Returns A SINGLE value as a result of applying a reducer function on each member of the array
var numbers = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
var sum = numbers.reduce(function (accumulator, currentValue){
return accumulator + currentValue;
}, 0);
// 15
const ammounts = [29.76, 41.85, 46.5];
const average = ammounts.reduce((total, amount, index, array) => {
total += amount;
if( index === array.length-1) {
return total/array.length;
}else {
return total;
}
}, 0);
average; // 39.37
DOM
- The DOM (Document Object Model) represents a hierarchy of objects, forming a model of your HTML document.
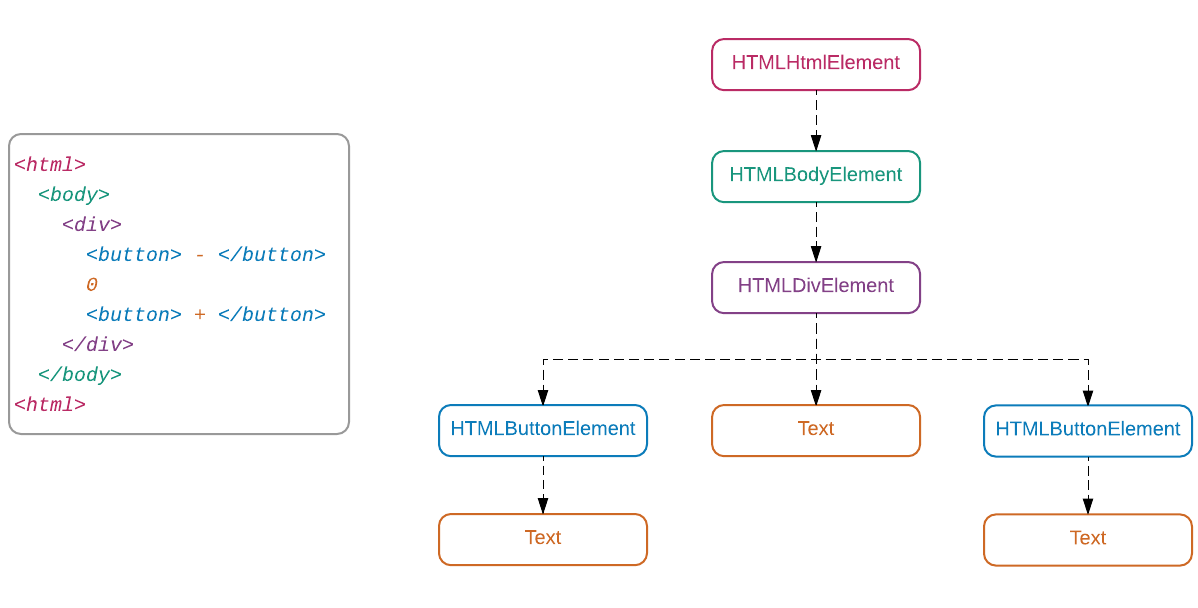
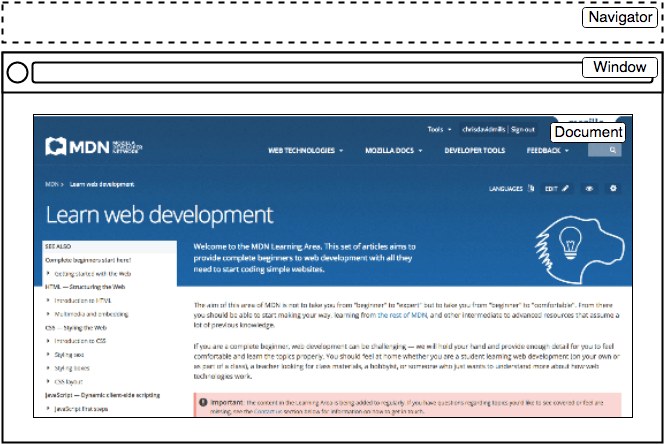
- Window - represents the browser window object
- Navigator - object linking to browser specific APIs
- Document - an object representing the page loaded in the window. Use this to get references to elements and manipulate any HTML or CSS related properties
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>Simple DOM example</title>
</head>
<body>
<section>
<img src="mustang.png" alt="A picture of a red Ford Mustang.">
<p>See all the prices <a href="https://www.ford.com/">here</a></p>
</section>
</body>
</html>DOM

<div id="main">
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="theimage" src="smiley.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="theimage" src="tongue.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="theimage" src="meh.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="theimage" src="sad.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
</div>Accessing DOM objects
- Getting elements by their id
var container = document.getElementById('main'); // get element with #main
container; // div#main object
container.style
container.addEventListener(...)
container.appendChild(...)<div id="main">
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="smiley.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="tongue.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="meh.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="sad.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
</div>Accessing DOM objects
- Getting elements by class name
// get elements with .theimage
var images = document.getElementsByClassName('theimage');
Array.from(images).forEach(pict => {
console.log(pict.tagName); // IMG, IMG, IMG, IMG
})<div id="main">
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="smiley.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="tongue.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="meh.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
<div class="pictureContainer">
<img class="image" src="sad.png" height="300" width="150"/>
</div>
</div>Accessing DOM objects
- Getting elements by CSS selectors
// get elements with .theimage
var images = document.querySelectorAll('theimage');
images; // NodeList(4) [img.theimage, img.theimage, img.theimage, img.theimage]
var picture = document.querySelector('.pictureContainer');
var container = document.querySelector('#main');
var notAnElement = document.querySelector('not-a-tag');
picture; // HTMLPictureElement
container; // HTMLDivElement
notAnElement; // null<div class="my-element">
This is the content of <span> my </span> element
</div>
Modifying the DOM
- Changing the content of an element
let elem = document.querySelector('.my-element');
elem.innerHTML = 'Some other content of <span> mine </span>';<p>One</p>
<p>Two</p>
<p>Three</p>
Modifying the DOM
- Adding a new node
var newElement = document.createElement('p'); // create a new <p> element
newElement.textContent = 'Four'; // change the text content
document.body.appendChild(newElement); // attach it to the DOM
// <p> One </p>
// <p> Two </p>
// <p> Three </p>
// <p> Four </p>let paragraphs = document.body.getElementsByTagName("p"); // all <p> elements
document.body.insertBefore(paragraphs[2], paragraphs[0]); // add third after first
// <p> Three </p> <-- dom element can only appear once in document
// <p> One </p>
// <p> Two </p>
// <p> Four </p>Modifying the DOM
- Changing/adding attributes
var button = document.querySelector('button');
button.disabled = false;
var paragraph = document.querySelector('p');
paragraph['data-secret']; // undefined
paragraph.getAttribute('data-secret'); // don't tell anyone<p data-secret="don't tell anyone">Title</p>
<button disabled="true">CLICK ME!</button>Modifying the DOM
- Modifying styles
const paragraph = document.querySelector('p');
paragraph.style.color = 'red'; // set new color to red
paragraph.style.height; // '' <- not explicitly set
window.getComputedStyle(paragraph).height; // '18px'
paragraph.style.height = '50px';
console.log(paragraph.style.height); // '50px'
window.innerWidth; // browser current width
window.innerHeight; // browser current height<p style="color: purple">
Some text
</p>Events
- Simple event listeners
var inputedText = ''
document.querySelector('input').addEventListener('input', function(event) {
inputedText = event.target.value; // display the last modified value of the input
})
function handler() { // handler function
console.log(inputedText); // get the curent text in the input
}
var button = document.querySelector('button')
button.addEventListener('click', handler); // register handler
button.removeEventListener('click', handler); // remove handler
<button>Click me!</button>
<input placeholder="Write here...">Events
- The event object
var button = document.querySelector("button");
button.addEventListener("mousedown", function(event) {
if (event.button == 0) {
console.log("Left button");
} else if (event.button == 1) {
console.log("Middle button");
} else if (event.button == 2) {
console.log("Right button");
}
});
<button>Click me!</button>
<input placeholder="Write here...">Events
- The event object
var button = document.querySelector("button");
window.addEventListener("keydown", function(event) {
if (event.key == "r") {
button.style.background = "red";
}
});
window.addEventListener("keyup", event => {
if (event.key == "v") {
button.style.background = "";
}
});<button>Click me!</button>
<input placeholder="Write here...">Events
- Event propagation
<div>
<button>Click me!</button>
</div>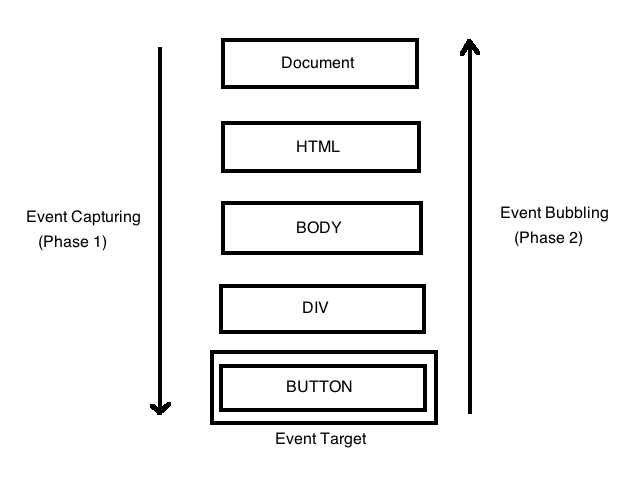
var div = document.querySelector('div');
var button = document.querySelector('button');
// button handler
button.addEventListener('click', function(event) {
console.log('button click');
event.stopPropagation(); // event stops here
});
// div handler
div.addEventListener('click', function(event) {
console.log('div click');
});Events
- Preventing default behaviour
<a href="https://developer.mozilla.org/">MDN</a>
var link = document.querySelector("a");
link.addEventListener("click", function(event) {
console.log("Won't navigate away");
event.preventDefault();
});Events
- Document ready
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
// the browser fully loaded HTML, and the DOM tree
// is built, but external resources like pictures <img>
// and stylesheets may be not yet loaded.
});
window.onload = function() {
// the browser loaded all resources (images, styles etc).
};Forms
- Client-side handling of forms
<form id="theForm" >
<input id="name" name="name">
<input type="submit">
</form>let form = document.querySelector('#theForm')
form.addEventListener("submit", function (event) {
event.preventDefault();
const nameInput = document.getElementById('name');
let nameValue = nameInput.value;
console.log(nameInput.validity.valid); // true/false
// do something depending on form state
});Events
- Timers
var timer = setTimeout(function() {
console.log("It's time"); // will call after aprox 500ms
}, 500);
let ticks = 0;
let clock = setInterval(function() {
console.log("tick", ticks++);
if (ticks == 10) {
clearInterval(clock); // stops the timer
console.log("stop.");
}
}, 200); // will call every aprox 200msjQuery
- Timers
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>jQuery Example</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="Scripts/jquery-3.3.1.min.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
...
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function () {
// some code
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
jQuery
- Selecting elements and traversing the DOM
$(document).ready(function () {
$("h2").each(function () {
this.style.color = "red"; // this -> currently selected element
});
});
- Tag name - $("h2")
- Element ID - $("#logo")
- Element class - $(".blue")
- An attribute on an element - $("input[type=text]")
jQuery
- Selecting elements and traversing the DOM
$( "span.subchild" ).parent();
- Parents
- Children
- Siblings
$( "div.grandparent" ).children( "div" ); // direct children only
$( "div.grandparent" ).find( "div" ); // all descendants$( "div.parent" ).siblings();
$( "div.parent" ).next();
$( "div.parent" ).prev();jQuery
- Adding, Removing, and Modifying Elements
- append( htmlString )
- html( htmlString )
- detach()
$("#list").append("<li>The new last list item</li>");$("#Warning").detach();$(".title").html("<h1>New Heading</h1>");
jQuery
- Adding, Removing, and Modifying Elements
$("#Warning").replaceWith("<p>Panic Over!</p>");
- replaceWith( htmlString)
- val()
- attr()
$("input[type=text]").val();
$(“button”).attr(disabled,”disabled”);
jQuery
- Styling elements
// GET
$(“p”).css(“font-size”);
$(“p”).css(“fontSize”);
// SET
$(“p”).css(“fontSize”, “10px”);
$(“p”).css({
fontSize: “10px”,
color: “red”
})
jQuery
- Styling elements
h1.addClass( "big" );
h1.removeClass( "big" );
h1.toggleClass( "big" );
if ( h1.hasClass( "big" ) ) {
...
}
jQuery
- Handling events
$(document).ready(function () {
$("#submit").bind(“click”, function () {
var userName = $("#NameBox").val();
$("#thankYouArea").replaceWith("<p>Thank you " + userName + "</p>");
})
});
- Use the jQuery selector function to find the item that initiates the event
- Use the bind method (or a shortcut) to bind the event handler to the event
jQuery
- Handling events
- click(), dblclick() : Binds to mouse click events.
- error() : Binds to occurrence of errors in the document such as broken links and missing images.
- focus(), focusin(), focusout() : Binds to element focus events.
- keydown(), keyup(), keypress() : Binds to user keyboard input events.
- hover(), mousedown(), mouseup(), mouseenter(), mouseleave(), mouseout(), mouseover(), mousemove() : Binds to mouse and cursor-related events.
- load(), unload() : Binds to events triggered when a specified element is loaded or unloaded on the page.
jQuery
- AJAX
// Using the core $.ajax() method
$.ajax({
url: "post.php", // The URL for the request
type: "GET", // Whether this is a POST or GET request
dataType : "json", // The type of data we expect back
success: function(data) { console.log(data) }
})
// POST: add data: {}CSS
Responsive web design
A bit of context


Responsive web design

Responsive web design
Definition
Responsive web design means designing your website so that it responds to your users environment based on screensize, platform and orientation.
Responsive web design
Definition
It looks diferent and things jiggle around, scale, re-order, appear, and disappear so it works well in your browser size or whatever device you’re using to view it...
Responsive web design
Responsive web design

Responsive web design

Responsive web design

Responsive web design

Responsive web design

Responsive web design

Responsive web design

Responsive web design
Mobile vs. Adaptive vs. Responsive
Responsive web design
New ways of thinking
- Works on everything - Design for many sizes at once
- Clean design - reduce clutter, essential content only
- Design from the content out - Let content decide breakpoints
- Less Graphic files - CSS gradients, font icons
Design patterns
Layouts

Mostly Fluid
Design patterns
Layouts
Column Drop

Design patterns
Layouts
Layout Shifter

Design patterns
Layouts
Off Canvas

Design patterns
Navigation
Toggle Navigation

Design patterns
Navigation
<select> Navigation

Design patterns
Navigation
Footer Navigation

Design patterns
Navigation
Stacked Top Links Navigation
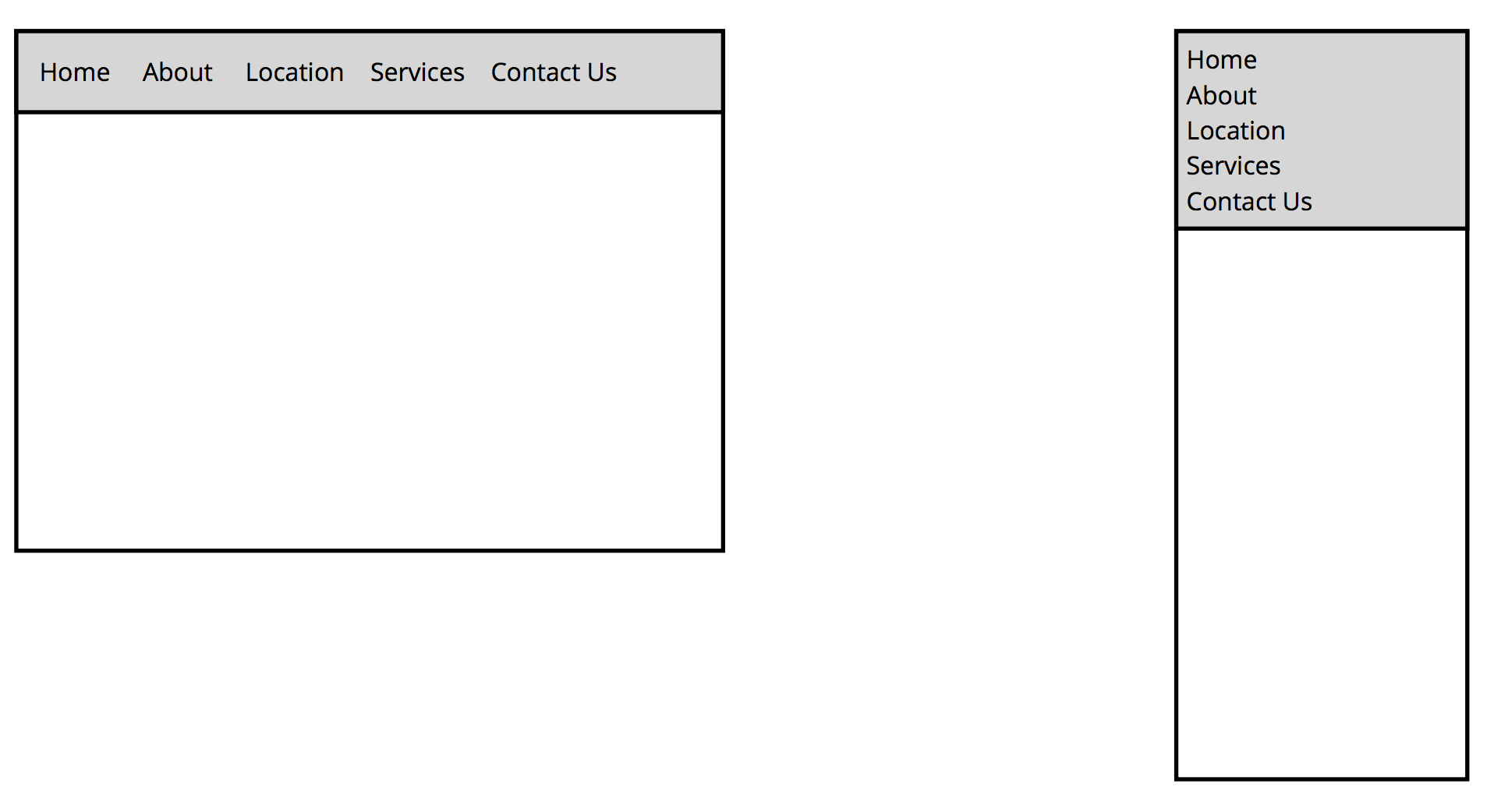
Design patterns
Navigation
Left Nav Flyout - aka Hamburger menu

Design patterns
Navigation
Priority+ Navigation

Design patterns
Navigation
Priority+ Navigation

Design patterns
Source order shift

Design patterns
Source order shift

RWD Components
-
Flexible, grid based layouts
- % widths and em units, not fixed pixels
-
Flexible images and media
- width/height not fixed
-
CSS3 Media Queries
- @media rule
Flexible layouts
Building the layout of a website with a flexible grid, capable of dynamically resizing to any width


Flexible layouts
Relative Viewport Lengths
- vw - Viewports width
- vh - Viewports height
- vmin - Minimum of the viewport’s height and width
- vmax - Maximum of the viewport’s height and width
.container {
width: 50vw;
height: 100vh;
}Flexible layouts
Flexible grids
// HTML
<div class="container">
<section>...</section>
<aside>...</aside>
</div>
.container {
width: 538px;
display: flex;
}
section,
aside {
margin: 10px;
}
section {
width: 340px;
}
aside {
width: 158px;
}

Flexible layouts
Flexible grids
target ÷ context = result
|
Flexible layouts
Flexible grids
section,
aside {
margin: 1.858736059%; /* 10px ÷ 538px = .018587361 */
}
section {
width: 63.197026%; /* 340px ÷ 538px = .63197026 */
}
aside {
width: 29.3680297%; /* 158px ÷ 538px = .293680297 */
}
Flexible layouts
Flexible grids
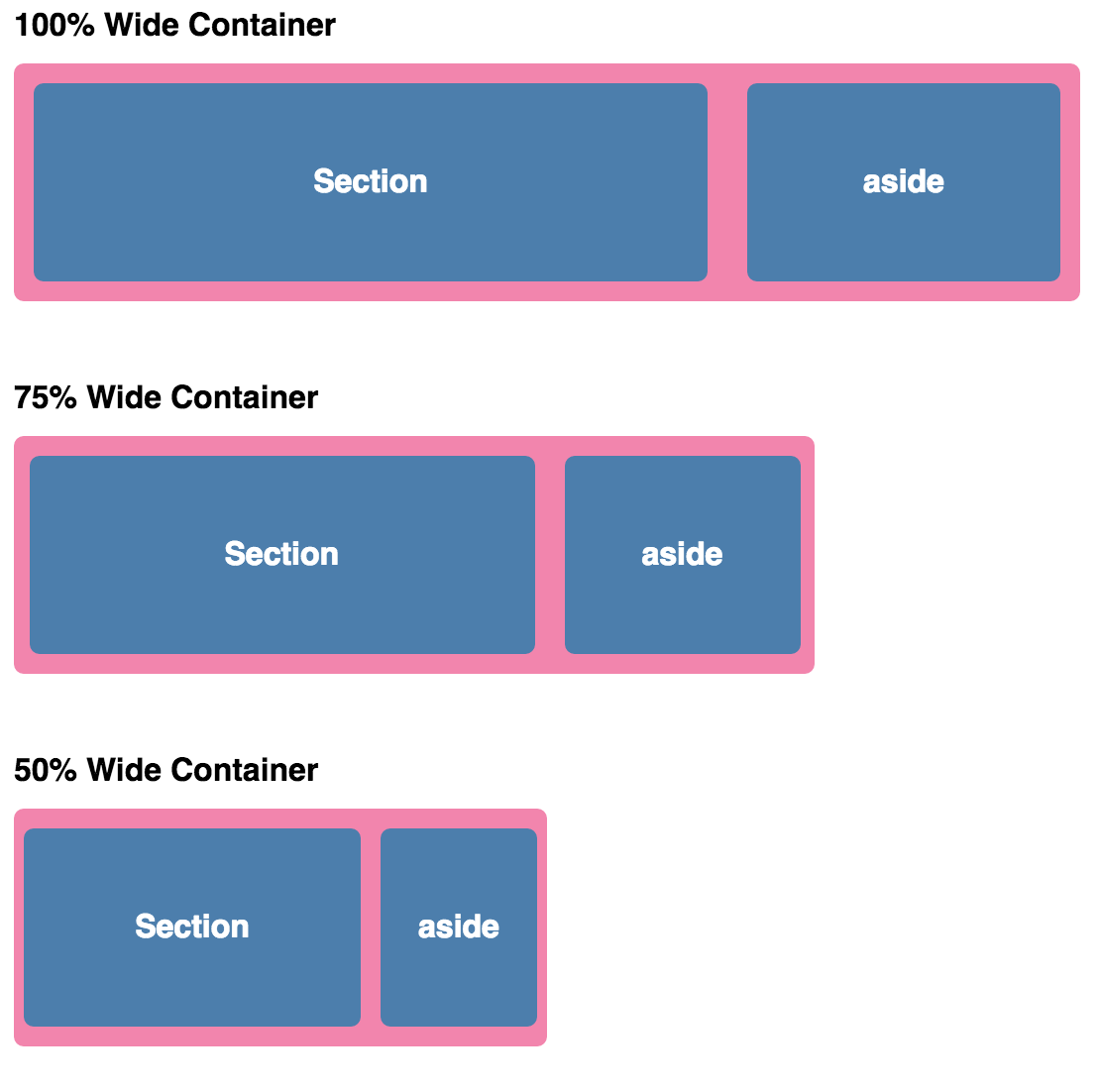
Media queries
Media queries provide the ability to specify different styles for individual browser and device circumstances -
apply uniquely targeted styles
<!-- Separate CSS File -->
<link href="styles.css" rel="stylesheet" media="all and (max-width: 1024px)">
/* @media Rule */
@media all and (max-width: 1024px) {...}
/* @import Rule */
@import url(styles.css) all and (max-width: 1024px) {...}
Media queries
Media queries provide the ability to specify different styles for individual browser and device circumstances -
apply uniquely targeted styles
<!-- Separate CSS File -->
<link href="styles.css" rel="stylesheet" media="all and (max-width: 1024px)">
/* @media Rule */
@media all and (max-width: 1024px) {...}
/* @import Rule */
@import url(styles.css) all and (max-width: 1024px) {...}
@media screen and ( min-width: 500px ) and ( max-width: 800px ) {
/* CSS declarations */
}This is for screen only (desktops, smartphones, not print)
media_type: all | aural | braille | handheld | print | projection | screen | tty | tv | embossed | speech
Media queries
Media queries
@media screen and ( min-width: 500px ) and ( max-width: 800px ) {
/* CSS declarations */
}The width of the window must be AT LEAST 500px
The width of the window must ALSO be NO MORE THAN 800px
media_feature: width | min-width | max-width | height | min-height | max-height | aspect-ratio | min-aspect-ratio | max-aspect-ratio | color | min-color | max-color | color-index | min-color-index | max-color-index | monochrome | min-monochrome | max-monochrome | resolution | min-resolution | max-resolution | scan | grid
Media queries
@media screen and ( min-width: 500px ) and ( max-width: 800px ) {
img {
border: 5px solid #!f;
}
}Images will have a white border when the window is from 500px to 800px wide
Media queries
@media all and (max-width: 420px) {
.container {
flex-direction: column;
}
}

ASSIGNMENT
Link 1
Link 2
Link 3
Link 4
Banner
Article 1
Article 2
Article 3
Article 4
Footer
max 1024px
1. Desktop ( > 900px)
12px
12px
12px
16px
16px
16px
8px
8px
Article 4
Banner
Article 1
Article 2
Footer
2. Tablet ( between 900px and 500px )
16px
16px
16px
Article 3
Article 4
Link 1
Link 2
Link 3
Link 4
Banner
Article 1
Footer
3. Phone (bellow 500px)
Link 1
Article 2
Article 3
Article 4
Link 2
Link 3
Link 4
Learning resources
Online learning resources (free and paid):
Learning resources
Learning resources
reach me at:
antal.a.andrei@gmail.com
Thank you!
http://bit.ly/2UBiCqM
HTML, CSS and JS intro
By Andrei Antal
HTML, CSS and JS intro
- 3,951



