Event Delegation in React 17
Ankita Masand
Principal Frontend Engineer at Treebo
Event Delegation
A pattern for handling events
Event Delegation
Single event handler for the common ancestor (Container) instead of assigning event handlers to each cell
There is only one event listener at the root table element and this helps in improving the performance of the application.
Event Delegation
We don't have to attach event handlers to all the cells in the table.
Can we attach onClick handlers for all the cells in a container?
Let's check on jsperf.com
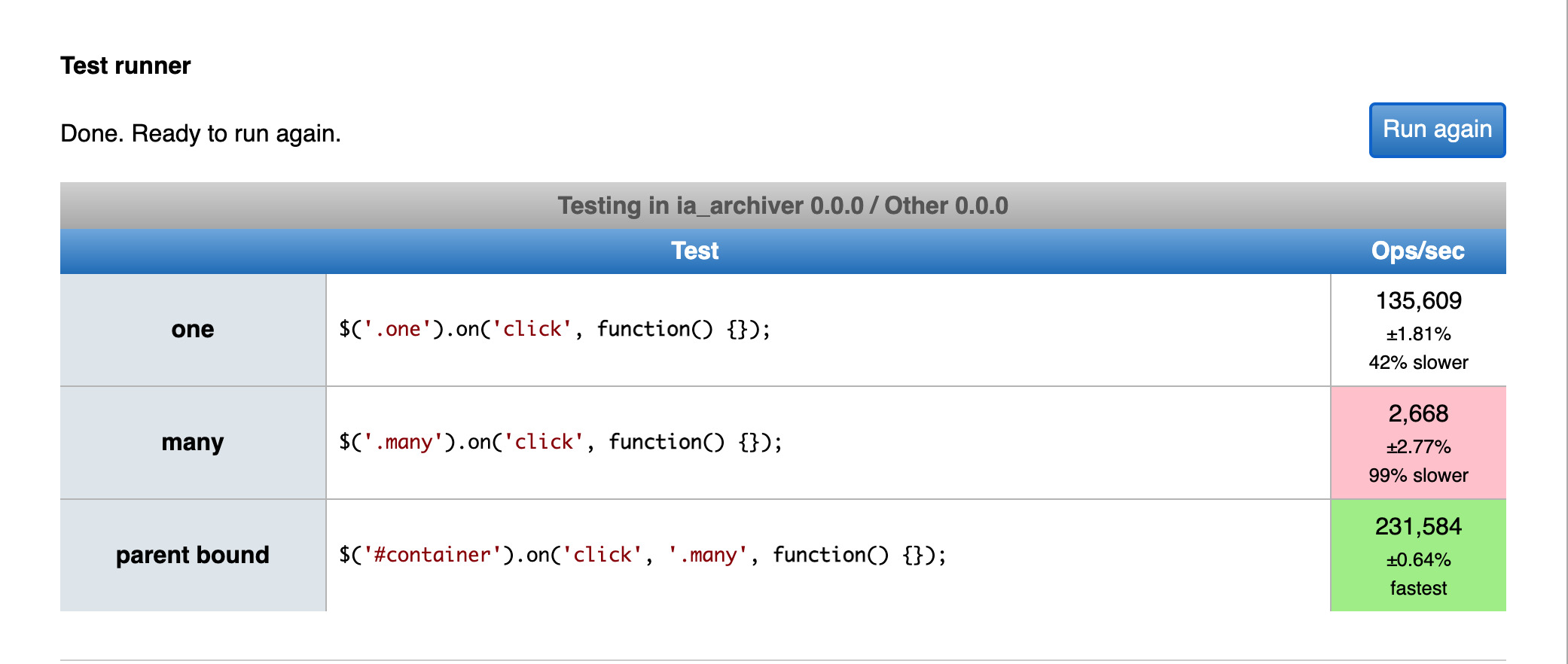
Click Event Perf Results
Learnings:
- Binding an event to many elements is much slower
- The most performant way is to bind an event to the parent and delegate it to the target nodes
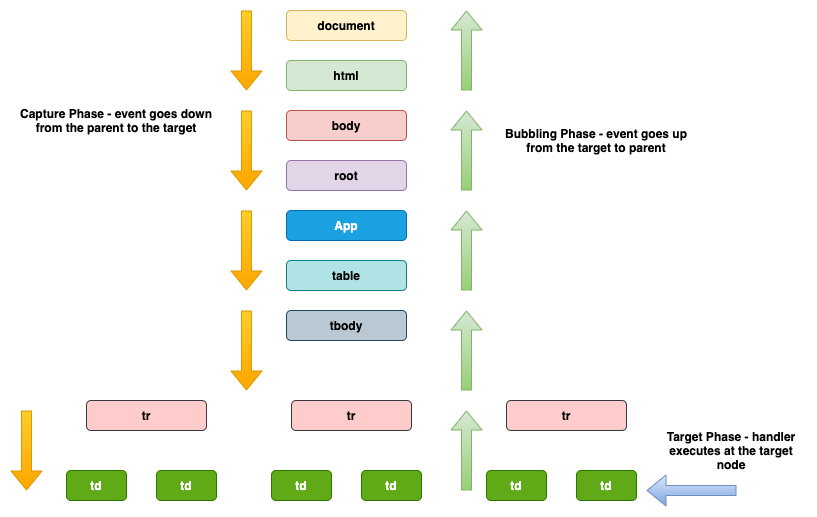
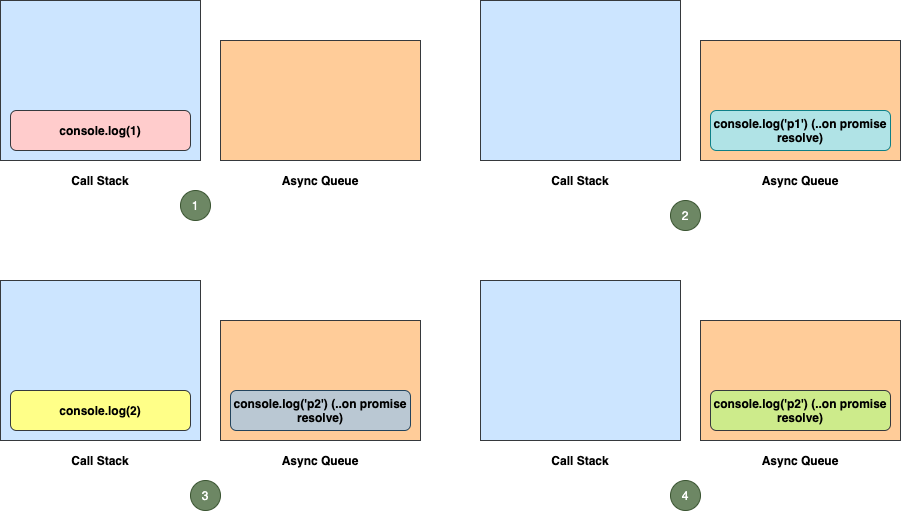
How do events propagate from the parent node (as the listener is attached to the parent) to the target?

Image by Holger Kraft from Pixabay
Event Phases
Event.None (0)
- No event being executed
Event.CAPTURING_PHASE (1)
- Event handlers are executed while descending down the tree
Event.AT_TARGET (2)
- Event handler being executed at the target node
Event.BUBBLING_PHASE (3)
- Event handlers are executed while ascending up the tree
Event Phases
Bonus tip on Event Listeners!
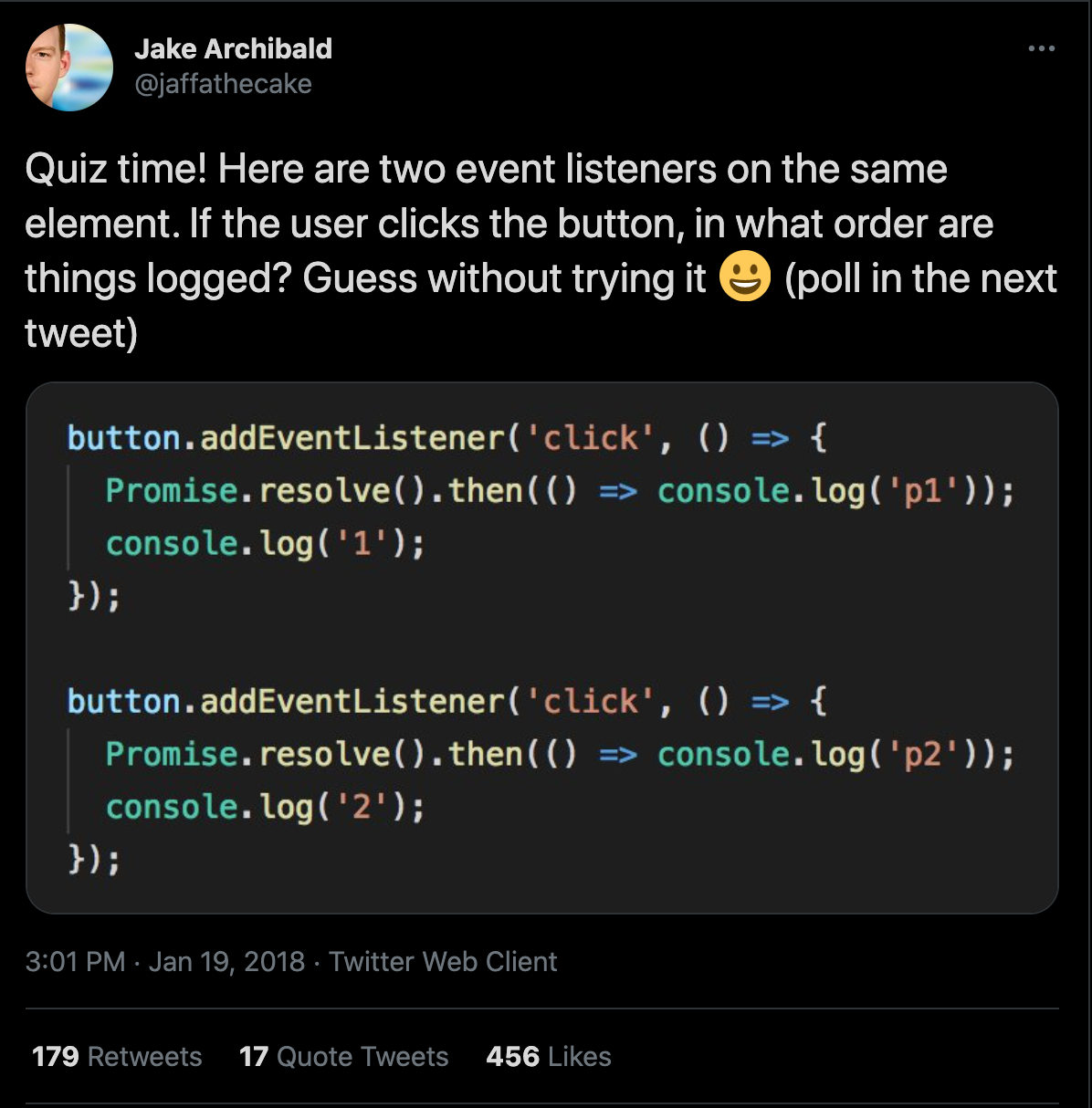
The Correct Answer is...
1, p1, 2, p2
- Both the click event listeners would be registered against the button element
- The call stack is empty between both of them and that's when the promise p1 is resolved.
- Promises resolve asynchronously and they would be executed when the stack is empty.
Let's get back to Event Delegation in React!
Image by Manfred Steger from Pixabay
Events in React
Wrapper around default browser events - Synthetic events
boolean bubbles
boolean cancelable
DOMEventTarget currentTarget
boolean defaultPrevented
number eventPhase
boolean isTrusted
DOMEvent nativeEvent
void preventDefault()
boolean isDefaultPrevented()
void stopPropagation()
boolean isPropagationStopped()
void persist()
DOMEventTarget target
number timeStamp
string typeSynthetic Event Attributes
Event Delegation in React
We don't write `document.addEventListener('click', () => {})` as we used to do in JavaScript, JQuery and other libraries.
React automatically attaches event listeners at the document node.
React follows event bubbling and executes event handlers during the bubbling phase.
Event Delegation in React 16 and earlier versions
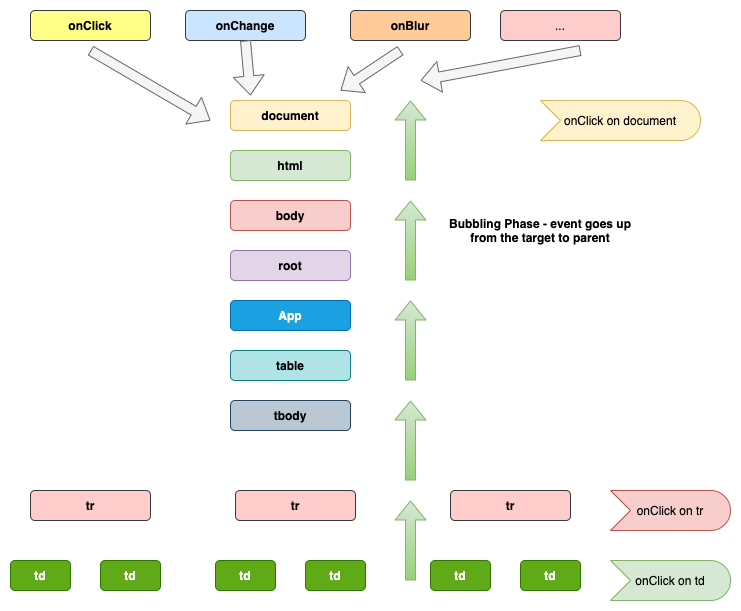
React 16 and earlier attaches event handler of each type to the document node
Event Delegation in React 16 and earlier versions
Attaching Event handlers at the document node caused some issues in the larger react Projects
Issue reported by the Atom editor while using two versions of React in nested React Trees - Link
Event Delegation in React 16 and earlier versions
We won't be able to track the events (example: analytics events) at the window level for the nested tree if it stops the event propagation in the handler
The events won't reach the outer event handler in larger projects where React is a smaller portion of the project and the other modules are written in different frameworks/libraries.
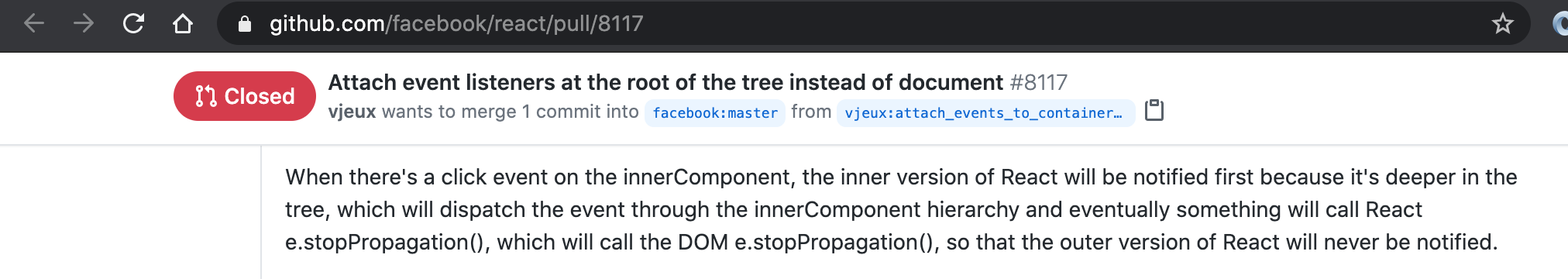
Event Delegation in React 17
React no longer attaches event handlers to the document node. It instead attaches event handlers to the react-dom container in which the react tree is rendered.
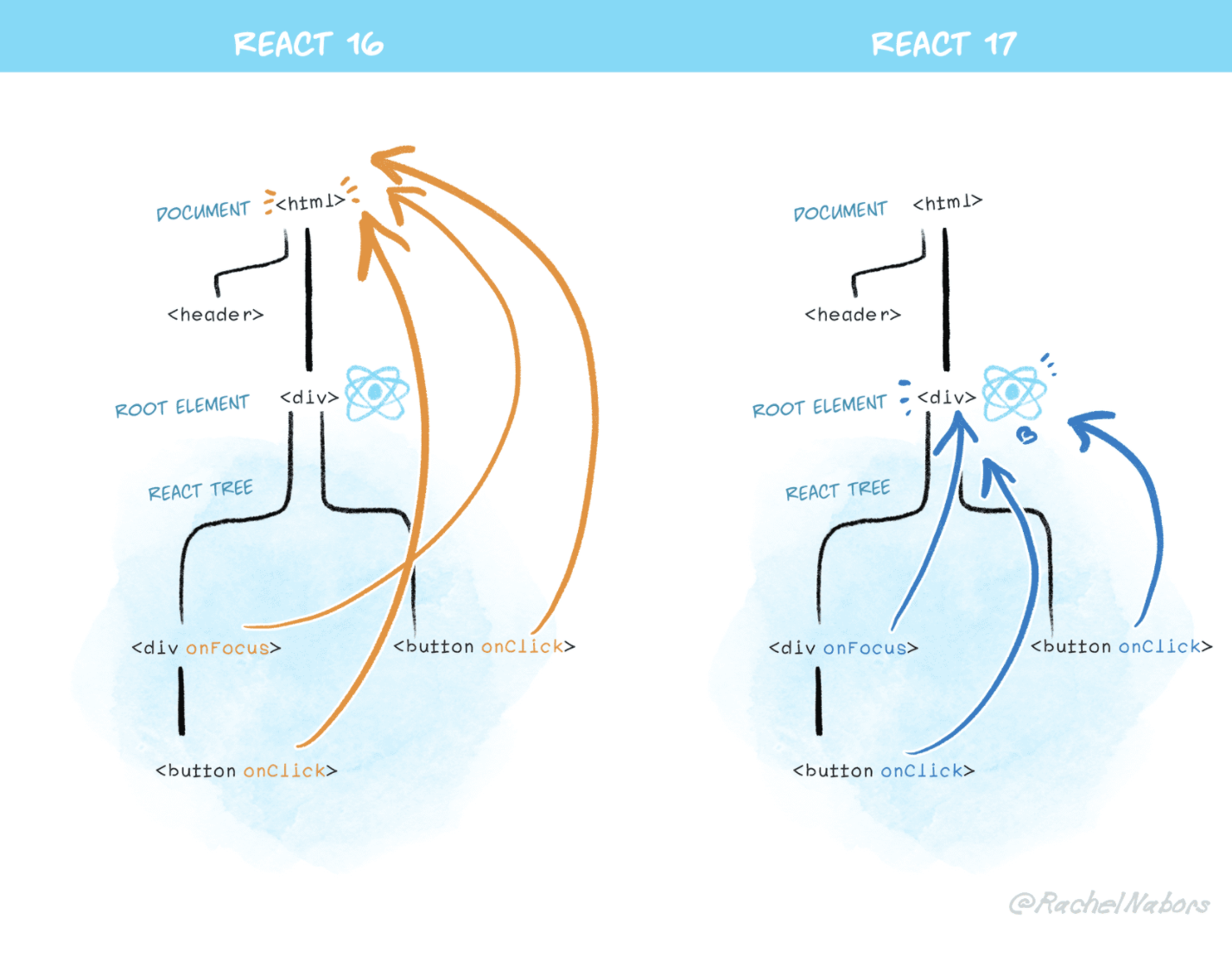
Reference: React blog
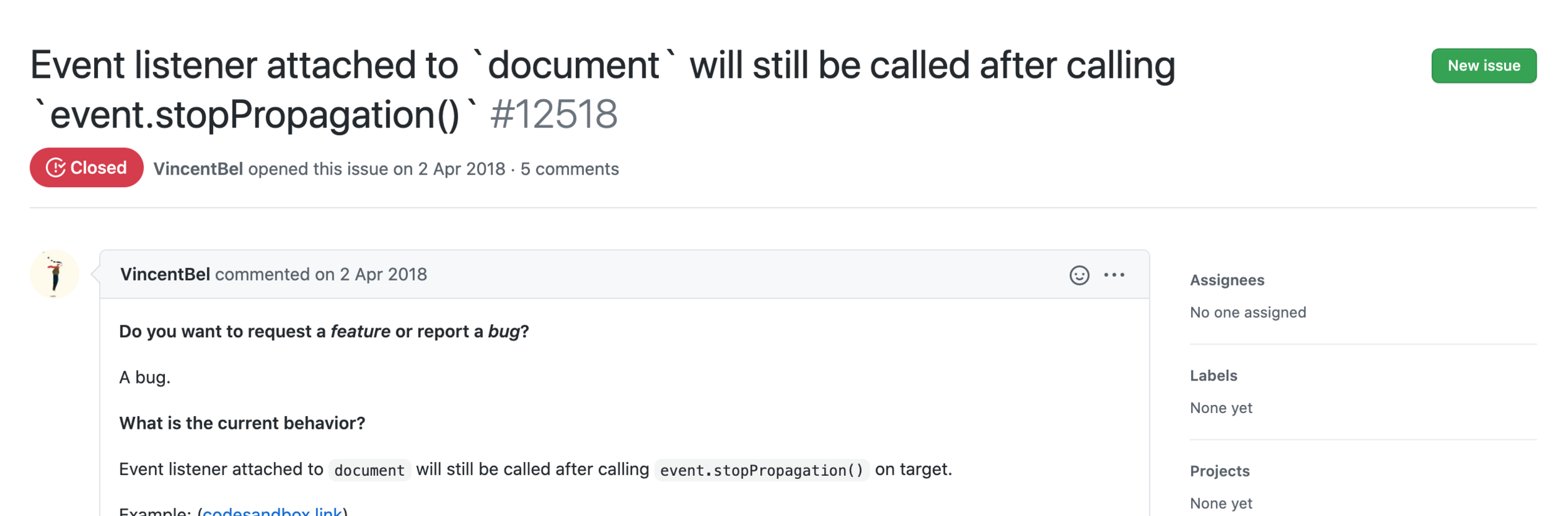
This solves for numerous bugs reported in the past
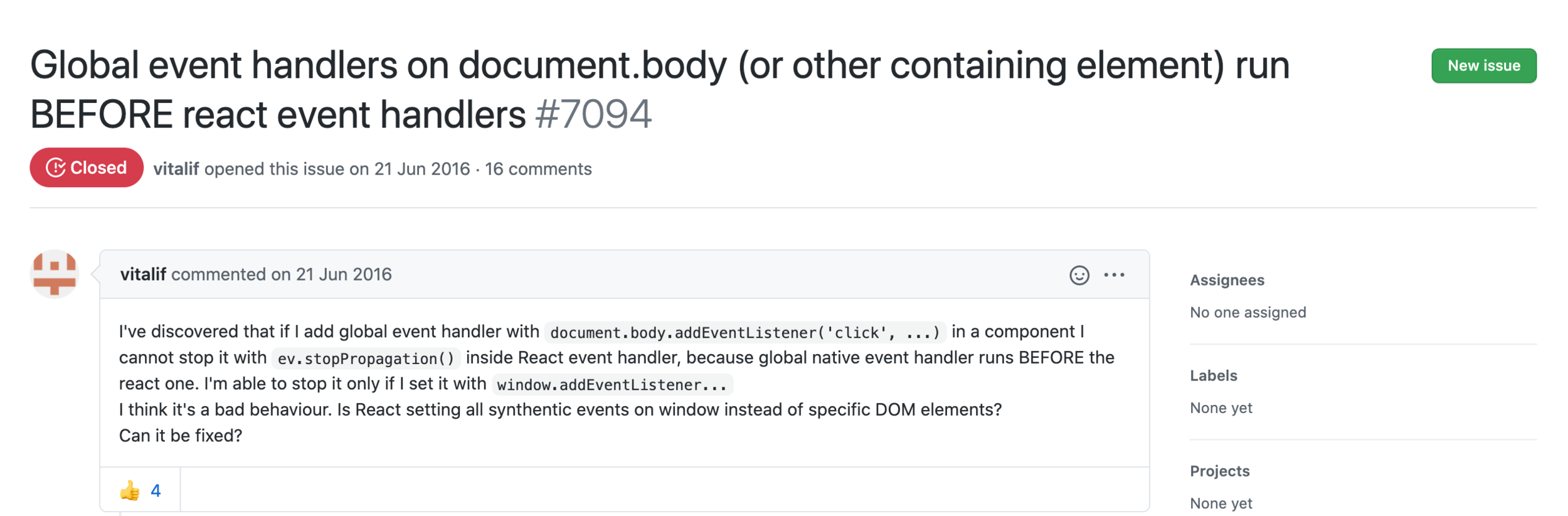
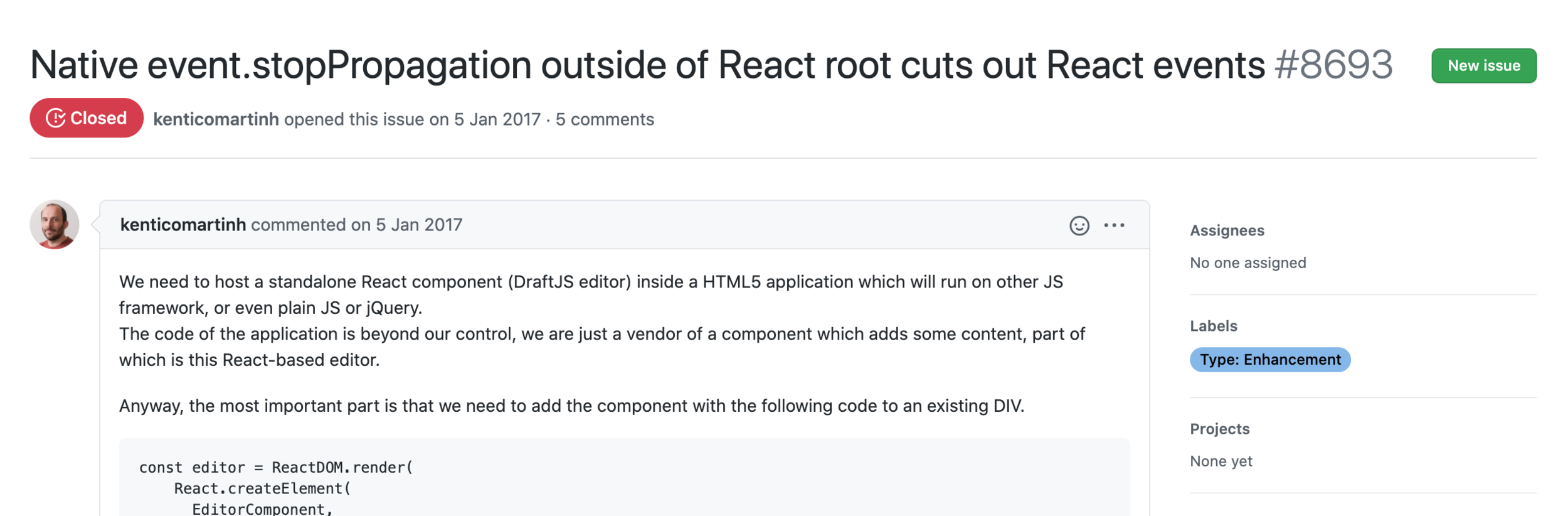
This solves for numerous bugs reported in the past
Quick Recap
Event Delegation
- Instead of having event listeners for all the child nodes, we can have event listeners of each type at the root node.
Event Phases
- Capturing Phase (parent to target node), Bubbling Phase (target to parent node)
Event Delegation in React 16 and earlier
- React automatically handles event delegation and attaches event handlers at the document node in React 16 and earlier versions
Event Delegation in React 17
- React 17 attaches event handlers at the root node in the react tree
Thank you!
Event Delegation in React 17
By Ankita Masand
Event Delegation in React 17
- 1,229