

React components
- Class Components
- Functional Components
function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}class Welcome extends React.Component {
render() {
return <h1>Hello, {this.props.name}</h1>;
}
}
Functional Component
- The simplest way to define a component
- No state
- No access to lifecycle hooks
- Each change calls re-render

Class Component
- The opposite to functional component
- Has state
- Has access to lifecycle hooks
- Re-render can be canceled

Component styling
- Global CSS
- CSS in JS
- Styled-Components

Global CSS
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="theme.css">
</head>
// or
import '../componetn.css' // sass, less...
<button className='btn'></button>
<button className='btn btn-primary'></button>
CSS in JS
- Sharing constants and functions between JS and CSS.
- True rules isolation.
- Faster
But

CSS in JS
const Button = ({classes, children}) => (
<button className={classes.button}>
{children}
</button>
);
const styles = theme => ({
button: {
background: theme.colorPrimary
},
label: { // useless
fontWeight: 'bold'
}
});
const StyledButton = injectSheet(styles)(Button);const theme = {
colorPrimary: 'green',
animationDuration: 300,
};
const App = () => (
<ThemeProvider theme={theme}>
<StyledButton>I am a button</StyledButton>
</ThemeProvider>
);
Styled-Components
- All advantages of CSS in JS
- Pretty view
- Has emmet
- Has access to props

(emotion, glamorous)

ContactItem
const ContactItem = styled.div`
// ... usual CSS
flex-direction: ${({ isHeader }) =>
(isHeader ? 'row-reverse' : 'row')};
${({ isHeader }) => !isHeader && 'padding: 10px 0;'}
`;const ContactItemComponent = ({
...
isHeader,
isChat
}) => {
const styleProps = { isHeader, isChat };
return (
<ContactItem {...styleProps}>
...
</ContactItem>
);
};

Textarea
const Textarea = styled.textarea`
line-height:
${({lines}) => lines === 1 ? 26 : 16}px;
height:
${({lines}) => lines === 1 ? 26 : lines * 16}px;
`;class ChatInput extends Component {
...
stateHandler ({ target: { value } }) {
const lines = value.split(/\r*\n/).length;
this.setState({message: value, lines})
}
render() {
return <Textarea
lines={this.state.lines}
onChange={this.stateHandler.bind(this)}
/>
}
}
React Router
- Not a tree
- It is matcher

React Router
const Routes = [
{
path: 'dashboard',
component: DashboardComponent
},
{
path: 'heroes',
component: HeroesComponent
children: [
{
path: 'view/:id',
component: HeroDetailComponent
},
{
path: 'edit/:id',
component: HeroEditComponent
},
]
},
];<Router>
<Route path="/" component={App}>
<Route path="about" component={About} />
<Route path="inbox" component={Inbox}>
<Route path="messages/:id" component={Message} />
</Route>
</Route>
</Router>
<Route/>
const HeaderComponent = ({ title, contacts }) => {
return (
<Header>
<Route
path="/chats/:id"
children={({ match }) => {
if (match) {
const { params: { id } } = match;
return <ChatHeaderComponent data={contacts[id]} />;
} else { // match is undefined
return <Title>{title}</Title>;
}
}}
/>
</Header>
);
};
export default connect(stateToProps)(HeaderComponent);
withRouter
const HeaderComponent = ({ match, title, contacts }) => {
return (
<Header>
{match.path === '/chats/:id' ?
<ChatHeaderComponent data={contacts[Number(id)]} />
:
<Title>{title}</Title>
}
</Header>
);
};
export default withRouter(HeaderComponent);
Animations
const ANIMATION_DURATION = 300;
const Animation = styled.div`
transform: translate3d(100%, 0, 0);
transition: transform ${ANIMATION_DURATION}ms;
&.is-animate {
transform: translate3d(0, 0, 0);
}
`;class ChatTransition extends Component {
state = {
complete: false,
animate: false,
};
componentDidMount() {
setTimeout(() =>
this.setState({ animate: true }), 5);
setTimeout(() =>
this.setState({ complete: true }),
ANIMATION_DURATION
);
}
render() {
if (this.state.complete) {
return <Redirect to={this.props.to} />;
} else {
return
<Animation
className={this.state.animate ? 'is-animate' : ''}
>
<ChatContent/>
</Animation>
}
}
}
Animations
const AnimatedRoute = ({ component, render, children, ...props }) => (
<Route
{...props}
render={() =>
<Animation>
<Route {...props}
component={component}
render={render}
children={children}
/>
</Animation>
}
/>
);<Router>
<Switch>
{routes.map(({ to, component }, i) => (
<AnimatedRoute key={i} path={to} component={component} /> // key is required
))}
</Switch>
</Router>Usage

ScrollToOnMount
const Chat = ({ match: { params: { id } } }) => (
<Layout>
<ScrollToTopOnMount/>
<ChatContent id={id} />
<ChatInput key={2} />
</Layout>
);
class ScrollToTopOnMount extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
window.scrollTo(0, 0)
}
render() {
return null
}
}
React performance
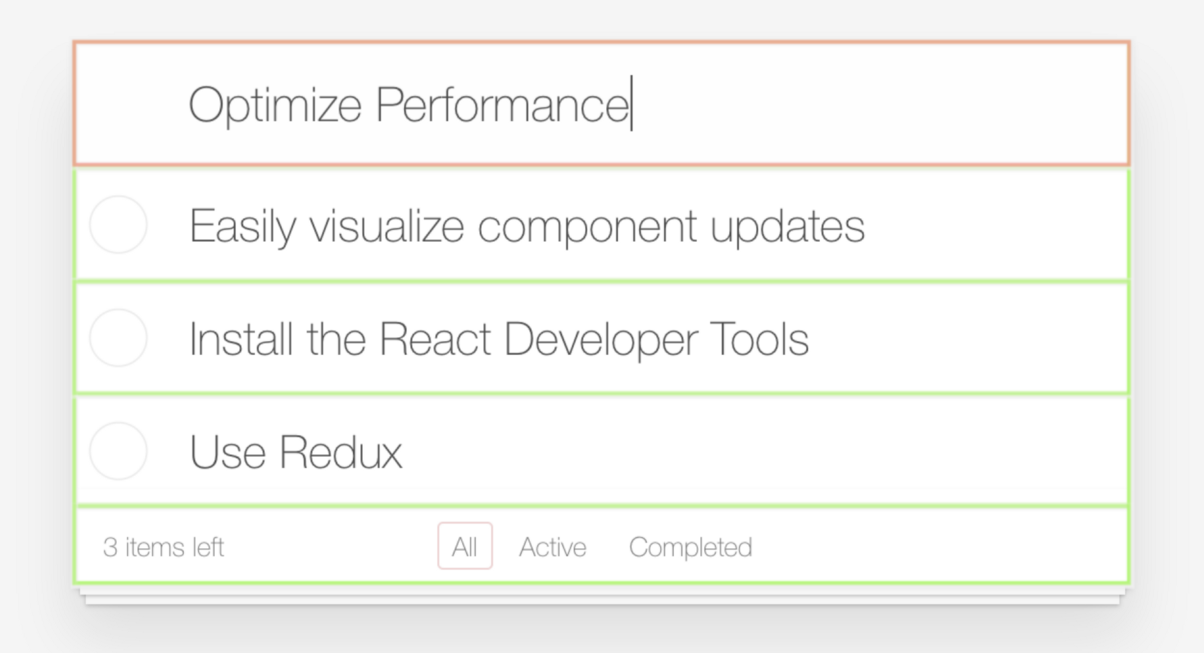

Render
Parse markup
and CSS
Create render tree
Reflow and Repaint

Rerender DOM causes
- Any dom updates
- Hide dom node
- Move / animation
- Style changes

Ways to optimizations
- Use lifecycle hooks
- Use Pure Components
- Use Redux

Lifecycle hooks
- componentWillMount()
- componentDidMount()
- componentWillReceiveProps()
- shouldComponentUpdate()
- componentWillUpdate()
- componentDidUpdate()
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (this.props.color !== nextProps.color) {
return true;
}
if (this.state.count !== nextState.count) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
React.PureComponent
React.PureComponent’s shouldComponentUpdate() only shallowly compares the objects. If these contain complex data structures, it may produce false-negatives for deeper differences.
class ContactItemPureComponent extends PureComponent {
render() {
const { name, imgPath, ...} = this.props;
return (
<ContactItem
name={name}
imgPath={imgPath}
/>
);
}
}
export default ContactItemPureComponent;!shallowEqual(prevProps, nextProps) ||
!shallowEqual(inst.state, nextState)
Use Redux Connect


Use Redux Connect
Technically, a container component is just a React component that uses store.subscribe() to read a part of the Redux state tree and supply props to a presentational component it renders.
const ContactItemWithConnect = ({ id, name, ... }) => (
<ContactItem
name={name}
...
/>
);
export default connect(
({ contacts: { data } }, { id }) => ({ ...data[id] }))
(ContactItemWithConnect);
Normalizing State Shape
// Contacts
[
{
id: 1,
imgPath: 'vboiko.jpg',
name:'Boiko Volodymyr',
isOnline: true,
lastSeen: '21.06.2017'
},
{
id: 2,
...
},
{
id: 3,
...
}
]// Contacts
{
data: {
1: {
imgPath: 'vboiko.jpg',
name:'Boiko Volodymyr',
isOnline: true,
lastSeen: '21.06.2017'
},
2: {...},
3: {...},
},
list: [1, 2, 3, n]
}

Use Redux Connect
Anytime any part of the state tree changes, TodoApp is gonna get rerendered
export default connect(state => state)(TodoApp)

Developer Tools
- React developer tools
- Redux developer tools
- React-addons-perf
- User Timing

React-addons-perf
As of React 16, react-addons-perf is not supported.
import Perf from 'react-addons-perf';
window.Perf = Perf;
// in console
Perf.start();
Perf.stop();
Perf.pringWasted();
// in Component
componentWillMout() {
Perf.start()
};
componentWillUnmout() {
Perf.stop()
Perf.pringWasted()
}

User Timing
The User Timing interface allows the developer to create application specific timestamps that are part of the browser's performance timeline.

User Timing
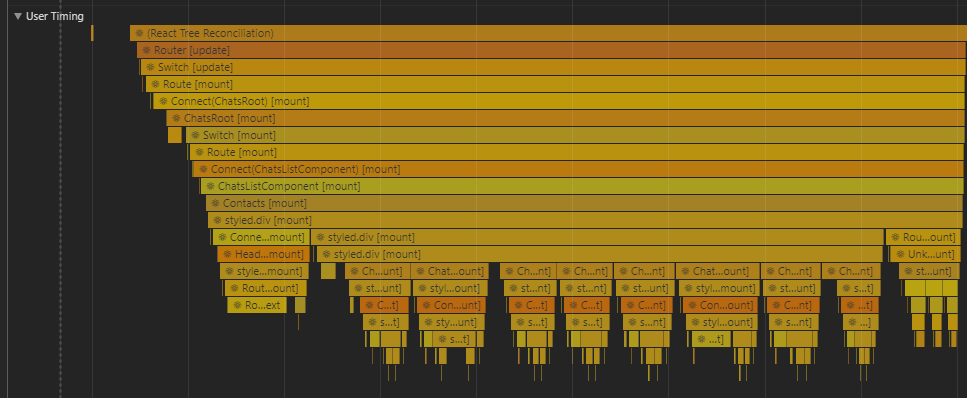
- In development mode
- react-create-app by default
- /?react_perf
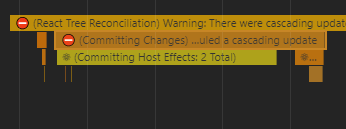

What to read

React Recipes
By Andrii Chubai
React Recipes
- 211



