
Agenda
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

What is iRODS?
Part 1: iRODS Lets You Control Your Data
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM


LETS YOU
CONTROL YOUR DATA
AND PROVE IT
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM


LETS YOU
Control access to data based on any characteristic of the data, connection, user, or resource.
Prove integrity and custody of the data.
Retain, archive, and destroy data according to policy.
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM


LETS YOU
Control and access data spread across storage in different sites, from different vendors.
Move huge data sets between multiple sites, quickly and verifiably.
Put the right data, in the right place, close to the right people (and out of reach of the wrong people).
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM


LETS YOU
Avoid buying the same data set twice.
Eliminate manual processing steps.
Keep track of processing steps applied, from raw data to finished product.
What is iRODS?
Part 2: iRODS is Open Source Data Grid Middleware
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

Photo: "Jefferson Memorial Pillars Inside" by Belal Khan, licensed under CC BY 2.0

iRODS is open source data grid middleware for...
- Storage Virtualization
- Data Discovery
- Workflow Automation
- Secure Collaboration
What Is iRODS?
Photo: "Jefferson Memorial Pillars Inside" by Belal Khan, licensed under CC BY 2.0

Cheat Sheet
iRODS is open source data grid middleware for...
- Storage Virtualization
- Data Discovery
- Workflow Automation
- Secure Collaboration
sits between the file system and the application
↓
← all your storage in a single namespace
← metadata annotation
← über cron
← shared access without compromising policy
iRODS is Middleware
User Application

"Logical" Layer






Storage Environment
"Physical" Layer
storagecluster.example.org:/managed
s3.amazonaws.com:/example/bitbucket
iRODS is Middleware

iRODS Clients
- Command Line Interface
- Web-based Interfaces (Java, PHP)
- "Mounted file system" interfaces (WebDAV, FUSE)
- Standalone Graphical Interfaces (Qt)
- Programming APIs (Python, Java, C++, REST)
Storage Resources
- Unix File System
- Object Storage
- Universal Mass Storage
iRODS presents multiple separate file systems in a unified namespace.
- Standard file systems: Any resource with a UNIX mount point.
- Archival storage: HPSS, TSM
- Object stores: DDN WOS, Ceph/Rados
- Cloud-based storage: Amazon S3
iRODS composable resources permit seamless distribution of files.
Storage Virtualization
Data Discovery
iRODS provides a catalog, the iCAT, that links data and metadata.
- Metadata can be system- or user-generated.
- Users can find data using features such as description, study ID, access date.
- Metadata can be used to link processed results to raw data (i.e., tracking provenance).
- Administrators can use metadata to control policy, such as archiving and access control policies.

Workflow Automation

iRODS lets you use any condition to trigger any action.
- User, file, and operating system activity caught by "policy enforcement points" (PEPs).
- iRODS' "rule engine" links PEPs to microservices.
Workflow Automation

iRODS lets you use any condition to trigger any action. For example:
- Metadata can be extracted once a file is placed in a landing zone.
- Data can be staged for high-performance computing (HPC) operations.
- Archiving and retention: data can be removed after an expiration date.
- Transformation: iRODS can kick off processes, send notification upon completion, and store results as metadata.
- Auditing: all iRODS user and file activity can be tracked in a log or separate database.
Secure Collaboration

Independently managed iRODS zones can be federated.
- Local users can grant access for users from remote zones to read/write data and metadata.
- Users log in (authenticate) through their home zones. Consistent interface across zones.
- Administrators exchange one set of keys. No need to compromise on data management policy.
History


• 15+ Year Development History
• Refactoring
- Pluggability
- Binary packages
• iRODS 4.0 and 4.1
The Future




• Messaging Framework
• Pluggable Rule Engine
• Reference Implementations
• Improved Manageability
- Zone Reporting
- Configuration Management
Who Uses iRODS?
Life Sciences
• Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute (20+ PB of iRODS Data)
• iPlant Collaborative (15k+ Users)
• Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center
• International Neuroinformatics Coordinating Facility (INCF)
• BGI
• Pharma
Research Infrastructure
• CC-IN2P3 (6+ PB of iRODS Data)
• EUDAT
• DataVerse Integration
Social Sciences
• Odum Institute
• Utrecht University (Youth Cohort Study)
Federal Users
• National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
• NASA
Oil & Gas, Media & Entertainment
How is iRODS Used?
Use Case: Sanger Institute
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
- Largest single contributor to original Human Genome Project
- Sequenced 1/3 of the human genome
- Data made publicly available by websites, ftp, direct DB access, APIs
- 1000 Genome Study → UK10k
- >45 PB raw storage
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

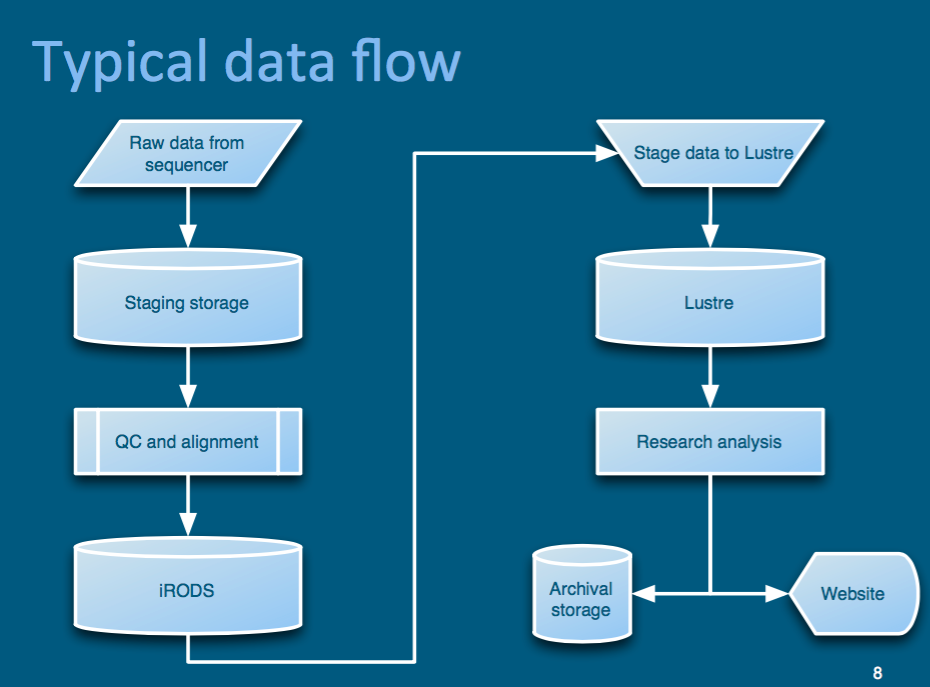
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

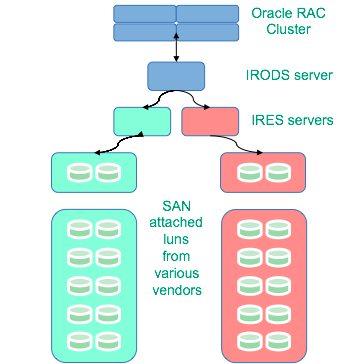
- Data preferentially placed on resource servers in the green data center (fallback to red)
- Data replicated to the other room.
- Checksums applied.
- Green and red centers both used for read access.
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

- Example metadata attributes
- Users query and access data from local compute clusters.
- Users access iRODS locally via the command line interface.
attribute: library
attribute: total_reads
attribute: type
attribute: lane
attribute: is_paired_read
attribute: study_accession_number
attribute: library_id
attribute: sample_accession_number
attribute: sample_public_name
attribute: manual_qc
attribute: tag
attribute: sample_common_name
attribute: md5
attribute: tag_index
attribute: study_title
attribute: study_id
attribute: reference
attribute: sample
attribute: target
attribute: sample_id
attribute: id_run
attribute: study
attribute: alignment
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

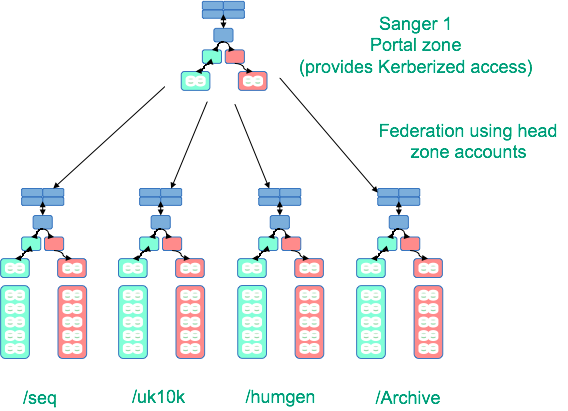
The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
Baton Client
Thin layer over parts of the iRODS C API
● JSON support
● Connection friendly
● Comprehensive logging
● autoconf build on Linux and OSX
Current state
● Metadata listing
● Metadata queries
● Metadata addition
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

How is iRODS Used?
Additional Use Cases
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

Other Use Cases
A Health Science Institute
- Landing Zone for automatic staging to/from HPC
- Metadata extraction, hierarchical metadata
- Automatic permission management
NIEHS
- Automating lab processes
- Report generation
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

The iRODS Consortium
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

Enterprise Readiness
• Modular, maintainable code
• Static analysis and continuous integration
• Sustainable funding and governance model
iRODS is free, open source software owned by a foundation called the iRODS Consortium.
-
Members pay an annual membership fee: 4 levels of membership.
-
Members have agreed upon iRODS as an area of cooperation, rather than competition.
-
Two monthly meetings: Technology Working Group (TWG), Planning Committee
-
Goal is to create a sustainable open source project.
-
Presently, funds a team of 10+ developers, application engineers, documentation, support staff










Sustainable Governance and Funding Model





+2
Contract Customers
Consortium Initiatives
- Professional services, training, and support.
- iRODS Partners Program
- iRODS Hub
- iRODS User Group Meeting 2015
- Chapel Hill, NC
- Training on June 9th
- Presentations on June 10th and 11th
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM


Getting Started
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

The Consortium Sales Model
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

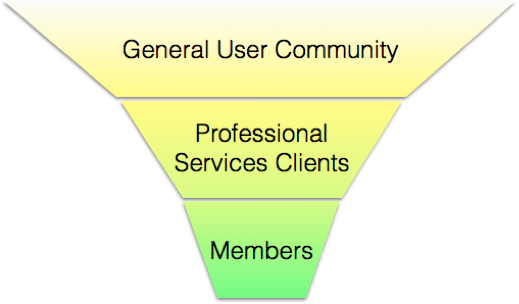
Initial Trial
- Documentation, training
- Blog posts, social media
- Cloud images
- Google Group
- iRODS Hub
Proof of Concept
- Occasional 1-on-1 Support
- Service Contract
Pilot
- iRODS Partners
- Service Contract
Production
- Consortium Membership
- iRODS Partners
- Service Contract
How to Begin
- Learn about iRODS at iRODS.org
- Identify the Need
- Demonstrate a Sample Application
- The Consortium Can Help!
- Collaborate
- Co-Deployment
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

Recognizing iRODS Customers
- DevOps
- Long term storage
- Genomics, life sciences
- >500 TB of data, or >100k files
- Mixed storage environment
- "Collaboration" between multiple (sub-)organizations
- "My HSM system isn't smart enough"
- "My scheduler doesn't talk to my storage system"
- "provenance," "metadata"
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

Highlights from the iRODS Roadmap
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

iRODS 4.1
- Released June 2015
- Hardening the legacy code base
- Coverity Clean: Over 1100 stability, reliability fixes
- JSON-Based configuration replaces scattered config files
- Zone Introspection: Which servers are in my Zone?
- Control Plane: Orderly shutdown
- Customer-Requested Features
- Atomic data-metadata puts
- Key-Value passthrough from the command line
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

iRODS 4.2
-
Messaging framework: i/f to external services
- e.g., Solr for full content indexing
- Pluggable rule engine
-
Next generation API
- Simpler client development, beginning with put/get/query
- Movement toward object semantics, move POSIX to the resource plugins
- Pluggable transport: iRODS to broker a connection, then get out of the way
- User Interface improvements, in coordination with DFC collaborators
And Beyond...
- Eventually, iRODS core is mainly connecting plugins: Need plugin registry and dependency model
- Using the new API to create new plugins, clients, interfaces
(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

(C) 2015 THE IRODS CONSORTIUM

iRODS Technology Overview
By beppodb
iRODS Technology Overview
- 2,598




