Docker for Primer

Disclaimer
I do not have have master level experience with Docker or Containers. Today's session are prepared based on my reading and past some months research on Docker.
Consider this as a mutual knowledge sharing session. It may give you some basic understanding of Docker and Containers
Today
- History & Current situation of IT
- What is Docker?
- Set up Docker Environment
- Docker Life Cycle & Commands
- Docker Compose
- Practical
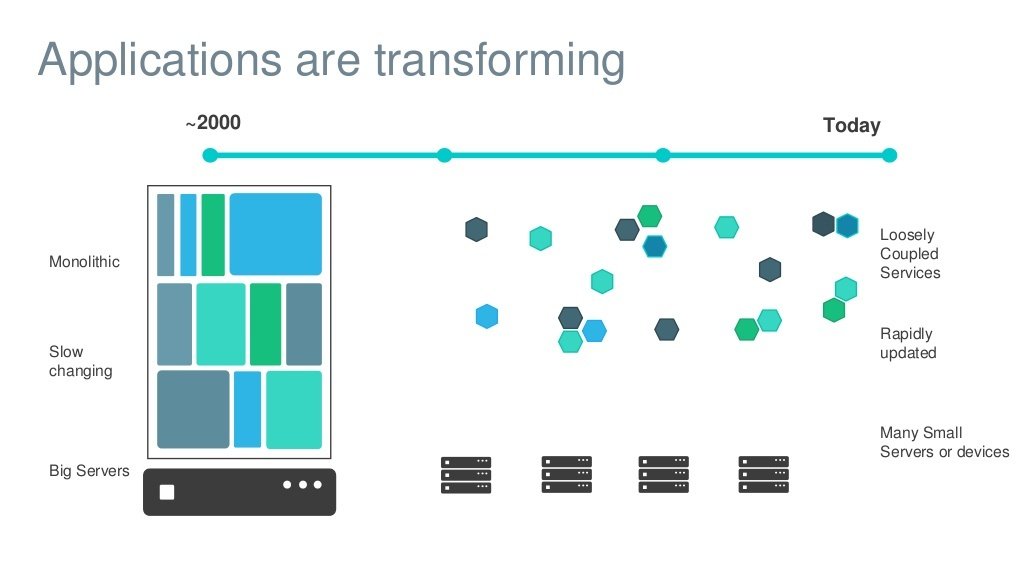
History of IT & Challenges
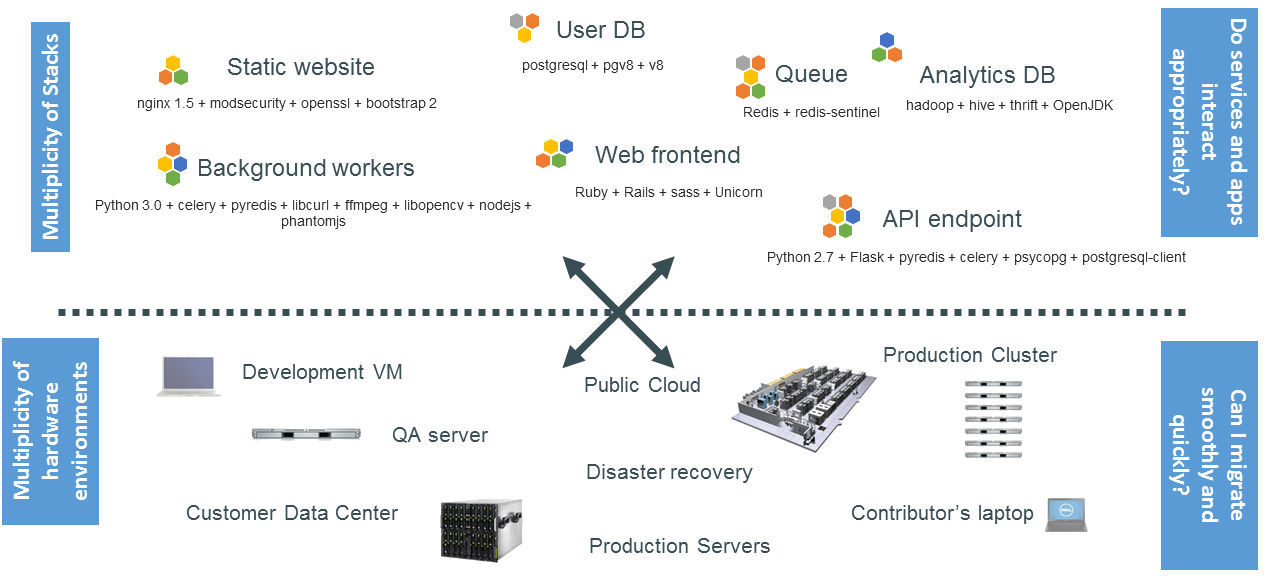

Tug of War
between
Two teams

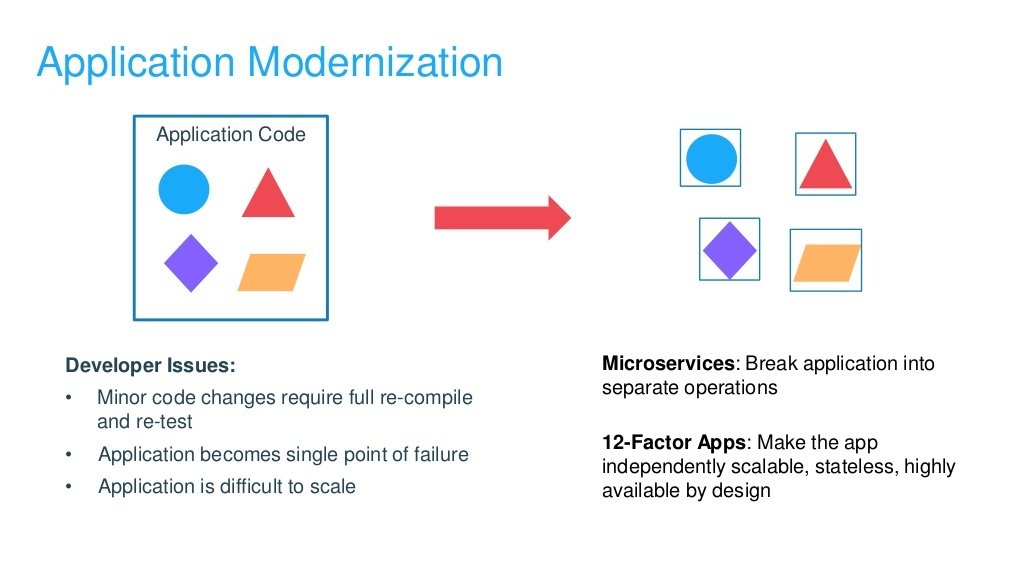
What is Docker?
Docker is
- An open-source project that automates the deployment of software applications inside containers by providing an additional layer of abstraction and automation of OS-level virtualization on Linux.
- Allows you to package an application with all of its dependencies into a standardized unit for software development.
- A container management service.
Virtual Machine
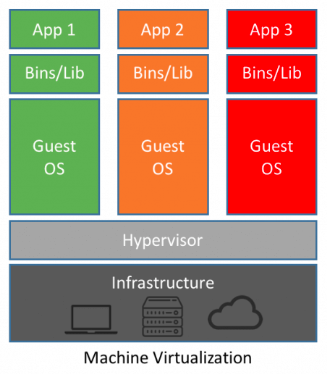
Benefits
- Better resource pooling.
- Easier to scale
- In the cloud: Rapid elasticity & Pay as Usage
Limitations
- Each VM requires: OS, CPU, Storage,RAM
- More VM needs more resources
- Application portability are not guaranteed
Container
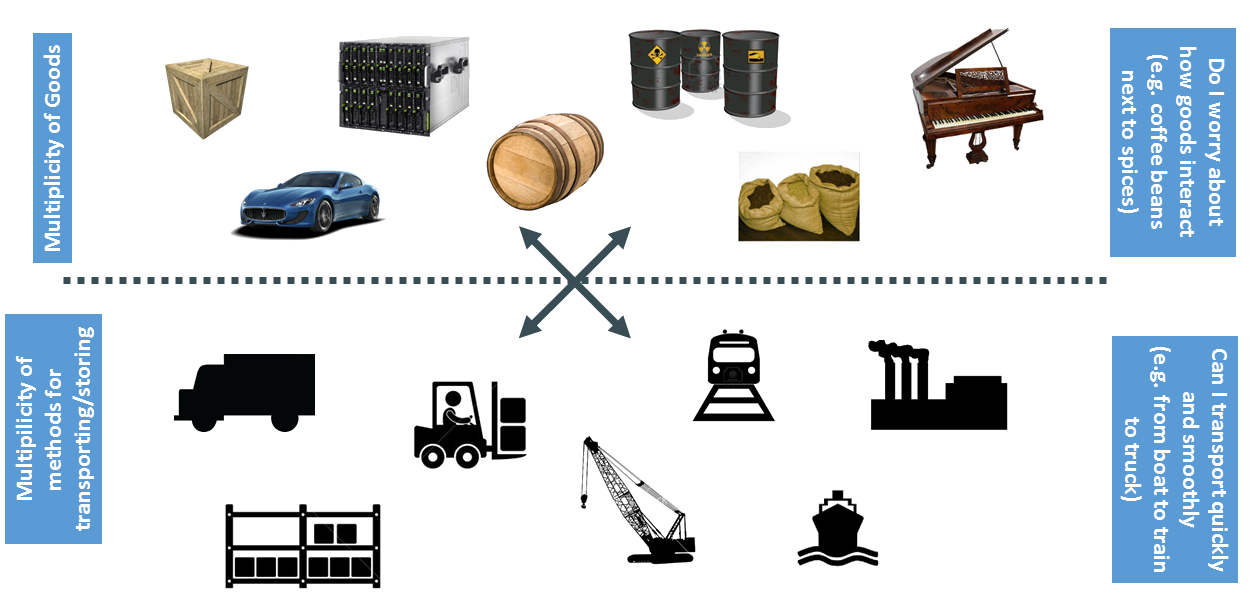
Cargo Transport Pre-1960
Cargo Transport in 20k
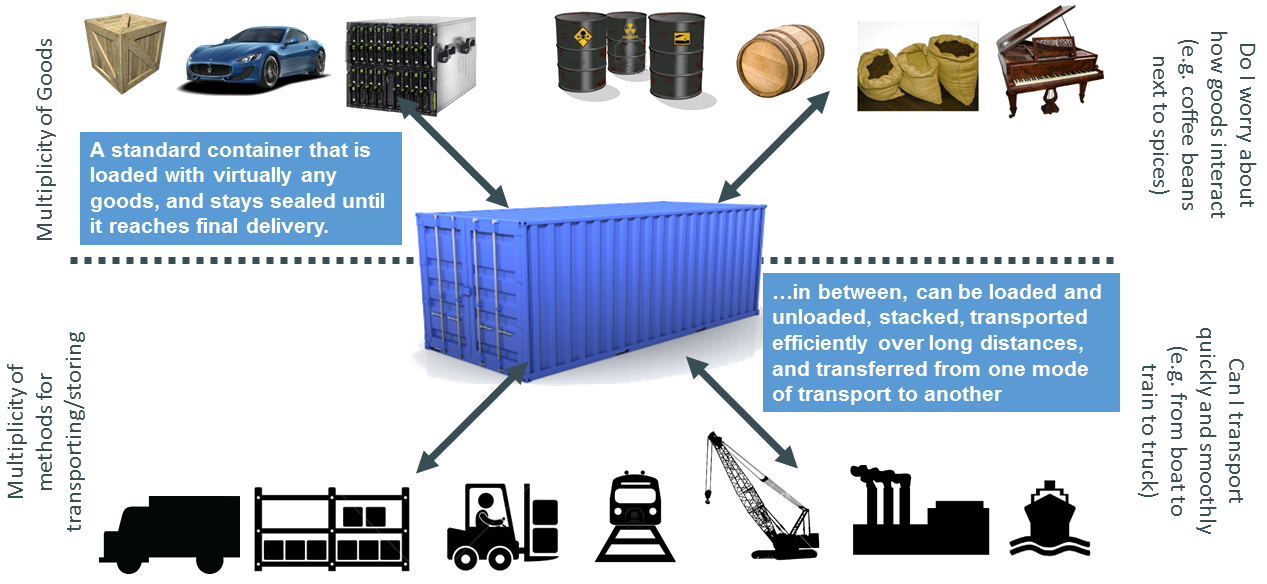
Container
- Container is built from an image.
- A container consists of an operating system, user-added files, and meta-data.
- That image tells Docker what the container holds, what process to run when the container is launched, and a variety of other configuration data.
- The Docker image is read-only.
- When Docker runs a container from an image, it adds a read-write layer on top of the image (using a union file system) in which your application can then run.
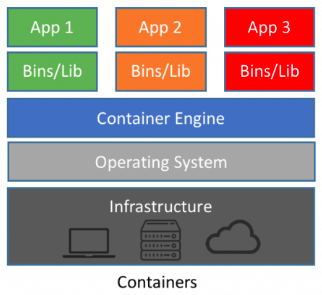
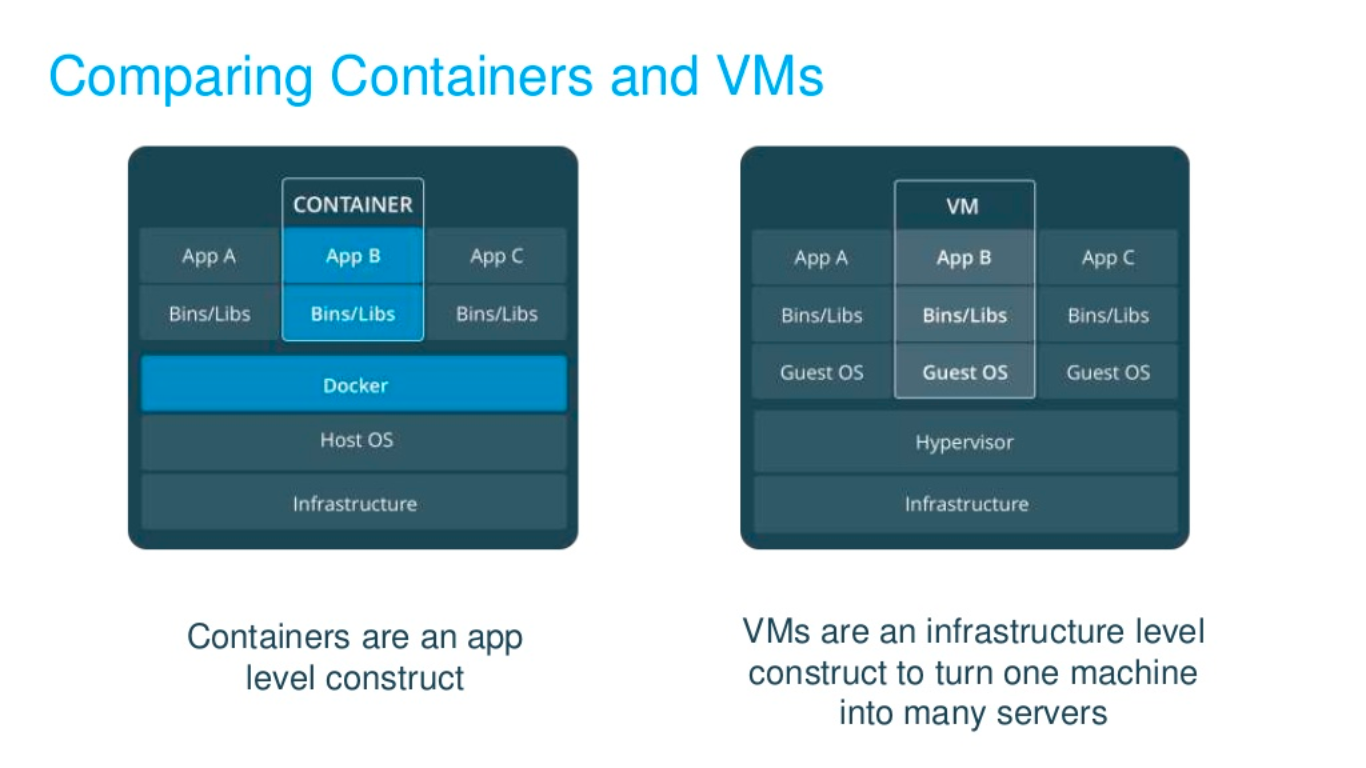
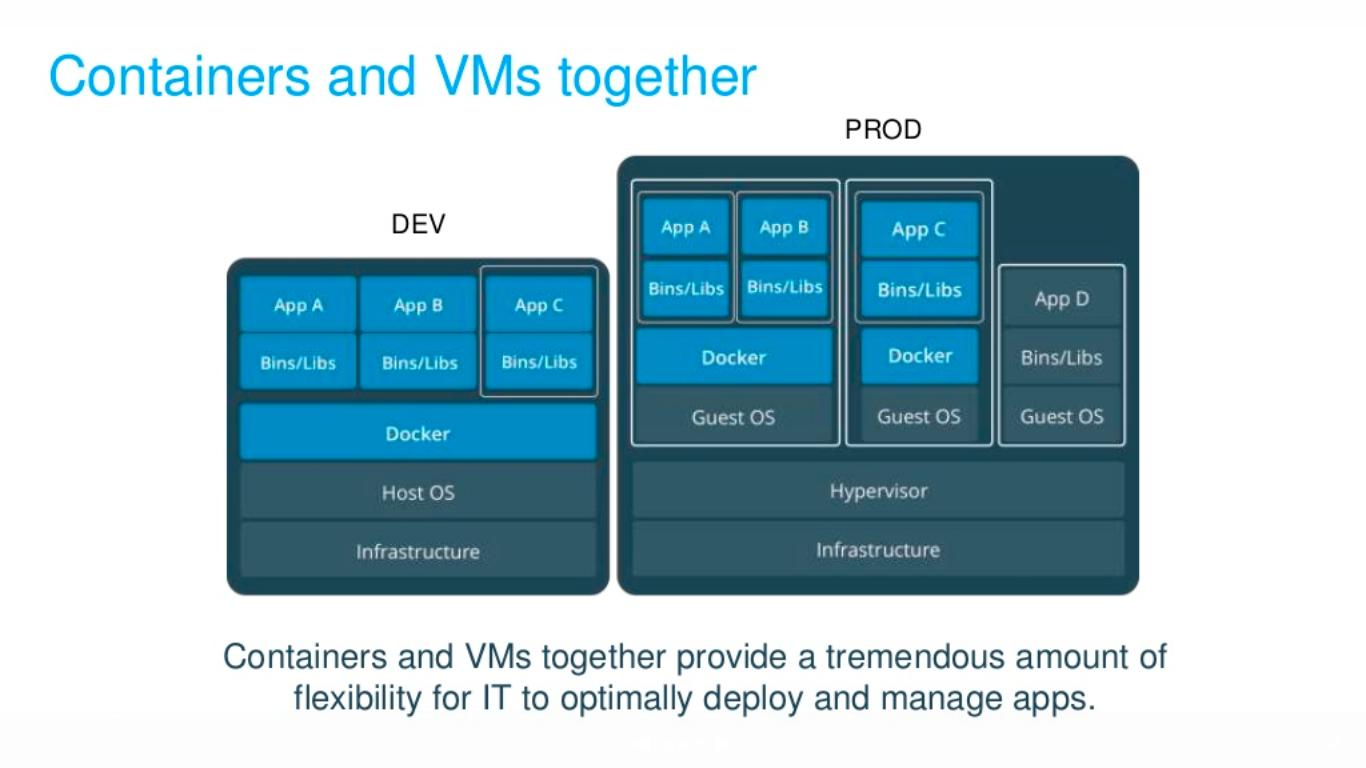
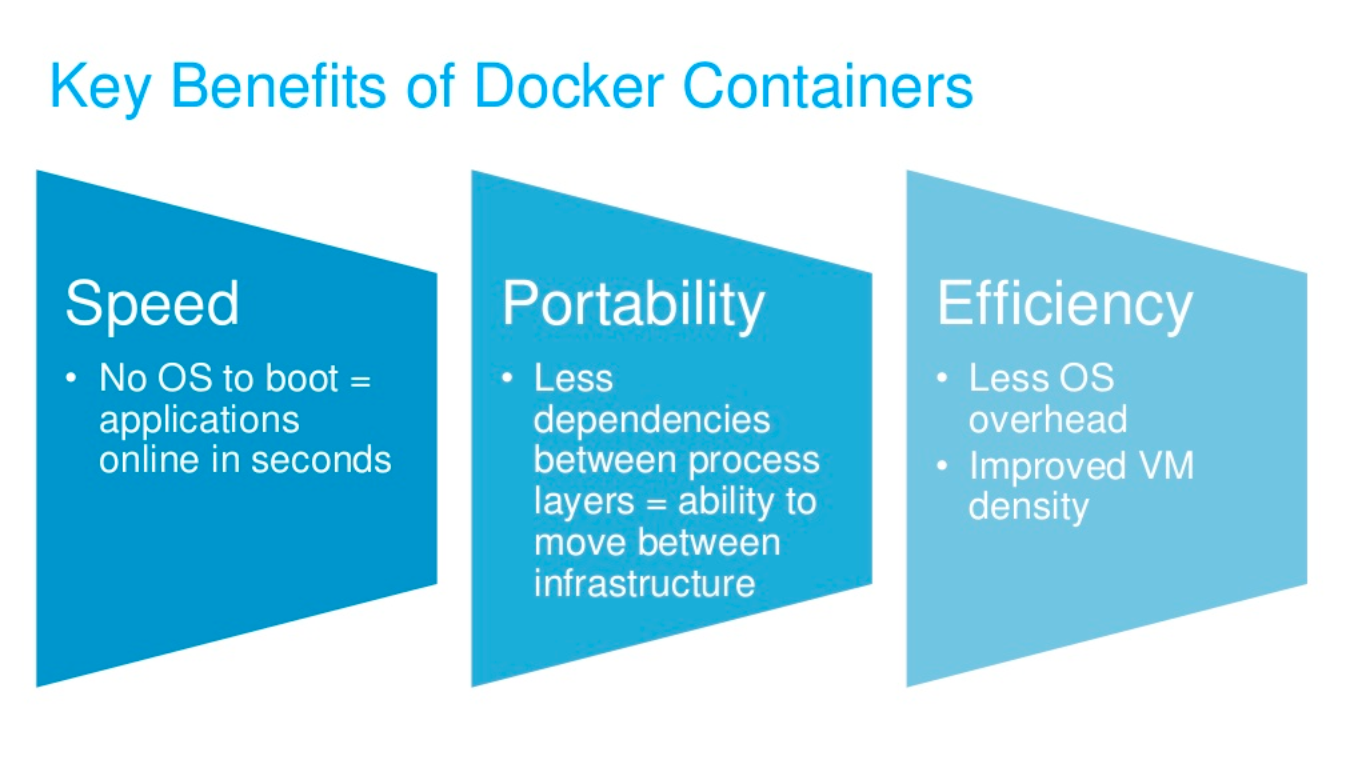

Set up Docker environment
Pre-requisite
Linux Environment
- Docker is only designed to run on Linux kernel version 3.8 and higher. Check
Linux information details:
uname -a
- Update the OS with the latest packages: sudo apt-get update
- Install Docker in Linux OS
Windows Environment - Memory 4GB, Virtualization should be enabled
- Download windows OS supported latest (Stable) build from below link
https://docs.docker.com/v17.09/docker-for-windows/install/#download-docker-for-windows
- Once successfully installed via
"Docker for Windows Installer.exe" file, following icon is
availabe on desktop.

Docker Install in Linux - 18.04
Steps
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
- curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
- sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64]
https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bionic stable"
- sudo apt-get update
- sudo apt-get install docker-ce
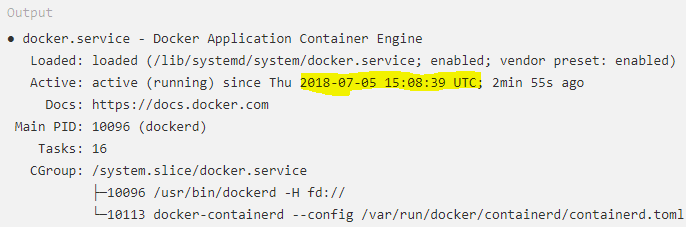
Docker should now be installed, daemon started, and the
process enabled to start on boot. Check that it's running:
- sudo systemctl status docker
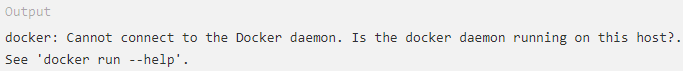
Executing the Docker Command
Without Sudo
By default, the docker command can only be run the root user or by a user in the docker group, which is automatically created during Docker's installation process. If you attempt to run the docker command without prefixing it with sudo or without being in the docker group, you'll get an output like this:
If you want to avoid typing sudo whenever you run the docker command, add your username to the docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker ${USER}
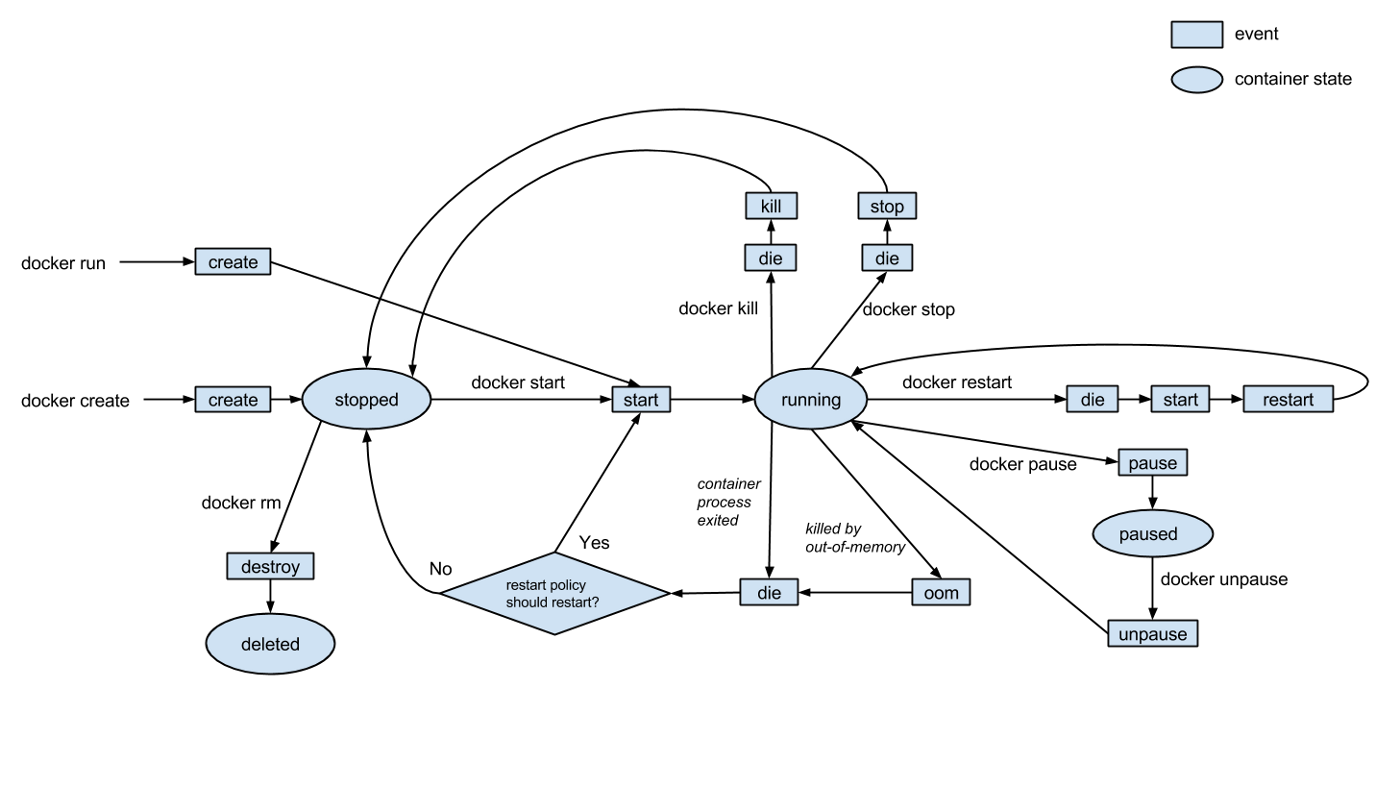
Lifecycle of Docker
Docker - Commands
For checking the number of images on system
docker images
For Checking the number of running docker instances
docker ps , docker ps -a
Runs a command in a new container
docker run
Starts one or more stopped containers
docker start
Stops one or more running containers
docker stop
For Remove Docker
docker rmi <image_id>
-f used for remove forcefully
Kill the process from running container
docker kill <container_id>
Restart container
docker restart <container_id>
Pause/unpause running containers
docker pause/unpause <container_id>
Build Docker image
docker build -t ImageName:TagName dir
Ex. docker build -t testimage:0.1 .
Docker Images
Docker images are built based on a Dockerfile. A Dockerfile defines all the steps required
to create a Docker image with your application configured and ready to be run as a container. The image itself contains everything, from the operating system to dependencies and configuration required to run your application.
Having everything within the image allows you to migrate images between different environments and be confident that if it works in one environment, then it will work in another.
The Dockerfile allows for images to be composable, enabling users to extend existing images instead of building from scratch. By building on an existing image, you only need to define the steps to setup your application. The base images can be basic operating system installations or configured systems which simply need some additional customisations.
Docker Compose
docker-compose
Docker Compose is used to run multiple containers as a single service. We can create one file which would start both the containers as a service without the need to start each one separately. We can get dozens of configurations applied by Compose under the hood. This will save us the hassle of scripting them with Bash or something else. we need to specify the version of the Compose file format, at least one service, and optionally volumes and networks.
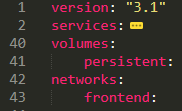
docker-compose
services
Services refer to container's configuration
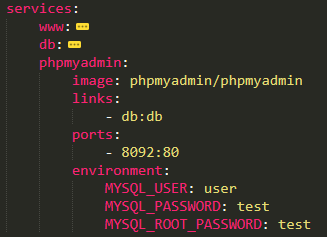
docker-compose
volumes & networks
volumes are physical areas of disk space shared between the host and a container, or even between containers. In simple words, a volume is a shared directory in the host, visible from some or all containers. networks define the communication rules between containers, and between a container and the host. Common network zones will make containers’ services discoverable by each other, while private zones will segregate them in virtual sandboxes.
Practical Session
Practical - 1
Building Container Images
Demo - Hello World
Create Dockerfile
FROM php:5.6-apache
COPY public/ /var/www/html/
Create one folder -> Name: public Create index.php file under public folder
index.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><meta charset="utf-8"><title>Docker PHP Hello World</title></head>
<body>
<? if ($_POST['who'] != '') {?>
<h1>Hello <? echo htmlspecialchars($_POST['who']); ?></h1>
<a href="index.php">Greet someone else</a>
<? } else { ?>
<form class="greetingForm" action="index.php" method="post">
<label for="who">Say hello to</label>
<input type="text" name="who">
<input type="submit" name="greet" value="Say Hello">
</form>
<? } ?>
</body>
</html>
Build & Run => Docker
docker build -t docker-php-hello-world .
docker run --name=docker-php-hello-world -it --rm -p 80:80 docker-php-hello-world
Practical - 2
Apache Web Server
Steps
- Create Dockerfile
-
FROM ubuntu MAINTAINER bugtechies@gmail.com RUN apt-get update RUN apt-get install –y apache2 RUN apt-get install –y apache2-utils RUN apt-get clean EXPOSE 80 CMD [“apache2ctl”, “-D”, “FOREGROUND”] - Build Dockerfile
- docker build –t=”mywebserver” .
- Run Dockerfile
- docker run –d –p 80:80 mywebserver
- Type 127.0.0.1:80 from browser
Practical - 3
Localhost php Website
Open shared git page
Clone this git repo to a local machine
Go to the downloaded folder
Run following command: docker-compose up -d
wait till process complete.....................!
Run following command: docker-compose exex db mysql -u root -p
Terminal will ask for mysql password, give password as per
docker compose file.
Browse localhost: http://localhost:8091
Steps


Docker for Primer
By Parag Dave
Docker for Primer
- 745



