Delegation in Veto Bargaining: An Experiment
Brandon Williams
Alistair Wilson
Richard Van Weelden
University of Pittsburgh
Behavioral and Experimental Brown Bag
Motivation
- Many "bargaining" contexts exist in which a less-informed (about preferences) party must decide what to offer to a more-informed party.
- For the proposers, offering more flexibility may result in the other party selecting a less favorable outcome... although not as bad as when their proposal is outright rejected.
Motivation




- Many "bargaining" contexts exist in which a less-informed (about preferences) party must decide what to offer to a more-informed party.
- For the proposers, offering more flexibility may result in the other party selecting a less favorable outcome... although not as bad as when their proposal is outright rejected.
- This bargaining environment takes many forms:
Motivation




- Many "bargaining" contexts exist in which a less-informed (about preferences) party must decide what to offer to a more-informed party.
- For the proposers, offering more flexibility may result in the other party selecting a less favorable outcome... although not as bad as when their proposal is outright rejected.
- This bargaining environment takes many forms:
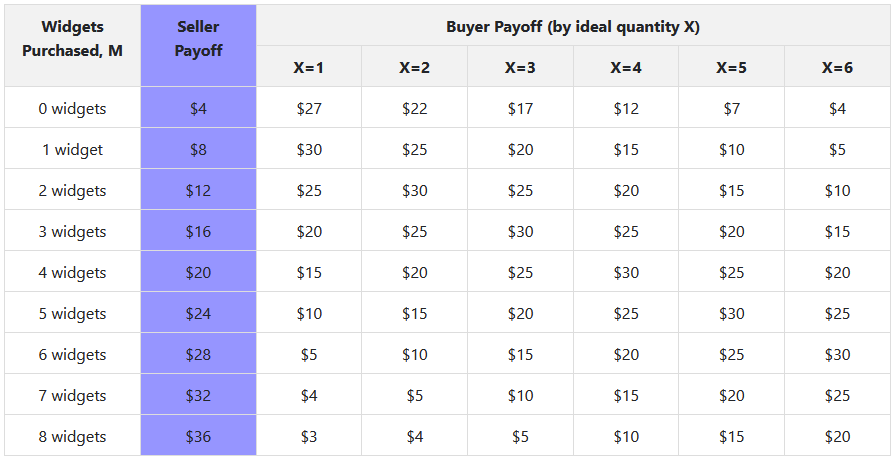
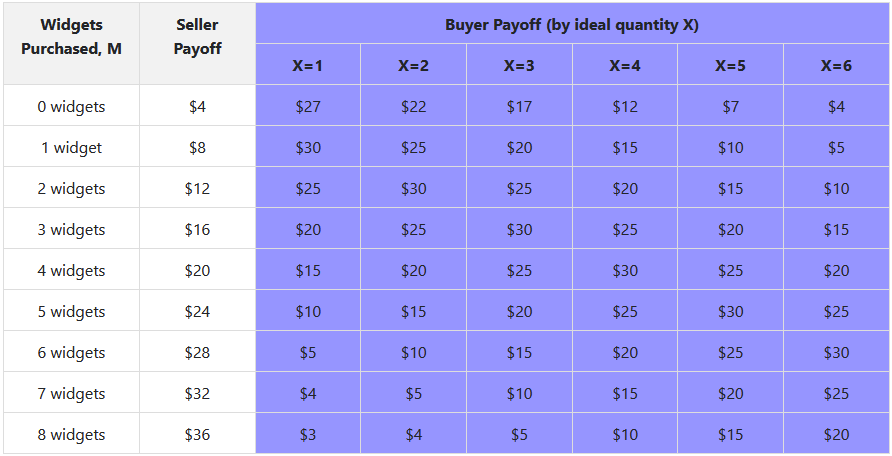
Experimental Design
- Constructed environment that models the veto bargaining framework: buyers and sellers
- Sellers want to sell as many widgets as possible
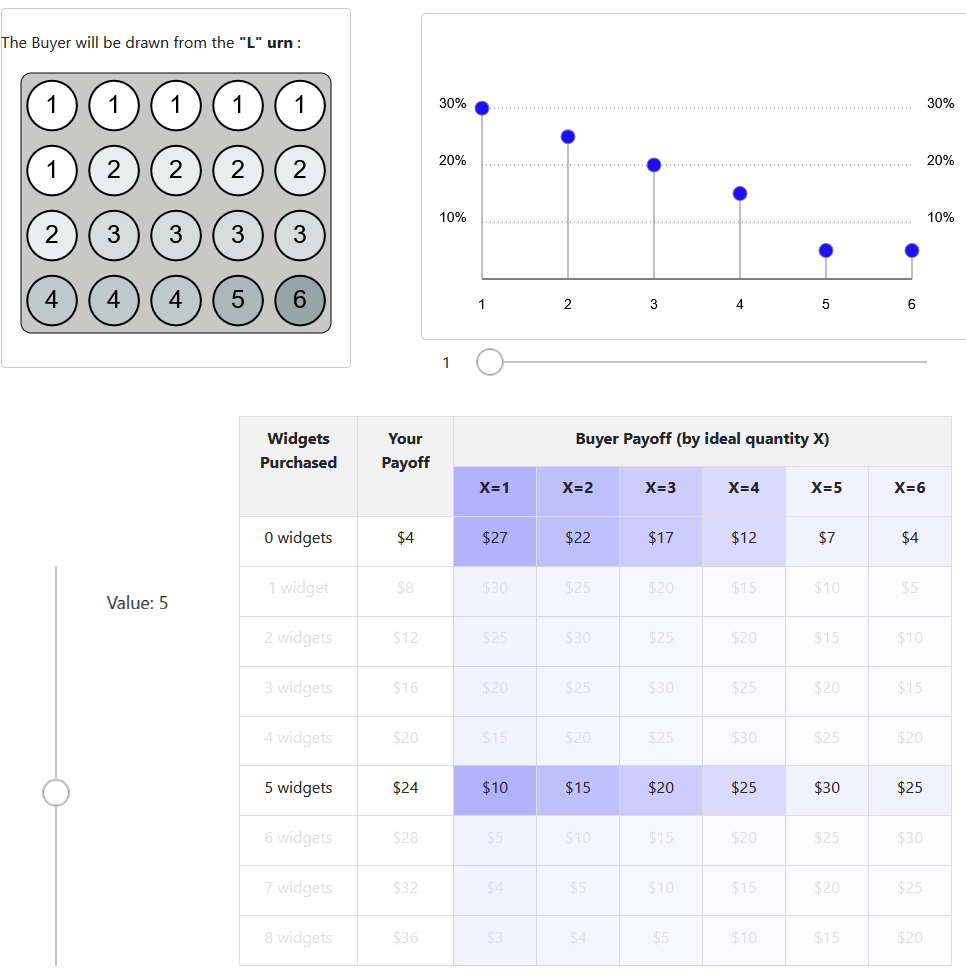
- Buyers have an ideal point X that determines the optimal purchase number of widgets
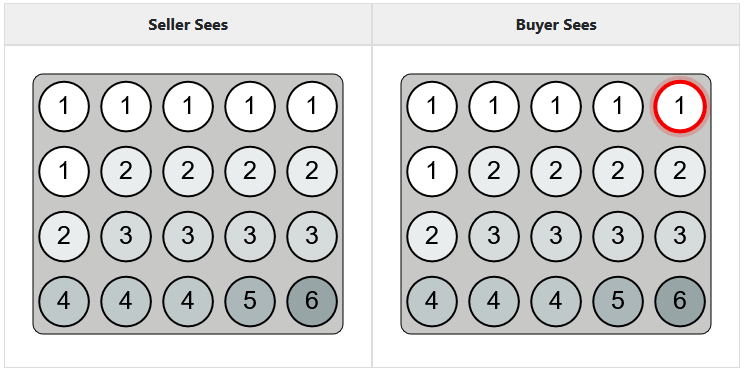
- The seller is unaware of the ideal point
- Both know the distribution from which the ideal point was determined
- Buyer can always "walk away" and not buy anything
Experimental Design
Experimental Design
Experimental Design
Experimental Design
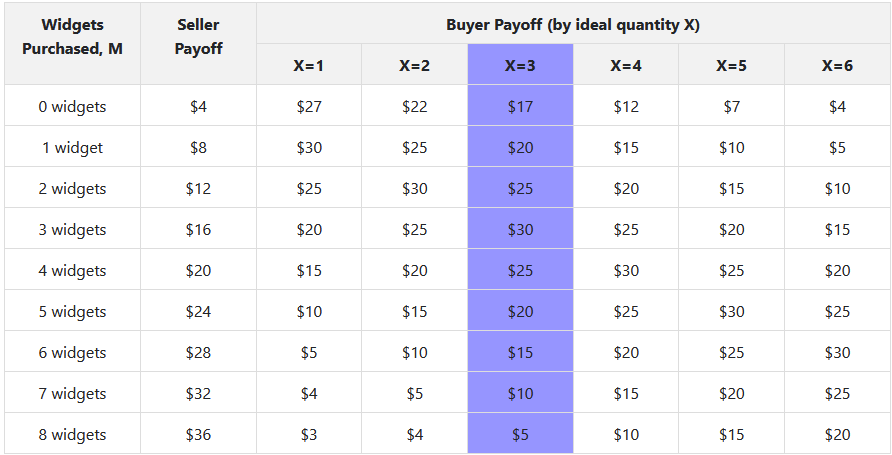
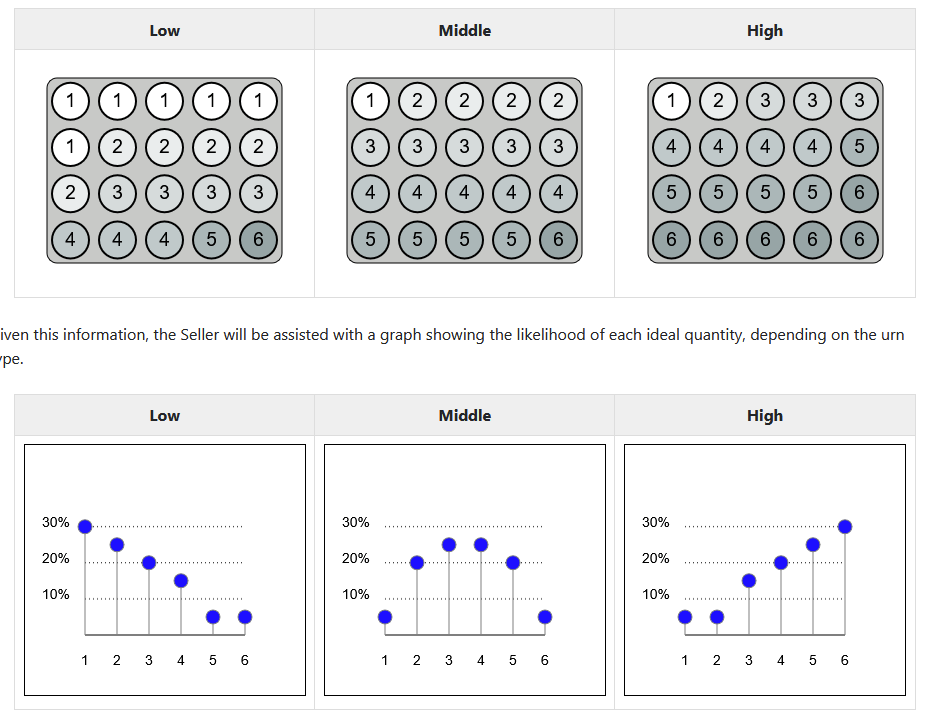
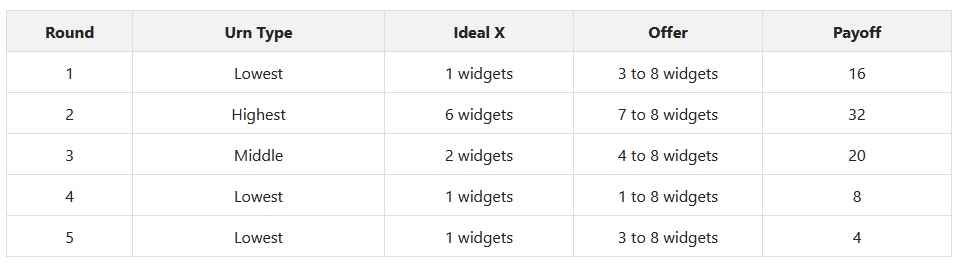
- The buyer's optimal point is drawn from an urn, and the possible draws from the urn are known to both
Experimental Design
- The buyer's optimal point is drawn from an urn, and the possible draws from the urn are known to both
Experimental Design
- The buyer's optimal point is drawn from an urn, and the possible draws from the urn are known to both

Experimental Design
- The buyer's optimal point is drawn from an urn, and the possible draws from the urn are known to both

Experimental Design
- The buyer's optimal point is drawn from an urn, and the possible draws from the urn are known to both

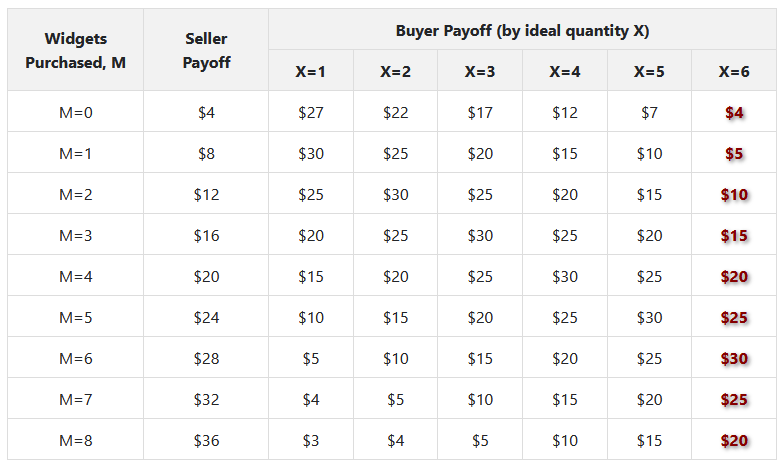

Experimental Design
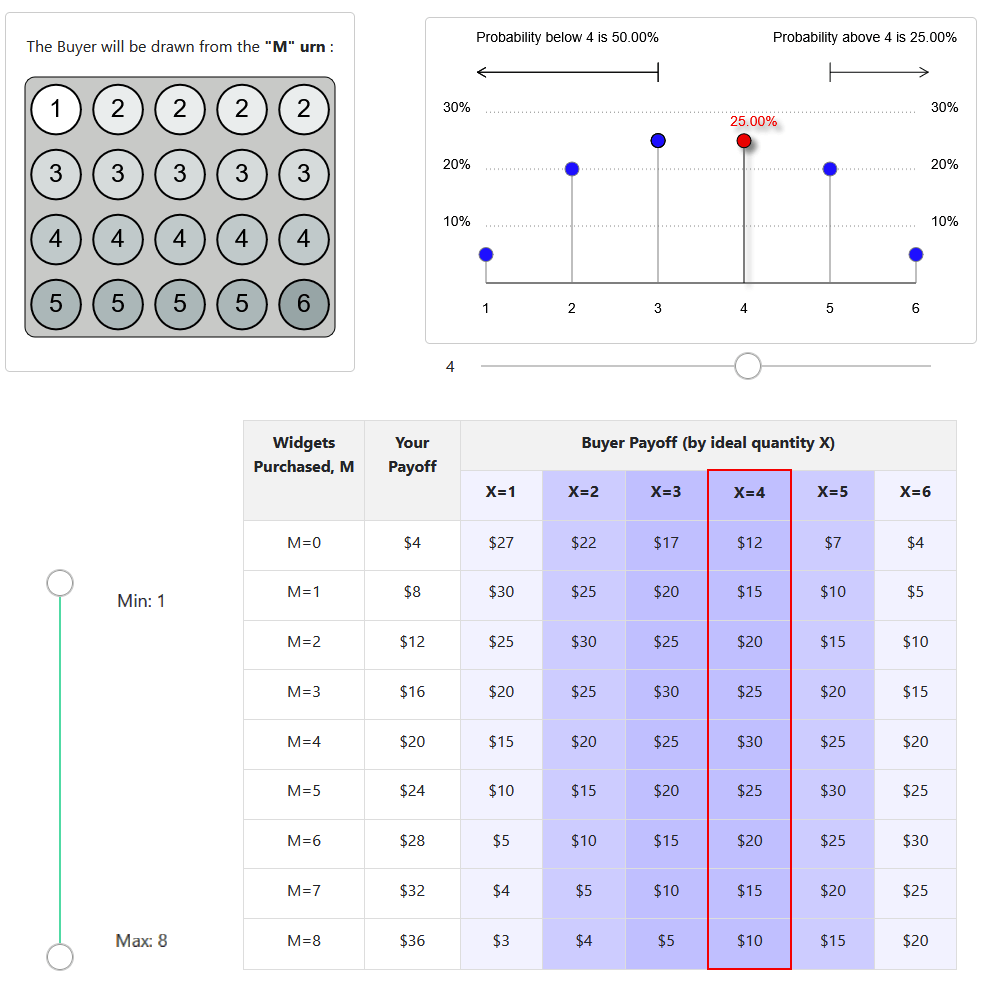
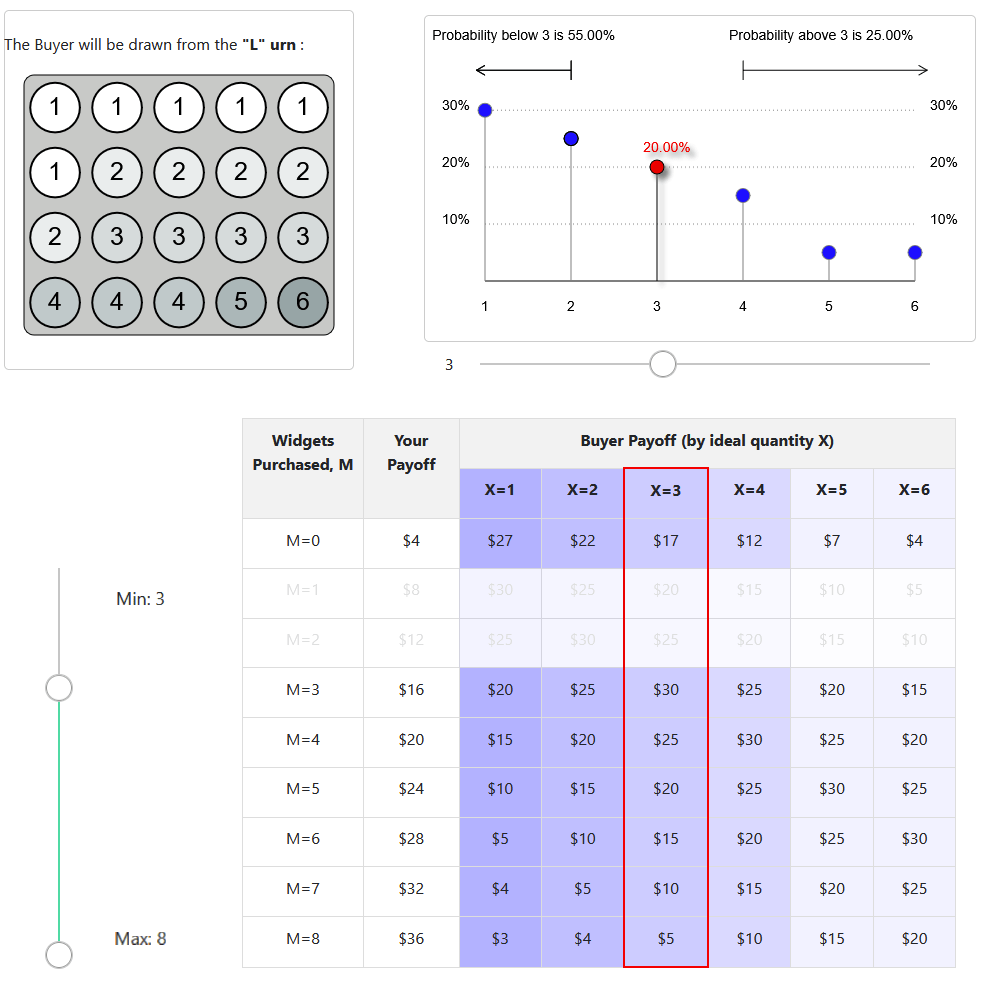
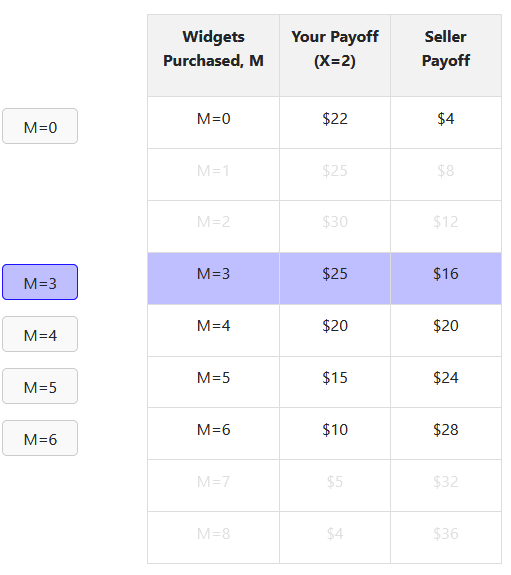
- The seller is tasked with making an offer that maximizes their payoff, which is contingent on the buyer accepting the offer
- In delegation treatment, the buyer can offer a menu range of options to buy
- In take-it-or-leave-it treatment, the buyer can only offer a single point
Experimental Design
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
Experimental Design
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Experimental Design
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Experimental Design
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
- Proposer can make a single point offer
- Vetoer must decide to accept or veto
Experimental Design
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
- Proposer can make a single point offer
- Vetoer must decide to accept or veto
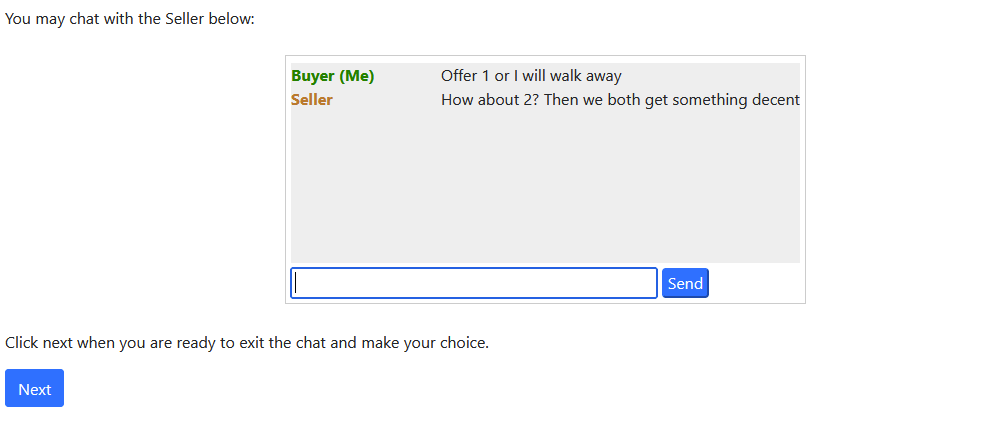
- Participants can coordinate in advance of decisions
Experimental Design
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
- Proposer can offer a range of choices for the vetoer to consider
- Vetoer can accept any of the options, or veto
Experimental Design
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
- Proposer can offer a range of choices for the vetoer to consider
- Vetoer can accept any of the options, or veto
- Participants can coordinate in advance of decisions
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Chat should bring meaningful improvement to coordination
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Chat should bring meaningful improvement to coordination
Over-revealing vetoers?
Over-credulous proposers?
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Chat shouldn't have much effect, but behaviorally uncertain
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Chat shouldn't have much effect, but behaviorally uncertain
High types see no benefit
Appeals to other regarding?
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
| No Chat | Chat | |
| Take-it-or-leave-it | ||
| Delegation |
Can chat create efficiency gains enough to reach delegation?
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Experimental Design
- Between-subject
- After 15 rounds, instead play against a robot player who simply optimizes response
- Lotteries over the same domain
- Within-subject
- Varying distributions for the vetoer
- Changing roles
Thank you!
Questions or Comments?
Theory
- Full delegation optimal if proposer is sufficiently risk-averse and/or distribution of vetoer is decreasing on the interval
Theory
- Full delegation optimal if proposer is sufficiently risk-averse and/or distribution of vetoer is decreasing on the interval
- No delegation optimal if distribution of vetoer is increasing on the interval
Theory
- Full delegation optimal if proposer is sufficiently risk-averse and/or distribution of vetoer is decreasing on the interval
- No delegation optimal if distribution of vetoer is increasing on the interval
- The optimal interval is increasing in risk aversion and decreasing in higher ex-ante alignment
Theory
- Full delegation optimal if proposer is sufficiently risk-averse and/or distribution of vetoer is decreasing on the interval
- No delegation optimal if distribution of vetoer is increasing on the interval
- The optimal interval is increasing in risk aversion and decreasing in higher ex-ante alignment
- Take-it-or-leave-it is strictly worse for proposer and often worse for both
Theory
- Full delegation optimal if proposer is sufficiently risk-averse and/or distribution of vetoer is decreasing on the interval
-
No delegation optimal if distribution of vetoer is increasing on the interval
- The optimal interval is increasing in risk aversion and decreasing in higher ex-ante alignment
- Take-it-or-leave-it is strictly worse for proposer and often worse for both
- Cheap talk does little for interval delegation but generates efficiency gains for take-it-or-leave-it
Literature
Models of similar bargaining forms have been proposed in theory...
- Under complete information - Romer and Rosenthal (1978)
- Under cheap talk negotiation - Matthews (1989)
- With valuable expertise involved - Holmström (1977)
- More recently: Kartik, Kleiner, Van Weelden (2021)
Literature
Models of similar bargaining forms have been proposed in theory...
- Under complete information - Romer and Rosenthal (1978)
- Under cheap talk negotiation - Matthews (1989)
- With valuable expertise involved - Holmström (1977)
- More recently: Kartik, Kleiner, Van Weelden (2021)
And used in experiments...
- Early bargaining - e.g. Roth and Murnighan (1980, 1982)
- Vetoes within committees - Kagel, Sung, and Winter (2010)
- Multiple rounds of bargaining - Nunnari (2021)
Literature
Models of similar bargaining forms have been proposed in theory...
- Under complete information - Romer and Rosenthal (1978)
- Under cheap talk negotiation - Matthews (1989)
- With valuable expertise involved - Holmström (1977)
- More recently: Kartik, Kleiner, Van Weelden (2021)
And used in experiments...
- Early bargaining - e.g. Roth and Murnighan (1980, 1982)
- Vetoes within committees - Kagel, Sung, and Winter (2010)
- Multiple rounds of bargaining - Nunnari (2021)
Theory

The vetoer is drawn from a distribution on the interval
Theory

The vetoer is drawn from a distribution on the interval
Theory

The vetoer is drawn from a distribution on the interval
Theory


Status quo
v
Theory


Status quo
v
Theory


Status quo
v
Full Delegation
Optimal if:
- Sufficiently risk-averse
- Density type is decreasing
Theory


Status quo
v
No Compromise
Optimal if:
- Vetoer density increasing
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
Optimal if:
- Unimodal distribution and linear loss utility
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
Comparative statics
c*
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
Comparative statics
- Discretion ↑ in risk aversion
c*
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
Comparative statics
- Discretion ↑ in risk aversion
- Discretion ↓ in ex ante alignment
c*
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
c*
Theory


Status quo
v
Take-it-or-leave-it
c*
Theory


Status quo
v
Take-it-or-leave-it
c*
Strictly worse off
Theory


Status quo
v
Take-it-or-leave-it
c*
Strictly worse off
May be worse off
Theory


Status quo
v
Take-it-or-leave-it
c*
Strictly worse off
May be worse off
or better off
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
c*
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
c*
Acquiesce
Veto Threat
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
c*
Acquiesce
Veto Threat
Theory


Status quo
v
Interval Delegation
c*
Acquiesce
Veto Threat
Optimal delegation allows for fewer veto results for the proposer than under cheap talk
Theory


Status quo
v
c*
Acquiesce
Veto Threat
Take-it-or-leave-it
Theory


Status quo
v
c*
Acquiesce
Veto Threat
Take-it-or-leave-it
Under take-it-or-leave-it, closer alignment can be achieved with cheap talk
Theory
Theory
0
1
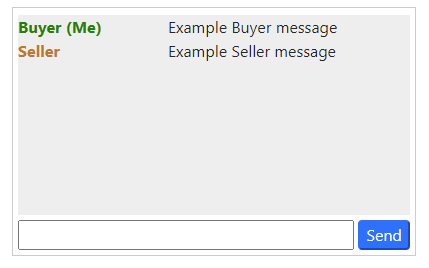
Type your message here
Click to send
your message
A history of messages
appears here
Theory

Proposer
0
1
Theory


v
Vetoer
0
1
Theory


v
???
0
1
Theory


v
???
0
1
Theory


v
Status quo
Theory


v
Status quo
Theory


v
Status quo
Theory


Status quo
Full Delegation
v
Theory


Status quo
No Compromise
v
Theory


Status quo
Interval Delegation
v
Theory


Status quo
Interval Delegation
v
Theory


Status quo
Interval Delegation
v
Copy of veto_delegation
By bjw95
Copy of veto_delegation
- 53



