Introduction
To
ADO.NET
Win Forms
Web Forms
Console App
ADO.NET
Data Storage
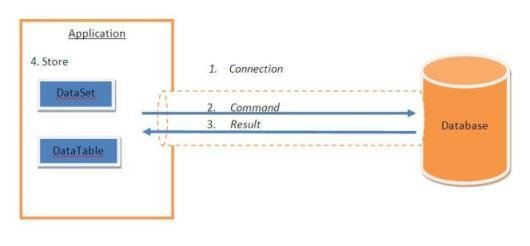
In a data access scenario we need :
- Connecting to DB
- Sending commands to DB(select, insert, update, delete...)
- Getting back the results (rows and/or number of rows effected)
- Storing result(s) and display it/them to the user
Connection
<connectionStrings>
<add
name="ConnStringDb1"
connectionString="Data Source=.\SQLSERVER;
Initial Catalog=YourDataBaseName;
Integrated Security=True;"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
OR...
<appSettings>
<add
key="ConnectionString"
value="Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;
Initial Catalog=YourDataBaseName;
Trusted_Connection=Yes;
Integrated Security=SSPI;
Connect Timeout=60"/>
</appSettings>Connection
private SqlConnection conn = null;
conn = new SqlConnection(ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["MyConnectionString"].ConnectionString);
//OR
conn = new SqlConnection(ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["ConnectionString"]);
Storing The Result(s)
-
DataReader - A DataReader is an object that can be used to access the results sequentially from a database. The DataReader is used to get forward only sequential results as the query executes. This is used with the Command object.
-
Dataset - The Dataset can be thought of as an in-memory representation of a database. A DataSet is a disconnected data access object. The result of the query can be stored in a Dataset. The DataSet contains DataTables. The DataTables contain DataRow and DataColumns. A DataSet or a DataTable can be used with a Command and a DataAdapter object to store query results.
-
DataAdapter - A DataAdapter object is used to fill a DataSet/DataTable with query results. This can be thought of as the adapter between the connected and disconnected data models. A Command object will be used to execute the query and a DataAdapter will use this Command object and fill the query results coming from the database into a DataSet/DataTable.
ExecuteScalar, ExecuteReader and ExecuteNonQuery
-
ExecuteScalar is going to be the type of query which will be returning a single value. An example would be selecting a count of the number of active users. Returns only 1x1 cell.
-
ExecuteReader gives you a data reader back which will allow you to read all of the columns of the results a row at a time. An example would be getting all of the information for each user in the system so you could display that information.
-
ExecuteNonQuery is any SQL(Structured Query Language) which isn't returning values really, but is actually performing some form of work like inserting deleting or modifying something. An example would be updating a user's personal information in the database. Returns count of effected records.
public List<Customer> GetAll()
{
List<Customer> customers = null;
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand {
Connection = conn,
CommandType = CommandType.Text,
CommandText = "Select * from Customer"
};
//If using SP
//var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
//{
// Connection = conn,
// CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
// CommandText = "sp_GetAllCustomers"
//};
conn.Open();
var reader = sqlCmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection);
if (reader.HasRows)
{
customers = new List<Customer>();
while (reader.Read())
{
var customer = new Customer
{
Id = reader.GetGuid(0),
FirstName = reader.GetString(1),
LastName = reader.GetString(2),
BirthDate = reader.GetDateTime(3),
Country = reader.GetString(4)
};
customers.Add(customer);
}
}
}
return customers;
}Code Sample: Get All Customers
public Customer GetById(Guid id)
{
Customer customer = null;
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand {
Connection = conn,
CommandType = CommandType.Text,
CommandText = "Select * from Customer Where Id=@Id"
};
//If using SP
//var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
//{
// Connection = conn,
// CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
// CommandText = "sp_GetCustomerById"
//};
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("Id", id));
conn.Open();
var reader = sqlCmd.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection);
while (reader.Read())
{
customer = new Customer
{
Id = reader.GetGuid(0),
FirstName = reader.GetString(1),
LastName = reader.GetString(2),
BirthDate = reader.GetDateTime(3),
Country = reader.GetString(4)
};
}
}
return customer;
}Code Sample: Get Customer By Id
public int GetCountOfCustomers()
{
int count = -1;
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
{
Connection = conn,
CommandType = CommandType.Text,
CommandText = "Select Count(*) from Customer"
};
//If using SP
//var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
//{
// Connection = conn,
// CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
// CommandText = "sp_GetCountOfCustomers"
//};
conn.Open();
count = (int)sqlCmd.ExecuteScalar();
}
return count;
}Code Sample: Get Count of Customers
public void Insert(Customer entity)
{
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
var sqlCmd =
new SqlCommand { Connection = conn, CommandText = "Insert into Customer
Values(@Id, @FirstName, @LastName, @BirthDate, @Country)" };
//If using SP
//var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
//{
// Connection = conn,
// CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
// CommandText = "sp_InsertNewCustomer"
//};
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("Id", entity.Id));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("FirstName", entity.FirstName));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("LastName", entity.LastName));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("BirthDate", entity.BirthDate));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("Country", entity.Country));
conn.Open();
sqlCmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Code Sample: Insert New Customer
public void Update(Customer entity)
{
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
var sqlCmd =
new SqlCommand { Connection = conn,
CommandText = "Update Customer Set FirstName=@FirstName,
LastName=@LastName,
BirthDate=@BirthDate,
Country=@Country Where Id=@Id" };
//If using SP
//var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
//{
// Connection = conn,
// CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
// CommandText = "sp_UpdateCustomer"
//};
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("Id", entity.Id));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("FirstName", entity.FirstName));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("LastName", entity.LastName));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("BirthDate", entity.BirthDate));
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("Country", entity.Country));
conn.Open();
sqlCmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Code Sample: Update An Existing Customer
public void Delete(Guid id)
{
using (var conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString))
{
var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand { Connection = conn,
CommandText = "Delete From Customer Where Id =@Id" };
//If using SP
//var sqlCmd = new SqlCommand
//{
// Connection = conn,
// CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure,
// CommandText = "sp_DeleteCustomer"
//};
sqlCmd.Parameters.Add(new SqlParameter("Id", id));
conn.Open();
sqlCmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}Code Sample: Delete An Existing Customer
thanks...
Introduction to ADO.NET
By Barış SÖNMEZ
Introduction to ADO.NET
- 548



