Feature selection

Feature Selection: что это
- Отбор признаков по какому-то критерию

Feature Selection: зачем
- Уменьшить overfitting
- Улучшить качество модели
- Ускорить работу моделей
- Упростить интерпретацию
Feature Selection: Подходы

FS: стандартные подходы
- Статистические тесты
- Корреляция с целевой переменной
- Исключение высоко коррелирующих признаков
- Исключение мультиколлинеарности
- Information value, weights of evidence
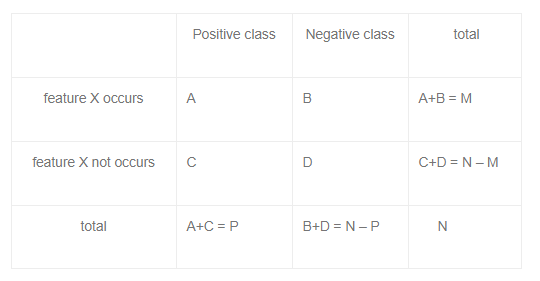
FS: Статистические тесты
- chi2
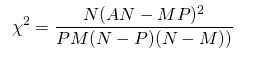
FS: Статистические тесты
- ANOVA
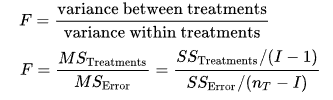
FS: Статистические тесты
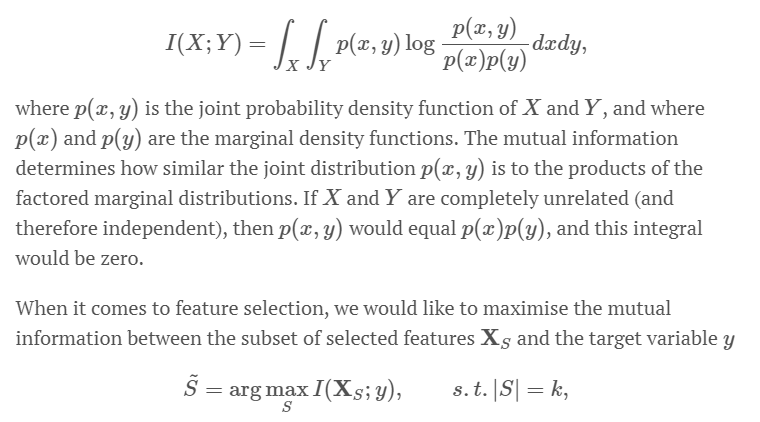
- Mutial information
FS: Статистические тесты

Статистические тесты: практика
>>> from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
>>> from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
>>> from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2
>>> iris = load_iris()
>>> X, y = iris.data, iris.target
>>> X.shape
(150, 4)
>>> X_new = SelectKBest(chi2, k=2).fit_transform(X, y)FS: Корреляция с целевой переменной
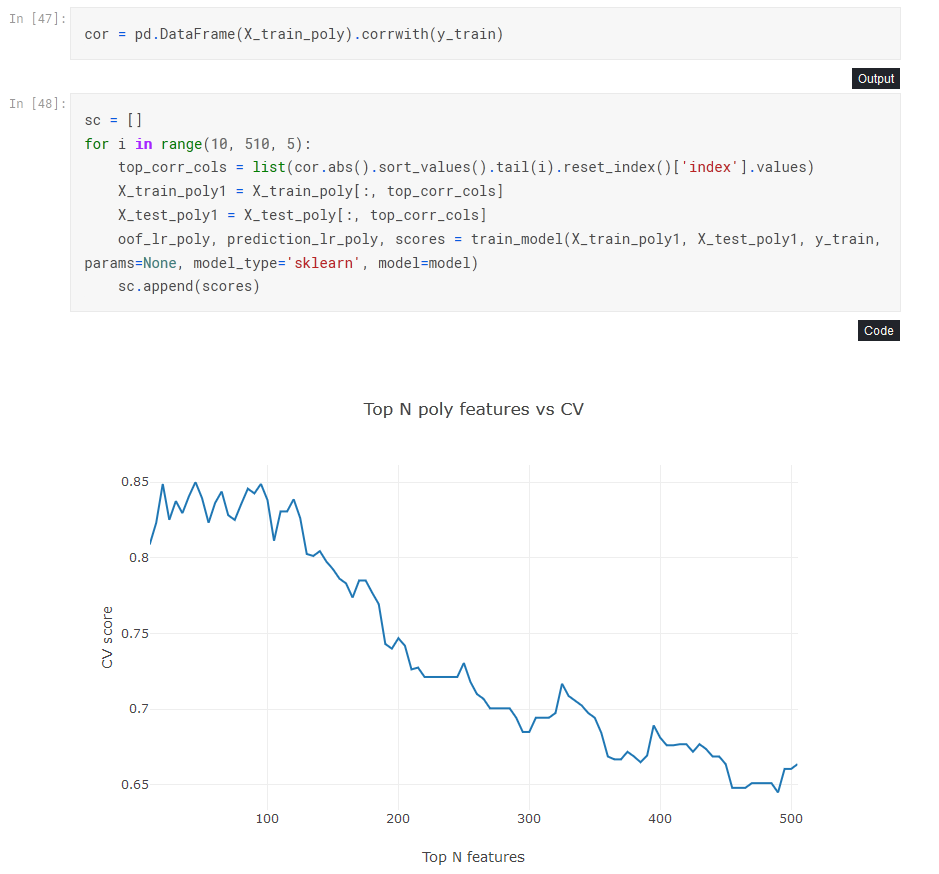
FS: скоррелированные признаки
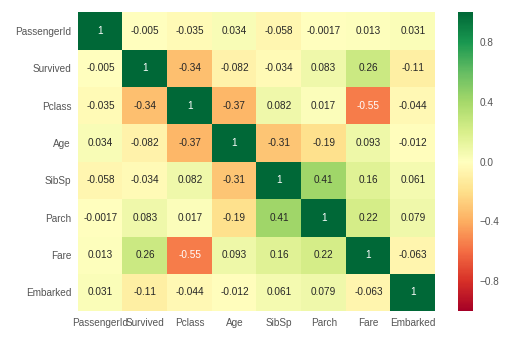
FS: мультиколлинеарность
from statsmodels.stats.outliers_influence import variance_inflation_factor
def check_vif(data, test, target_name, cols_to_drop, verbose=0):
if verbose == 1:
print('Checking VIF values')
X_train_multicoll = data.drop([target_name], axis=1).copy()
X_train_multicoll['intercept'] = 1
max_vif_value = float('inf')
if verbose == 1:
print(X_train_multicoll.shape)
while max_vif_value > 100:
vif = [variance_inflation_factor(X_train_multicoll.values, i) for i in
range(X_train_multicoll.shape[1])]
g = [i for i in list(zip(X_train_multicoll.columns, vif))]
g = [i for i in g if i[0] != 'intercept']
max_vif = max(g, key=itemgetter(1))
if verbose == 1:
print(max_vif)
if max_vif[1] < 100:
if verbose == 1:
print('Done')
break
else:
X_train_multicoll.drop([max_vif[0]], axis=1, inplace=True)
cols_to_drop.append(max_vif[0])
data.drop([max_vif[0]], axis=1, inplace=True)
test.drop([max_vif[0]], axis=1, inplace=True)
if verbose == 1:
print(X_train_multicoll.shape)
max_vif_value = max_vif[1]
return data, test, cols_to_dropFS: IV, WOE
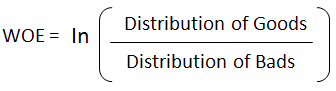
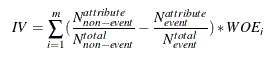
FS: Перебор признаков

Text
FS: Feature importance
- Линейные модели: коэффициенты
- Tree-based models: split, gain, coverage
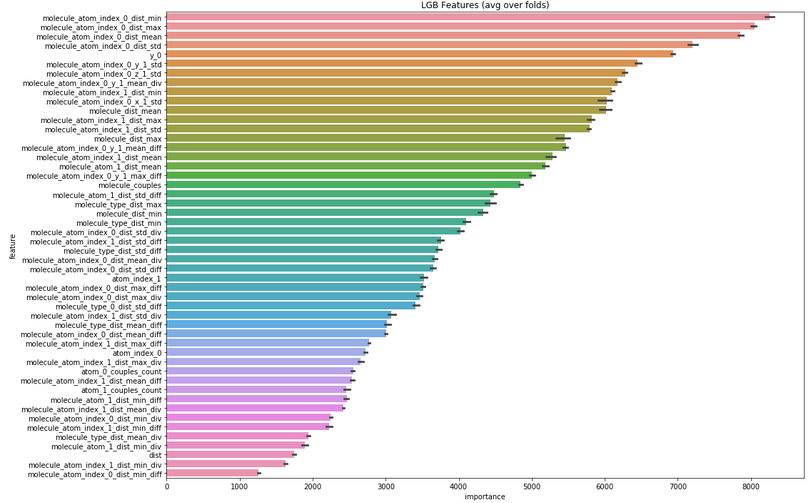
FS: Feature importance
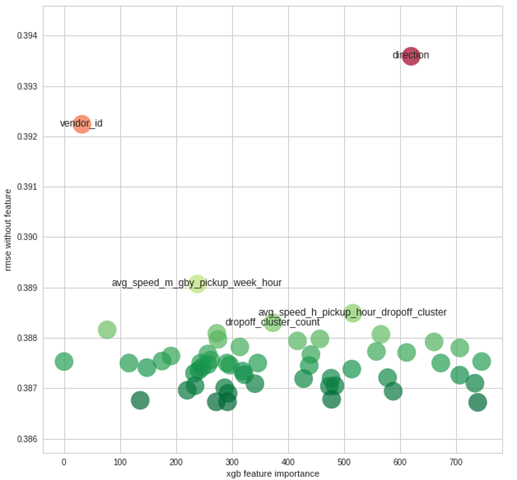
FS: регуляризация
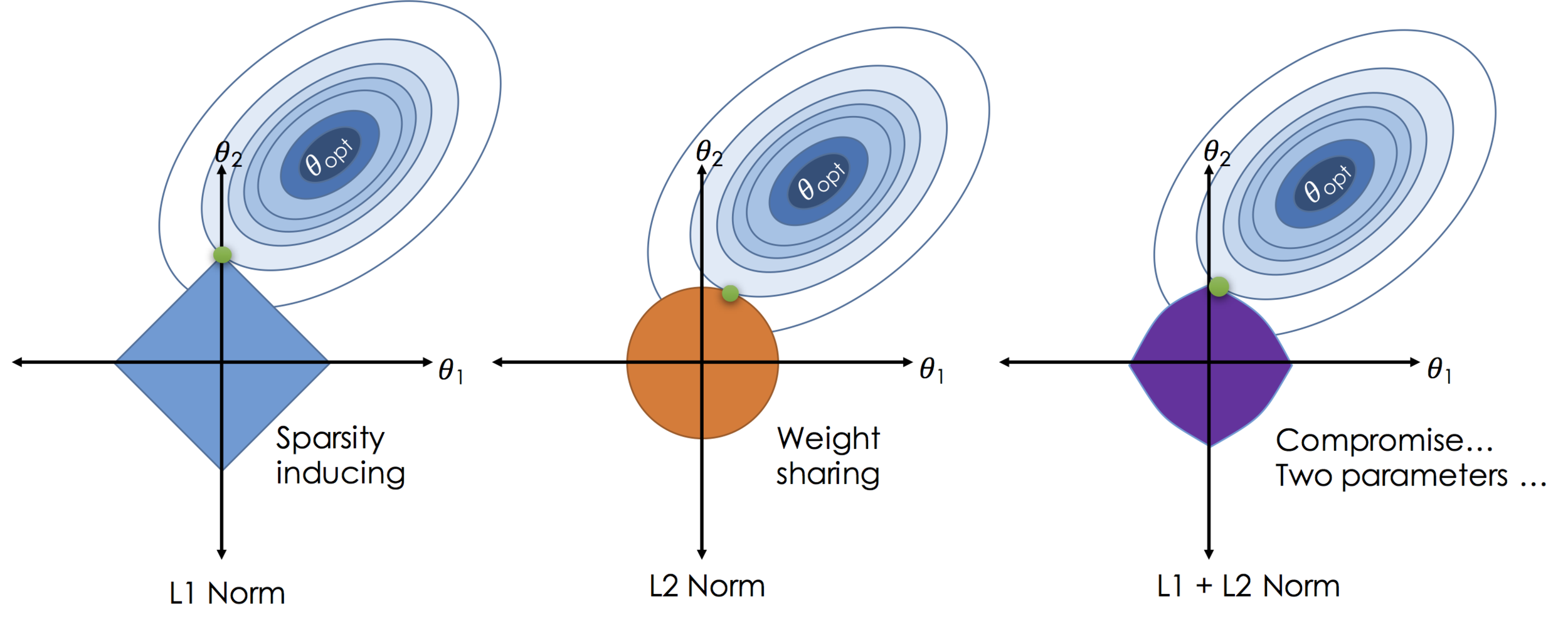
FS: "другие" инструменты
- Permutation importance
- Recursive feature elimination
- ELI5/SHAP
- Boruta/Boostaroota
- Adversarial validation
FS: Permutation importance
FS: Permutation importance
def permutation_importances(rf, X_train, y_train, metric):
baseline = metric(rf, X_train, y_train)
imp = []
for col in X_train.columns:
save = X_train[col].copy()
X_train[col] = np.random.permutation(X_train[col])
m = metric(rf, X_train, y_train)
X_train[col] = save
imp.append(baseline - m)
return np.array(imp)perm = PermutationImportance(model, random_state=1).fit(X_train, y_train)
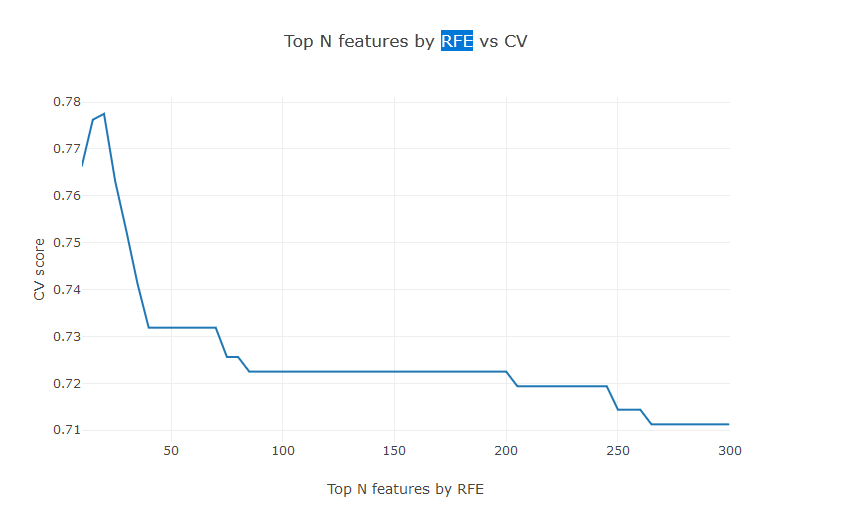
eli5.show_weights(perm, top=50)FS: RFE
- На каждом шаге тренируем заданную модель и отбрасываем наименее важные признаки
FS: ELI5/SHAP
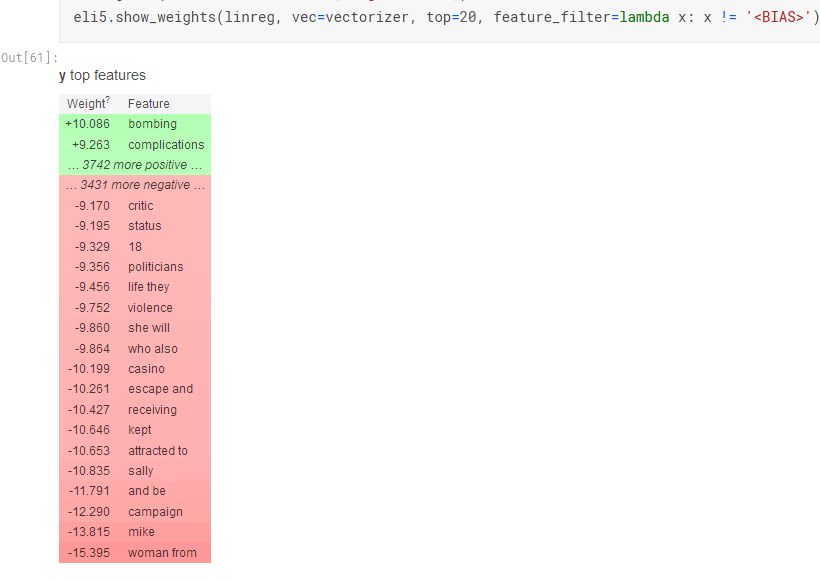
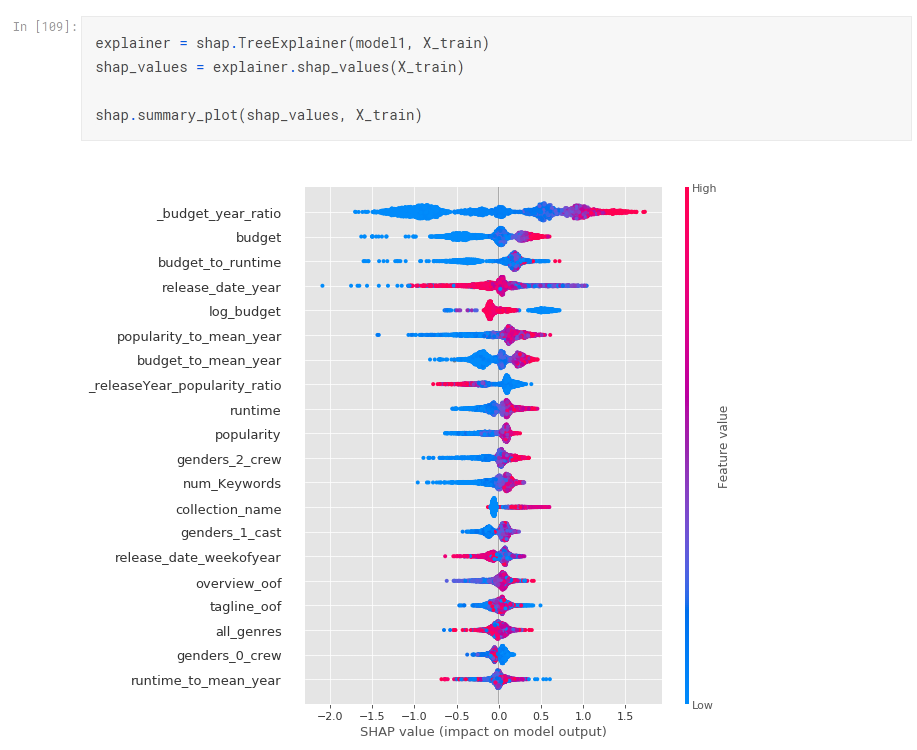
https://www.kaggle.com/artgor/eda-feature-engineering-and-model-interpretation
FS: ELI5/SHAP
https://www.kaggle.com/artgor/eda-feature-engineering-and-model-interpretation
FS: Boruta
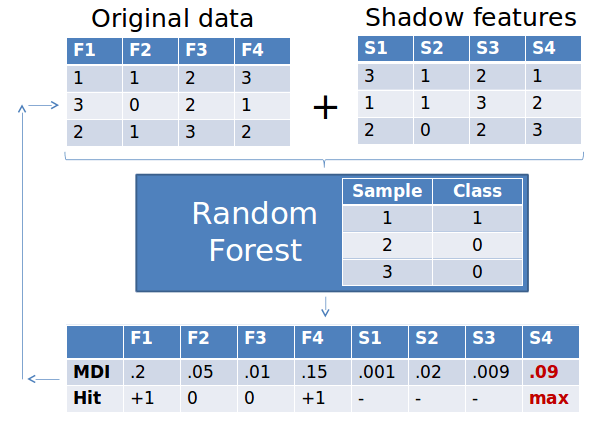
FS: Boruta
from boruta import BorutaPy
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_jobs=-1, class_weight='balanced', max_depth=5)
# define Boruta feature selection method
feat_selector = BorutaPy(rf, n_estimators='auto', verbose=2, random_state=1)
# find all relevant features - 5 features should be selected
feat_selector.fit(X, y)
# check selected features - first 5 features are selected
feat_selector.support_
# check ranking of features
feat_selector.ranking_
# call transform() on X to filter it down to selected features
X_filtered = feat_selector.transform(X)FS: BoostARoota
from boostaroota import BoostARoota
br = BoostARoota(metric='logloss')
#Fit the model for the subset of variables
br.fit(x, y)
#Can look at the important variables - will return a pandas series
br.keep_vars_
#Then modify dataframe to only include the important variables
x1 = br.transform(x)FS: Adversarial validation

FS: Adversarial validation
features = X_train.columns
X_train['target'] = 0
X_valid['target'] = 1
train_test = pd.concat([X_train, X_valid], axis =0)
target = train_test['target']
# train modelFS: bonus ideas
Guided Regularized Random Forests
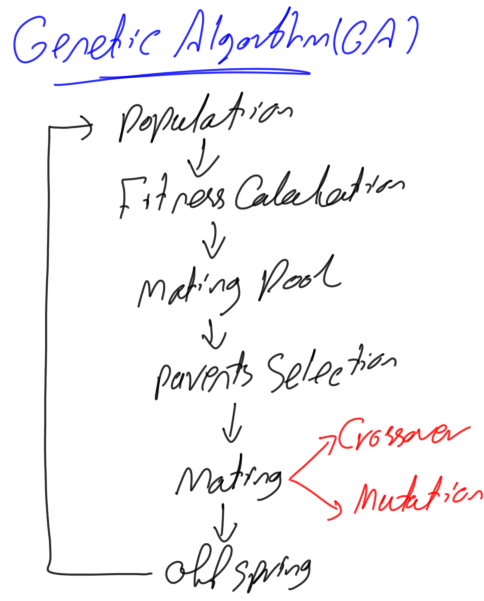
Генетические алгоритмы
Feature selection
By Andrey Lukyanenko
Feature selection
- 645



