Basics of
Remote Sensing+
Google Earth Engine


Britta Ricker, PhD
GEO3-2419
Land Use Change Science
Objectives of this course
https://osiris.uu.nl/osiris_student_uuprd/OnderwijsCatalogusZoekCursus.do
- Use the basic functionalities of GIS for spatial data processing;
- Develop land use change scenarios;
-
Identify and assess global and local historical, current and future drivers of land use change;
in this slide deck
- GIS & Remote Sensing
- Goog Earth Engine + Land cover classification
- Review: How do these concepts relate to land use change?
Disaster and Land Use


Maps can help reduce complexity


Vanacker (2016) Impact of deforestation on slope stability
Geographic Information
Science
Geographic Information Systems(GIS)

Geographic Information Systems (GIS)




Online "slippy" maps

Remote Sensing


Temporal Resolution: Revisit Every 5 days
True Color

Details
From Sentinel 2
Date of image: 22 Feb 2017
Spatial Resolution:
Each pixel represents 20 m
2325 columns
2960 rows of pixels

Sentinel 2
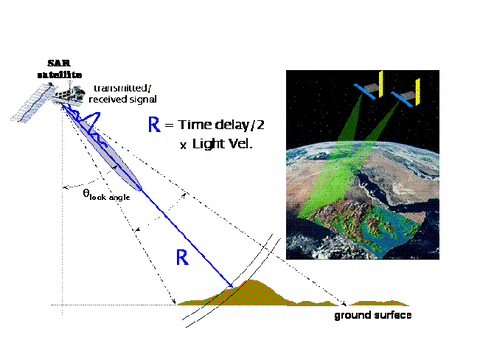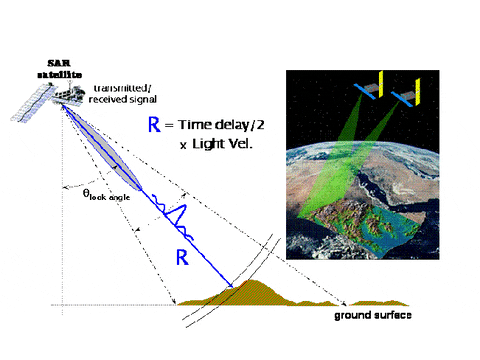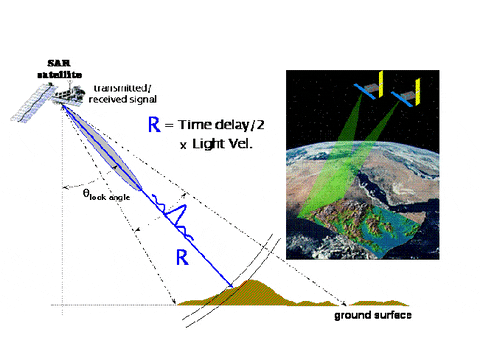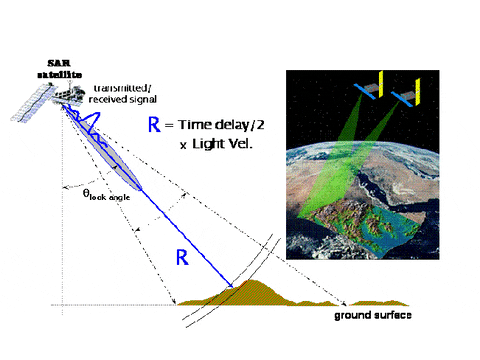
Active Sensor
Passive Sensor

Lidar


1 m resolution!
Electromagnetic Energy
Features on the Earth reflect, absorb, transmit, and emit electromagnetic energy from the sun.

Properties of electromagnetic energy
Multispectral imagery
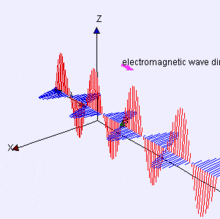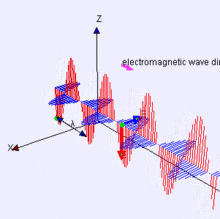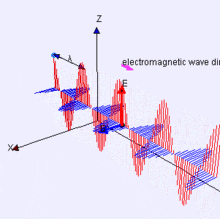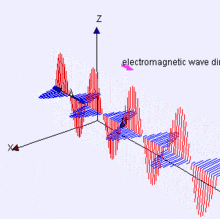
wavelength, fequency, amplitude

The visible spectrum is small!

What else is collected?
Bands and spectral ranges

Spectral signature

How are images rendered on our screen?
3 bands projected light
The primary colors are Red, Green, Blue
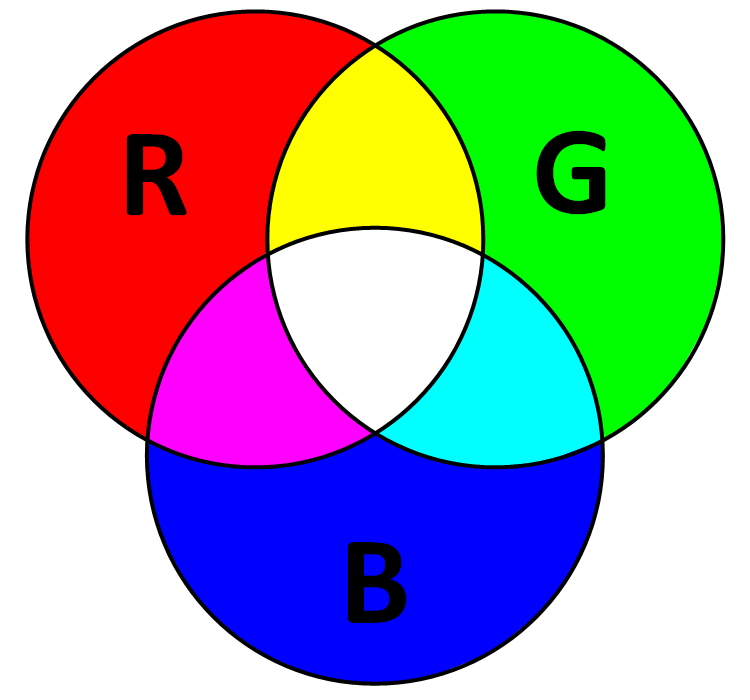
True Color
= Band 4 Red
= Band 3 Green
= Band 2 Blue

False Color Composites

Urban areas

Urban=Purple
= Band 12 SWIR II
= Band 11 SWIR I
= Band 4 Red
Vegetation
= Band 8 NIR
= Band 4 Blue
= Band 3 Red


Spectral signature
Bands and spectral signatures


Healthy vegetation


Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
NDVI=NIR-IR/NIR+IR
Animation
Possible Assignments - Maps
Can landslides be correlated to land use change?
Future Lessons:
Quantify Change over time between two different images
(atmospheric correction)
Possibilities Classification
Supervised & Unsupervised

Supervised Classifciation - User trains the machine to find what they are looking for specifically
Unsupervised Classifciation - the machine groups pixels into classes based on spectral signatures alone
Animation
Big Data and
CyberGIS
Cloud Computing






-
valuable for information dissemination
-
faster and more data processing that was not previously possible
-
data access
Google Earth Engine




-
Cloud-based platform for geospatial analysis
-
Access over 40 years of satellite imagery
-
Upload own data sets to integrate with publicly available data
-
Apply range of common algorithms to data
-
Export images, tables, charts, map outputs


Hansen et al (2013)
High-Resolution Global Maps of 21st-Century Forest Cover Change, Science
15 Nov. Vol. 342, Issue 6160, pp. 850-853 DOI: 10.1126/science.1244693.
Summary
Benefits of CyberGIS
- Data access
- Distributed data processing
- Information dissemination through interactive visualizations
Review!
In your own words...

What is the difference between an active and passive sensor?
What is a spectral signature?
What is a false-color composite?
How are they useful for land use change monitoring?
Spatial and
temporal resolution
What do these terms mean and how are they different?

Name two strengths of CyberGIS and cloud computing?
Name two different Visualization techniques to show change over time.
Thank you!

Land Cover 2024
By Britta Ricker
Land Cover 2024
- 393



