File I/O: The universal I/O Model
File I/O: The Universal I/O Model

Overview
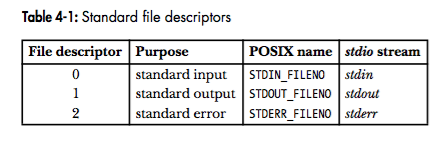
Overview
/* Open a file */
fd = open(file_path, flags, mode);
/* Read a file */
num_byte_read = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
/* Write a file */
num_byte_write = write(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
/* Close a file */
close_st = close(fd);Open
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int open(const char *paht, int flags, ... /* mode_t mode */);
/* Return file descriptor on success, or -1 on error. */Open
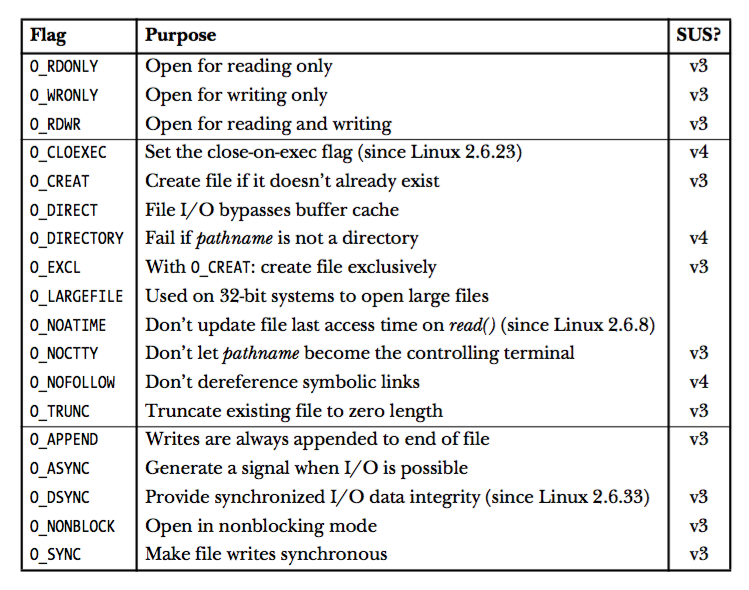
File Access mode flags
File creation flags
Open file status flags
can be change by fcntl
cannot be change by fcntl
can be change by fcntl
Read
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buffer, size_t count);
/* Return number of bytes read, 0 on EOF, or -1 on error. */Write
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t write(int fd, void *buffer, size_t count);
/* Return number of bytes written, or -1 on error. */Creat
#include <fcntl.h>
int creat(const char *paht, mode_t mode);
/* Return file descriptor, or -1 on error. */Equivalent to
fd = open(file_path, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, mode);Close
#include <unistd.h>
int close(int fd);
/* Return 0 on success, or -1 on error. */lseek
#include <unistd.h>
off_t lseek(int fd, off_t offset, whence);
/* Reutnr new file offset, or -1 on error. */What kernel doing?
Kernel maintain a read-write offset (pointer)
lseek
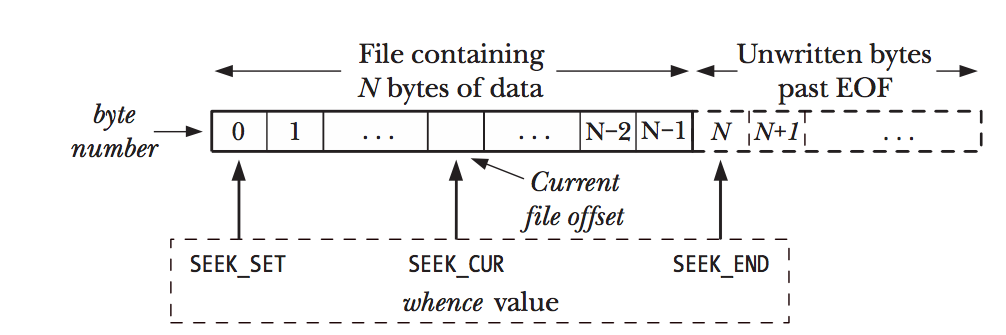
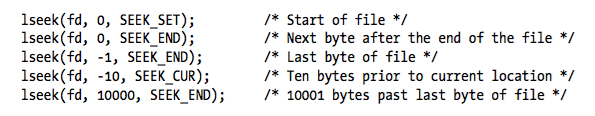
File I/O: Further Detail
File Control Operation - Fcntl
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... );
/* Return on success depend on command, or -1 on error. */Relationship between fd and open files
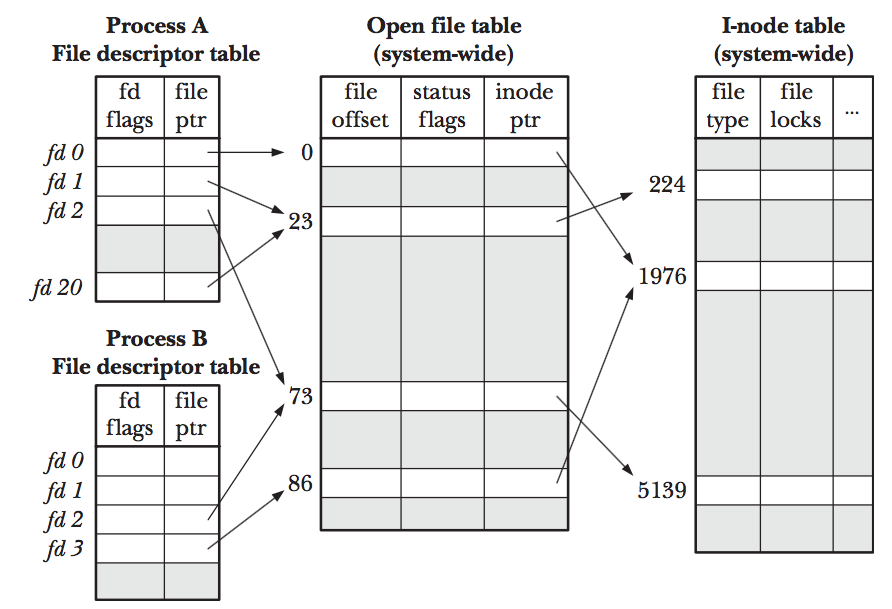
Duplicating File Descriptor
# Redirection STDERR to STDOUT
$ ./SomeCommand 2>&1How to do redirection in C?
#include <unistd.h>
int dup(int oldfd);
/* Return (new) file descriptor on success, or -1 on error. */Duplicating File Descriptor
/* close STDERR */
close(2);
/* dup STDOUT to newfd */
newfd = dup(1);
/* print something to STDOUT */
write(newfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
# Redirection STDERR to STDOUT
$ ./SomeCommand 2>&1Equivalent to
Duplicating File Descriptor
/* close STDERR */
close(2);
/* dup STDOUT to newfd */
newfd = dup(1);
/* print something to STDOUT */
write(newfd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
/* combine close and dup */
dup2(1,2);
/* print something on STDOUT */
write(2, buffer, sizeof(buffer));Equivalent to
File I/O at specified offset
#include <unistd.h>
ssize_t pread(int fd, void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset);
/* Return number of bytes read, 0 on EOF, -1 on error. */
ssize_t pwrite(int fd, void *buf, size_t count, off_t offset);
/* Return number of bytes read, -1 on error. */
Scatter-Gather I/O
Idea: Transfer multiple buffers of data in a single system call
scatter-input & gather-output
Scatter-Gather I/O
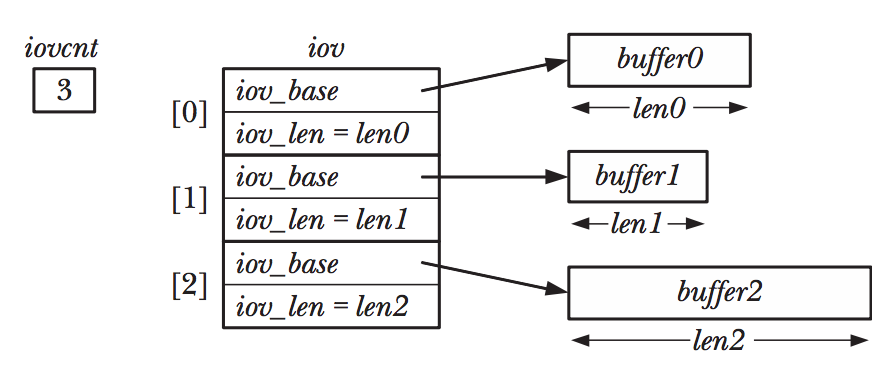
Scatter-Gather I/O
#include <sys/uio.h>
ssize_t readv(int fd, const struct iovec, int iovcnt);
/* Return number of bytes read, 0 on EOF, or -1 on error. */
ssize_t writev(int fd, const struct iovec, int iovcnt)
/* Return number of bytes write, or -1 on error. */struct iovec {
void *iov_base;
size_t iov_len;
};struct iovec define
Atomicity and Race Conditions
if (-1 != (fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY))) {
printf("[PID %ld] File \"%s\" already exists\n", (long)getpid(), argv[1]);
close(fd);
} else {
if (errno != ENOENT) {
perror("Failed fo unexpected reason");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
} else {
printf("[PID %ld] File \"%s\" doesn't exist yet\n", (long)getpid(), argv[1]);
if (2 < argc) {
sleep(6);
printf("[PID %ld] Done sleeping\n",(long)getpid());
}
if (-1 == (fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT , S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR))) {
perror("open");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("[PID %ld] Create file \"%s\" exclusively\n", (long)getpid(), argv[1]);
}
}Atomicity and Race Conditions

Atomicity and Race Conditions
How to solve this problem?
fd = open(argv[1], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_EXCL, S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR)Create Temporary File
#include <stdlib.h>
int mkstemp(char *template);
/* Return file descriptor on success, or -1 on error */#include <stdio.h>
FILE *tmpfile(void);
/* Return file pointer on success, or NULL on error *//dev/fd/n
n: file descriptors for the process
fd = open("dev/fd/1", O_WRONLY);
/* Equivalent to */
fd = dep(1);See also /proc/[pid]/fd
Using in shell
$ ls | diff - oldfilelist
# Equivalent to
$ ls | /dev/fd/0 oldfilelistHow many file descriptor can be used?
# per process
$ ulimit -n
# system
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-maxFile I/O VS. Buffering I/O
Why Buffering I/O usually has good performance?
The minimum unit of data which read from disk is block
Thanks for comming
Basic Concept about File I/O
By chang-ning tsai
Basic Concept about File I/O
- 363



