Announcements
1. I start recording attendance today
2. Sign up sheet for student led discussions is posted on Moodle, Please sign up for two dates.
What is the Middle East?
- Environment
- people
- Religion
- politics
Environmental trends across the region
- Diverse range of environmental ecosystems:
- Deserts climates in North Africa, Gulf, Iraq, Israel, Iran, Syria, Jordan
- Forests historically found throughout the region, notably in Lebanon (biblical, historical and architectural evidence document the widespread use and popularity of Lebanese Cedar). Some of these forest still exist but are endangered by mismanagement.
- Aridity encourages higher energy cost, higher cost for the production of food, and greater challenges for water management.
Making the Desert productive?

Saudi Arabia has created a successful dairy program
by importing feed from large landholdings in the U.S. and the use of technology to keep the cows cool.

14 of the world 33 water stressed countries in the Middle East
Water Scarcity
Water sources
- Rivers
- The river Jordan
- Nile River
- Tigris and the Euphrates
- Aquifers
- non-renewable in Saudi Arabia
- desalinated water
Water Scarcity and Conflict
Yemen: Before the outbreak of conflict, water shortage threatened the capital
Israel/Palestine: Unfair distribution
Syria: large migration of syrians from Agriculture areas to large cities
Water Scarcity
Politically, water scarcity leads to social and political change
- More people leaving agricultural lands
- large numbers of poor without access to safe drinking water
- food shortage
Water problems in Beirut
- Climate change threaten the city of Beirut with rising sea water and salinization of supply
- Saline levels are currently 5x the acceptable level
- raw sewage
- unmetered water connections
- rapidly increasingly population
- over exploitation of wells
- During the summer months there are daily water shortages
Climate Change in the Middle East:
Century predictions for the Middle East show that rising heat mixed with air pollution threaten to make areas within the region uninhabitable, at least for parts of the year.
Climate and Civil War in Syria:
"Beginning in the winter of 2006/2007, Syria and the greater Fertile Crescent (FC), where agriculture and animal herding began some 12,000 years ago (1), experienced the worst 3-year drought in the instrumental record (2).
The most significant consequence was the migration of as many as 1.5 million people from rural farming areas to the peripheries of urban centers"
Kelley et.al.(2015). Climate Change in the Fertile Crescent and implications of the recent Syrian Drought. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 112(11) 3241-3246
People
The Middle East is NOT synonmous with Arabs. Arab is an ethnic group denoting people who have biological links to peoples who originated within the Arabian peninsula, current day Saudi Arabia, Yemen, Oman. Those who claim an Arab identity also share in similar linguistic and cultural practices.
The largest ethnic group in the region are Arabs.
Other important groups:
Bedouin= Nomadic Arabs
Berber= Indigenous to North Africa (Maghreb)
Persian= Iran
Kurds= Syria, Turkey, Iran, Iraq
Turks= North and central Asia
Demographics
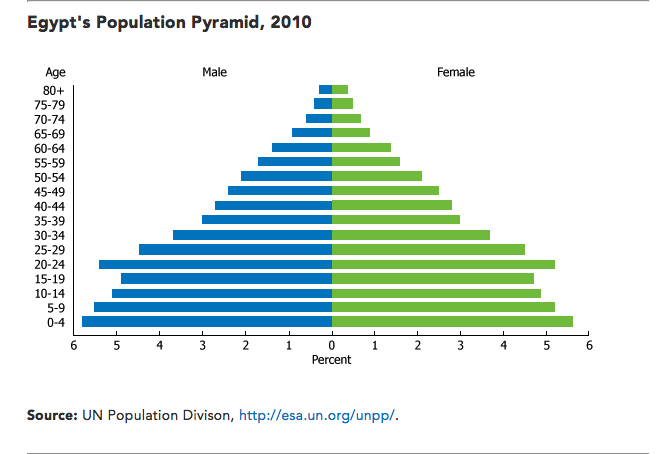
The Middle East has a large young populace.
In 2011, the 'Youth Bulge' was credited with playing a significant role in the Arab Spring.
Two ways to think about youth in the Middle East
Individuals between 18-29
Individuals who are unmarried and live in the family home

A generation in waiting
Across the region, youth suffer from unemployment and subsequently limited opportunities for entering into adulthood.
Unemployment in Egypt officially stands at 12.8%, of the population of youth in the country, 30% are unemployed
Youth unemployment directly impacts: the growth in informality, brain drain, and political stability. It also adds to the ongoing refugee crisis.
There is also the paradox that those with college degrees are less likely to be employed.
Adel Abdel Ghafar, Brookings Institute (Doha)
https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/en_youth_in_egypt.pdf
Religion
Regionally, Islam is practiced by the majority of inhabitants with sizable Christian and Jewish communities.
Within each of these faiths there is a wealth of diversity. For this class, we will primarily focus on Islam but I don't want students to forget that Islam is one of many faiths in the Middle East and North Africa.
The advent of Islam
Before the rose of Islamic 6th century Arabia, the area spanning from the Levant to the Hijaz and parts of North Africa had communities of several different faiths.
Both poly and monotheism present.

Jahiliyyah
'A time of Ignorance'

Life in early Arabia:
Tribal
Due to arid conditions, a mix of Oasis Agriculture and Pastoral Nomadism.
Arabia, specifically the city of Mecca becomes an important trading center and the city itself become a place for settled life and the accumulation of wealth.
The Quraysh
The Quraysh are a Meccan Tribe that controlled Mecca and organized trade within the city. It is into this tribe that the Prophet Mohammad is born around 570 CE.
Although he is Quraysh, he has no wealth and shortly after his birth he is orphaned. He grows up under the care of his uncle, Abu Talib.

Prophethood
Prophet Mohammad known as a man of integrity and trustworthiness. He also has a penchant solitude and meditation.
The Message is reveal to him by the Angel Gabriel at the age of 40. It is his wife, Khadijia, and her uncle who help Mohammad realize he is a prophet.

Clash with the Qurasyh
- Initially, the prophet is met with derision in Mecca. However, he builds a following amongst the outcasts of society. As his influence grows, the prophet becomes a threat.
After the deaths of his wife and his uncle, The prophet flees Mecca for Medina with his followers in 622 CE. After a series of battles with Meccans, he returns to the city triumphant in 630 CE.
Islam, peaceful Submission
The Holy Quran is the primary text of this faith. It is a complication of God's communication through Mohammad to Muslims and other 'people of the book'.
In addition to the Quran, followers look toward the Sunnah and Hadiths to understand appropriate action
Five pillars of Faith
Shahada: Testimony
Salat: Prayer
Zakat: Charity
Sawm: Fasting
Hajj: Pilgrimage
Sunni Islam
The majority of Muslims adhere to Sunni Islam. Which believe in the succession of leaders after the death of the prophet.
The Rightly Guided Prophets:
Abu Bakr 632-634
Umar 634-644
Uthman 644-656
Ali 657-661
Shi'a Islam
Does not agree with the succession of rulers after the death of the prophet Muhammad. Believes Leadership should have gone to a member of the prophet's family.
Violence and Middle East (class 2)
By cesmit5
Violence and Middle East (class 2)
- 1,000



