Version Control Systems: git
Andrei Mustață
- Software engineer etc
- Love me some git
This talk
- What VCS are
- Benefits of using one
- Basic `git`
Version Control System
- ... version control
- "Records changes to a [...] set of files"1
- "recall specific versions later"1
What is it?
Version Control System
- CTRL+Z has its limits
- Creates a safe environment for work
- Encourages innovation
Why bother?
Version Control System
- Google Docs
- ?
Examples
Version Control System
- What?
- Why?
Intro - wrap-up
Version Control System
- Copy files to separate directories
- Timestamp in filenames
- Error-prone
Local - manual
Version Control System
- File versioning is handled, which is nice
- HDD corruption
- What about collaboration?
Local - Issues?
Version Control System
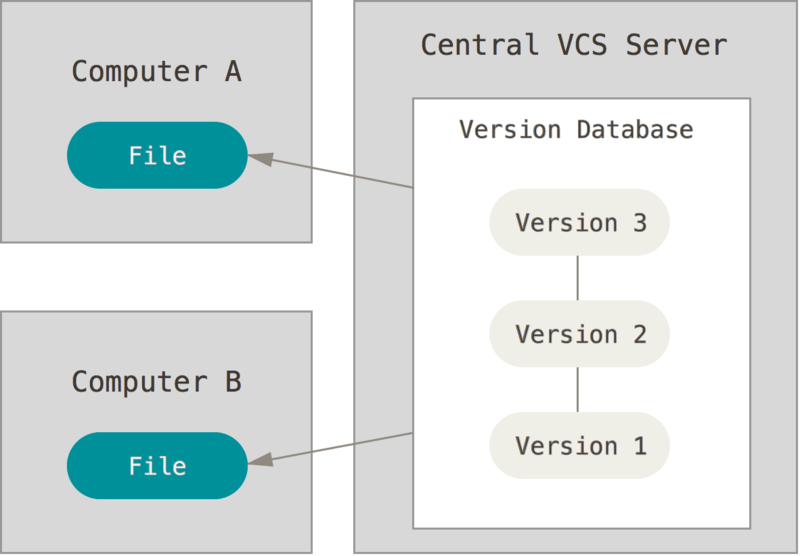
Centralised (CVCS)
Version Control System
- Files are on a single server
- More people can access it
- Teamwork makes the dreamwork
- Examples: CVS, SVN, Perforce
Centralised (CVCS)
Version Control System
- Files are still versioned
- Collaboration is allowed
- ?
- Single-point of failure
- HDD corruption
Centralised (CVCS) - Issues?
Version Control System
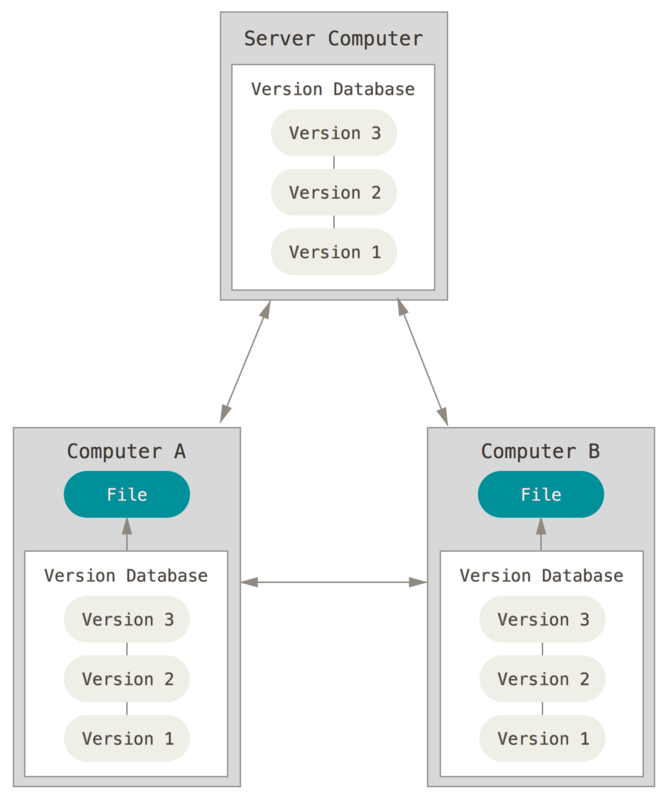
Distributed (DVCS)
Version Control System
- More arrows
- Clients fully mirror the repo
- Server dies, client repos can serve as backups
- Allows for different workflows
- Examples: git, Mercurial, Bazaar
Distributed (DVCS)

Version Control System
Distributed (DVCS) - git
- Created by Linus Torvalds for the Linux kernel
- Great for large projects
- Great for branching
Version Control System
Distributed (DVCS) - Issues?
- ?
- Surely there are some
Version Control System
Types - wrap-up
- Local - manual
- Local - using tools
- Centralised - server-client
- Distributed - server-client-like, but not necessarily
git
-
How it works
-
Installation, setup
-
Most used commands
git
How it works
- Snapshots
- Most operations are local
- Check-sums
- Fear of the data-loss
- Three states
git
Everything (almost) is local
- Most operations are done on the local file system
- No network overhead = offline work
- Differences in files between now and 7 days ago
- Commit away
git
Everything is check-summed
- Before storing files, git always check-sums it
- Can't change stuff without git knowing about it
- SHA-1, based on file content
git
Everything is (pretty) safe
- Once the commit has been made, it's pretty safe
- It's hard to get git to do things that are not undoable
- Freedom to try new things without losing the initial state
git
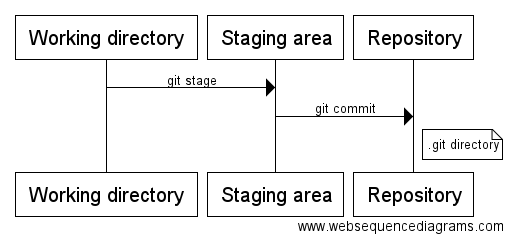
The three states
- Working directory
- Staging area
- Repository (local .git directory)
git
Basic workflow
- Modify files on your machine
- Stage the files
- Commit
DEMO TIEM
git
Basics - wrap-up
- Safety-net
- Three states: working, staging, repository
- Modify-Stage-Commit
git
Setup
- Install - cmd or GUI
- SourceTree from Atlassian
- Configure user.name, user.email
- on you go!
git
Setup
- Create an Atlassian (BitBucket) account
git
Local repository
- Create your own
- Clone an existing one
git
Create local repository
$ mkdir hello-world-git
$ cd hello-world-git
$ git init
$ ls -lagit
Recording changes
- staging files
- committing files
git
Staging files
$ date >>README.md
$ git stage README.mdgit
Committing changes
$ git commitgit
Recording changes
- modify (hacky thingy changy)
- stage (git stage <filename>)
- commit (git commit)
- you're done, go home
git
Status
- what the repository status is
$ git statusgit
Status of a file
- Untracked - new file, not added anywhere yet
- Staged - file in git staging area
- Unmodified - ...
- Modified - file is tracked by git; changed
git
Diff
- differences
$ git diffgit
Branches
- at least one branch, default master
- add stuff without interfering with the main branch
- allows for experimenting without fear of breaking
$ git branch my-featuregit
Merge
- bring changes from a branch into another branch
$ git merge my-feature-branchgit
Clone remote repository
$ rm hello-world-git
$ git clone https://bitbucket.org/andreimic/hello-world-git.git
$ cd hello-world-git
$ ls -la- git clone downloads a full copy of the repository
- access to the whole public history of the project
git
Push
- don't keep changes to yourself
- push to the common git server (remote)
$ # git push <remote> <branch>
$ git push origin mastergit
Code review
- Pull/merge request
- Lookie what I did
- Comments
git
Less important stuff
- ignoring files
- hm
but important still
git
Ignoring files
- pls no binaries
- pls no zip files
- .gitignore file
- https://github.com/github/gitignore
*.class
# Mobile Tools for Java (J2ME)
.mtj.tmp/
# Package Files #
*.jar
*.war
*.ear
# virtual machine crash logs, see http://www.java.com/en/download/help/error_hotspot.xml
hs_err_pid*git
Commit early
- pls
- made some progress? commit!
Reading material
Practice material
References
Happy weekend!
Version Control Systems: git 2019
By andreimoustache
Version Control Systems: git 2019
- 83