Computer Vision
What is computer vision?
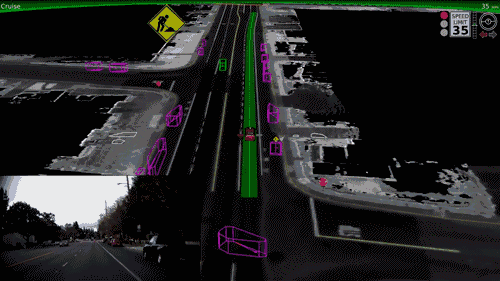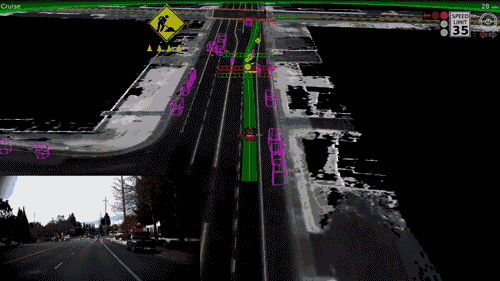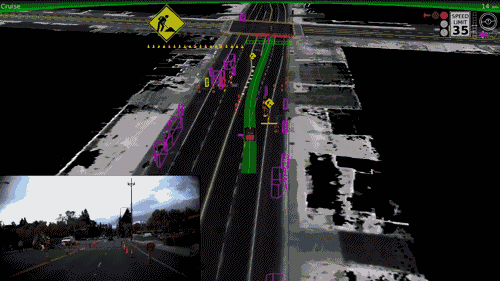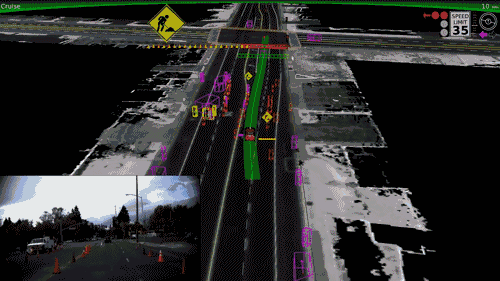
Self Driving Cats?

Customer Tracking?

The Matrix?
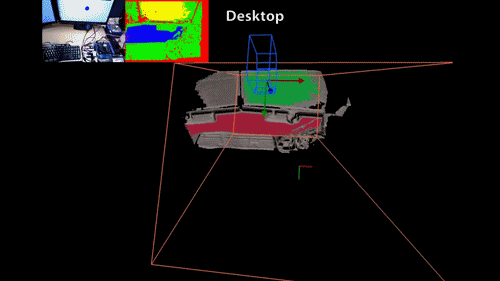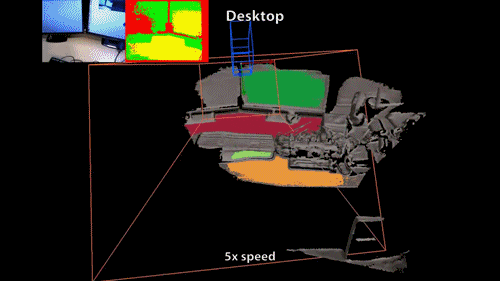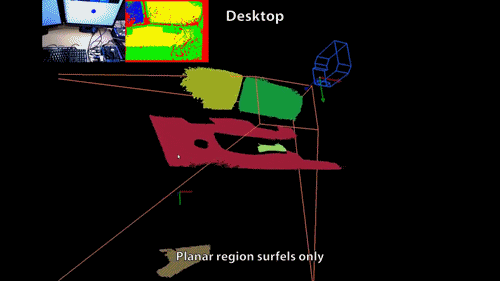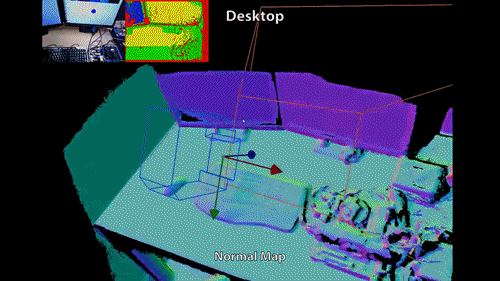
3D Scanning?
Yes.
Formal Definition
Computer vision is a field that includes methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing, and understanding images and, in general, high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g., in the forms of decisions.
What does this mean?
Matrices.
(A lot of them!)
A Brief History

Purposive Vision
Main Fields
Event Detection
Scene reconstruction
Learning
Big Brother
Motion Estimation
Image restoration
Object / feature recognition

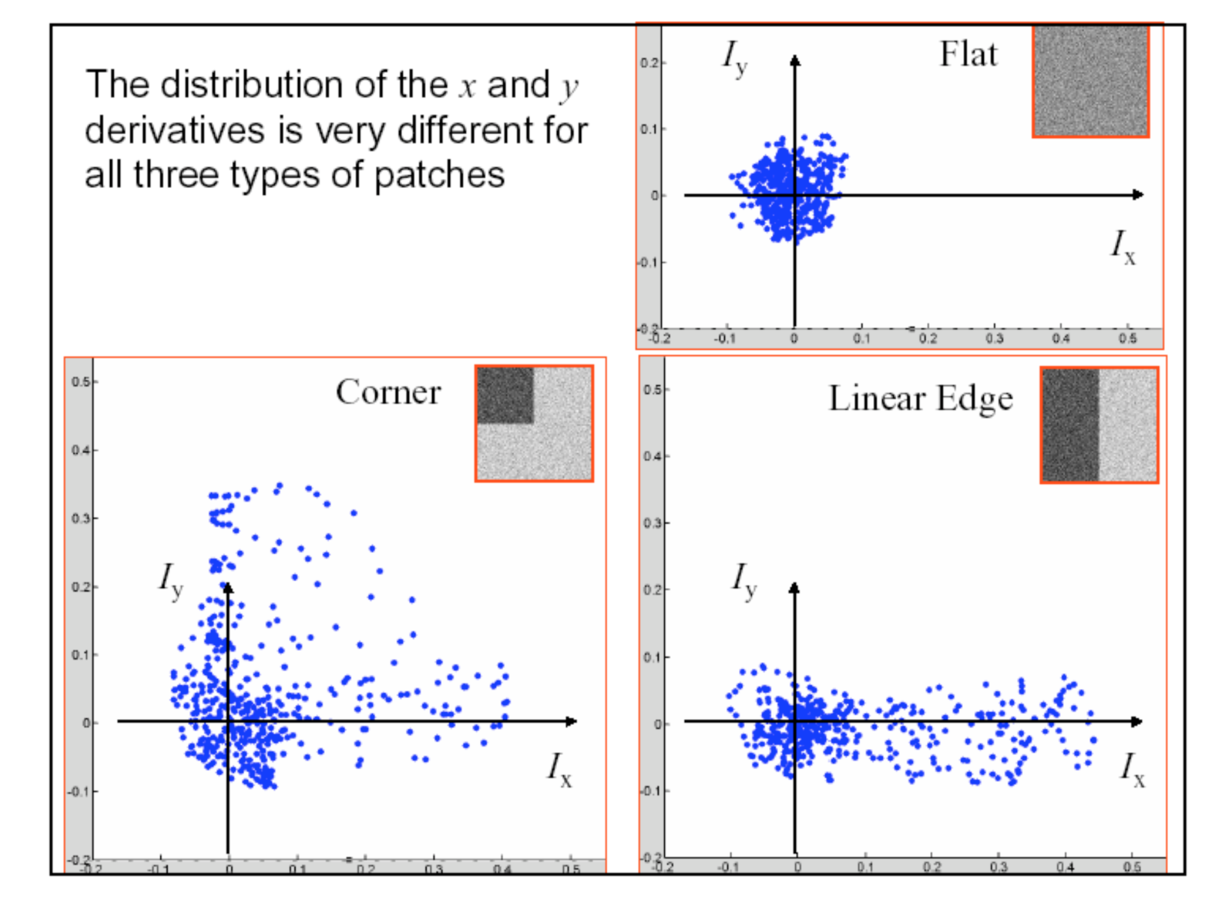
Corner Detection

Corner Detection
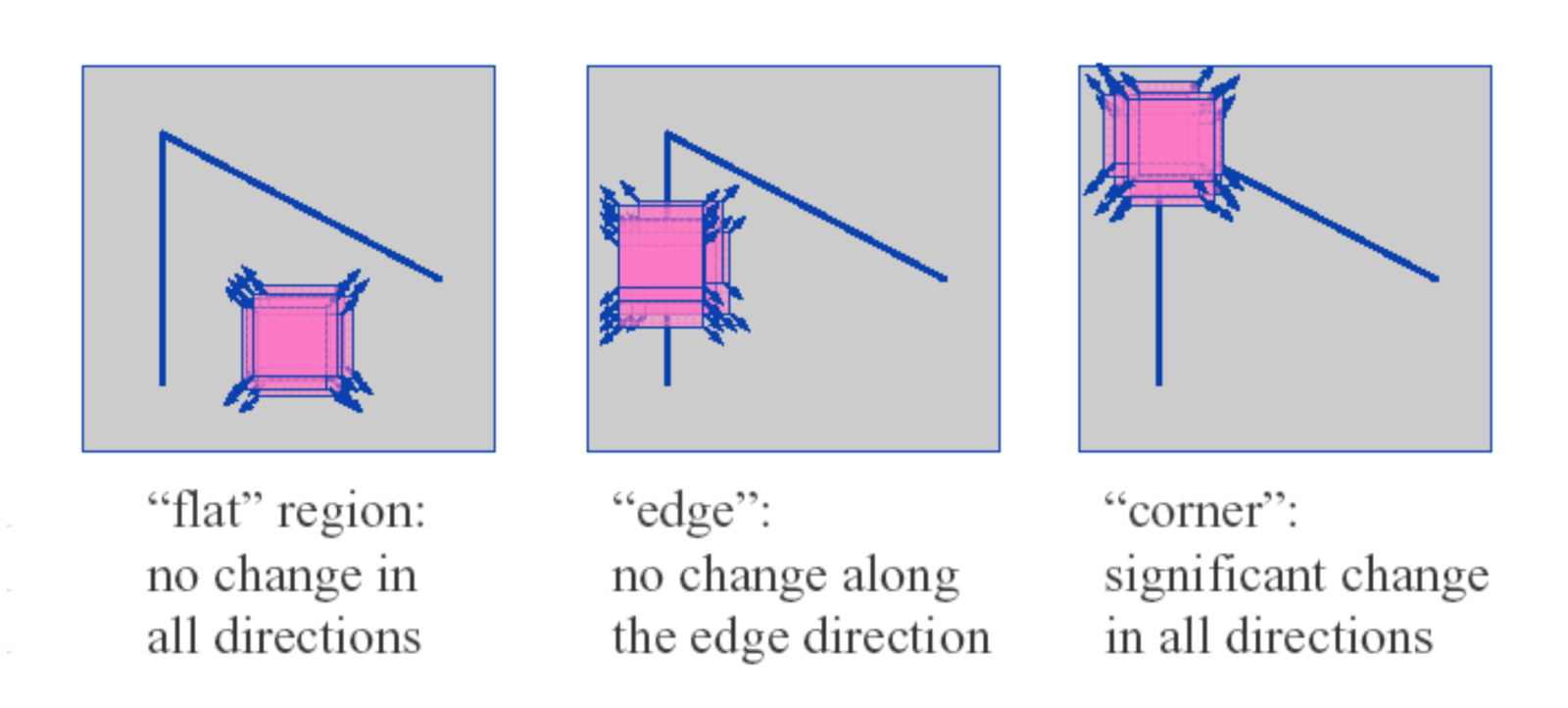
Use sliding window over edge detected image and measure change in multiple directions.
SimpleCV Example
motion = img.getCorners()

Cat
Optical Flow
Title Text

Calculate the motion between two image frames which are taken at times t and ∆t at every pixel
Optical Flow
Find how much a given pixel (or patch of pixels) moved between frames.

For a pixel that moved (∆x, ∆y) in ∆t, the following will hold:
I(x, y, t) = I(x + ∆x, y + ∆y, t + ∆t)
Lucas–Kanade Method
Flow for neighboring pixels is similar, so solve equation for neighborhood pixels, too.
Fails at tracking uniform regions
SimpleCV Example
motion = img.getMotion()
Haar Cascades
- Train descriptor
- Search image for descriptor
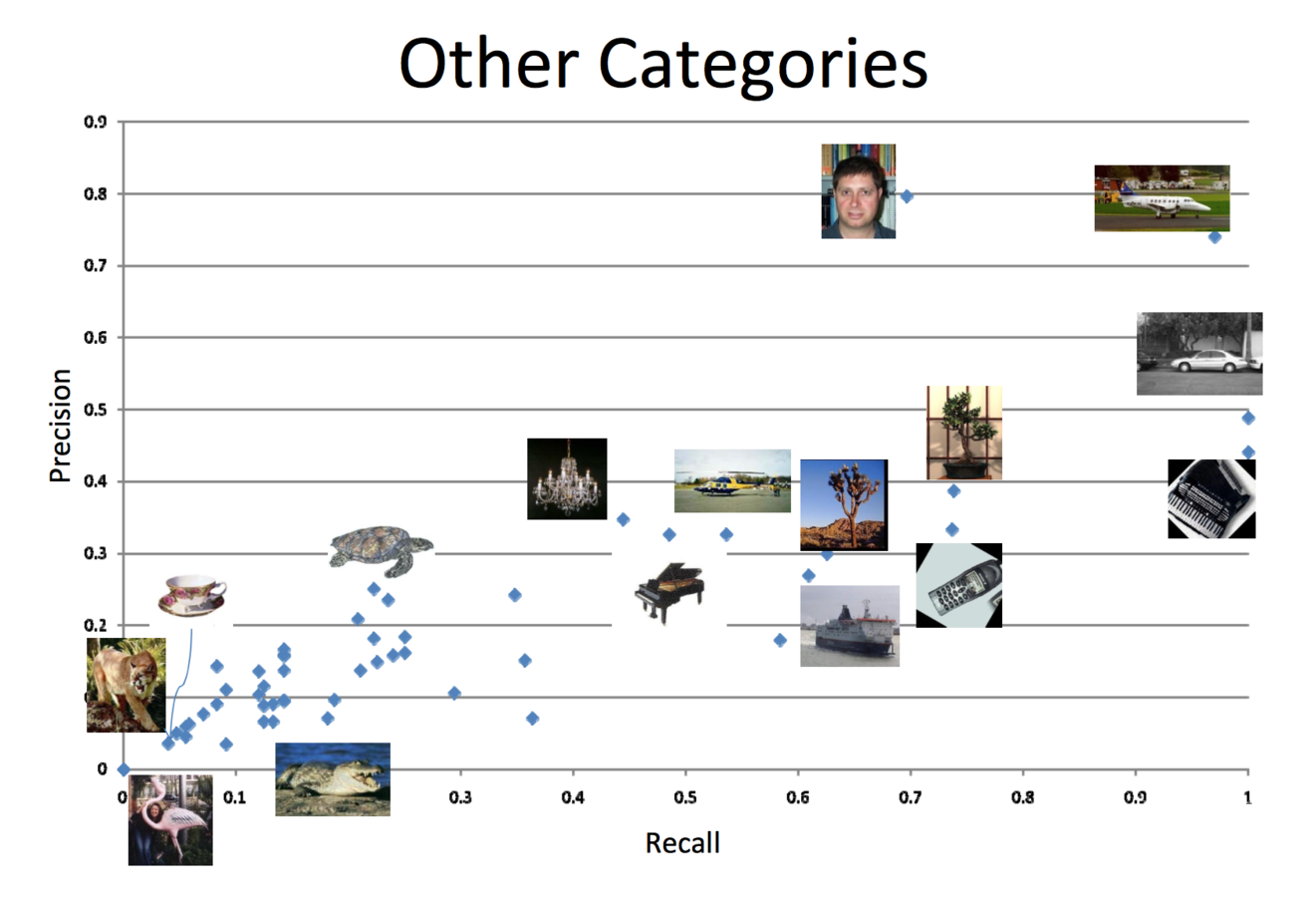
Haar Accuracy
SimpleCV Example
faces = HaarCascade("face.xml")
img.findHaarFeatures(faces)
HOG
(histogram of oriented gradients)
Object Detection
Easy, right?

Not always

Descriptor
Train on 40-60 example images by normalizing + combining their gradients to produce descriptor

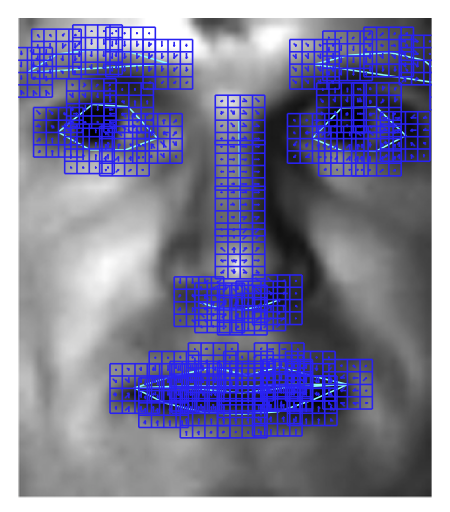
End Result
Computer Vision
By Brent Baumgartner
Computer Vision
- 401


