Debugging 101
be gone bug!
Benjamin Kampmann (@sirDonQui)
for Hackership (@hacker_ship)
Berlin, July 2015
What is "debugging"?
Debugging is
the methodical process of finding and eliminating bugs (defects) in a software programme.
Debugging Methods
-
static code analysis
-
(unit) testing
-
code reviews
-
lexical analysis
-
interactive debugging
Interactive Debugging
all debugging, which involves a human, interacting with the computer (or its output).
Mostly used to track down known bugs.
Process
The process (after a bug was reported) usually goes as follows:
- Developer tries to reproduce the bug
- defines minimal set of conditions, environment, state and inputs to trigger the bug
- setup conditions/trigger bug
- analyse (try to find the bug)
- make a change
- rinse, repeat
Debugging Tools
-
(post mortem) logs analysis
-
code execution walk-through
-
REPLs
-
history bisecting
-
in process debuggers
Log Anaylsis

Code Walk through
dry line-by-line execution of code in your head or on a piece of paper

L2: With items = ["a", "b", "a"]
L3: found = {}
L4: FOR: key = "a"
L5: key not in found -> skip to L7
L7: found= {"a": None}
L8: len(found) < 10 -> skip to L4
.....
REPL
(Read-Eval-Print-Loop)

History Bisecting
`git bisect` to find the error

interactive Debugger
get inside your process

interactive Debugger
The base idea of an interactive debugger is to allow you to stop execution (using breakpoints) of your program at any time, jump into an interactive session and allow you to examine the state at that time and continue step by step to observe what is going on or resume execute.
FF Developer Tools
in-browser Javascript debugging

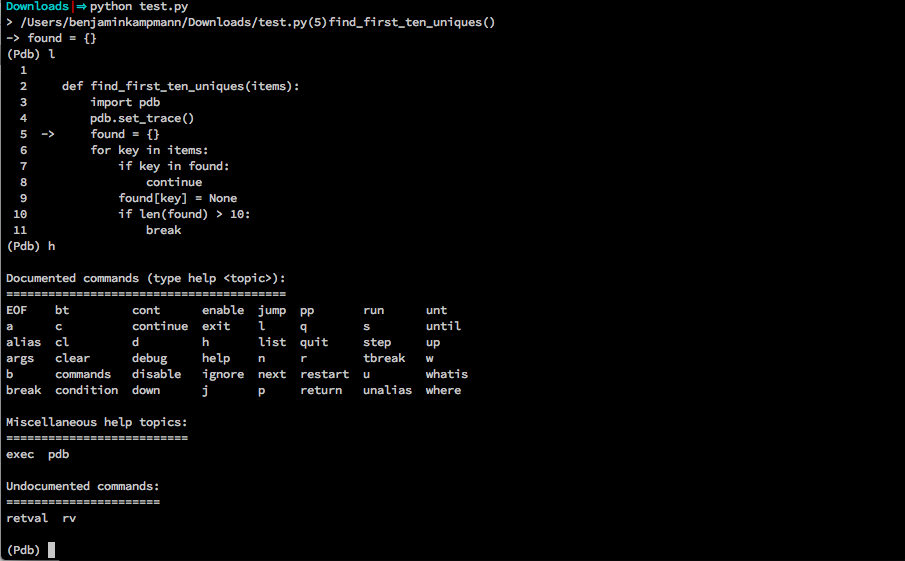
Python Debugger
import pdb; pdb.set_trace()

Pry+Byebug for Ruby
require 'pry'; binding.pry


NodeJS debugger
debugger; node debug script.js


Questions?
Let's debug
debugging-101
By Benjamin Kampmann
debugging-101
- 1,740



