Reactive state management in Angular
Voxxed Days 2018 - Bucharest
Antal Andrei
slides.com/andreiantal/reactive_state_ng/
Hello, world!
Andrei Antal
@andrei_antal

- frontend engineer (since I can remember)
- web & JS technologies enthusiast
- passion for UI design and UX
- perpetual learner
organizer of ngBucharest

@ngBucharest
groups/angularjs.bucharest


Contents
-
Intro
-
State management in frontend applications
-
Redux
-
NgRX
INTRO
Why Angular?
- Well defined practices - but not 100% opinionated
- Streamlined development process - mostly thanks to the CLI
- Rich ecosystem
- Emphasis on standards
The pillars of Angular
- Component driven architecture
- Unidirectional data flow
- Dependency Injection
- Observables as a backbone
- TypeScript
AngularJS 1.x
Module
Config
Routes
$scope
controller
service
view
directive
- The (main) building blocks
Angular
Module
- The (main) building blocks
Routes
Service
Component
Angular - a common pattern
Metadata - decorator
ES6 Class
Angular
Module
- The (main) building blocks
Routes
Service
Component
ES6 Modules
- ES6 modules provide organization at a language level
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { ItemsService, Item } from '../shared';
export class ItemsComponent implements OnInit {}Modules export things that other modules can import
@NgModule
- Provides organization at a framework level
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
ItemsComponent,
ItemsListComponent,
ItemDetailComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
HttpModule,
Ng2RestAppRoutingModule
],
providers: [ItemsService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }define view classes that are available to the module - the other view classes in the module
define a list of other modules that the current module needs
define a list of services the module makes available
defines the component that should be bootstrapped
Angular
Module
- The (main) building blocks
Routes
Service
Component
Routes
- A route, in the simplest form, contains a path and a component reference
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { Routes, RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { ItemsComponent } from './items/items.component';
const routes: Routes = [
{path: '', redirectTo: '/items', pathMatch: 'full' },
{path: 'items', component: ItemsComponent},
{
path: 'widgets',
loadChildren: '../modules/books/books.module#BooksModule',
},
{path: '**', redirectTo: '/items', pathMatch: 'full'}
];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule],
providers: []
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }Super-easy lazy load of routes
Angular
Module
- The (main) building blocks
Routes
Service
Component
Services/Providers/Injectables
Decorator necessary only if service injects other providers
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/map';
import 'rxjs/add/operator/toPromise';
const BASE_URL = 'http://localhost:3000/items/';
@Injectable()
export class ItemsService {
constructor(private http: Http) {}
loadItems() {
return this.http.get(BASE_URL)
.map(res => res.json())
.toPromise();
}
}Angular
Module
- The (main) building blocks
Routes
Service
Component
Components
Metadata - the @Component decorator
Class
Template
Bindings
events
properties
Components
- component - "Just a class, with a decorator"
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-component',
template: `
<h1> Hello, {{ name }}! </h1>
<button (click)="changeName()">CHANGE NAME</button>
`,
})
export class AppComponent {
name = 'Andrei';
logGreet() {
this.name = 'Andrew';
console.log(`Name has been changed to ${ this.name }`);
}
}Angular - a common pattern
Module
Component
Provider
Directive
Pipe
metadata
metadata
metadata
metadata
metadata
class
class
class
class
class
Angular CLI
-
Scaffold a full working project in 3 steps:
- npm insall -g @angular/cli
- ng new [project name]
- ng serve
- Project elements generator (components, service, etc.) that adheres to best practices (naming, structure etc.)
- Schematics for custom flows
STATE MANAGEMENT
State in Frontend Apps
User Interface = function(State)
(Data projection)
const bookTitle = "Alchemy for beginners";
const chaptersTitles = [ "Equipment" ]
let book = {
title: bookTitle,
chapters: chapterTitles
}
.....
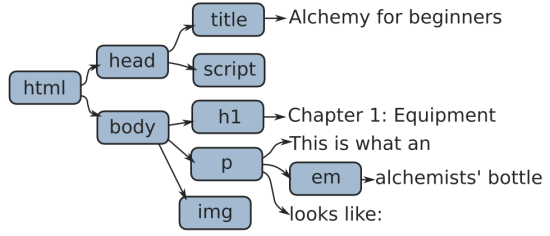
Strings, numbers, arrays, objects etc.
Document Object Model
(DOM)
(rendering)
State in Frontend Apps
State (in the broadest sense) is the complex of all of the values held by the application as properties or variables at any given time, and the application is conceived of as acting by executing methods/functions that change the current state to another state.
State changeing over time
- User input (event callbacks)
- Async requests
- Timers (setInterval, setTimeout)
Application state
-
Data from a remote source
- API server responses
- WebSocket
-
User info
- authentication details
-
User input
- form data
-
UI state
- table pagination
- selected tabs
-
Router / location state
- current URL/route
The need for
state management
- move state management outside of components
- model the application state
- read and update state values
- observe/push state changes
REDUX
Model - View - *
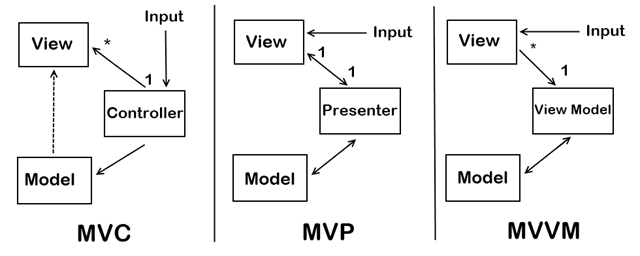
Problems with MVC
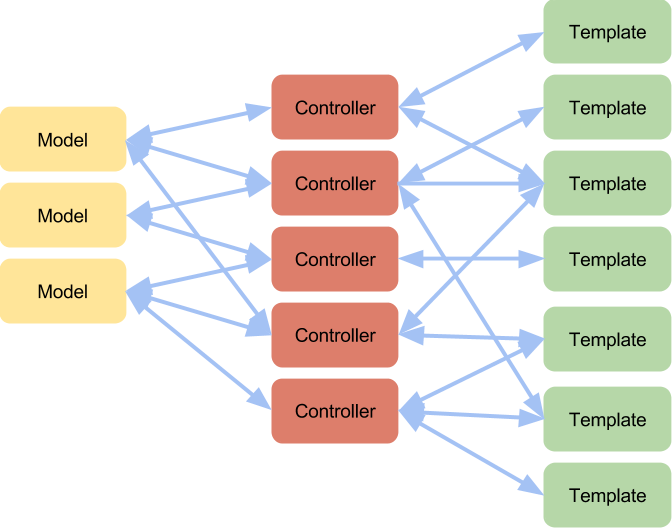
Unidirectional data flow - Flux
VIEW
STORE
ACTION
DISPATCHER
ACTION
Unidirectional data flow - Flux
FLUX
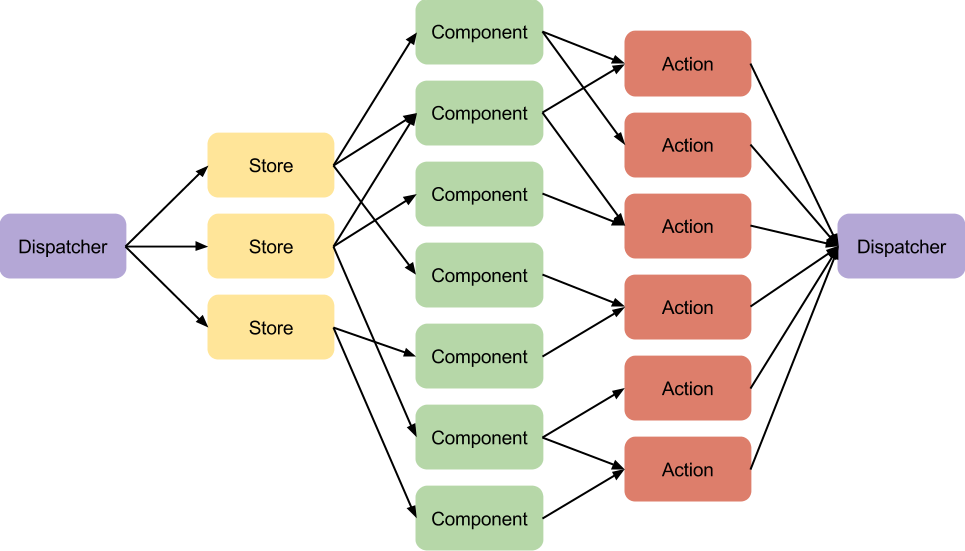
data flow
REDUX
The 3 main principles:
-
Single source of truth
- one source tree inside a Store
- helps predicatability
-
State is read-only
- dispatch actions to change the state (indirect change)
- immutable update
-
Pure functions update state
-
reducers as pure functions
- respond to actions
- return new state
-
reducers as pure functions
REDUX concepts
- The single state tree
- Actions
- Reducers
- Store
- One way data flow
The single state tree
- One big JavaScript object
- The state object results from reducer composition
// initial state object
const state = {
books: [],
movies: [],
}Actions
- An action is an object that has 2 properties:
- action type - string, usually the name of the action
- action payload [optional] - data attached to the action
// book addition action object
const action = {
type: 'ADD_BOOK',
payload: {
id: 123,
title: '1984',
author: 'George Orwell',
read: false,
},
};- Actions are dispatched to reducers
Reducers
- They're just (pure) functions
- Receive the action object as a parameter
- Use the action type and payload to compose and return the new state
- reducers as pure functions are super easy to test
Reducers
// reducer function
function booksReducer(state, action) {
switch(action.type) {
case 'ADD_BOOK':
const newBook = action.payload;
const books = [
...state.books,
newBook
];
return {
...state,
books,
}
break;
...
}
}new state
Store
- A container for state
- Use it in components:
- subscribe to parts of the store state
- dispatch actions to it
- Takes care of data flow:
- invoke reducers with previous state and action
- composes new state
- notifies subscribers
- invoke reducers with previous state and action
One way data flow
ACTION
STATE
COMPONENT
REDUCER
STORE
dispatches
sent to
returns new
update -> render
One way data flow
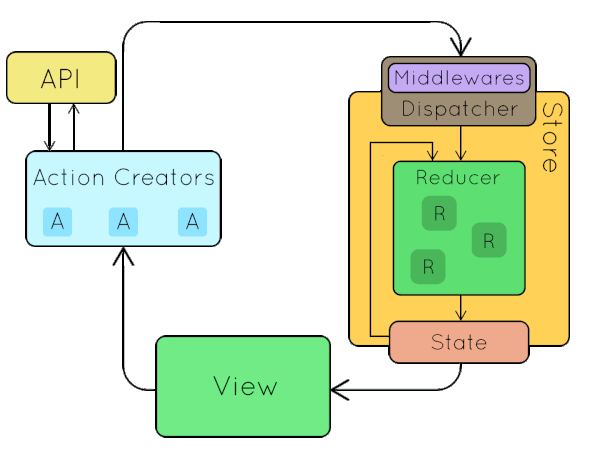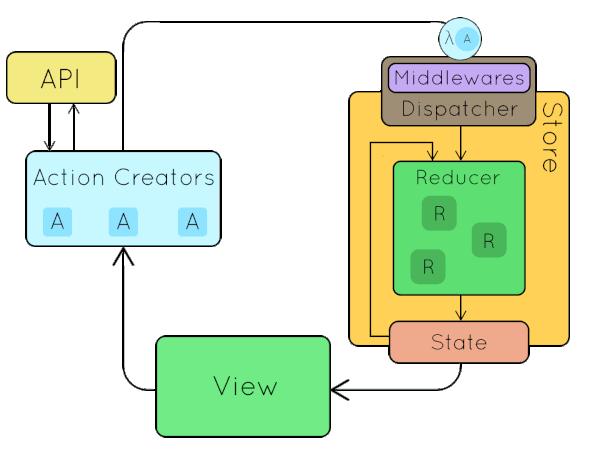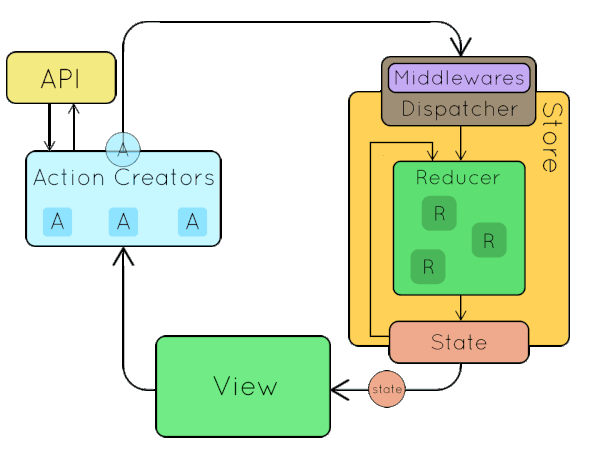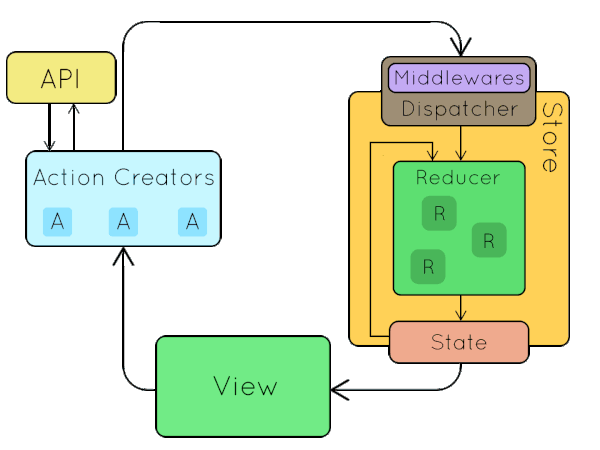
Let's build our own!
NgRX
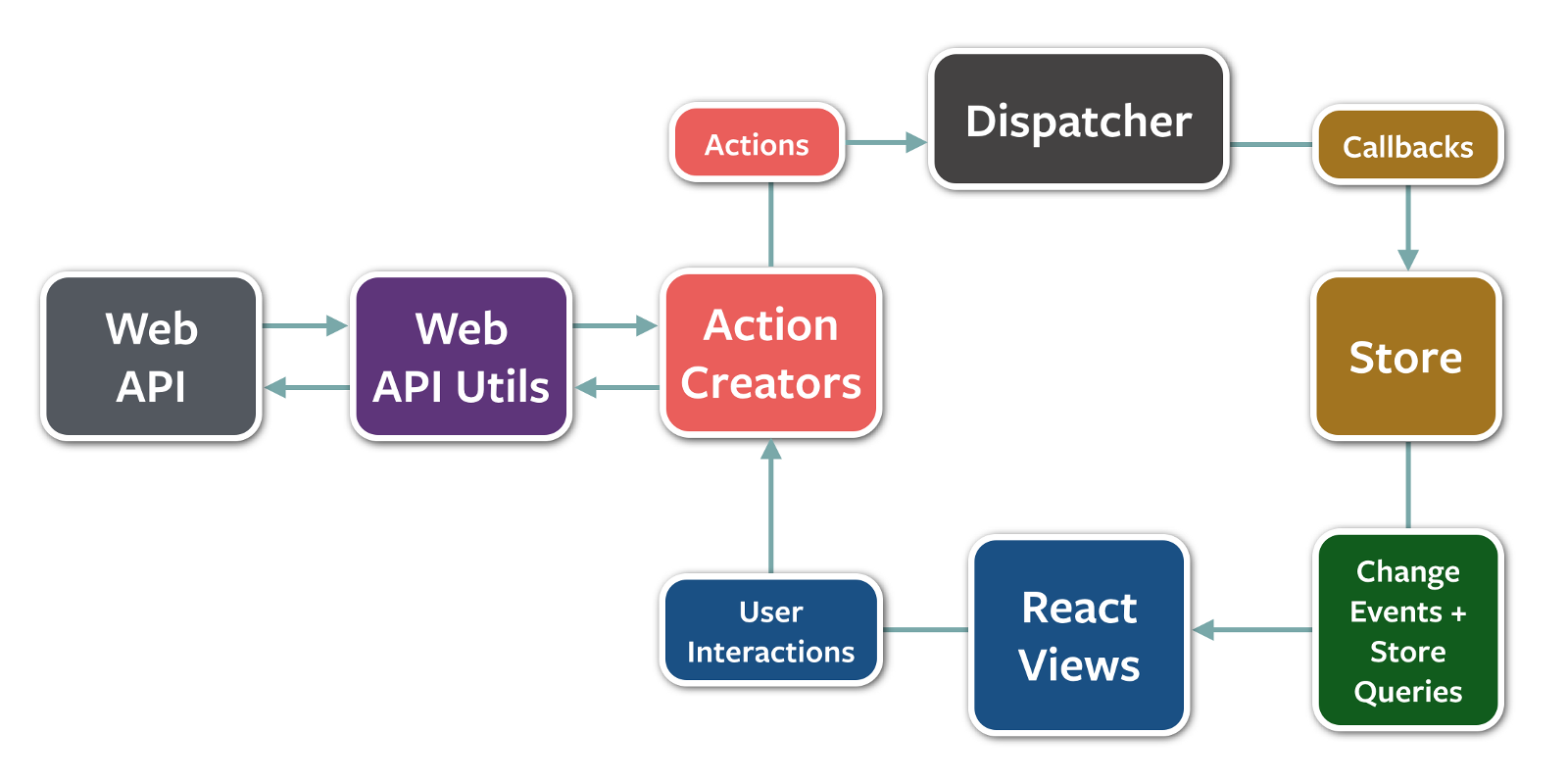
NgRX
A reactive state management library
- made of Angular
- based on Redux principles
- written with Observables
Main benefits
- better patterns for managing data flow in you application
- tooling (redux dev tools)
- testability
NgRX

npm install @ngrx/store --saveOther packages augment the functionalities of the library
Smart and dumb components
Container components
- uses (injects) the Store
- dispatches actions to the store
- reads data from the store
Presentational components
- Not aware of store and does not dispatch actions
- Reads all data it needs from @Inputs
- Signals events to parent via @Outputs
Smart and dumb components
Container Component
Dumb Component
Dumb Component
STORE
@Output
@Output
@Input
@Input
Dispatch
Select
Including ngrx in our project
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'
import { StoreModule } from '@ngrx/store';
import { todosReducer } from './todos';
@NgModule({
imports: [
BrowserModule,
StoreModule.forRoot({ todos: todosReducer })
]
})
export class AppModule {}- only used once, for the root module
- for a feature or lazily loaded modules, we should use the forFeature static method
Actions
import { Action } from '@ngrx/store';
import { Book } from './model/book';
export const LOAD_BOOKS = '[Books] Load books';
export const ADD_BOOK = '[Books] Add book';
export class LoadBooks implements Action {
type = LOAD_BOOKS;
}
export class AddBook implements Action {
type = ADD_BOOK;
constructor(public payload: Book) {}
}Action types
export class AddBook implements Action {
type = 'ADD_BOOK';
constructor(public payload: Book) {}
}- Commands
export class Books implements Action {
type = 'BOOKS';
constructor(public payload: Book[]) {}
}- Documents
export class BooksLoaded implements Action {
type = 'BOOKS_LOADED';
constructor(public payload: any) {}
}- Events
Dispatch actions
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Store } from '@ngrx/store';
import { AddBook } from './store.actions';
import { Book } from './model/book';
@Component({
selector: 'books',
templateUrl: './books.component.html'
})
class BooksComponent {
constructor(private store: Store<any>) {}
addBook(title: string, author: string) {
this.store.dispatch(
new AddBook(new Book(title, author))
);
}
}Reducers
export interface BookaState {
books: Book[];
loading: boolean;
}
export const initialState: BookaState = {
books: [],
loading: false,
};
export function reducer(state = initialState, action): BookaState {
switch (action.type) {
case LOAD_BOOKS: {
return {
...state,
loading: true,
};
}
case ADD_BOOK: {
return {
...state,
books: [...state.books, action.payload],
};
}
}
return state;
}Selectors
@Component({
selector: 'books',
template: `
<div class="book" *ngFor="let book of books$ | async">
<span>{{book.title}}</span> - <span>{{book.author}}</span>
</div>
`
})
class TodosComponent {
public books$: Observable<Book[]>;
constructor(private store: Store<any>) {
this.books$ = store.select('books');
}
...
}Advanced selectors
export interface BookState {
data: Book[];
loading: boolean;
error: any;
}
export interface BooksState {
books: BookState;
}
export const getBooks = (state: BookState): Book[] => state.data;
export const getProductsState
= createFeatureSelector<BooksState>('booksFeature');
export const getBooksState = createSelector(
getProductsState,
(state: BooksState): BookState => state.books,
);
export const getAllBooks = createSelector<BooksState, BookState, Book[]>(
getBooksState,
getBooks,
);Advanced selectors
import { BooksState, getAllBooks } from './books.reducers';
@Component({
selector: 'books-component',
template: `
<book-item *ngFor="let book of books$ | async" [book]="book">
</book-item>
`
})
export class BooksComponent implements OnInit {
books$: Observable<Book[]>;
constructor(private store: Store<BooksState>) {}
ngOnInit() {
this.books$ = this.store.select(getAllBooks);
}
}Data flow
Component
Action
Reducer
State
dispatch
new state
render
STORE
sent to
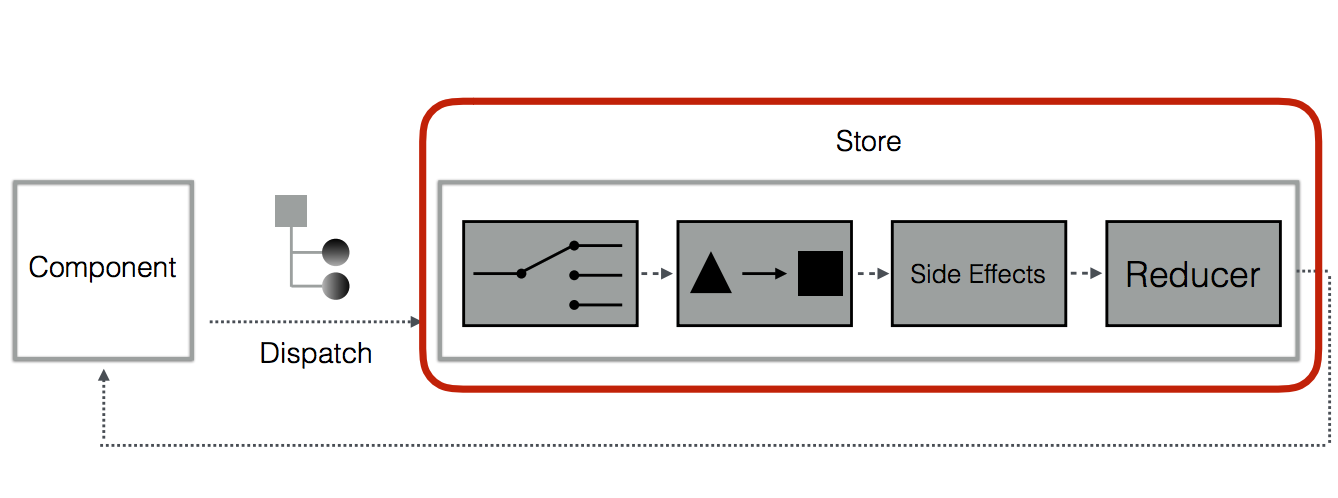
Data flow - with side effects
Component
Action
Reducer
State
dispatch
new state
render
STORE
sent to
EFFECTS
EFFECT
SERVICE
Action
Effects
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { Actions, Effect } from '@ngrx/effects';
import { of } from 'rxjs/observable/of';
import { concatMap, map, catchError } from 'rxjs/operators';
@Injectable()
class BooksEffects {
constructor(private actions$: Actions, private http: Http) {}
@Effect()
addBook$ = this.actions$.ofType('ADD_BOOK').pipe(
concatMap(book =>
this.http.post('api/book', book)
.pipe(
map(responseBook =>
({type: 'BOOK_ADDED', payload: responseBook}),
catchError(error =>
of({type: 'BOOK_ADD_FAIL', payload: error}))
)
)
);
}"message bus"
Effects - reducer
export interface BookState {
books: Book[];
loading: boolean;
error: boolean;
}
export const initialState: BookState = {
books: [],
loading: false,
error: undefined,
};
export function reducer(state = initialState, action): BookState {
switch (action.type) {
case ADD_BOOK: {
return { ...state, error: undefined, loading: true };
}
case BOOK_ADDED: {
return { ...state, loading: false, books: [...state.books, action.payload] };
}
case BOOK_ADD_FAIL: {
return { ...state, error: action.payload, loading: false };
}
}
return state;
}Commands and events
@Injectable()
class TodosEffects {
constructor(private actions$: Actions, private http: Http) {}
@Effect()
addBook$ = this.actions$.ofType('ADD_BOOK')
.pipe(
concatMap(book => this.http.post('api/book', book)
.pipe(
map(() => ({type: 'BOOK_ADDED', payload: book}))
)
);
}
function booksReducer(state: Book[] = [], action: any): Book[] {
switch (action.type) {
case('BOOK_ADDED') {
return [...books, action.payload];
}
}
return todos;
}This action is not handled in the reducer, it's dispatched just for the effect
Store
Credits to:
Effect classes
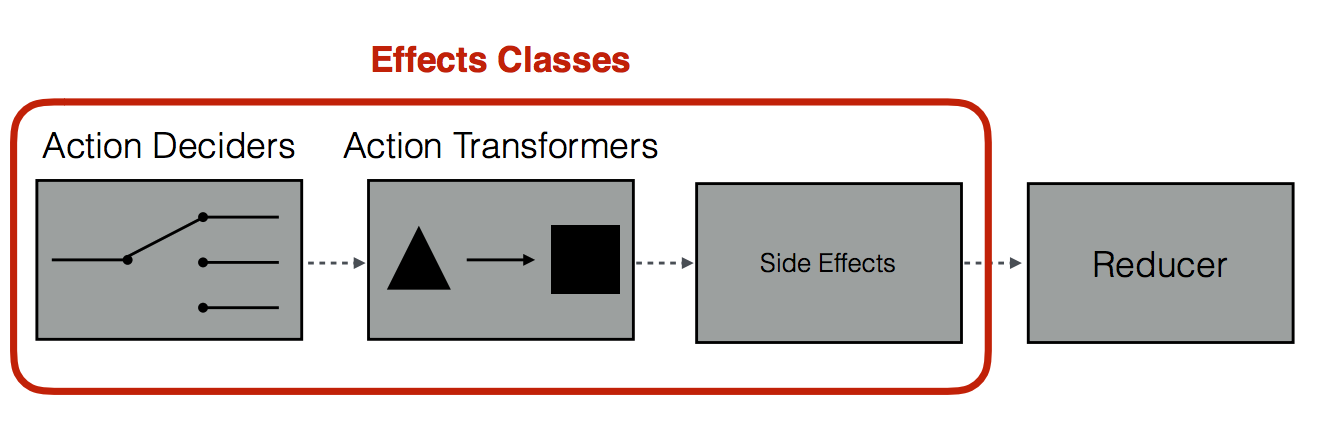
Effect classes
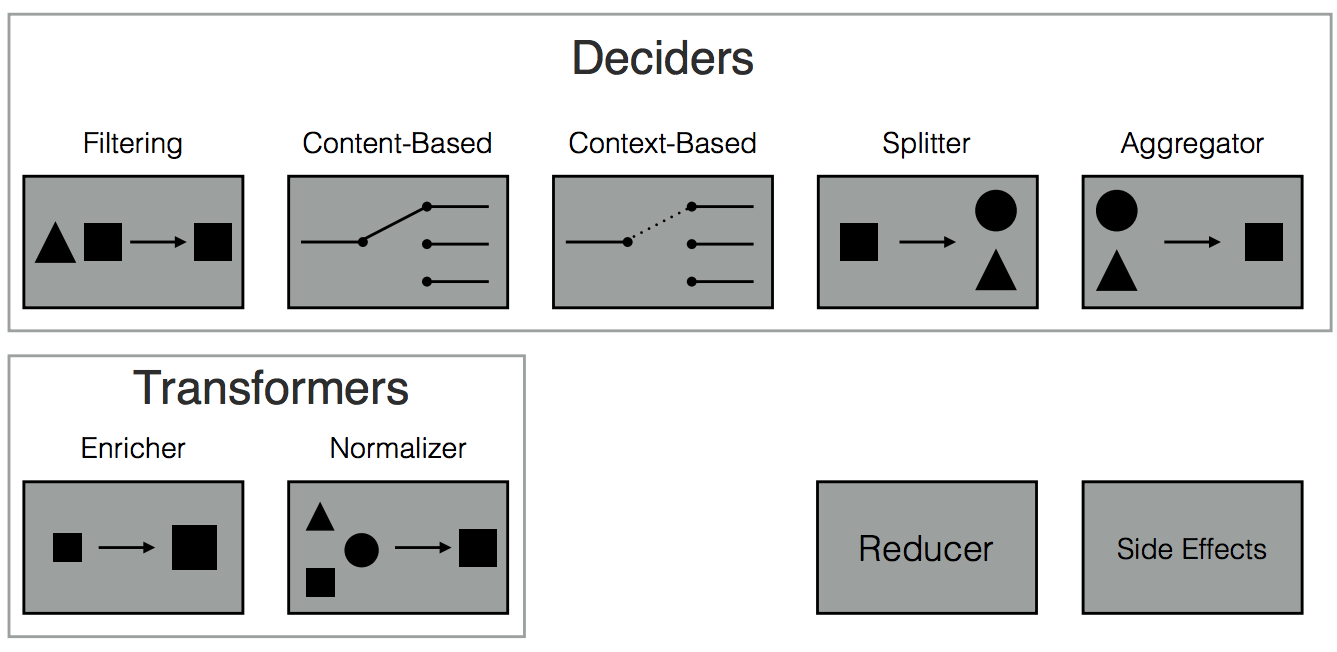
Effect deciders examples
class BooksEffects {
constructor(private actions: Actions, private env: Env) {}
@Effect()
addBook = this.actions.typeOf('ADD_BOOK').pipe(map(addBook => {
if (this.env.confirmationIsOn) {
return ({type: 'ADD_BOOK_WITH_CONFIRMATION', payload: addBook.payload});
} else {
return ({type: 'ADD_BOOK_WITHOUT_CONFIRMATION', payload: addBook.payload});
}
});
}- Context-Based Decider
class TodosEffects {
constructor(private actions: Actions) {}
@Effect()
addBook = this.actions.typeOf('REQUEST_ADD_BOOK').pipe(flatMap(add => [
{type: 'ADD_BOOK', payload: add.payload},
{type: 'LOG_OPERATION', payload: {loggedAction: 'ADD_BOOK', payload: add.payload}}
]);
}- Splitter
Action Transformers example
class BooksEffects {
constructor(private actions$: Actions, private currentUser: User) {}
@Effect()
addBook$ = this.actions$.ofType('ADD_BOOK').pipe(
map(add => ({
action: 'ADD_BOOK_BY_USER',
payload: {...add.payload, user: this.currentUser}
}))
);
}- Content Enricher
ngrx advanced stuff
- ngrx/router
- state preload with route guards
- advanced redux dev tools
- selector and state composition
- testing
Your turn!
http://bit.ly/2HWGuiq
Thank you!
Build awesome shit!
Reactive state management in Angular
By Andrei Antal
Reactive state management in Angular
Voxxed Days 2018 Bucharest Workshop - Reactive state management in Angular by Andrei Antal
- 1,943



