Pipeline EEG
- Acquisition
- Pre-processing
- Spindle detection
- Spindle analysis
- Reconstruction
Acquisition (CoRe)
- Saturation of extra ECG fixed
- Checking and saving impedance measures before and after each task- and sleep-EEG recordings -> quality of EEG signal for later analysis
- Size and reference of used EEG caps saved -> building cap templates for each size using database from Paris
Preprocessing:
MRI + registration
- Freesurfer
- Non-linear registration T1 to MNI152
- Inverse warp a cap template to subject space
EEG pre-processing
- Gradient artifact removal (FASTR - Niazy et al., 2005, NeuroImage)
- ECG QRS-peak detection: automatic channel selection
- Downsampling (250Hz)
- BCG correction (FASST; ICA-based algorithm)
- Bandpass filter (0.5-25Hz)
- Re-referencing to averaged mastoids (M1-M2)
- Extra Fast Kernel ICA (removal of movement-related artifacts)
- Bad interval detection
-
Automatic script (Matlab):
- Wavelet-based algorithm (Warby et al. 2014 Nature Methods) Github: https://github.com/Mensen/swa-matlab
- Detect Spindles
- Remove spindles detected during Bad Intervals
- Add sleep scoring to spindle detection output
- Write VMRK (marker file - brainvision)
- Extract specific spindles depending on sleep stage
- Add sleep scoring
- Github: https://github.com/arnaudbore/spindlesDetection
Spindle detection
Matlab structure
- Ref_Region: electrodes
- Ref_TypeName: Fast or Slow spindle
- Ref_Start: Beginning of the spindle
- Ref_End: End of the spindle
- Ref_NegativePeak
- Ref_PositivePeak
- Ref_Peak2Peak: spindle amplitude
- Ref_Length: spindle duration
- Ref_NumberOfWaves: determination of spindle frequency
- scoring: Sleep Stage
Spindle detection - Outputs
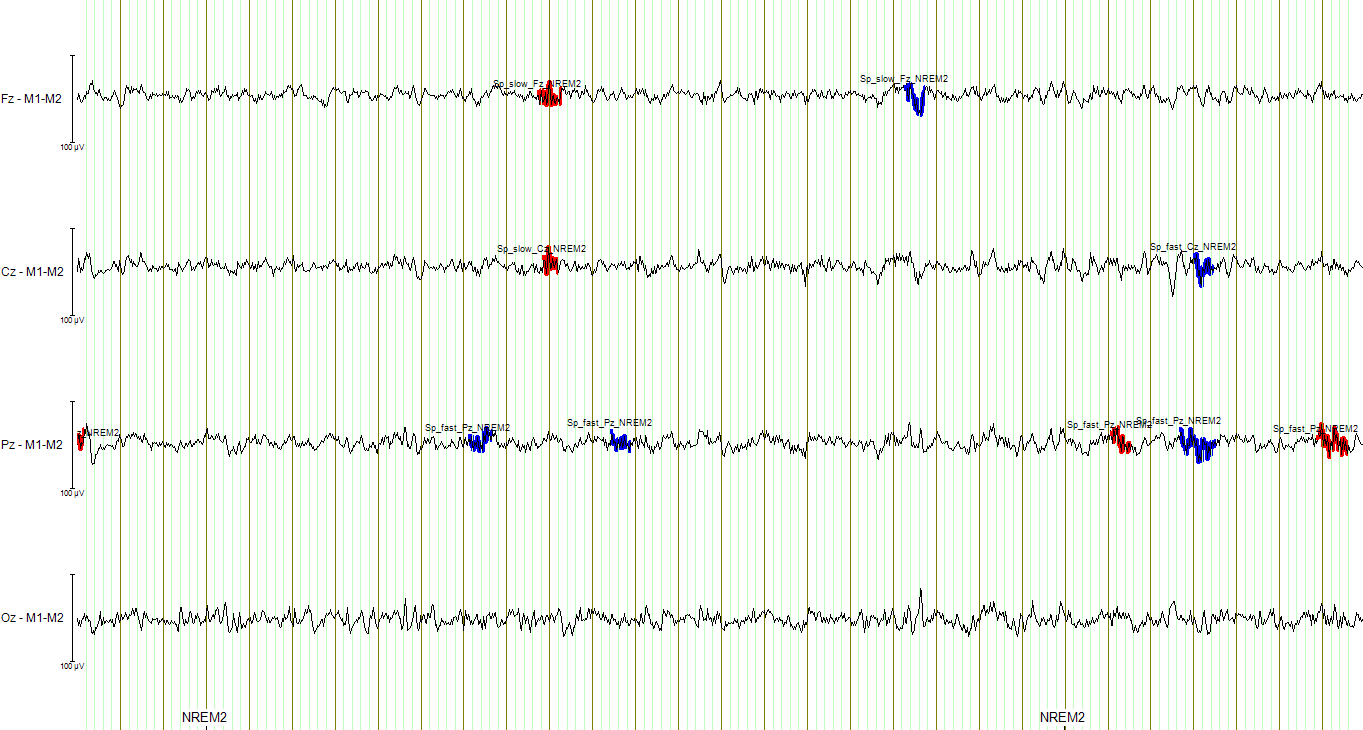
Spindle detection - Outputs
Manual validation
Spindle analysis
- Spindle features
- Type (slow vs. fast, NREM2 vs. NREM3)
- Number
- Amplitude
- Duration
- Frequency
- Density
- Topographic distribution and propagation
- Connectivity (coherence & phase-locking )
- Hemispheric differences in spindle features and power (e.g., C3-C4; Nishida & Walker, 2007, PloSOne)
Reconstruction
- Brainstorm (Tadel et al., 2011, Comp. Int. & Neuro.)
- BEM head model
- Import EEG epochs based on spindle markers (-600 to 2000ms)
- Remove DC offset (-600 to -100ms)
- Noise covariance estimation
- Bandpass filtering (spindle range: 11-17Hz)
- Source estimation (minimum norm)
- Signal projection and power estimate
- Dynamic visualization (movie)
- Deep sources?
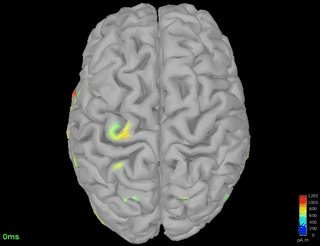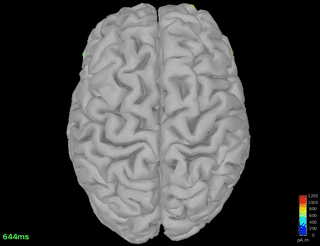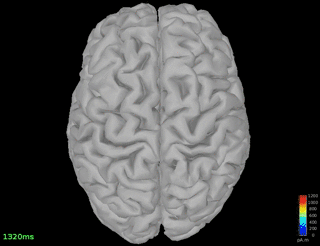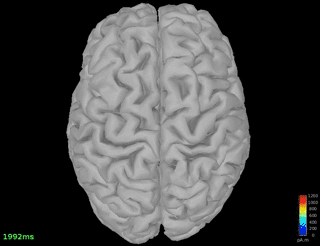
Single spindle-event detected on Pz
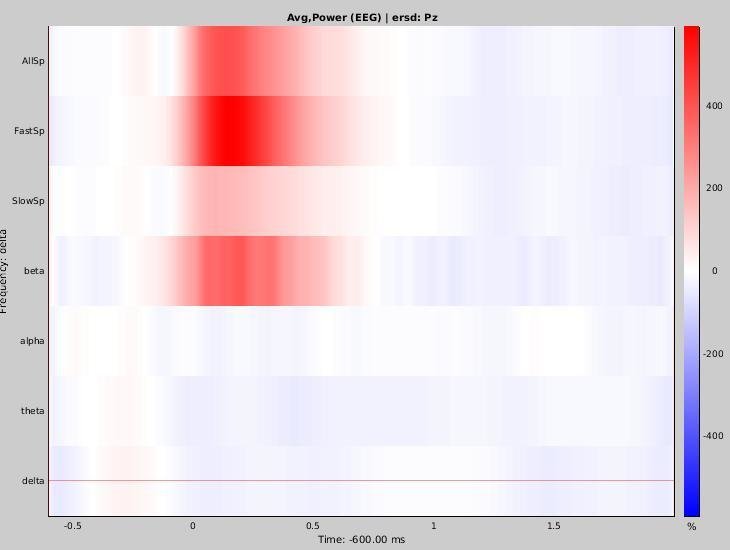
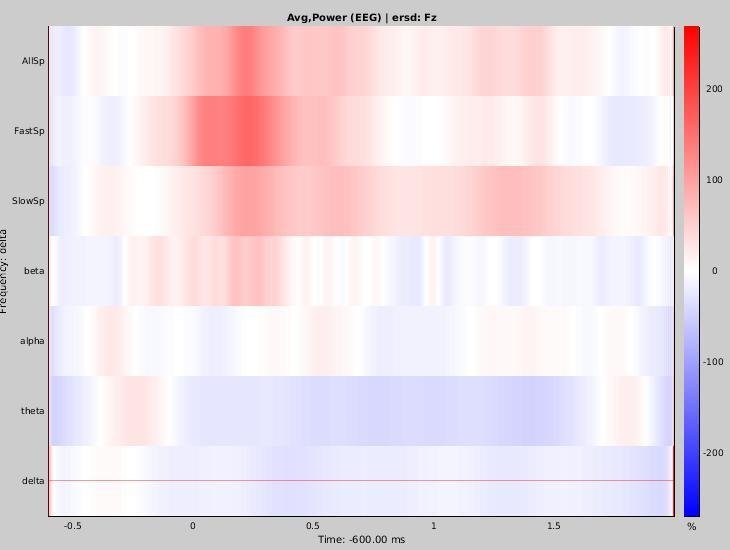
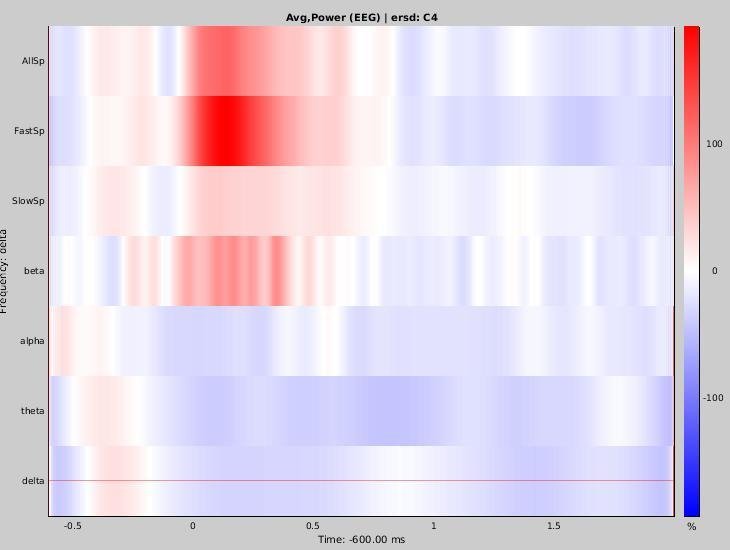
Time-frequency maps (detected on Pz)
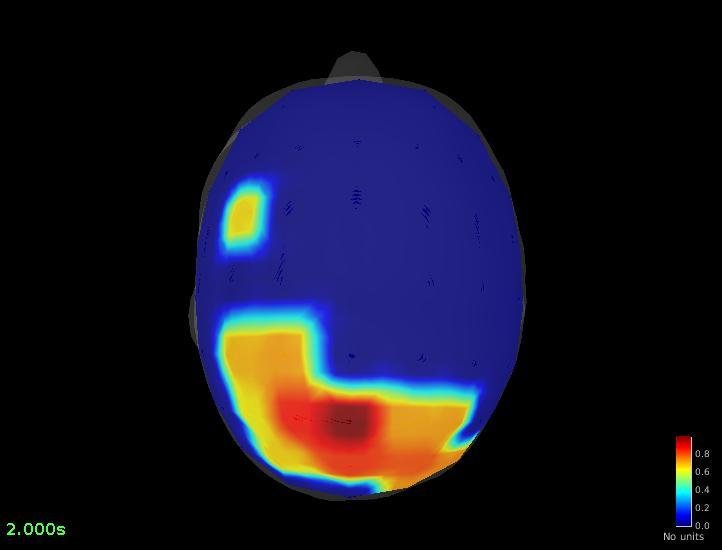
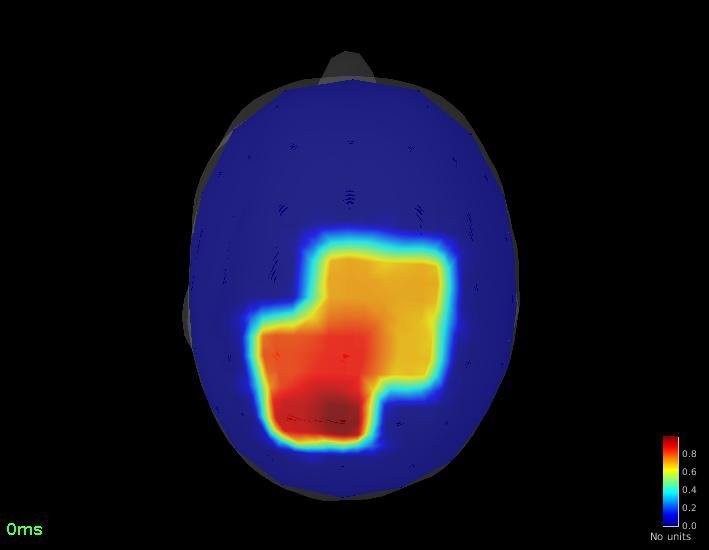
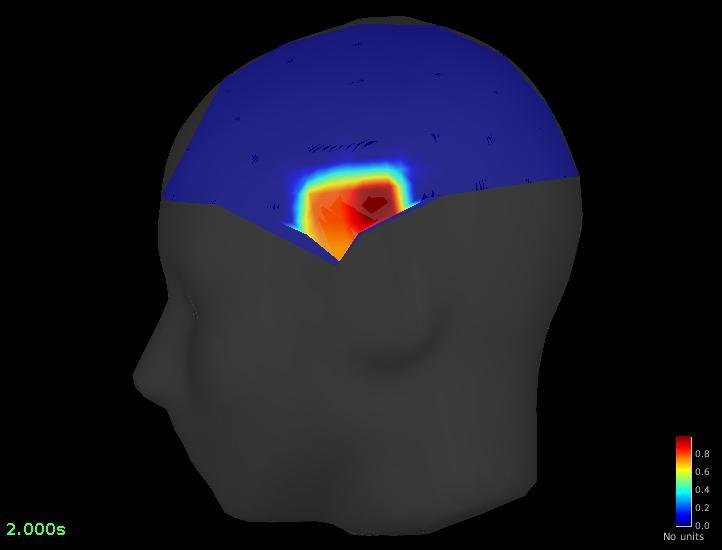
Pz
Fz
C4
% increase in the specific frequency band
Time-frequency maps (detected on Pz)
% increase in the delta frequency band
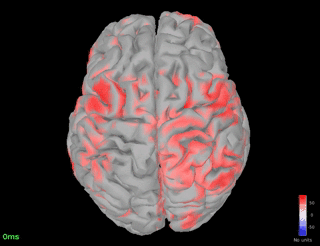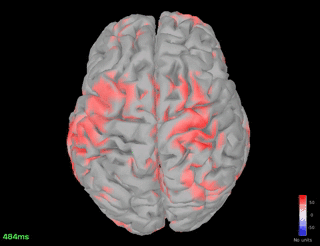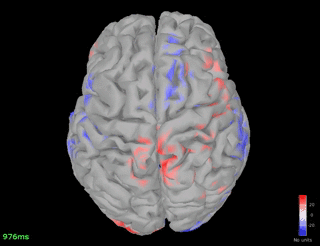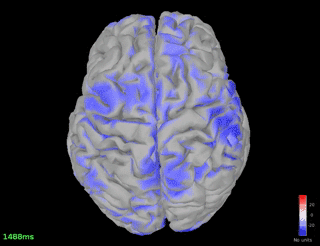
% increase in the spindle frequency band
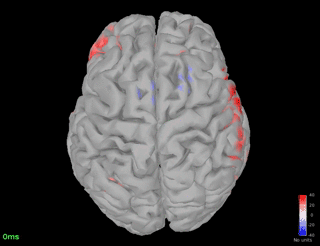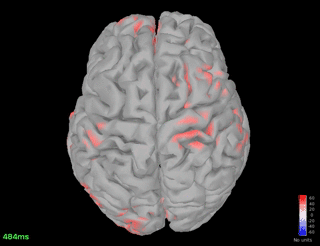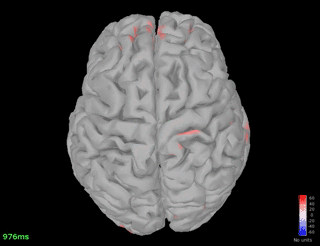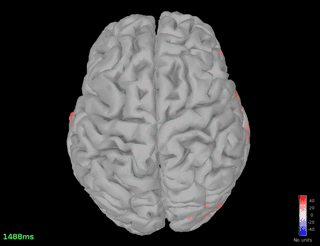

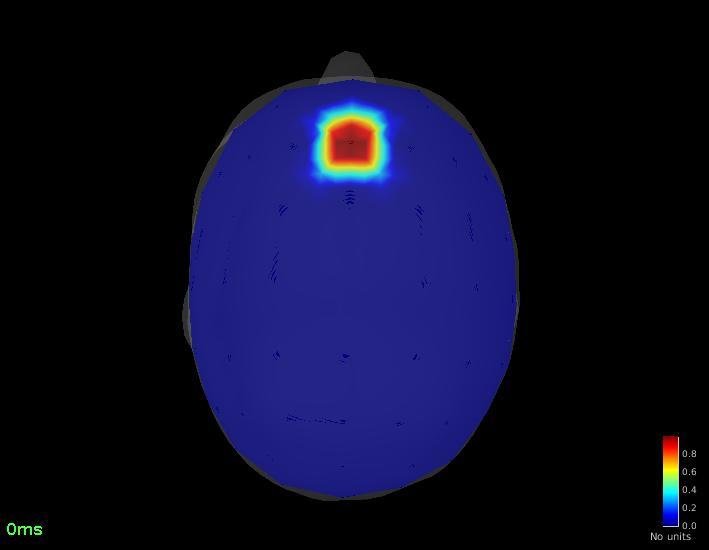
Connectivity - Coherence (detected on Pz)
Pz - spindle band
Fz - spindle band
Fz - theta band
Pz - theta band




Connectivity - Coherence (detected on Pz)
Pz - spindle band
Fz - spindle band
Fz - theta band
Pz - theta band
T7 - spindle band
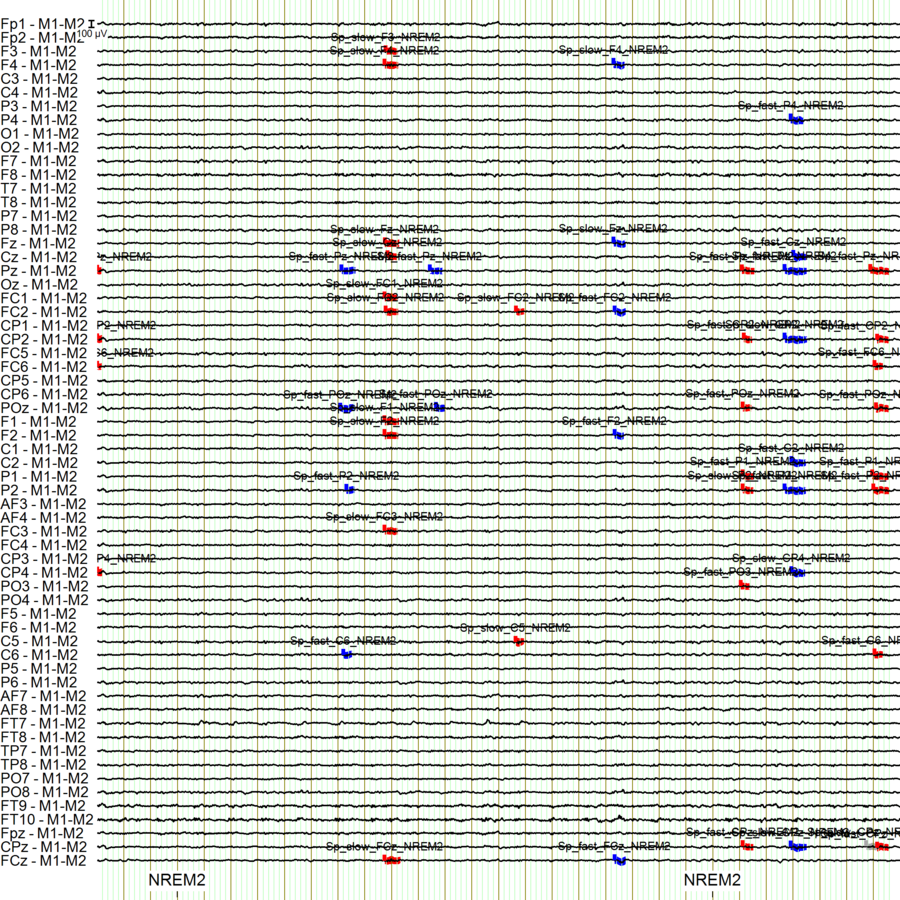
All channels
Pipeline EEG
By Arnaud Boré
Pipeline EEG
Presentation Pipeline
- 691



