Angular 2
2 is a bigger number than 1, True Story.
Why it be
What it do
How you do
Angular 2 is pretty different
Consider the Timeline
- Angular was first developed in 2009
- Knockout, backbone, jQuery
- Then came HTML5 and angular and frameworks!
Why the changes
New Things
- ES6
- Isomorphic rendering
- More complex apps with demanding performance requirements
- Web Components
- Explosion of useful Javascript libraries
Why the changes
DOM
&
DATA
Interacting
with
the dom
by Angular 2
Components
Components are how things are built in angular.
- Applied to a class using a decorator
- Selector is the name used to identify the component to other components
- Mustache brackets here to stay


Template Bindings
- Bind to any DOM property
- Bind to nested properties
- Styles and classes included

Template Bindings
- Handle DOM event
- Any DOM event
- Two way binding
- One way bind to title
- handle titleChanged DOM event
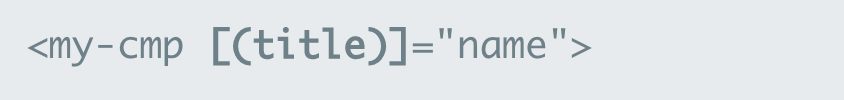
#Variables & Embedded templates
- Variables allow us to reference elements by naming them with a #
- * will turn the current element into an embedded template
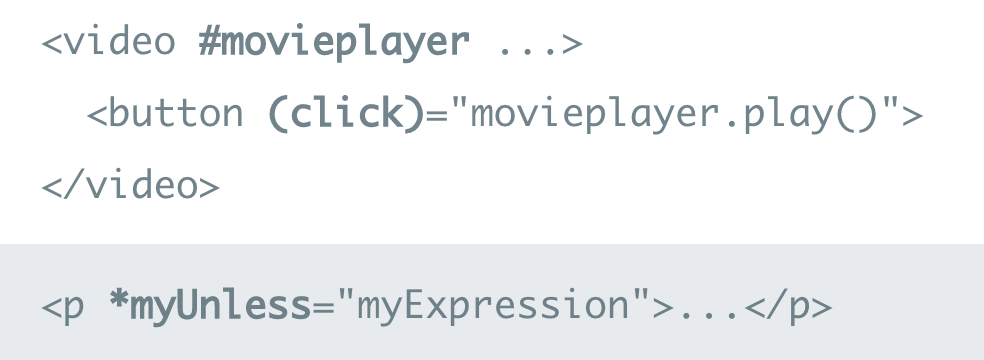
Why the *

These are the same
Built in Directives - pt 1
- ngIf toggles whether elements are on the DOM.
- Use [style.display] to toggle the display property
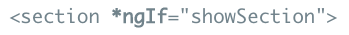

ngSwitch for conditional layouts
Built in Directives - pt 2
ngClass for multiple classes


*ngFor for repeating an element
Nested Components
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { AppComponent } from './app.component';
import { ChildComponent } from './child/child.component';
import { FriendsService } from './friends.service';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent,
ChildComponent
],
imports: [
BrowserModule,
FormsModule,
HttpModule
],
providers: [FriendsService],
bootstrap: [AppComponent]
})
export class AppModule { }
<h1>
{{title}}
</h1>
<app-child></app-child>
@Component({
selector: 'app-child',
templateUrl: './child.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./child.component.css']
})
export class ChildComponent implements OnInit {
title: string;
friends: Array<string>;
newFriend: string;
friendName: string;
test: string;
constructor(private friendsService: FriendsService) {}
getFriends(): void {
this.friends = this.friendsService.friends;
}
addFriend(friend: string): void {
this.friendsService.friend = friend;
this.newFriend = '';
}
ngOnInit() {
this.title = 'Child Class!';
this.getFriends();
this.test = 'foo';
}
}
Data
and
Services
by Angular 2
JavaScript
Typescript
Typescript


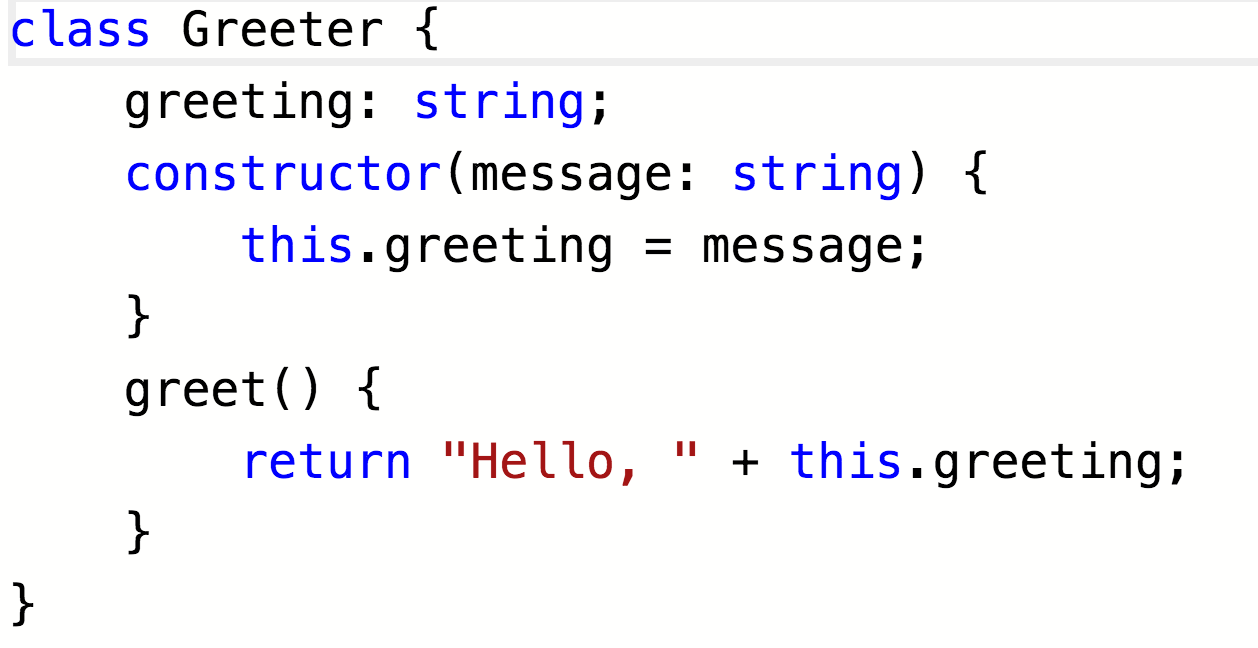

A Service - Pt 1
- ES6/Typescript Class
- Import and use other pieces as needed


A service - pt 2
- Import and register as a provider
- This is more javascript less angular
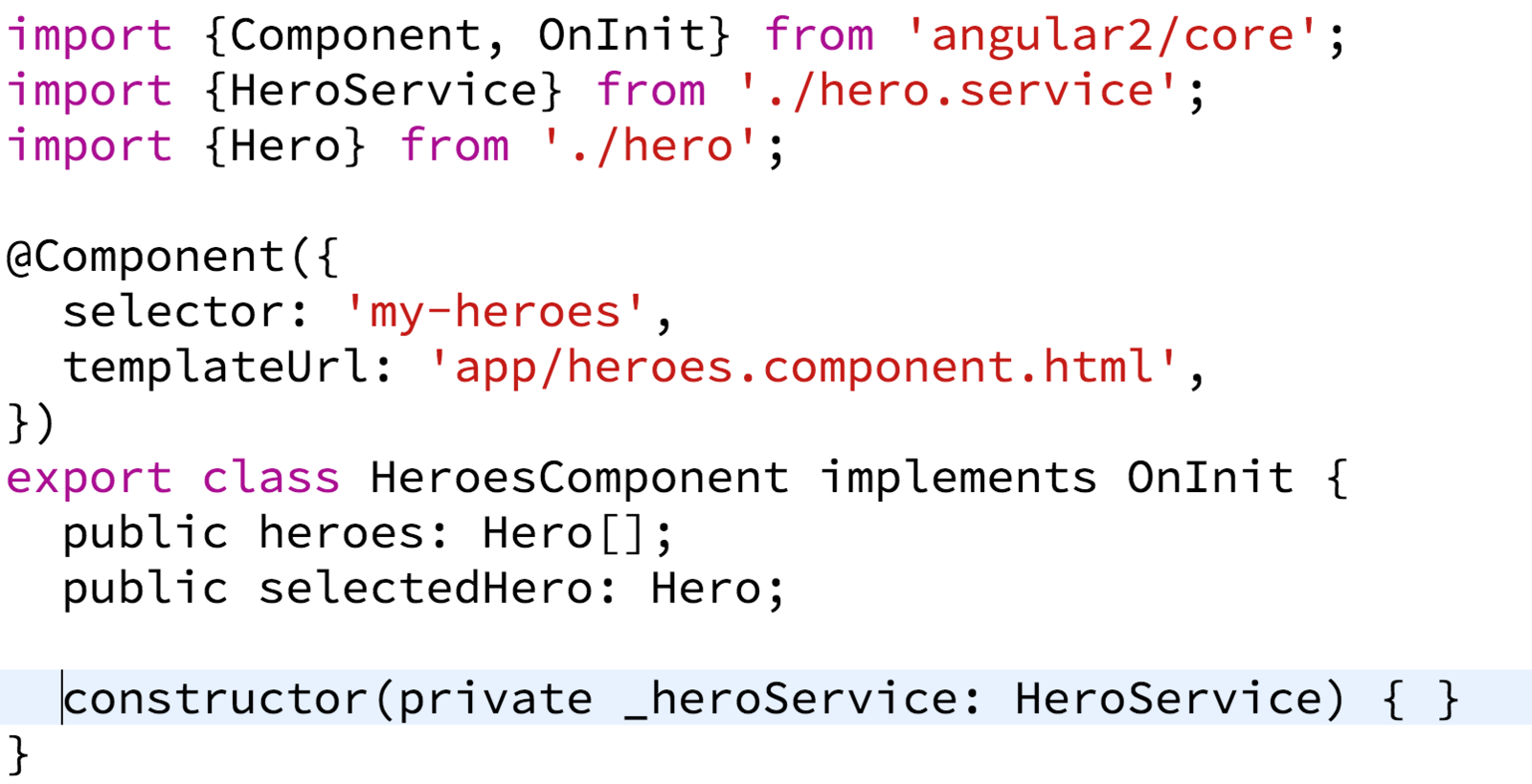
A service - pt 3
- Include in constructor using Type
- Is a singleton instance

Http
Some Gotchas
- "A browser ignores HTML tags and attributes that it doesn't recognize. So does Angular"
- * are important on certain directives
- Many docs/examples are in Typescript
- HTTP gives you an observable, not a promise
Prepping for 1.x to 2
- Migrate to Typescript
- Use 'require' or 'import' via gulp/webpack/babel
- Write components using directives
- templateUrl
- Controller (ControllerAs)
- Isolated scope
- Nest them and pass data through the isolate scope
Angular 1 component

See component API in Angular 1.5
Summary
- More Javascript less 'Angular'
- Flexibility
- Interoperability
- Swappability
- Modifiability
- Modular component tree structure
- More explicit in its syntax
- Still Learning curve
- Keeping:
- Dependency Injection
- Declarative template syntax
- Toolbox of useful things like HTTP
Copy of Angular 2 Crash Course
By Brett Caudill
Copy of Angular 2 Crash Course
- 905



