Dependency Injection
&
Services
in
Drupal 8
GOAL
Understand the driving concepts and reasons for using Dependency Injection
Understand the pattern and its usages in Drupal 8 specifically, via the Service Container and specific methods
implements
INVERSION
OF CONTROL
DEPENDENCY INJECTION
is a
DESIGN
PATTERN
enables
LOOSE
COUPLING
DESIGN PATTERN
Reusable solution for common software design problems.
Examples:
- Singleton
- Dependency Injection
- many many others
LOOSE COUPLING
Less
interconnection
Less
knowledge about each other
Less
coordination
is a PRINCIPLE,
which offers
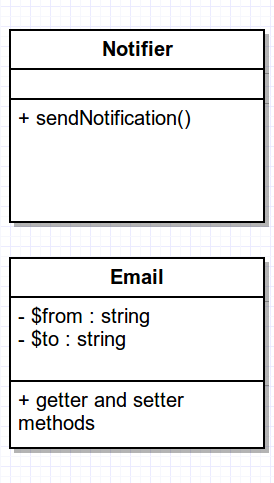
Example of tight coupling
Example of tight coupling
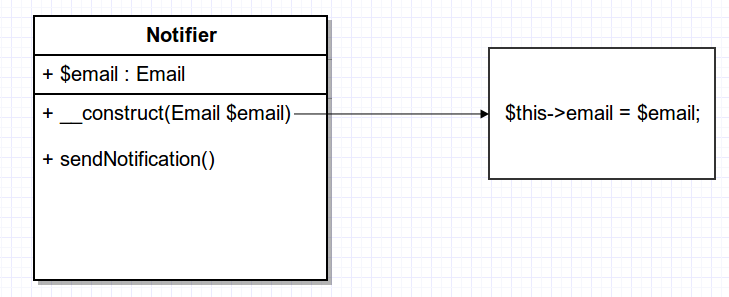
Example of less tight coupling
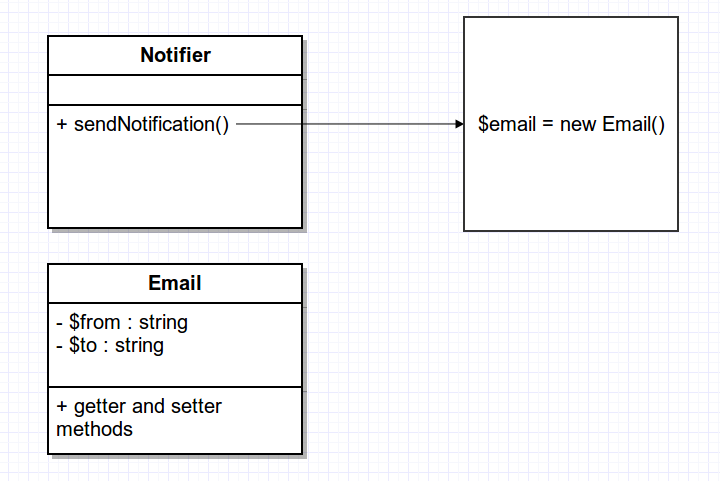
What happens if SMS notification is needed?
Example of tight coupling
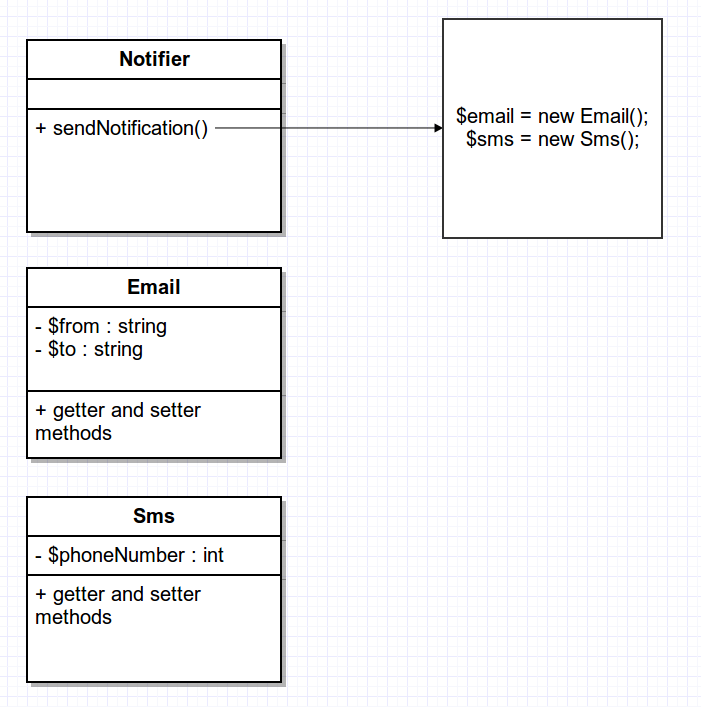
Example of less tight coupling
Loose Coupling
Who is responsible for instantiating the Notifier class?
Custom Code
- our custom code is responsible for instantiating the Notifier
class and its dependencies - our custom code is responsible for the control of the flow
Framework
- control is passed to a framework, which is designed to discover our implementations
- it is also responsible to instantiate and inject the dependencies for our implementations
VS.
Inversion of Control
-
describes a design in which a re-usable library calls the custom code and not the other way around
- control is passed to a framework, which is designed to discover our implementations
- it is also responsible to instantiate and inject the dependencies for our implementations
Inversion of Control
Inversion of Control
in Drupal
Drupal 7
The hook system
Drupal 8
- Dependency Injection
-
Event Listener/
Observer pattern
Short Recap
implements
INVERSION
OF CONTROL
DEPENDENCY INJECTION
is a
DESIGN
PATTERN
enables
LOOSE
COUPLING
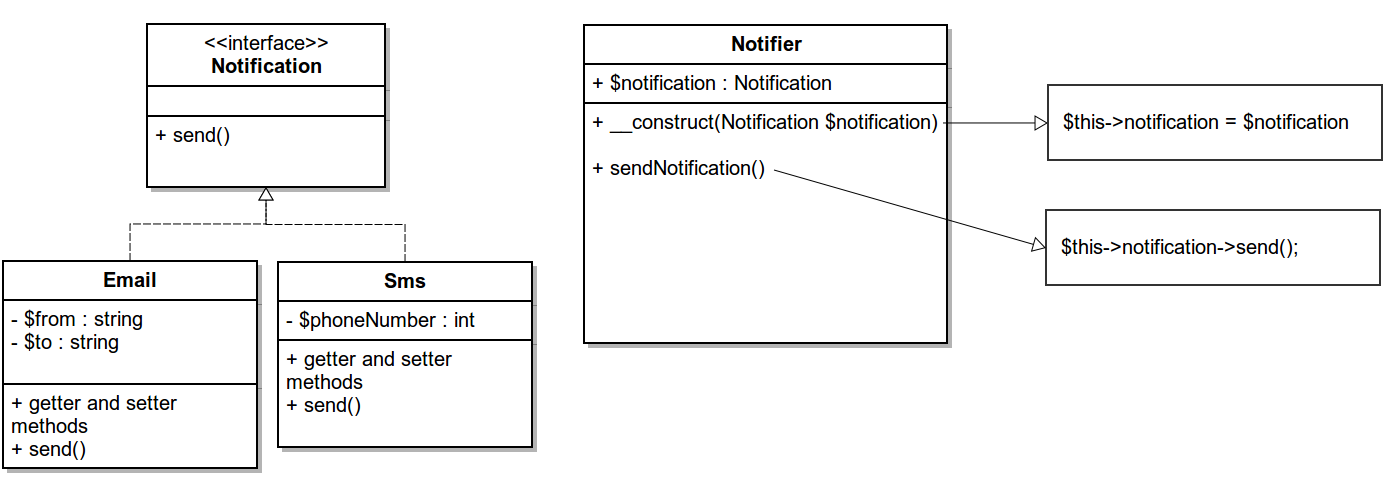
3 types of Dependency Injection
- Constructor injection
- Setter injection
- Interface injection
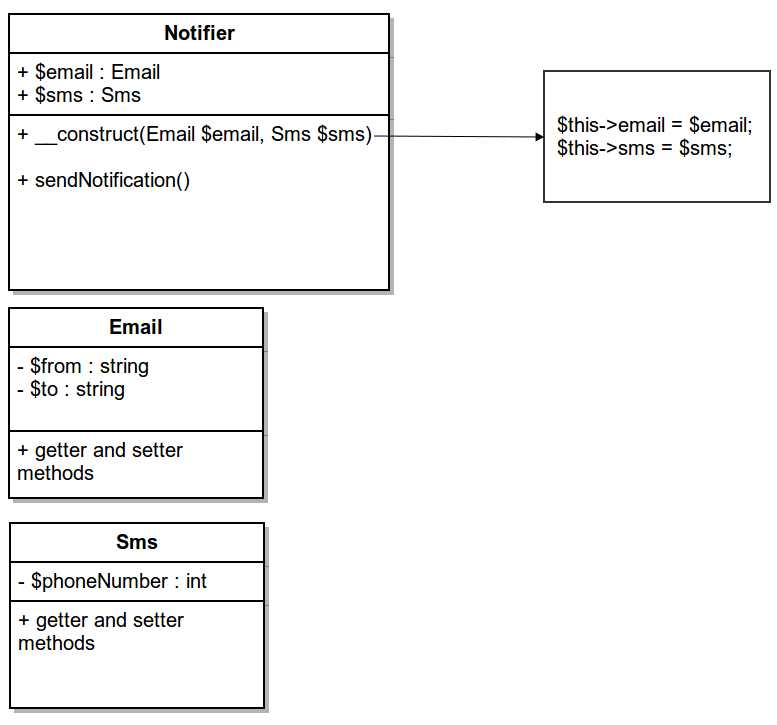
Constructor injection
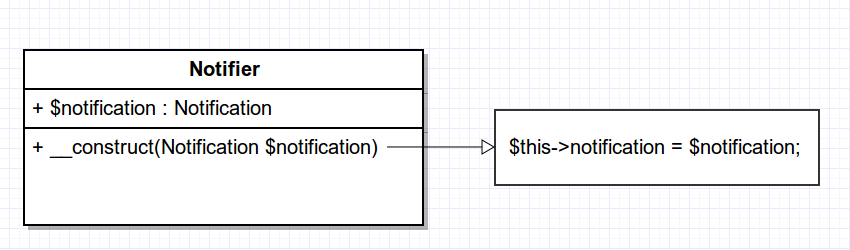
Setter Injection
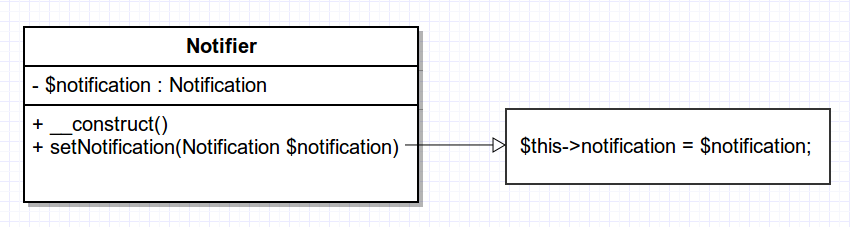
Interface Injection
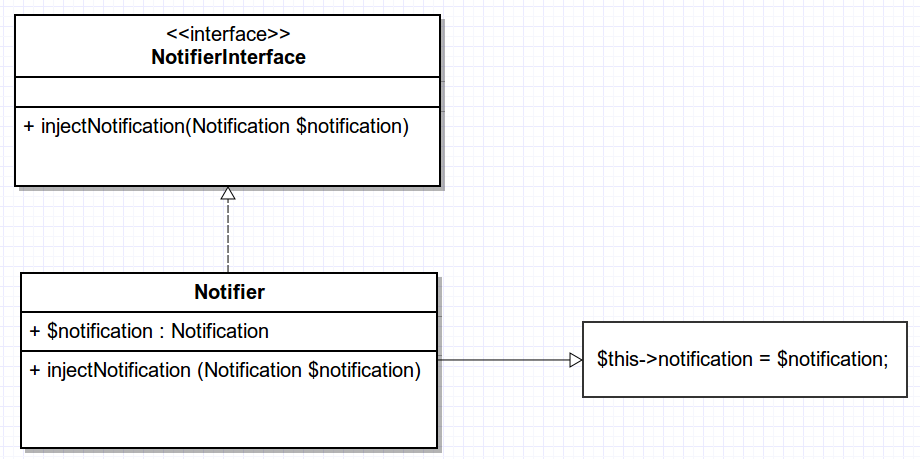
In real life applications
Dependency injection involves four roles:
- the service object(s) to be used (e.g. Email, Sms classes)
- the client object that is depending on the services it uses (e.g. Notifier class)
- the interfaces that define how the client may use the services (e.g. Notification interface)
- the injector, which is responsible for constructing the services and injecting them into the client (a service container of a Framework, in our case the Drupal 8 service container)
Conclusion
"When you go and get things out of the refrigerator for yourself, you can cause problems. You might leave the door open, you might get something Mommy or Daddy doesn't want you to have. You might even be looking for something we don't even have or which has expired.
What you should be doing is stating a need, "I need something to drink with lunch," and then we will make sure you have something when you sit down to eat."
John Munsch, 28 October 2009.
Questions so far?
DI In Drupal 8
D8 Service Container
public static function create()
The Service Container:
Why and what?
Drupal 7
- Inversion of Control exists
- Loose Coupling is lacking
- Too much interdependency when writing custom modules
Drupal 8
- defines the term "service"
which is reusable functionality - defines its services in configuration
- uses the Service Container to use a defined service
What is a Service?
What is a Service?
- one of the four roles in the Dependency Injection pattern
- in Drupal 8 it's used to decouple reusable functionality and makes these services pluggable and replaceable by registering them with a service container
Service configuration example
services:
http_kernel:
class: Stack\StackedHttpKernel
http_kernel.basic:
class: Symfony\Component\HttpKernel\HttpKernel
arguments: ['@event_dispatcher', '@controller_resolver', '@request_stack']
What is a Service Container?
What is a Service Container?
- it is an array of definitions specified in .services.yml configuration files
- Drupal 8 compiles the definitions in these files into a single object that contains all the service definitions
The service container
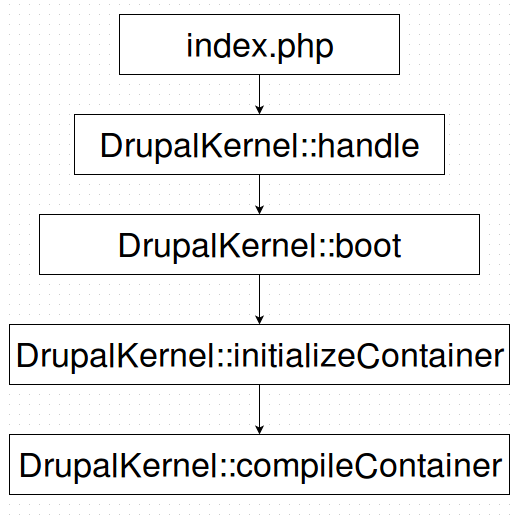
Who is responsible for instantiating our services?
public static function create()
- ContainerInjectionInterface
- ContainerFactoryPluginInterface
- ContainerDeriverInterface
Dependency Injection Example in a
Custom Controller
Example
services:
module_name.notifier:
class: Drupal\module_name\Notifier
arguments: ['']
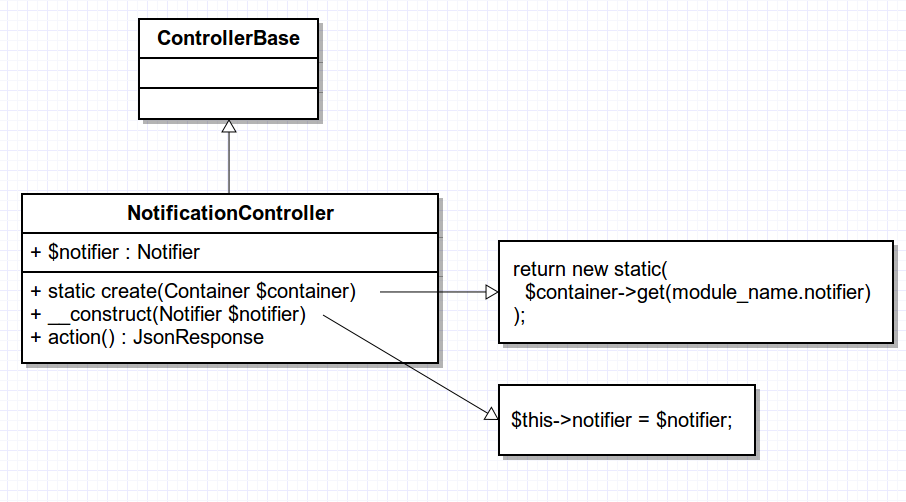
Example
Container::get
Creates an instance of the service with all the necessary dependencies by calling the Container::createService method.
How does it work?

Execution flow in our example
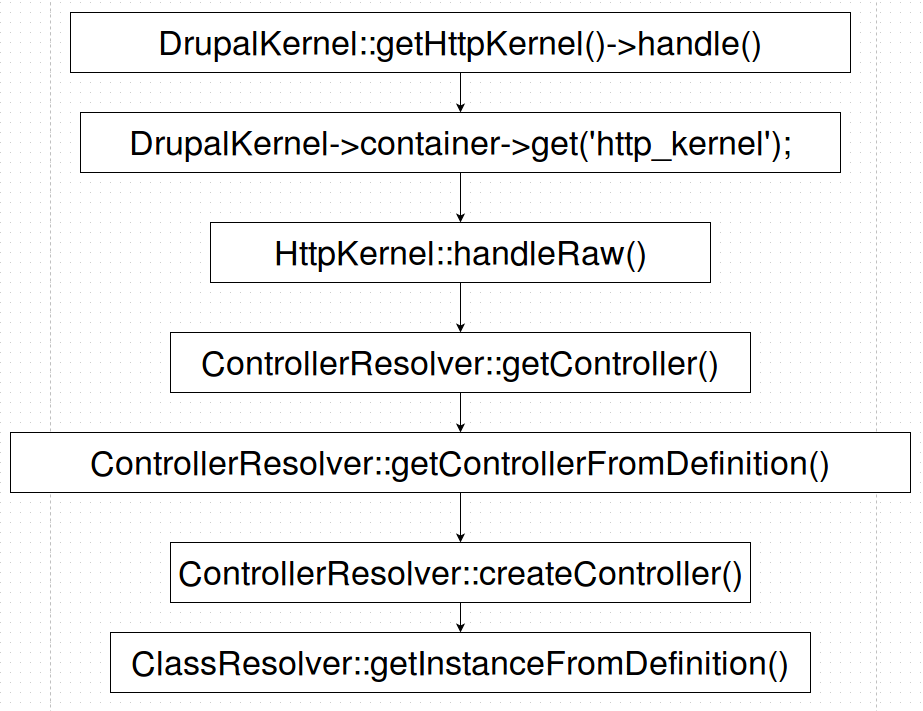
public function getInstanceFromDefinition($definition) {
if ($this->container->has($definition)) {
$instance = $this->container->get($definition);
}
else {
if (!class_exists($definition)) {
throw new \InvalidArgumentException(sprintf('Class "%s" does not exist.', $definition));
}
if (is_subclass_of($definition, 'Drupal\Core\DependencyInjection\ContainerInjectionInterface')) {
$instance = $definition::create($this->container);
}
else {
$instance = new $definition();
}
}
if ($instance instanceof ContainerAwareInterface) {
$instance->setContainer($this->container);
}
return $instance;
}Questions?
Bibliography
Thanks!
Services and Dependency Injection
By benelori
Services and Dependency Injection
- 586

