Career Growth in Software Development
Touhid Arastu
Feb 2024
- Director of engineering at Snapp!
- Active in the tech industry since 2008.
- Collaborated with numerous talented Software engineers, contributing to successful project outcomes.
- Find me on social media with the handle: @arastuq
$ whoami?


Lets talk about
the ladder!
I’m not a great programmer; I’m just a good programmer with great habits.
– Kent Beck
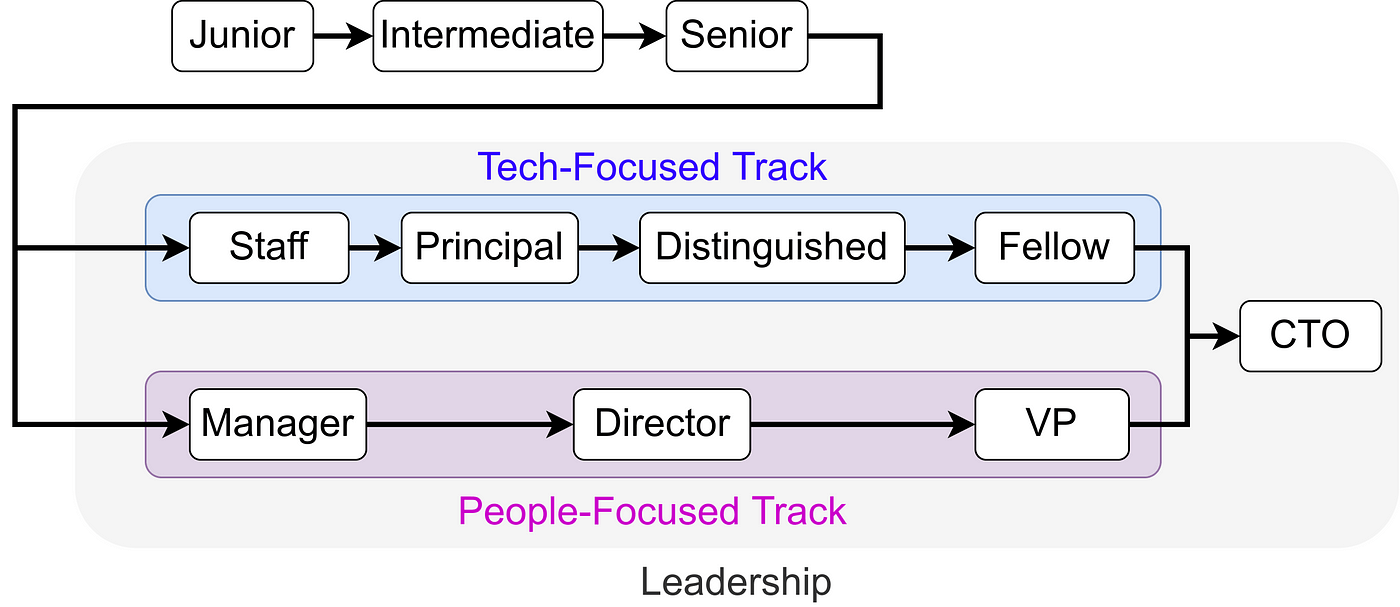
Junior level
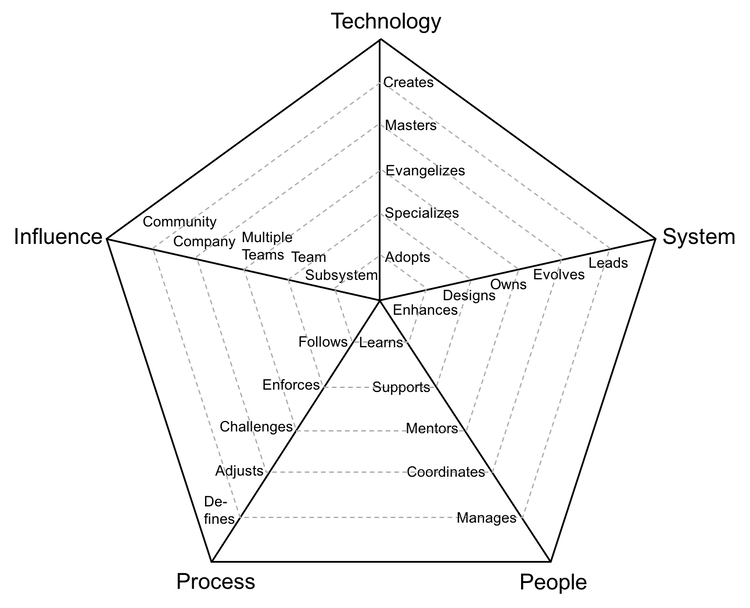
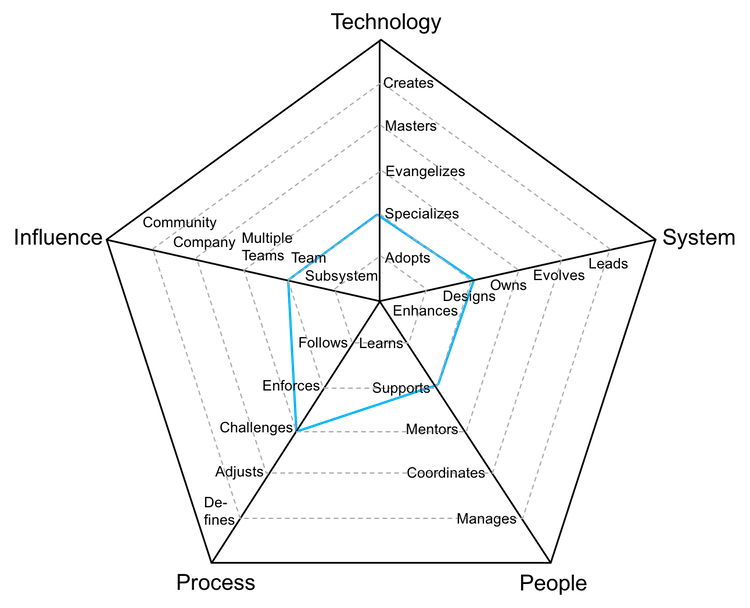
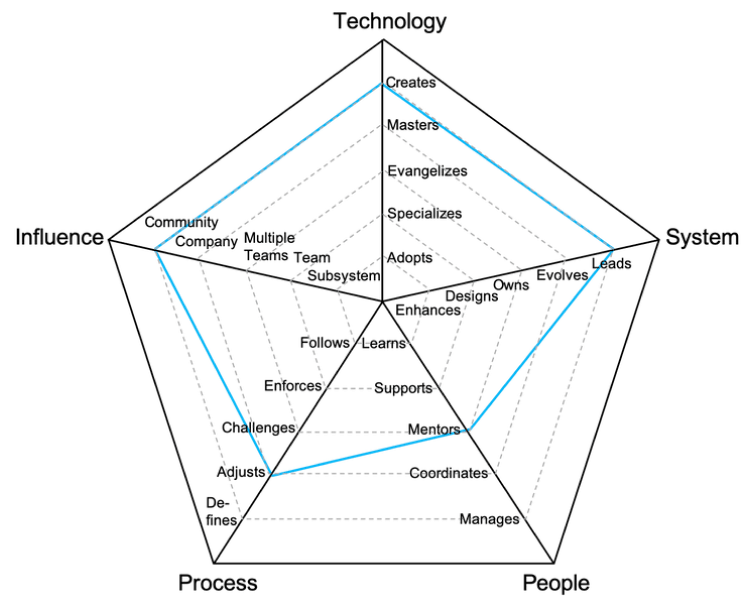
Radar Chart explained
knowledge of the tech stack and tools
1
Technology
level of ownership of the system(s)
2
System
relationship with the team(s)
3
People
level of engagement with the development process
4
Process
scope of influence of the position
5
Influence
Levels
- Adopts: actively learns and adopts the technology and tools defined by the team
- Specializes: is the go-to person for one or more technologies and takes initiative to learn new ones
- Evangelizes: researches, creates proofs of concept and introduces new technologies to the team
- Masters: has very deep knowledge about the whole technology stack of the system
- Creates: designs and creates new technologies that are widely used either by internal or external teams
Technology
-
Enhances: successfully pushes new features and bug fixes to improve and extend the system
-
Designs: designs and implements medium to large size features while reducing the system’s tech debt
-
Owns: owns the production operation and monitoring of the system and is aware of its SLAs
-
Evolves: evolves the architecture to support future requirements and defines its SLAs
-
Leads: leads the technical excellence of the system and creates plans to mitigate outages
System
- Learns: quickly learns from others and consistently steps up when it is required
- Supports: proactively supports other team members and helps them to be successful
- Mentors: mentors others to accelerate their career-growth and encourages them to participate
- Coordinates: coordinates team members providing effective feedback and moderating discussions
- Manages: manages the team members’ career, expectations, performance and level of happiness
People
- Follows: follows the team processes, delivering a consistent flow of features to production
- Enforces: enforces the team processes, making sure everybody understands the benefits and tradeoffs
- Challenges: challenges the team processes, looking for ways to improve them
- Adjusts: adjusts the team processes, listening to feedback and guiding the team through the changes
- Defines: defines the right processes for the team’s maturity level, balancing agility and discipline
Process
- Subsystem: makes an impact on one or more subsystems
- Team: makes an impact on the whole team, not just on specific parts of it
- Multiple Teams: makes an impact not only his/her team but also on other teams
- Company: makes an impact on the whole tech organization
- Community: makes an impact on the tech community
Influence
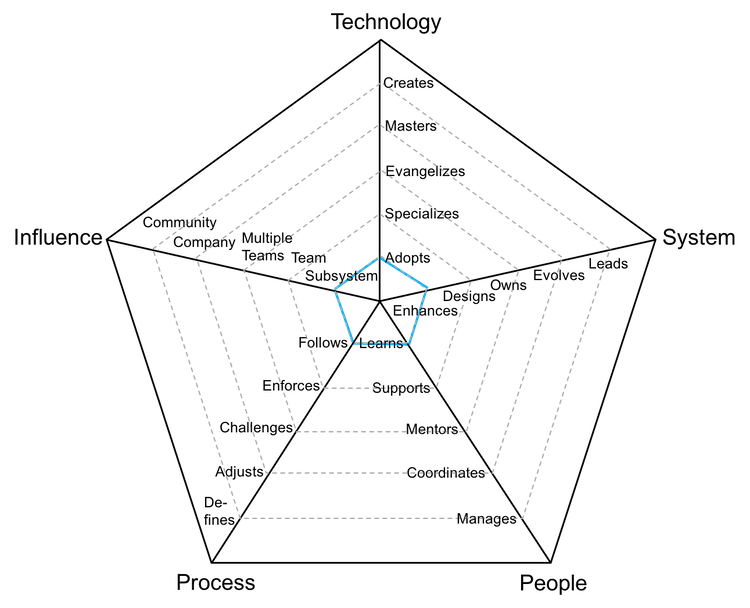
Medior/Intermediat level
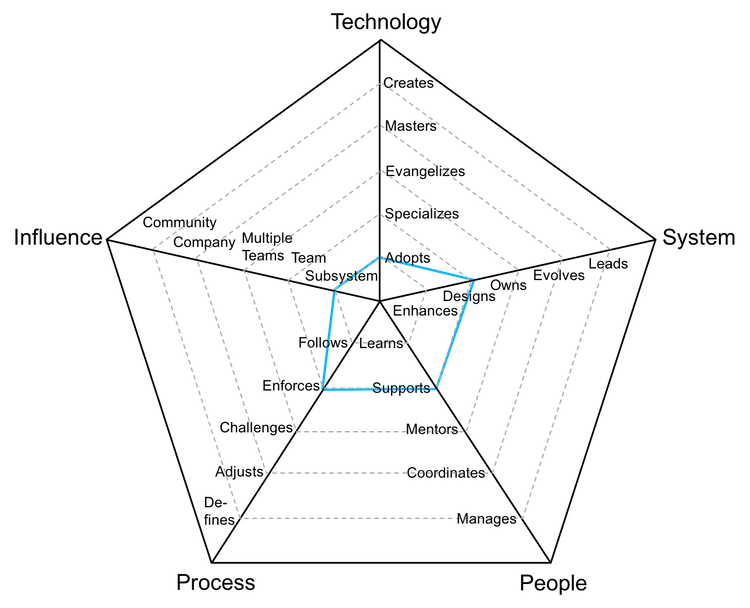
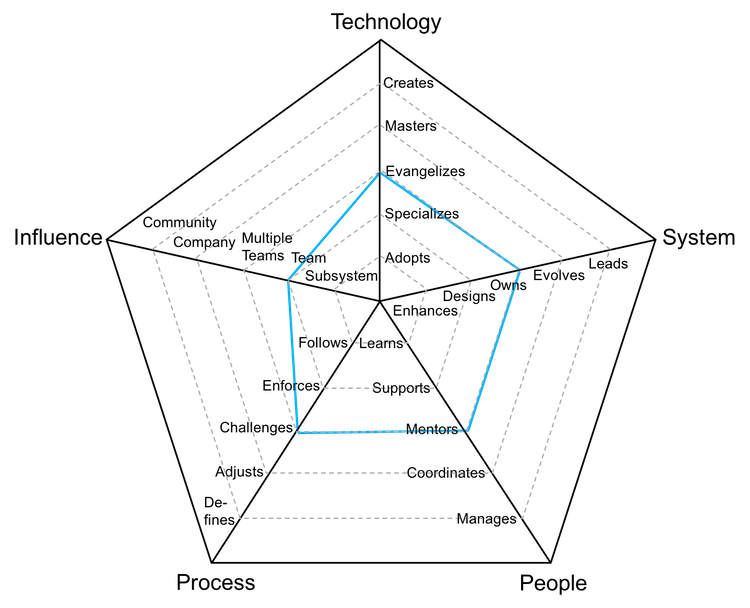
Senior level
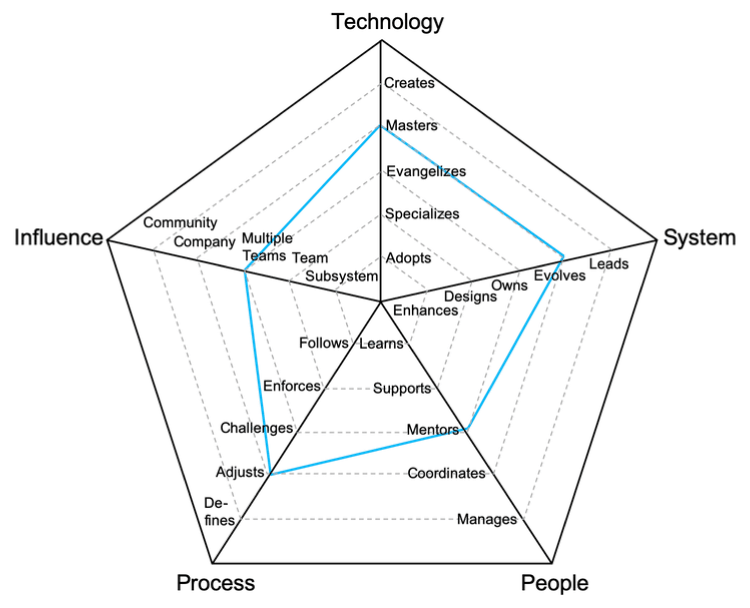
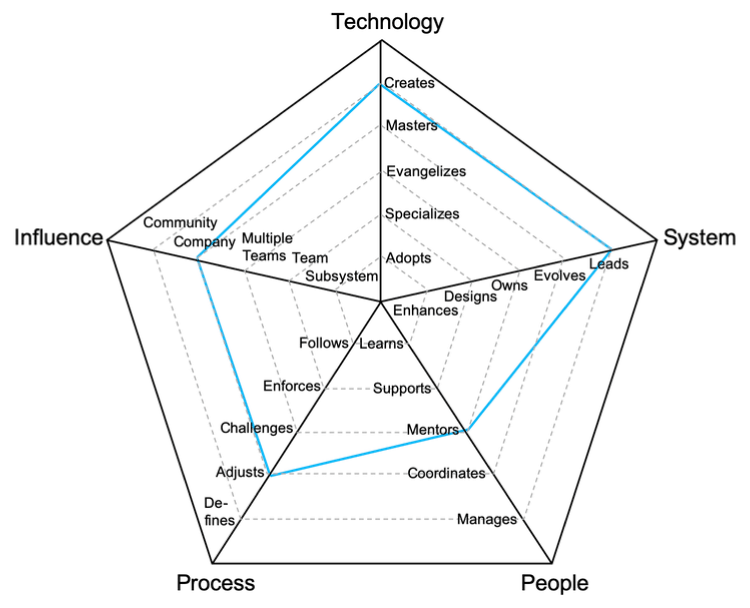
Lets talk about tech/code

What makes a successful software engineer?
Software engineering is not just coding, but a continuous learning journey.
Adapting to new technologies, mastering skills, and creating innovations are key to growth.
All you need is the plan, the road map, and the courage to press on to your destination.
– Earl Nightingale
https://roadmap.sh
roadmap.sh is a community effort to create roadmaps, guides and other educational content to help guide developers in picking up a path and guide their learnings.
Be a go-to Person
In software engineering, if you're the go-to person for, say, a programming language like Python, your colleagues might come to you for help with complex Python code, best practices, or when they need someone to lead a project that requires advanced Python skills.
Being a go-to person shows you've specialized in something valuable and are willing to share your knowledge and help your team.
Follow the trends
Good engineers research and introduce new technologies to their team, often through proofs of concept.

Achieves deep understanding across the technology stack and learn how to model business problems
Innovates by designing new technologies or processes.
Essential Skills for Successful Software Engineers
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in at least two language.
- Algorithms and Data Structures: Understanding of basic algorithms, complexity, and efficient data handling.
- Version Control Systems: Knowledge of tools like Git for code management.
Core Technical Skills
- System Design: Ability to design scalable and maintainable systems.
- Cloud Computing: Familiarity with cloud services for deploying and managing applications.
- DevOps Practices: Understanding continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) practices.
Advanced Technical Skills
- Problem-Solving: Creative and analytical approach to solving complex problems.
- Teamwork and Collaboration: Ability to work effectively in diverse teams.
- Communication: Clear and concise communication of technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
Essential Soft Skills

- Project Management: Understanding the basics of project management and agile methodologies.
- Code Quality: Emphasis on writing clean, maintainable code with documentation.
Real-World Application
People Focused Track
- Maintains an understanding of technical projects but shifts focus towards management.
- Organizes and oversees projects to ensure timely completion.
- Responsible for team performance and project success.
- Guides team members, fosters their professional growth, and communicates with stakeholders.
Engineering Manager
- Strategic oversight over multiple projects, ensuring technical excellence.
- Manages larger teams or multiple smaller teams, focusing on scaling team efficiency.
- Influences broader product or technology decisions, ensuring alignment with business goals.
- Develops leaders within the team, negotiates with other departments, and sets a vision for the team.
Senior Engineering Manager
- Oversees the technical strategy for multiple teams or departments.
- Focuses on long-term goals, resource allocation, and optimizing processes.
- Drives significant contributions to the company's overall strategy and success.
- Represents engineering teams at the executive level, mentors managers, and shapes company culture.
Director of Engineering
- Conceptualization
- Product Design
- Development
- UI/UX Testing
- Branding
Our Services
Career Growth in Software Development
By Touhid Arastu
Career Growth in Software Development
- 290