Introduction
Advanced Programming
SUT • Spring 2019
Outline
-
Course information
-
Programming paradigm
-
Introduction to Java
-
Java History
-
Java Characteristics
Course Information
Topics
-
Introduction to java language
-
Java syntax, operators, conditions, loops, …
-
Strings
-
Arrays
-
-
Object Oriented Programming
-
Interface
-
Inheritance
-
Polymorphism
-
-
Software Quality
-
Refactoring
-
Test
-
Pattern
-
Topics
-
Advanced Java Programming
-
Exception Handling
-
Generics
-
Collections
-
Threads
-
Files and Streams
-
Networking
-
Reflection
-
...
-
Grades
| Final Exam | 5 points |
| Midterm Exam | 3 points |
| Quizzes/Take Homes | 2 points |
| Home work | 4 points + (20% bonus) |
| Project | 6 points + (20% bonus) |
Resources
-
Quera
-
Assignments
-
Discussions
-
Announcements
-
-
Books
-
Java How to Program (11th Edition)
-
Deitel & Deitel
-
-
-
Bruce Eckel
-
-
Refactoring: Improving the Design of Existing Code
-
Martin Fowler, Kent Beck, John Brant, William Opdyke, Don Roberts
-
-
Tutorials
- Tutor
- Behnam Hatami
- Email: behnam.hatami@gmail.com
- Telegram: @behnamhatami
- Head-TA
- Mohammad Haghighat
- Class Session
- Sat-Mon 4:30 - 6:00 PM
- Office Hour
- Sat-Mon after 6:00 PM
- Midterm Exam
- 11 ordibehesht - 4:30 - 7:30 PM
Programming paradigm
-
-
state the order in which operations occur
-
they allow side effects
-
#include <iostream>
int n;
int function_one(){
n += 1;
n *= 2;
}
int function_two(){
n *= 3;
}
int main(){
cin >> n;
function_one();
function_two();
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}Programming paradigm
-
-
disallows side effects
-
from functools import reduce
items = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
def map_function(x):
return x * x
def filter_function(x):
return x % 2 == 0
def reduce_function(x, y):
return x + y
filtered_items = filter(filter_function, items)
mapped_items = map(map_function, filtered_items)
print(reduce(reduce_function, mapped_items))Programming paradigm
-
-
do not state the order in which to execute
-
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>This is a title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello world!</p>
</body>
</html>Programming paradigm
-
-
code is organized into objects that contain state
-
States only modified by the code that is part of the object
-
-
-
groups code into functions
-
class Number{
private int a = 0;
public void add(int b) {
this.a += b;
}
}
Java History
Java History
-
Java was created in 1991
-
by James Gosling in Sun Micro systems
-
-
Initially called Oak
-
in honor of the tree outside Gosling's window
-
-
Its name was changed to Java
-
because there was already a language called Oak.
-
-
Sun Micro systems released the first public implementation as Java 1.0 in 1995
-
Java syntax is similar to C and C++.
Java Motivation
-
The need for platform independent language
-
To be embedded in various consumer electronic products
-
like toasters and refrigerators
-
-
Platform independent?!
-
Hardware
-
Operating System
-
Java Motivation
-
At the same time, the World Wide Web and the Internet were gaining popularity.
-
Java could be used for internet programming.
-
Why?
-
Platform independence
-
-
Creation of Applets
The Java technology
-
A programming language
-
Java can create all kinds of applications
-
-
A development environment
-
A compiler (javac)
-
An interpreter (java)
-
A documentation generator (javadoc)
-
…
-
-
Compare it to C++
High-Level Languages

Compile and Execution Stages

-
Compare to C++ and Assembly
-
.NET Framework
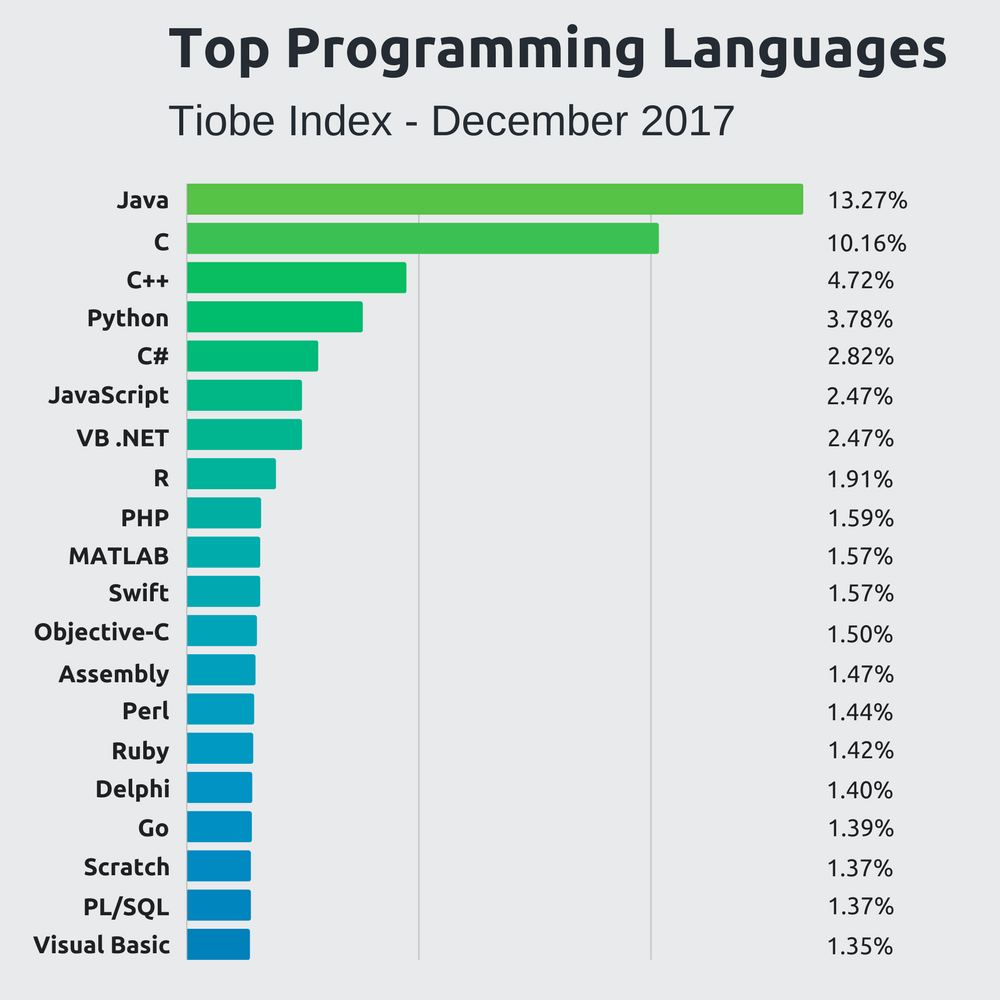
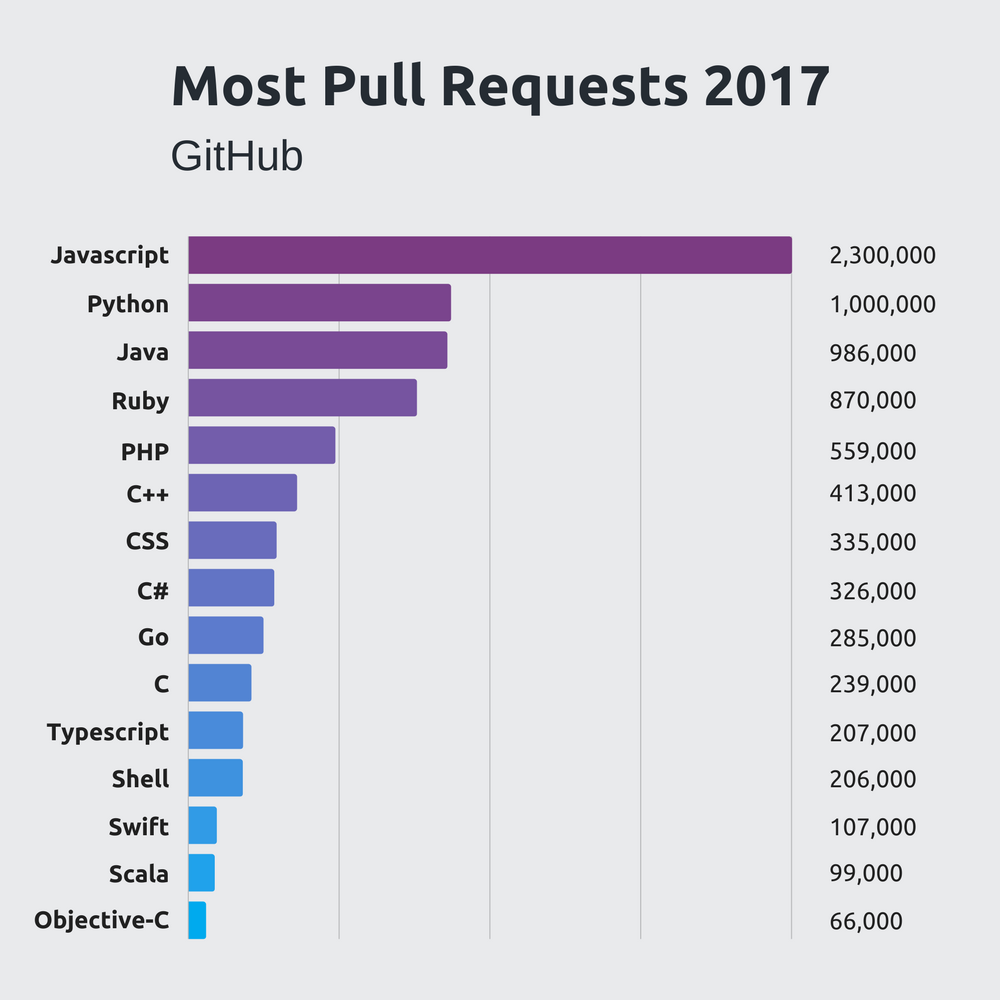
Java is Popular
-
Some reports on programming languages popularity
-
According to
-
Job advertisements
-
Book sales
-
Finding code on the web
-
…
-
-
Characteristics of Java
-
Java is simple
-
Java is object-oriented
-
Java is architecture-neutral
-
Java is portable
-
Java is interpreted
-
Java is multi threaded
-
Java is secure
-
Java is robust
First Example
-
Create a file named First.java
-
Java class files have .java extension
-
Note to naming convention
-
-
Copy this lines to the file
-
Note: File name and class name should be the same.
-
public class First{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}TODO
-
Download and install JDK
-
JDK 9
-
-
Write a program that prints your name on the console
-
Compile and run the program
Title Text

Introduction
By Behnam Hatami
Introduction
Introduction / Advanced Programming Course @ SUT, Spring 2019
- 1,475



