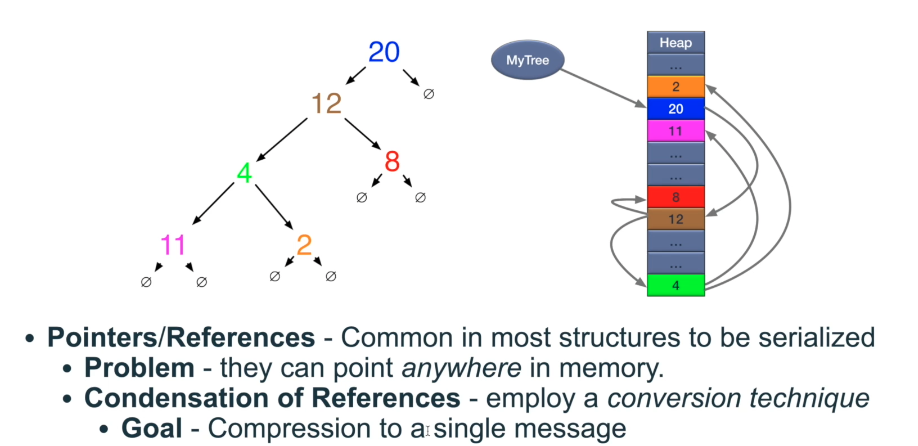
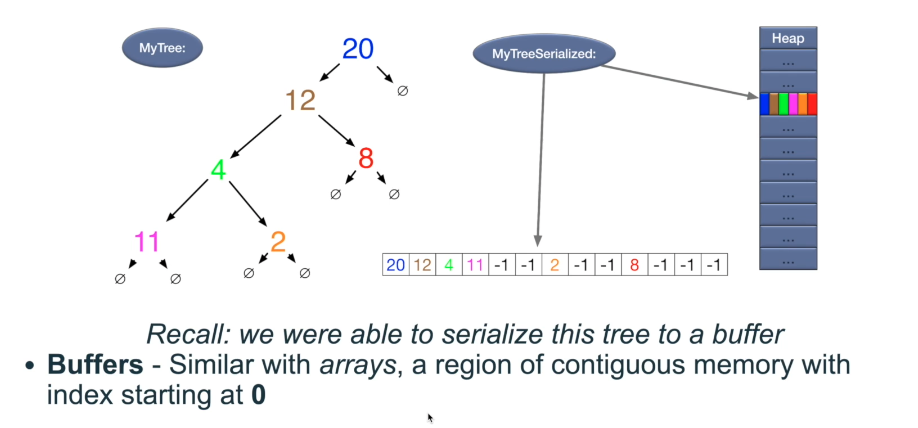
Data engineering basis
Background
- What's your experience with big data?
- Explain what's big data for you ??
- Which role?
- Which technologies ?
- Do you have questions about the decks before We start?
- Experience with hadoop cluster?
- Experience with map reduce , spark, pig , HDFS?
Structure vs Unstructured
- Do we more data Structure or Unstructured ?
- > 80% unstructure
- Defined vs Undefined Data
- Qualitative vs Quantitative Data
-
Where is usually store ?
- Storage in Data Houses vs Data Lakes
- Any experience with products?
- Ease of Analysis
- Predefined Format vs Variety of Formats
Conclusion: Structure is better for data analysis but 80% is unstructure so our business will go blind if we leave it out
Data Format
- Why choosing a data format is one of the key decisions in a big data project ?
- Analysis is faster
- Size of the storage
- Specialized for write or read
- Compression can go faster or slower
- Safe money
- Security
| Json | CSV | Avro | Protocol Buffers | Parquet | ORC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row or Column | Row | Column | Column | |||
| Schema | Best | Good | Better | |||
| Read or Write | Write | Read | Read | |||
| Compression | Good | Better | Best | |||
| Splitability | Good | Good | Best | |||
| Human Readable | Good | Best | meh | meh | meh | meh |
| Types | CSV | JSON | XML | AVRO | Protocol Buffers | Parquet | ORC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| text versus binary | text | text | text | metadata in JSON, data in binary | text | binary | binary |
| Data type | no | yes | no | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Schema enforcement | no (minimal with header) | external for validation | external for validation | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Schema evolution | non | yes | yes | yes | non | yes | non |
| Storage type | row | row | row | row | row | column | column |
| OLAP/OLTP | OLTP | OLTP | OLTP | OLTP | OLTP | OLAP | OLAP |
| Splittable | yes in its simpliest form | yes with JSON lines | non | yes | non | yes | yes |
| Compression | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Batch | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Stream | yes | yes | non | yes | yes | non | non |
| Typed data | non | non | non | non | yes | non | non |
| Ecosystems | popular everywhere for its simplicity | API and web | enterprise | Big Data and Streaming | RPC and Kubernetes | Big Data and BI | Big Data and BI |
Row or Column
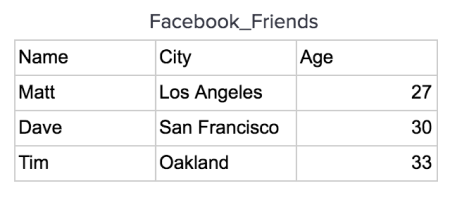

Row
Column

Serialization and Deserialization
Compression
Coding the data into more compact forms
Let’s first examine an encoding technique that can be used by row or column oriented databases. The example of one of the columns being for states of the United States will show dictionary and bitmap encodings.
- There are 50 so we could encode the whole database with 6 bits since this would provide us 64 unique patterns.
- To store the actual abbreviations would require 16 bits since this would provide us with 256 unique patterns for each of the two ASCII characters.
- Worst of all if we stored the full name the lengths would be variable and the amount of bits needed would be a lot more.
Now let’s take a look at Run-length encoding. This allows you to replace any sequence of the same value with a count and value indicator. For instance we can replace aaaab with 4a1b. This becomes even more powerful when you create projections with columns that are sorted since all values that are the same are next to each other.
Schema
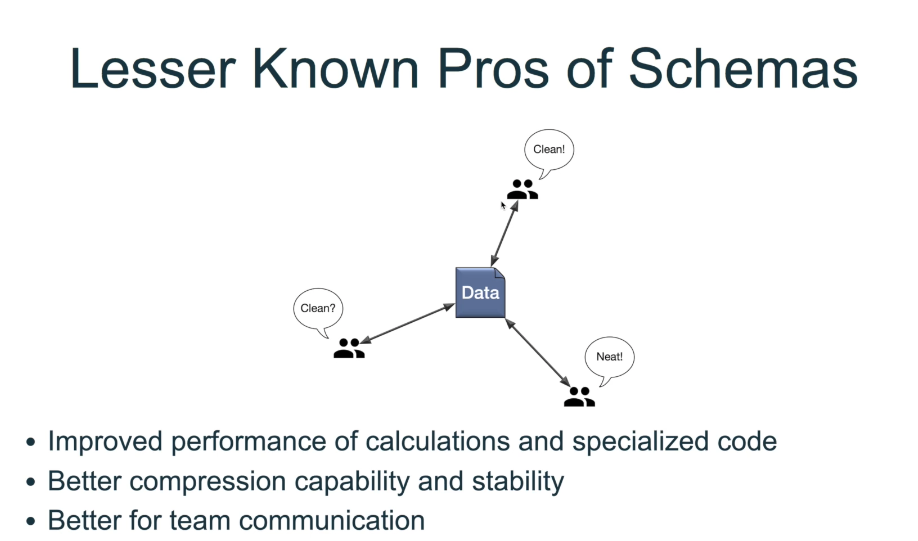

Streaming Vs Batch
Who knows the difference?
What's the most common common ?
What's the ideal world?
Common Structure of ETL or Streaming?
Why are we migrating from hadoop ?
Tools?
Things to think About?
Stateless streaming vs stateful ? stateful scenario : I'm receiving the sales data of my car company , I want near realtime to know aggregated data.
Different workers require to store the state
Imagine a streaming process on a huge cluster
Checkpoints ?
Where is the dataset being processed? Be careful with therminology
Nifi, Airflow,Informatic
Spark,Flink, Cloudflow
Suggestion check Kappa Architecture vs Lambda
Data-bricks
Title Text
- Bullet One
- Bullet Two
- Bullet Three
deck
By Camilo Andres Hernandez
deck
- 140

